2 Installing and Configuring the LDAP Gateway
The LDAP Gateway acts as the intermediary between Oracle Identity Manager and the connector components on the mainframe. You can install the LDAP Gateway either on a Microsoft Windows or RHEL Linux platform.
Hardware Requirements for Installing the LDAP Gateway
These are the recommended hardware requirements that are designed to give you optimal system performance from the LDAP gateway.
Table 2-1 Hardware Requirements for Installing the LDAP Gateway
| Requirement Type | Processor | RAM | Hard Disk | Network Interface |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum hardware requirement | 2 GHz single-core processor | 4 GB RAM | 10GB hard disk drive | 1 |
| Recommended hardware requirement | 2 GHz multicore processor | 16 GB RAM | 50GB hard disk drive | 1 |
Installing the LDAP Gateway
You can install the LDAP Gateway on Windows and Linux platforms.
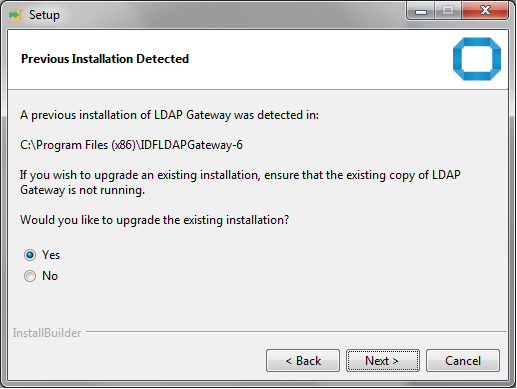
Upgrading the LDAP Gateway
If you already have an earlier version of the LDAP Gateway (for example, version 5.x), then you can upgrade it to the latest version 6.x by running the LDAP gateway installer.
Note:
Before you begin the upgrade procedure:- On the computer hosting the gateway, stop the running instance of the gateway. If you are using a Microsoft Windows Service to run the gateway, then uninstall the Windows service.
- In the target system environment, shut down any agents (for example, Pioneer or Voyager) that may be running.
- Disable any cron jobs.
Configuring the LDAP Gateway
Configure the LDAP gateway to connector to the target system and access the data.
Note:
The following procedures are for a fresh installation only. If you already have a running setup or if you want to upgrade, then you do not have to perform these procedures.Setting Connection Properties
The LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf directory contains the tops.properties.example file that contains sample entries and is used as the basis for configuring the gateway.
LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf location by creating a copy of the tops.properties.example file. Use this properties file to specify connection information that the gateway uses to connect to your target system. To do so:Creating the Connector Configuration
To allow the gateway to work with the target system, you must create and configure the customer-configuration.properties file for the type of connector and its related parameters for the operations.
Note:
In this guide, LDAP_INSTALL_DIR is the standard term used to refer to the directory in which the gateway has been installed. For example, for a Microsoft Windows host machine, the default installation directory for the gateway is . .\Program Files (x86)\IDFLDAPGateway-6\.The LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf directory has the customer-configuration.properties.example file that contains sample configuration entries and is used as the basis for creating the connector configuration. As the customer-configuration.properties.example file is only a sample file, you must create a separate properties file (for example, customer-configuration.properties) in the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf directory to include and configure entries specific to your connector from the customer-configuration.properties.example file.
Configuring the LDAP Gateway for Multiple Installations of the Target System
You can instantiate the same type of connector multiple times to represent multiple different endpoints of the same target system. This is in addition to the gateway supporting the ability to run connectors for various target systems within a single gateway instance.
Overriding the Default System Configuration
You can override the default system configuration by modifying the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/customer-configuration.properties file.
configuration.properties file (located in the conf/ folder) and copy it to customer-configuration.properties file and provide a new value.
Note:
Not all properties can be modified and must be done in consultation with Support.LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/configuration.properties file. If required, you can override any of these system configurations by copying relevant properties from the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/configuration.properties file to the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/customer-configuration.properties file, and then providing a new value.
Note:
Do not editLDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/configuration.properties file directly as it will be overwritten when you upgrade the gateway.Configuring the Windows Service for the LDAP Gateway
In a Windows environment, the LDAP Gateway can also be installed as a Windows Service. The Windows Service for the LDAP Gateway is installed using the IdentityForge batch file (IDF-Win-Service) that is included in the installation media.
Installing and Configuring the Windows Service for the LDAP Gateway
You can install the Windows Service by running the IDF-Win-Service install command.
LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/win_service directory in a command window and then run the IDF-Win-Service install command. If you encounter any issues with the installation, then uncomment the CG_PATH_TO_JVM variable in theLDAP_INSTALL_DIR/win_service/IDF-Win-Service.bat file and ensure that the path is accurate. The following is the code snippet from the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/win_service/IDF-Win-Service.bat file that you need to uncomment:
rem -- 7. Set this if you want to use a different JVM than the one configured in your registry, or if it is not configured in the windows registry rem set CG_PATH_TO_JVM=C:\Program Files\Java\jre7\bin\server\jvm.dll
If you need to modify the Windows service settings, then it is recommended to first uninstall the service, make the modifications, and then reinstall the service until it installs and runs correctly.
> net start IdentityForgeService
> net stop IdentityForgeService
Uninstalling the Windows Service for the LDAP Gateway
Uninstall the Windows service for the LDAP Gateway by running the IDF-Win-Service remove command.
LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/win_service directory in a command window and then run the IDF-Win-Service remove command.Configuring Memory Pool Settings
You can configure the memory pool size for the Windows service by setting values for the CG_JVMMS and CG_JVMMX variables in the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/win_service/IDF-Win-Service.bat file.
CG_JVMMS and CG_JVMMX variables are set to 1024 MB and 2048 MB, respectively. If the LDAP gateway processes a large number of records, then you might encounter the "Out of memory" exception. In such a scenario, you can allocate higher memory for your Windows service by increasing the values of the CG_JVMMS and CG_JVMMX variables.Configuring Transformation of the LDAP Gateway Attributes
You can configure transformation of LDAP Gateway attributes in search results by adding relevant entries to the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/customer-configuration.properties file.
LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/customer-configuration.properties file as an inline Jtwig template. For more information about Jtwig templates, see http://jtwig.org/documentation.For example, you can add a transformation rule to render the value of the sn attribute in the People OU in uppercase. To do so, you must add the following line in the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/customer-configuration.properties file:
cnctr.tops.tops1.transformation.People.read.sn.template.inline={{sn|upper}}This entry will render all the letters in the sn attribute in uppercase.
Configuring Multiple Instances of the LDAP Gateway
You can configure and run multiple instances of the LDAP Gateway on the same host by entering unique port values for each instance of the LDAP Gateway.
To do so, install and configure the LDAP Gateway for each instance that you want to run. While installing the LDAP Gateway, ensure that the installation directory is different for each instance of the gateway.
Then, update the default values for each property listed in Table 2-3 so that the value is unique for each instance of the LDAP Gateway that is installed on the host. Suppose you are using the default values in the property files for instance 1, then for instance 2, replace the default value with a unique value for the property. For example, for instance 2, change the default value 6398 of the system system.port property in theLDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/customer-configuration.properties file to a unique value such as 8389.
Table 2-3 Property Values To Be Updated for Running Multiple Instances of the LDAP Gateway
| Property Name and Location | Property Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
|
The |
Gateway listening port (LDAP) |
|
|
The |
Gateway listening port (LDAPS) |
|
|
The |
OpenDJ listening port (LDAP) |
|
|
Set the value of the |
Gateway config to read OpenDJ |
|
|
The |
OpenDJ listening port (LDAPS) |
|
|
The |
OpenDJ Administration port |
|
|
The |
OpenDJ Replication Server |
|
|
The |
OpenDJ Replication Server Port |
|
Encrypting Data
Learn about encryption performed by the LDAP gateway and how to configure it.
Understanding Encryption
The LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/encryption.properties file allows the ability to configure what properties, associated with the connector, must the LDAP Gateway manage as encrypted values.
LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/encryption.properties file is a common file containing properties of various modules that need to be securely protected. Use this file to define and encrypt any property located in the following files:
- connection properties file (created in Setting Connection Properties)
LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/customer-configuration.properties
When the LDAP gateway starts, it uses the encryption.properties file to examine the properties that it must represent in encrypted format.
For example, when the LDAP gateway starts, it reads the following entry from the encryption.properties file:
file.customer-configuration=adminUserPassword,altAdminUserPassword
This entry implies that there exists a properties file called customer-configuration.properties that contains sensitive properties adminUserPassword and altAdminPassword. The LDAP gateway searches for the customer-configuration.properties file, and if found, replaces any clear-text values for the adminUserPassword and altAdminPassword properties with an encrypted version.
Similarly, at start up, the LDAP gateway also reads the following entry from the encryption.properties file:
class.TopsModule=_secretKeyValue_
This entry implies that there exists a connector called TopsModule and its associated properties file (the one created in Setting Connection Properties) contains the sensitive property _secretKeyValue_ . The LDAP gateway searches for this properties file and replaces the clear-text value for the _secretKeyValue_ property with an encrypted value.
Encrypted values within property files are always represented using the ENC(ENCRYPTED_STRING) format. To add or replace an existing encrypted value with a new value, replace the entire encryption string if present (including the ENC(ENCRYPTED_STRING)) with a new clear-text value, and then restart the gateway. Once the gateway restarts, the newly added clear-text value goes through an encryption process with the result being written back out to the property file replacing the original clear-text value.
During the encryption process, the encryption framework that the gateway uses automatically detects the highest level of encryption possible by examining the version of the Java Virtual Machine running, along with any additional encryption libraries that may have been installed alongside the JVM. By default, Java 1.8 supports 128-bit AES encryption and Java 1.7 supports 40-bit AES encryption. You can install additional encryption libraries by BouncyCastle into the JVM allowing for up to 256-bit AES encryption.
The encryption process in the LDAP gateway also allows for automatic migration of encryption values from a lower bit strength to a higher strength as it becomes available. For example, if the gateway is initially deployed on a system running Java 1.7 with 40-bit AES and that system is upgraded to Java 1.8 running 128-bit AES, then upon the next restart of the gateway, all encrypted values remaining at the 40-bit AES level are automatically re-encrypted at the higher 128-bit and stored back out in the property files. This process eliminates the need to manually replace the values in every property file in order to take advantage of the higher bit strength.
The gateway uses the private key located in the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/idf.properties file for all the encryption and decryption that it performs. The idf.properties file is created in the conf directory when the LDAP gateway is started for the first time. It is recommended that access to this file is restricted.
Note:
Once the gateway is deployed and started for the first time, the value of the autogenerated encryption key in the idf.properties file should not be changed. However, you can change the file name and its location. For example, to store the idf.properties file to a more secure location, the default location (where the gateway resides) can be overwritten and defined assystem.idfprops.filepath=ABSOLUTE_PATH_OF_THE_NEW_FILE in the customer-configuration.properties file.Configuring Encryption
You can configure encryption by editing the encryption.properties file located in the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/ directory.
- the
adminUserPasswordandaltAdminPasswordproperties in theLDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/customer-configuration.propertiesfile. - the
_secretKeyValue_property in the connection properties file (created in Setting Connection Properties).
If you want to encrypt additional properties in the customer-configuration.properties file, then you must include them as a comma-separated list in the following property of the encryption.properties file:
file.customer-configuration=adminUserPassword,altAdminUserPassword
For example, if you want to encrypt the schema and suffix properties of the customer-configuration.properties file, then include them in thefile.customer-configuration property of the encryption.properties file as follows:
file.customer-configuration=adminUserPassword,altAdminUserPassword,schema,suffix
If you want to encrypt additional properties in the connection properties file, then include them as a comma-separated list in the following property of the encryption.properties file:
class.TopsModule=_secretKeyValue_
For example, if you want to encrypt the _host_ and _port_ properties of the connection properties file, then include them in the class.TopsModule=_secretKeyValue_ property of the encryption.properties file as follows:
class.TopsModule=_secretKeyValue_,_host_,_port_
If you want to change the values any encrypted properties, then remove the ENC along with the value and then add the new value.
For example, if the value of the adminUserPassword property in the customer-configuration.properties file is encrypted, then from the adminUserPassword=ENC(t8+B0TbafPKyFFf0KoTlAmde82aRnwtf) value, remove ENC(t8+B0TbafPKyFFf0KoTlAmde82aRnwtf) and replace it with the new value, without the prefix ENC. Whenever the gateway is restarted, it automatically overwrites the clear-text value with its encrypted counterpart.
Understanding the Caching Layer
The LDAP gateway features an optional and configurable caching layer, which is a temporary storage area where frequently accessed data is stored for rapid access.
An expiration policy defines the time dependency for the cached resource. For example, the cachingMaxAge parameter specifies the maximum time in minutes when the data is not in sync with the target system. You can pair the caching layer with an incremental reconciliation (to maintain the most recently updated data in the caching layer. This improves the performance of the LDAP gateway. In addition, the caching layer opens the LDAP gateway for more advanced features defined by the LDAPv3 RFC.
Benefits of Using the Caching Layer
- Faster search operations (when the cache is primed)
- A unified Base DN for both provisioning and reconciliation data
- The ability to perform advanced LDAP search filters against the gateway.
- The ability to query an RFC compliant ChangeLog for delta reconciliation.
Note:
In an environment where the items noted above may not be required, you can disable the caching layer.
Considerations for Using the Caching Layer
The LDAP gateway can suffer a performance penalty when all of the following conditions are met:
- There is no data in the cache, or the cache is stale based on the configuration.
- An LDAP search operation is performed to retrieve the children of an Organizational Unit. For example, the contents of
ou=People. Such an LDAP search operation returns only DNs (along with RDN components). - The connector only returns key information when returning a list of objects.
- The
cachingIterateBehaviorproperty in theLDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/configuration.propertiesfile remains set to the default ofAUTOand not overwritten within thecustomer-configuration.propertiesfile.In such a scenario, an LDAP search operation initially retrieves the list of results, containing only DN and RDN values. The caching layer then iterates through each result, fetching and caching the details from the target system. Finally, the full set of results are returned to Oracle Identity Manager.
To avoid this scenario, it is recommended that you use the caching layer in combination with scheduled reconciliation. With reconciliation setup and the staleness settings configured properly the above conditions will not be met.
How to Enable or Disable the Caching Layer?
The caching layer is enabled by default. To override this default setting or disable the caching layer, copy the cnctr.coreBean.nexus.cachingEnabled property from the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/configuration.properties file to the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/customer-configuration.properties file and then set its value to false.
You can enable the caching layer by setting the value of the cnctr.coreBean.nexus.cachingEnabled property in the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/customer-configuration.properties file to true .
Configuring Scheduled Reconciliation
Scheduled reconciliation allows for establishing a periodic synchronization between the Identity Store associated with the LDAP Gateway and that represented by your target system reachable by way of the connector.
LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/dist/scheduled-recon.jar) is a tool that ships with the IdentityForge LDAP Gateway. It provides the ability to perform a full recon against a configurable target system, placing the results in the internal identity store of the gateway. This utility provides a basic scheduling service for kicking off the built-in batched reconciliation of the connector on a configurable interval.LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf folder. Use this file to configure scheduled reconciliation.About Parsing Grammar Protocol 1.0
Grammar is necessary for properly parsing user and group listings that come into the gateway from the mainframe agent during search requests and reconciliation events.
The grammar represents line-by-line parsing instructions that convert the semi-structured textual data into LDAP attributes and their respective values. Each line (ending in CRLF) of the listing received from the agent can be represented by an individual grammar definition and specified in the grammar file. The grammar file is present in the <conf/parser-grammar/ > folder.
Grammar files with the default grammar are present in the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/parser-grammars/tops directory. It parses user and group listings that come into the gateway from the mainframe agent during search requests and reconciliation events.
ACCESSORID = 0518AA NAME = 0518AA TYPE = USER SIZE = 1024 BYTES DEPT ACID = DEPTX DEPARTMENT = LARGE-DEPT-TEST CREATED = 05/19/15 16:50 LAST MOD = 07/29/15 22:02 ----------- SEGMENT CICS OPCLASS = 09 OPIDENT = ABC OPPRTY = 010 SCTYKEY = 001,005,007,009,011,097 SITRAN = F FACILITY = *ALL* ----------- SEGMENT LU6.2 #APPL = APTRA_VISION_USER|ATM_CONFIG_USER|CS_REVIEW SET1DISP = AB|AC|AD|AE| ------------ SEGMENT NETVIEW DOMAINS = 09 INIT CMD = 09 ----------- SEGMENT OMVS ROOT = 09 ----------- SEGMENT WORKATTR ACCOUNT = 123 ADDRESS1 = ADDR 1 ADDRESS2 = ADDR 2 ADDRESS3 = ADDR 3 ADDRESS4 = ADDR 4 BUILDING = BLDG 17 DEPARTMENT = DEPART 1 NAME = NAME ROOM NUMBER= ROOM B1 XA DATASET = ADBFLE OWNER(00123 21322 ) ACCESS = READ,WRITE XA DATASET = TDBFLE OWNER(00123 54232 ) ACCESS = READ,DELETE,WRITE XA DATASET = TDBFLE OWNER(00123 ) PASSWORD = EXPIRES = 06/18/15 INTERVAL = 030
Using the above listing, if you want to parse out the OPCLASS value from the listing and assign it to an LDAP attribute called “opcls”, then you can construct the following <Line> element in the grammar file:
<Line id=”opclassVal” enabled=”yes” sig=”[ ]*OPCLASS = (?<opcls>.*)"/>
The signature attribute (sig) in the Line element above is a regex that represents the rules for pulling out the value and assigning it to an LDAP attribute. Regex named groups are used as the convention for assigning the discovered values to LDAP attributes exposed through the connector.
The following table lists the attributes of a line element. The allowed values for these attributes are yesor no.
| String | Mandatory? | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| id | Yes |
Unique ID that is given to the line definition. Used primarily for internal referencing purposes, such as with the 'dependson' attribute. Values allowed:any |
| enabled | No | Specifies whether the line is eligible for participating in the parsing process. Use this flag to override files (turn off lines).
Default value: yes |
| signature | Yes | Defines the rules for what values are to be extracted for each line of the listing and which LDAP attributes should be assigned the values. |
| required | No | Defines whether an attribute is required or not.
Default to: |
| multiline_sig | No | An optional regex expression to define the signature of a follow-on line that could represent whether the value was wrapped around two additional lines in the document.
Values allowed: Any valid regex containing attribute matching key and attribute name. Defaults to:empty value |
| repeats | No | Represents whether the line can show up multiple times in the document. If set to no, then once the line is found, this Line definition is not evaluated again for the rest of the document.
Defaults to: |
| overflow | No | Represents whether data for an associated attribute can overflow to the next line. In case of an overflow, the final value of an attribute is derived by concatenating all values.
Defaults to: |
| multivalue_parser | No | An optional regex expression that defines how the found values are to be parsed out and turned into a multivalued list, such as using '(\S+)' to parse values that are space delimited.
Values Allowed: Any valid regex Defaults to:empty value |
| applyCompositeRef | no | An optional comma-separated list of composite attributes to be built immediately after processing the line. Each value in the comma-separated list must correspond to the "id" attribute of a CompositeAttribute definition. |
| defaultvalue | No | Defines the default value for an attribute. If this line does not match with any line of input, then this default value will be assigned to attribute. |
Customizing Grammar Rules
The grammar file with the default grammar is present in the conf folder. It parses user and group listings that come into the gateway from the mainframe agent during search requests and reconciliation events. You can apply new grammar rules to append to or override rules that come out of the box. To define new grammar rules or override the existing rules, create a grammar file parser-grammars.cust file in the <conf/parser-grammar/ > folder.
You can apply new grammar rules to append to or override rules that are available by default in the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/parser-grammars/tops directory.
To define new grammar rules or override the existing rules, you must create a custom grammar file (for example, tops_FindAllUsers.cust) in the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/parser-grammars/tops directory.
Note:
-
If the Id of the existing attribute matches with the attribute in the grammar line, it overrides the existing grammar definition.
-
If the Id of the existing attribute does not match with the attribute in the grammar line, it creates a new grammar definition.
-
The
parser-grammars.custgrammar file must be at the same location where the default grammar files are located (LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/parser-grammars/tops). -
The name of the grammar file must be the same except the
custextension. -
The name of the grammar file must be the same except the
custextension. For example, if you need to customize the grammar for theLDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/parser-grammars/tops/tops_FindAllUsers.xmlfile, then create a custom grammar fileLDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/parser-grammars/tops/tops_FindAllPeople.cust. -
For the grammar definitions to override, the ID attribute from both the files should match.
Nomenclature of the parsing grammar files
Each grammar file is named for the type of operation and listing it is responsible for parsing.
-
tops_FindAllUsers.xml– fetches the IDs of all users. -
tops_FindUserById.xml– fetches all the details of a single user (for the given ID).
Overriding default existing grammar definitions
The grammar definitions specified in the grammar file parser-grammars.cust override the default grammar definitions specified in the property files. To enable overriding of the particular line, the ID attribute in the custom provided attribute should match with the default grammar definition.
The grammar definitions specified in the custom grammar file override the default grammar definitions. To enable overriding of a particular line, the ID attribute in the custom provided attribute should match with the default grammar definition.
<Protocol><Lines> <Line id="elId" enabled="yes" sig="[ ]*ELID[ ]*=[ ]*(?<ELID>.*)"/> </Lines>/Lines>
<Protocol><Lines> <Line id="elId" enabled="no" sig="[ ]*ELID[ ]*=[ ]*(?<ELID>.*)"/> </Lines></Protocol>
New grammar definitions
DEPT_ACID=001 DEPT_NAME=hr.
<Protocol><Lines> ="deptAcid" enabled="yes" sig="[ ]*DEPT_ACID[ ]*=[ ]*(?<deptacid>.*?) [ ]*DEPT_NAME[ ]*=[ ]*(?<department>.*)" /> </Lines></Protocol>