1 About the Connector
Oracle Identity Manager automates access rights management, security, and provisioning of IT resources. Oracle Identity Manager connectors are used to integrate Oracle Identity Manager with external, identity-aware applications. This guide discusses the connector that enables you to use SAP HRMS as an authoritative (trusted) source of identity data for Oracle Identity Manager.
In the identity reconciliation (trusted source) mode of the connector, identities are created or modified only on the target system and data about these identities is reconciled into Oracle Identity Manager. The user data reconciled from the target system is used to create or update OIM Users.
Note:
At some places in this guide, SAP HRMS is referred to as the target system.This chapter contains the following sections:
- Certified Components
- Usage Recommendation
- Certified Languages
- Connector Architecture
- Features of the Connector
- Connector Objects Used During Reconciliation
Note:
In this guide, the term Oracle Identity Manager server refers to the computer on which Oracle Identity Manager is installed. At some places in this guide, SAP HRMS has been referred to as the target system.1.1 Certified Components
Table 1-1 lists the certified components for the connector.
Table 1-1 Certified Components
| Component | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Oracle Identity Governance or Oracle Identity Manager | You can use one of the following releases of Oracle Identity Governance or Oracle Identity Manager:
Note: In this guide, Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.1 has been used to denote Oracle Identity Manager release 11g release 1 (11.1.1) and future releases in the 11.1.1.x series that the connector will support.
Note: In this guide, Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.2 has been used to denote Oracle Identity Manager release 11g release 2 BP04 (11.1.2.0.4) and future releases in the 11.1.2.x series that the connector will support.
The connector does not support Oracle Identity Manager running on Oracle Application Server. For detailed information about certified components of Oracle Identity Manager, see the certification matrix on Oracle Technology Network at http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/documentation/oim1014-097544.html Note: If Oracle Identity Manager is running on Oracle WebLogic Server and using JRockit, then the scheduled task configured as a listener on Oracle Identity Manager might fail. It is recommended that you use SUN JVM. The listener is described later in this chapter. |
| JDK |
For Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.x and 11.1.2.x, Sun/IBM JDK 1.6 update 18 or later. Note: JRockit is not supported because it is incompatible with the SAP JCo libraries. |
| Target system |
The target system can be any one of the following:
Note: From version 6.40 onward, SAP WAS is also known as "SAP NetWeaver." |
| External Code | The connector works with SAP JCo 3.0.2 or later. The following SAP custom code files are required:
Note: There are different distribution packages (JCo) 3.0.2 available for various supported platforms and processors. See, JCo documentation for more information about using JCo 3.0.2 packages as per your environment. |
1.2 Usage Recommendation
If you are using any of the following versions of Oracle Identity Manager, then you must use the 9.1.2.x version of this connector:
- Oracle Identity Governance 12c (12.2.1.4.0) and any later BP in this release track
- Oracle Identity Governance 12c (12.2.1.3.0) and any later BP in this release track
- Oracle Identity Manager 11g Release 2 PS3 (11.1.2.3.0) or later
- Oracle Identity Manager 11g Release 2 PS2 (11.1.2.2.0) or later
- Oracle Identity Manager 11g Release 2 PS1 (11.1.2.1.0) or later
- Oracle Identity Manager 11g Release 2 BP04 (11.1.2.0.4) or later
- Oracle Identity Manager 11g Release 1 PS2 (11.1.1.7.0) or later
- Oracle Identity Manager 11g Release 1 PS1 (11.1.1.5.0) or later
- Oracle Identity Manager 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.3.0) or later
1.3 Certified Languages
The connector supports the following languages:
- Arabic
- Chinese (Simplified)
- Chinese (Traditional)
- Danish
- English
- French
- German
- Italian
- Japanese
- Portuguese (Brazilian)
- Korean
- Spanish
1.4 Connector Architecture
Note:
This guide provides only an overview of the SAP data components and processes that are used during reconciliation with the target system. For detailed information about ALE, see the SAP Help documentation at http://help.sap.com.The target system is configured as a trusted source of identity data for Oracle Identity Manager. In other words, identity data that is created and updated on the target system is fetched into Oracle Identity Manager and used to create and update OIM Users.
IDocs (interchange documents) are the medium of data interchange between SAP HRMS and Oracle Identity Manager. IDocs are ASCII-based flat files containing lines of text that are ordered into data fields. A typical IDoc contains a header line (control record) followed one or many data lines (data records). In the Oracle Identity Manager context, IDocs are used to transfer user data from the target system to Oracle Identity Manager. You can set the number of user records that must be recorded in an IDoc.
An IDoc type defines the structure of data in an IDoc. All IDocs adhere to the structural requirements imposed by their IDoc type. In other words, individual IDocs can be seen as instances of an IDoc type. The connector supports all IDoc types that are associated with the HRMD_A message type. A message type is a definition of the type of data generated and sent out from the target system.
See Also:
Structure of a Sample IDocThe method by which IDocs reach Oracle Identity Manager depends on the type of reconciliation that you configure:
Full Reconciliation
Figure 1-1 shows the flow of data during full reconciliation.
Figure 1-1 Data Flow During Full Reconciliation
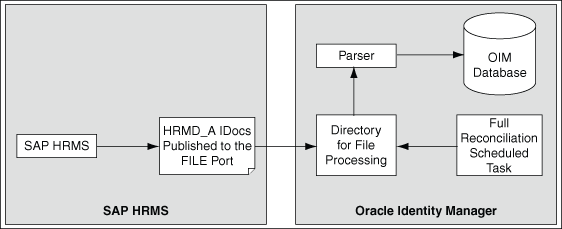
Description of "Figure 1-1 Data Flow During Full Reconciliation"
In full reconciliation, you run a transaction that generates IDocs for all existing target system users. These IDocs are captured in flat files and sent to a file port that you configure. You copy these flat files to a directory on the Oracle Identity Manager host computer and then run a scheduled task. A parser program called by the scheduled task converts the IDocs into reconciliation events.
Note:
After you deploy the connector, you first perform full reconciliation to create OIM Users for all existing target system users.Incremental reconciliation
Figure 1-2 shows the flow of data during incremental reconciliation.
Figure 1-2 Data Flow During Incremental Reconciliation

Description of "Figure 1-2 Data Flow During Incremental Reconciliation"
In incremental reconciliation, a change doc is created whenever a user record is created or updated. An IDoc is created for each change doc generated by the system. Scheduled tasks that you configure on the target system send these IDocs to a transactional remote function call (tRFC) port.
A scheduled task that you configure on Oracle Identity Manager acts as a listener and accepts IDocs from the tRFC port. The listener then calls the parser, which converts the IDocs into reconciliation events.
Note:
You configure the listener scheduled task to run continuously on Oracle Identity Manager. Configuring the Listener on Oracle Identity Manager provides information about this scheduled task.Whenever required, you can switch from incremental to full reconciliation and then switch back to incremental reconciliation.
1.5 Features of the Connector
The following are features of the connector:
- Dedicated Support for Trusted Source Reconciliation
- IDoc-Based Reconciliation
- Configurable Attribute Mapping
- Reconciliation of Effective-Dated Lifecycle Events
- Setting the Start Date and End Date Values Based on the Life Cycle Events of the Target System User Record
- Synchronization of Employee Type Data and Reconciliation by Employee Type
- Reconciliation of the Manager ID Attribute
- Reconciliation of Person Record Deletion
- Support for Both Unicode and Non-Unicode Modes
- Validation and Transformation of User Datas
- SAP ER Connector Support for IDoc in XML Format
1.5.1 Dedicated Support for Trusted Source Reconciliation
The connector provides all the features required for setting up SAP HRMS a trusted (authoritative) source of identity data for Oracle Identity Manager.
The connector cannot be used for setting up SAP HRMS as a target resource. In other words, the connector does not support provisioning operations and target resource reconciliation with SAP HRMS. This is because person records maintained in SAP HRMS are not accounts that users can use to log in to the system and perform business-related work.
1.5.2 IDoc-Based Reconciliation
The connector supports IDoc-based reconciliation. Both tRFC and file ports can be used as modes of communication between the target system and Oracle Identity Manager. The following are features of IDoc-based reconciliation:
- Standard BAPIs provided by the target system are used for reconciliation.
- Reconciliation is in real time. Changes made on the target system can be immediately sent to Oracle Identity Manager.
- You can specify the infotypes that must be fetched from the target system during reconciliation. You can also specify custom infotypes that have been added on the target system by extending IDoc types.
- The connector processes only person records. In the SAP context, this means that the connector processes only records of the P (person) object type. IDocs of all other object types, such as organization and position, are ignored even if they are sent to Oracle Identity Manager.
1.5.3 Configurable Attribute Mapping
You can specify the segments from which you want to reconcile changes.
In addition, you can customize attribute mappings between the target system and Oracle Identity Manager. During reconciliation, only changes to infotypes in segments that you specify are used to create IDocs. When an IDoc is processed by Oracle Identity Manager, attribute mappings are applied to filter out attributes that are used to create reconciliation events.
Extended IDoc types can be used for reconciliation. This means that you can add both standard and custom target system attributes can be added for reconciliation.
See sections Configuring Segment Filtering and Removing or Adding Attributes for Reconciliation for more information:
1.5.4 Reconciliation of Effective-Dated Lifecycle Events
The connector can distinguish between hire events and other events in the life cycle of a user record on the target system.
These events may be either current dated or future-dated (in other words, effective-dated). A current-dated event is one in which the date of the event is less than or equals the current date. A future-dated event is one in which the date the event takes effect is set in the future. For example, if the current date is 30-Jan-09 and if the date set for an event is 15-Feb-09, then the event is future dated. During reconciliation, the manner in which an event is processed depends on the type of the event:
- If both the hire event and changes to other infotypes are current dated, then the OIM User is created by using information from all infotypes.
- If the hire event is current dated and some other infotypes are future dated, then the OIM User is created by using only information from the current-dated infotype attributes. Future-dated infotype attributes are stored in reconciliation events to which the Event Deferred state is applied in the reconciliation manager.
- If the hire event is future dated, then depending on the value of the Create deferred event for future dated hire entry in the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.Configuration lookup definition, one of the following actions are performed:
- If the Create deferred event for future dated hire entry is set to Yes, then no OIM User is created. However, in the reconciliation manager, a reconciliation event (containing the future-dated infotype attributes) is created and the Event Deferred state is applied.
- If the Create deferred event for future dated hire entry is set to No, then an OIM User is created and the Start Provisioning date is set to the future date in the Action infotype in the target system record.
See Also:
Structure of a Sample IDoc for the location of the Action infotype in an IDoc.
- If the future-dated event is not a hire event, then it is set to the Event Deferred state.
The Process Deferred Recon Events scheduled task is used to process reconciliation events that are in the Event Deferred state. For each event in the Event Deferred state, the scheduled task compares the event date with the system date. If the Start Provisioning date is less than or equals the system date, then the event is forwarded to the Reconciliation Manager in Oracle Identity Manager.
1.5.5 Setting the Start Date and End Date Values Based on the Life Cycle Events of the Target System User Record
The Start date and End date process form fields are optional on Oracle Identity Manager. However, in the target system, the attributes corresponding to the Start date and End date process form fields are mandatory. Depending on whether you want to populate values for the Start date and End date process form fields, you set values for the OIM start date field and OIM end date field entries in the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.Configuration lookup definition.
The values for the Start date and End date process form fields are populated depending on the events in the life cycle of a user record on the target system. The Lookup.SAP.HRMS.HireEvents, Lookup.SAP.HRMS.TerminateEvents, and Lookup.SAP.HRMS.RehireEvents lookup definitions are used to determine values for the Start date and End date process form fields. See Predefined Lookup Definitions for more information about these lookup definitions.
If you set the values of the OIM start date field and OIM end date field entries in the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.Configuration lookup definition to None, then no values are populated in the Start date and End date process form fields.
If you set the values of the OIM start date field and OIM end date field entries in the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.Configuration lookup definition to Start date and End date respectively, then the following scenarios explain how these values are populated:
- For a particular target system user record, if IDoc contains information about both Hire or Re-hire event and Terminate events, then:
The value for the Start date field is the start date of the corresponding Hire or Re-hire event, which is determined from the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.HireEvents or Lookup.SAP.HRMS.RehireEvents lookup definitions.
The value for the End date field is the start date of the corresponding Terminate event, which is determined from the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.TerminateEvents lookup definition.
- For a particular target system user record, if IDoc contains events other than the Terminate event, then:
The value of the Start date field is the start date of the corresponding Hire or Re-hire event, which is determined from the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.HireEvents or Lookup.SAP.HRMS.RehireEvents lookup definitions.
The value of the End date field is the end date of the last event created for the user record.
1.5.6 Synchronization of Employee Type Data and Reconciliation by Employee Type
The Lookup.SAP.HRMS.EmployeeType lookup definition enables you to specify mappings between the following items:
- Employee Group and Employee Subgroup combinations on the target system
- Employee types defined in Oracle Identity Manager
You use the SAP HRMS EmployeeType Lookup Recon scheduled task to synchronize this lookup definition with changes made on the target system. See Lookup.SAP.HRMS.EmployeeType for more information.
In addition, you can use the Employee Type Query attribute of the SAP HRMS User Recon scheduled task to specify the employee types for which you want to fetch data for reconciliation. This additional filter is applied during the reconciliation process.
1.5.7 Reconciliation of the Manager ID Attribute
Note:
Configuring Reconciliation of Manager ID Attribute Values provides information about implementing this feature. The target system also provides the Supervisor attribute, which is a free-text field on the target system UI. If you want to bring values from this attribute into Oracle Identity Manager, first create a UDF for this attribute and then follow the instructions given in Adding Attribute Mapping.Managers are not defined for individual users on the target system. Instead, managers are defined for organizations and users are members of these organizations. The Manager ID attribute is one of the predefined OIM User form attributes.
Summary of the Manager ID Reconciliation Process
The following is a summary of the steps involved in reconciling the manager ID value for a particular OIM User:
- The organization ID of the OIM User is determined from the user's record on the target system and populated in the Org Unit attribute.
- The personnel number of the manager for that organization is determined from the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.OrgManager lookup definition. This lookup definition holds information about the managers for each organization.
If it is determined that the user is also the manager of the organization or if the position of the user's manager is currently vacant, then:
- The parent organization of the user's organization is determined from the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.OrgHierarchy lookup definition.
- The personnel number of the manager for the parent organization is determined from the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.OrgManager lookup definition.
- The manager's personnel number determined in Step 2 is populated in the Manager ID attribute of the OIM User form.
Note:
If the manager of the organization is changed, then the change is not automatically propagated to individual OIM User records. This is because the connector only fetches changes to person records, and not organization records. Running the SAP HRMS Update Manager Scheduled Task describes how you can reconcile Manager ID values in this scenario.The sequence of steps can be illustrated by the following example:
Suppose Richard is a user belonging to organization 50000147 on the target system. Drew is the manager of this organization. During reconciliation of Richard's user record:
- The organization ID of Richard's organization is determined from his user record.
- The personnel number of Richard's manager (Drew) is determined from Lookup.SAP.HRMS.OrgManager lookup definition.
- Drew's personnel number is used to populate the Manager ID attribute of Richard's OIM User form.
During reconciliation of Drew's user record:
- The organization ID of Drew's organization is determined from her user record.
- From the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.OrgManager lookup definition, it is determined that Drew is the manager of the organization to which she belongs.
- The parent organization of Drew's organization is determined from the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.OrgHierarchy lookup definition.
- The personnel number of the manager for the parent organization is determined from the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.OrgManager lookup definition.
- The personnel number of the manager is populated in the Manager ID attribute of Drew's OIM User form.
Detailed Steps of the Manager ID Reconciliation Process
To determine the manager ID of a particular target system user, the following approach is applied during reconciliation:
- The organization ID of the OIM User is determined from the user's record on the target system and populated in the Org Unit attribute.
- The personnel number of the manager for that organization is determined from the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.OrgManager lookup definition.
If it is determined that the user is also the manager of the organization, then:
- The parent organization of the user's organization is determined from the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.OrgHierarchy lookup definition. The Code Key column of this lookup definition holds the ID of an organization and the Decode column holds the ID of the corresponding parent organization.
Table 1-2 shows sample entries in this lookup definition.
Table 1-2 Sample Entries in the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.OrgHierarchy Lookup Definition
Code Key Decode 00000001 00000001 00000100 00000001 00001001 00000100 50000147 00001001 50000148 00001001 50000149 00001001 There can be multiple organization hierarchies on the target system. The Code Key and Decode entries are the same for the topmost organization in a particular organization hierarchy. The first row in the preceding table is an entry for a topmost organization.
- The personnel number of the manager for the parent organization is determined from the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.OrgManager lookup definition. The Code Key column of this lookup definition holds the ID of an organization and the Decode column holds the personnel number of the organization's manager.
Table 1-3 shows sample entries in this lookup definition.
Table 1-3 Sample Entries in the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.OrgManager Lookup Definition
Code Key Decode 00000001 00001009 00000100 00001017 00001001 00001018 50000147 00001019 50000148 00001020 50000149 00001021
- The parent organization of the user's organization is determined from the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.OrgHierarchy lookup definition. The Code Key column of this lookup definition holds the ID of an organization and the Decode column holds the ID of the corresponding parent organization.
- The personnel number of the manager is populated in the Manager ID attribute of the OIM User form.
1.5.8 Reconciliation of Person Record Deletion
The connector can process IDocs that bring data about deleted person records to Oracle Identity Manager. The details of the target system attribute that provides information about deleted person records are stored in the Delete Indicator entry of the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.Configuration lookup definition.
See Setting Up the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.Configuration Lookup Definition in Oracle Identity Manager for information about this lookup definition.
1.5.9 Support for Both Unicode and Non-Unicode Modes
An SAP application can be run in either Unicode or non-Unicode mode.
The connector supports both modes. You use the Unicode mode parameter of the IT resource to specify whether the target SAP application is running in Unicode or non-Unicode mode. Configuring the IT Resource provides more information about this parameter.
1.5.10 Validation and Transformation of User Datas
You can configure validation and transformation of user data that is brought into Oracle Identity Manager during reconciliation.
See the following sections for more information:
1.5.11 SAP ER Connector Support for IDoc in XML Format
The Connector supports processing of IDocS in xml format. This feature works similar to a flat file IDoc processing. XML IDoc (Standard IDoc/Extended IDoc/Custom IDoc) is parsed and the values are retrieved using JCo parser. Once IDoc is parsed, then the post processing is performed similar to a flat file.
To accomplish this feature, you must enter the value "yes" in the configuration lookup for the entry "Is IDoc File Format in XML."
Xml IDoc files must be placed at a defined folder location in the schedule task which can be accessed by IDM. SAP ER Connector reads these files from this location and parses the contents of the files. The connector creates reconciliation events for each record in IDM.
1.6 Connector Objects Used During Reconciliation
This section discusses the following topics:
1.6.1 User Fields for Reconciliation
Predefined attribute mappings for reconciliation between the target system and Oracle Identity Manager are stored in the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.AttributeMapping lookup definition. See Lookup.SAP.HRMS.AttributeMapping for more information.
1.6.2 Reconciliation Rule
The Personnel Number attribute of the target system can hold only numeric values. The User ID attribute of the OIM User form can hold alphanumeric values. If you use the target system as a trusted source, then all User ID values would have to be numeric values. This restriction might not be compatible with other target systems of Oracle Identity Manager in your operating environment.
To work around this restriction, the Personnel Number attribute of the target system is mapped to the following attributes on the OIM User form:.
- User ID attribute
- Personnel Number UDF
In addition, a two-component reconciliation rule is applied to reconciliation events:
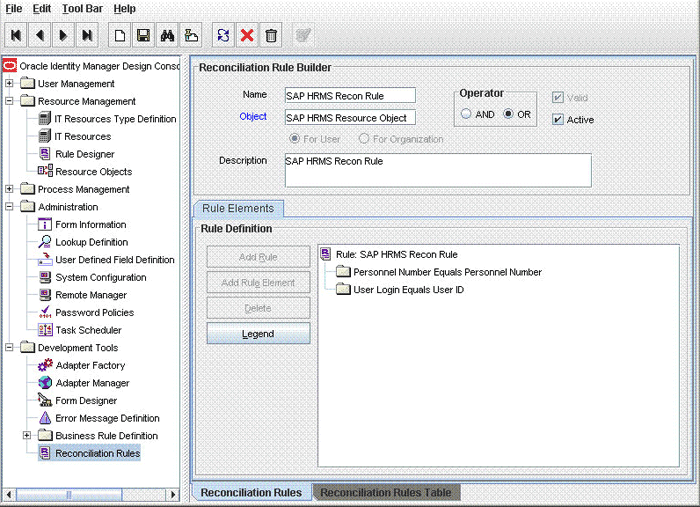
Rule name: SAP HRMS Recon Rule
Rule element: (Personnel Number Equals Personnel Number) OR (User Login Equals User ID)
- The Personnel Number attribute to the left of "Equals" represents the Personnel Number UDF created on the OIM User form.
- The Personnel Number attribute to the right of "Equals" represents the Personnel Number attribute of the target system.
- The User Login attribute represents the User ID attribute on the OIM User form.
- The User ID attribute represents the Personnel Number attribute of the target system.
When an OIM User is created during a reconciliation run, the Personnel Number value from the target system is used to populate both the User ID attribute and the Personnel Number UDF on the OIM User form. You are allowed to change the User ID value according to your requirements, but you cannot change the Personnel Number value on the OIM User form. The advantage of this feature is illustrated by the following example:
Suppose you have configured SAP HRMS as a trusted source and Microsoft Active Directory as a target resource. During reconciliation with SAP HRMS, the Personnel Number and User ID attributes are populated with Personnel Number values. For OIM User John Doe, you can manually change the User ID value to the samAccountName value of John's account on Microsoft Active Directory. During subsequent reconciliation runs with Microsoft Active Directory, the User ID attribute of the OIM User is used for matching purposes.
If you create an OIM User and then perform reconciliation with SAP HRMS, then the second component of the rule is used to determine a match between the OIM User and an existing account for the same individual on the target system.
After you deploy the connector, you can view the reconciliation rule for trusted source reconciliation as follows:
Note:
Perform the following procedure only after the connector is deployed.
- Log in to the Oracle Identity Manager Design Console.
- Expand Development Tools.
- Double-click Reconciliation Rules.
- Search for SAP HRMS Recon Rule. The following screenshot shows the reconciliation rule:
1.6.3 Reconciliation Action Rules
Application of the matching rule on reconciliation events would result in one of multiple outcomes. The action rules for reconciliation define actions to be taken for these outcomes. Table 1-4 lists the action rules for reconciliation.
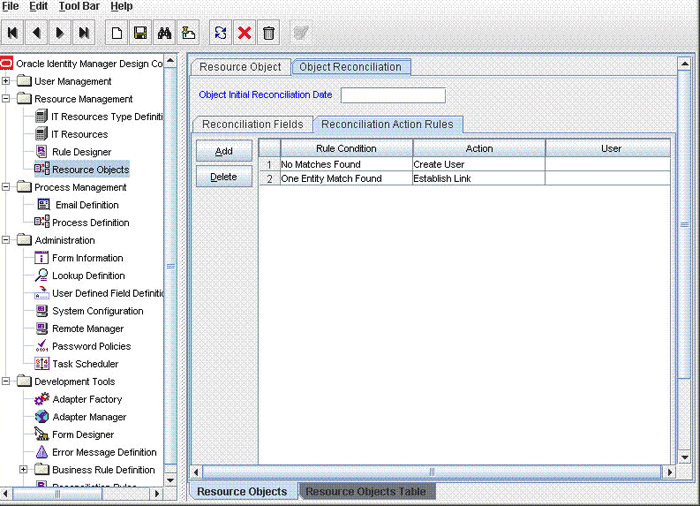
Table 1-4 Action Rules for Trusted Source Reconciliation
| Rule Condition | Action |
|---|---|
| No Matches Found | Create User |
| One Entity Match Found | Establish Link |
Note:
No action is performed for rule conditions that are not predefined for this connector. You can define your own action rule for such rule conditions. See Setting a Reconciliation Action Rule in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Manager for information about modifying or creating a reconciliation action rule.After you deploy the connector, you can view the reconciliation action rules for target resource reconciliation by performing the following steps:
- Log in to the Oracle Identity Manager Design Console.
- Expand Resource Management.
- Double-click Resource Objects.
- Search for and open the SAP HRMS Resource Object resource object.
- Click the Object Reconciliation tab, and then click the Reconciliation Action Rules tab. The Reconciliation Action Rules tab displays the action rules defined for this connector. The following screenshot shows the reconciliation action rules:
1.6.4 Predefined Lookup Definitions
The following are predefined lookup definitions:
Lookup.SAP.HRMS.ITResourceMapping
The IT resource for this connector contains the connection properties required to establish a connection with the target system. The entries listed in the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.ITResourceMapping lookup definition are mappings between:
- Code Key: Some of the connection properties defined for the ServerDataProvider and DestinationDataProvider interfaces of SAP JCo 3.0
- Decode: Parameters of the IT resource
The SAP JCo API recognizes only values assigned to the connection properties. The mappings in the lookup definition are used to forward values of the IT resource parameters to the appropriate SAP JCo connection properties.
See Also:
The Javadocs shipped with SAP JCo 3.0 for detailed information about these connection properties. See Specifying Values for the Connection Properties (IT Resource Configuration) for information about modifying this lookup definition.Lookup.SAP.HRMS.AttributeMapping
The Lookup.SAP.HRMS.AttributeMapping lookup definition holds default attribute mappings between the target system and Oracle Identity Manager. Table 1-5 lists the default attribute mappings stored in this lookup definition. The following is the format of values stored in this table:
- Code Key: Name of the OIM User field
- Decode: Combination of the following elements:
SEGMENT_NAME;SUB_TYPE;SAP_ATTRIBUTE_NAME;START_POSITION;END_POSITION;[Text|Date]
Table 1-5 Entries in the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.AttributeMapping Lookup Definition
| Code Key | Decode | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| First Name | E2P0002001;NONE;VORNA_40;790;829;Text | Default OIM User attribute |
| Middle Name | E2P0002001;NONE;NACHN_40;670;709;Text | Default OIM User attribute |
| Last Name | E2P0002001;NONE;NACHN;148;172;Text | Default OIM User attribute |
| Personnel Number | E2PLOGI001;NONE;OBJID;68;75;Text | UDF |
| Org Unit | E2P0001001;NONE;ORGEH;189;196;Text | UDF |
| City | E2P0006003;NONE;ORT01;197;221;Text | UDF |
| Street | E2P0006003;NONE;STRAS;167;196;Text | UDF |
| Country | E2P0006003;NONE;LAND1;257;258;Text | UDF |
| District | E2P0006003;NONE;ORT02;222;246;Text | UDF |
| Postal Code | E2P0006003;NONE;PSTLZ;247;256;Text | UDF |
| Telephone Number | E2P0006003;NONE;TELNR;259;272;Text | UDF |
| Department | E2P0030001;NONE;ORGEH;142;149;Text | UDF |
| Email Id | E2P0105002;NONE;USRID_LONG;172;412;Text | Default OIM User attribute |
| Linked User Id | E2P0105002;0001;USRID;142;171;Text | UDF |
| Cost Center | E2P0001001;NONE;KOSTL;179;188;Text | UDF |
| Idoc Number | EDI_DC40;NONE;DOCNUM;14;29;Text | Tracking the Idoc Number |
| Position | E2P0001001;NONE;PLANS;197;204;Text | UDF |
Lookup.SAP.HRMS.HireEvents, Lookup.SAP.HRMS.TerminateEvents, and Lookup.SAP.HRMS.RehireEvents
You use the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.HireEvents, Lookup.SAP.HRMS.TerminateEvents, and Lookup.SAP.HRMS.RehireEvents lookup definitions to hold the target system event IDs for Hire, Terminate, and Rehire events, respectively. When you deploy the connector, these lookup definitions are created without any entries. You add event IDs for Hire, Terminate, and Re-hire events as entries in these lookup definitions by performing the procedure described in the Configuring Reconciliation of Effective-Dated Target System Events.
Note:
On Oracle Identity Manager, the status of a terminated employee is set to Disabled and the status of a deleted employee (record) is set to Deleted.Lookup.SAP.HRMS.EmployeeType
On the target system, there is no direct equivalent for the Employee Type attribute of the OIM User. As a workaround, a combination of the Employee Group and Employee Subgroup attributes can be used for each employee type defined in Oracle Identity Manager.
You run the SAP HRMS EmployeeType Lookup Recon scheduled task to populate the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.EmployeeType lookup definition. After the scheduled task is run, the Code Key column of this lookup definition is populated with a concatenated combination of Employee Group and Employee Subgroup values from the target system. The tilde (~) character is used as the delimiter. The following are sample Code Key entries:
1~DZ
1~Q5
1~Q4
1~Q6
2~M6
OIM Employee Type is one of the Code Key values in the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.Configuration lookup definition. The value of this entry is "End User." When the scheduled task is run, the Decode column of the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.EmployeeType lookup definition is populated with "End User." After the scheduled task has run, you manually modify the employee type for each employee group and subgroup combination to individual employee types of your choice.
See Configuring the Scheduled Job for Lookup Field Synchronization for instructions on configuring the SAP HRMS EmployeeType Lookup Recon scheduled task.
Lookup.SAP.HRMS.Configuration
The Lookup.SAP.HRMS.Configuration lookup definition is used to capture information about the following items:
- Message type and IDoc type used for communication between the target system and Oracle Identity Manager
- Connector components used during reconciliation
See Setting Up the Lookup.SAP.HRMS.Configuration Lookup Definition in Oracle Identity Manager for a listing of the entries in this lookup definition.
Lookup.SAP.HRMS.Constants
The Lookup.SAP.HRMS.Constants lookup definition is used to store constants that are used by the connector. You must not modify the entries in this lookup definition.
Lookup.SAP.HRMS.CustomQueryMapping
You can configure limited reconciliation to specify the subset of target system records that must be fetched into Oracle Identity Manager. This subset is defined on the basis of attribute values that you specify in a query condition, which is then applied during reconciliation.
The Lookup.SAP.HRMS.CustomQueryMapping lookup definition maps resource object fields with OIM User form fields. It is used during application of the query condition that you create. See Limited Reconciliation for more information.
Lookup.SAP.HRMS.ReconValidation
This lookup definition is used to configure validation of user attribute values fetched from the target system during reconciliation.
You have to manually create entries in this lookup definition.
See Configuring Validation of Data During Reconciliation for more information.
Lookup.SAP.HRMS.ReconTransformation
This lookup definition is used to configure transformation of user attribute values that are fetched from the target system during reconciliation.
You have to manually create entries in this lookup definition. See Configuring Transformation of Data During User Reconciliation for more information.