 Understanding Journal Management Features
Understanding Journal Management Features
This chapter provides overviews of journal management features and allocations and discusses how to:
Establish journal approval processing.
Create, edit, copy, and approve manual journals.
Post and unpost journals.
Publish journals.
 Understanding Journal Management Features
Understanding Journal Management Features
There are several processes with which you can manage journals. If you must quickly add missing subsidiary information, for example, or enter an adjustment that is based on updated information, instead of reloading the source ledger, you can create a manual journal entry.
Journal entries are defined for a specific consolidation business unit, scenario, fiscal year, and accounting period. They can be created after the ledger preparation process is run and before or after consolidation processes are run.
PeopleSoft Global Consolidations provides two types of journal entries:
Manual journal entries are those that you create. They can be set up to reverse, recur at specified intervals, and require approval. They must always be edited (validated) before they can be posted.
System-generated journals are created during several consolidation processes, such as inter-company eliminations, equitization, and currency translation. They are identified with a Global Consolidations source code so you can track them to the process that created them. They are automatically approved, edited (validated), and posted if they meet tolerance requirements.
You can do the following with manual journals:
Establish approval options.
For a specified consolidation business unit and scenario, you can indicate whether all journals should require security- based approval, workflow-based approval, or no approval.
Copy journals.
For example, if you have multiple consolidation scenarios that are based on the same data and you need to make the same journal entry to each of these scenarios, you can create the entry, then copy the journal to those scenarios.
See Copying Journals.
Reverse journals.
At the time you are creating a manual journal, you can also specify the period in which it should be reversed with a reversal batch.
Generate recurring journals.
You can create recurring journal entries that you can schedule in advance with a one-time setup.
Post and unpost journals.
You can access the Performance Management Warehouse ledger post application to post or unpost journals for a specified consolidation business unit, scenario, fiscal year, period, and journal ID.
Publish journals.
You can use data mapper rules to publish selected journals back to the source general ledger in either a PeopleSoft General Ledger format, or a Global Consolidations format. You can also use data mapper rules to transform data during the journal publish process.
See Publishing Journals.
View a proforma trial balance.
Before approving or posting journals, you can see the results as if they had been posted on a proforma trial balance.
See Viewing Proforma Trial Balances, Viewing Proforma Trial Balances.
Lock scenarios to prevent posting.
You can lock a scenario or a specified node on the consolidation tree for a specific period to prevent posting or unposting of journal entries.
See Locking Scenarios.
Track journal flow information.
You can specify flow codes on journal entry line items and use them to track cash flow, fixed asset activity, and other types of flow information.
 Understanding Allocations
Understanding Allocations
The Allocations application engine (PF_ALLOC_ENG) that comes with the Enterprise Performance Management Warehouse generates journal entries to distribute amounts, such as overhead costs, across multiple ChartFields such as book codes or business units, based on the allocation rules that you define. Some examples of reasons why you might need to process allocations against the consolidation ledger are to:
Allocate taxes.
For example, U.S. taxes include paid local taxes but are usually calculated on the consolidated total.
Allocate centralized functions, such as information technology, human resources, and other similar departments.
Charge interest on intercompany balances.
Allocate harmonization entries.
For example, book code is a dimension that you can use as an allocation source, basis, target, and offset amounts as well as the book code ChartField to segregate the journal created from the source.
Note. When you set up allocations that use a consolidation ledger as the target, you must use the delivered value object %GC_ALLOCATION to format the GC_SOURCE field on either the Target, Residual, or Offset pages of the allocation rule. This populates GC_SOURCE with 07, indicating that the source was an allocation entry.
See Also
PeopleSoft Customer Connection red paper entitled “PeopleSoft Enterprise Global Consolidations Alocations ”
Defining Allocation Manager Rules
 Establishing Journal Approval Processing
Establishing Journal Approval Processing
This section provides an overview of journal approval processing and discusses how to establish journal approval options.

 Understanding Journal Approval Processing
Understanding Journal Approval Processing
You have the option of establishing approval processing for manual journals before posting. This option is established using the business unit and scenario that you specify on the Warehouse Business Unit Scenario Definition page. For consolidations, you associate this with the common consolidation business unit. The following options are available for journal approval processing:
Workflow-based approvals, in which you use approval rules and workflow processes.
Security-based approvals, in which you limit access to the journal approval page to only the appropriate people within your organization.
Automatic pre-approvals for all journals.
System-generated journals (which are generated from running consolidation processes) are not subject to approvals.
Before journals that require approval can be posted, they must be approved.
Note. Unapproved journals are included in proforma results. This enables you to see the impact of journals on the consolidated results before approving them.
Workflow-Based Approvals
The delivered workflow definition requires two separate approvals, one local and one corporate. The local approval includes routings based on the journal monetary amount, with different approvers authorized for different amounts. This table shows the delivered workflow objects:
|
Object |
ID |
|
Business Process |
GC_JOURNAL_ENTRY_APPROVAL |
|
Approval Rule Set |
GC_JOURNAL_ENTRY_APPROVAL |
|
Approval Rule Set |
GC_JOURNAL_ENTRY_APPROVAL_HQ |
The procedure for using workflow to approve journals is:
A user enters a new manual journal.
The approval status is initially None, and Approve is the default approval action.
(Optional) The user saves the journal without initiating the workflow process.
In this case, the approval status remains set to None.
The user clicks Submit on the Approvals page to initiate the approval process.
If there are no errors in the manual journal entry, the system begins the journal approval process:
If the approver for the journal sets the approval action to Deny, the system changes the status to Denied, and an email is sent to the user who entered the journal.
If the approver for the journal sets the approval action to Approve, the virtual approver is called to see if the user is authorized to approve the journal, and if so, then the approval status is set to Approved.
Otherwise, the status is set to Pending Approval, and a worklist item is generated for the next user in the approval hierarchy.
When a supervisor or manager approves the journal from a worklist, the worklist links directly to the approval page. The supervisor or manager can keep the default action of Approve or change the action to Deny.
You can create your own business process or modify the delivered objects to suit your implementation.
See Enterprise PeopleTools PeopleBook: Workflow Technology.
Security-Based Approvals
There are no email notifications, approval rules, or worklist entries for security-based approvals. You can, however, restrict which business unit-scenarios a user can approve by setting up the appropriate row level security in the Enterprise Performance Management Warehouse.
Authorized users who create journal entries, but do not approve journals, should have read-only access to the Journal Approvals page. They can see the approval status of journals but cannot approve them. Authorized users who can approve journals should have full access to the page. The process flow for security-based journal approvals is:
Enter a manual journal.
The approval status is initially None, and Approve is the default approval action.
(Optional) Save the journal without initiating the workflow process.
In this case, the approval status remains set to None.
Click Submit on the Approvals page to initiate the approval process.
If there are no errors in the manual journal entry, the system begins the journal approval process:
If a user does not have access to the approval page, then the approval action remains None.
The system updates the journal approval status to Pending Approval.
If a user does have access to the approval page, then the user can change the approval action to either Approve or Deny, and the status changes accordingly.
Authorized personal who can approve journals must periodically query the database to see if there are any journals with a Pending Approval status.
These individuals have full access to the approval page (contingent on row-level security), and can change the action from the default value of None to either Approve or Deny by clicking the Submit for Approval button to update the status accordingly.
(Optional) The person entering the journal can click the Notify button to send an email to authorized personal for approving the journal.
Preapproved Journals
The process flow for preapproved journals is:
Enter a manual journal.
The approval status is initially None, and Approve is the default approval action.
If there are no errors in the manual journal entry, the system changes the journal approval status to Approved.
See Also

 Page Used to Set Up Journal Approval Processing
Page Used to Set Up Journal Approval Processing

 Establishing Journal Approval Options
Establishing Journal Approval Options
Access the Warehouse Business Unit Scenario Definition page.
|
Manual Journal Approval Option |
Specify the type of approval that you require by selecting a value from the drop-down list box. You options are as follows: Approval Required - Security Select if you require security-based journal approvals. The ability to approve a journal is controlled by each user's security access to the Journal Approvals page. Approval Required - Workflow Select if you require workflow-based journal approvals. Workflow rules control the approval process. Pre-Approved Select if you do not require an approval process. When you save manual journals, the system approves their status. |
For workflow-based journal approvals, also complete these fields:
|
Business Process Name |
Specify the business process to use for approvals. GC_JOURNAL_ENTRY_APPROVAL is the delivered business process. |
|
Specify the approval rule set to use for approvals. GC_JOURNAL_ENTRY_APPROVAL is the delivered approval rule set. |
Remember that you can modify the approval rule set and business process definitions or create and use your own to suit your implementation. If you use the delivered approval rules, you can change the amounts at which different approvers are set.
See Also
Understanding Journal Approval Processing
Enterprise PeopleTools PeopleBook: Workflow Technology
 Creating, Editing, Copying, and Approving Manual Journals
Creating, Editing, Copying, and Approving Manual Journals
This section provides an overview of manual journals and discusses how to:
Create a manual journal.
Create a manual journal with a reversal batch.
Create a recurring journal template.
View a recurring journal.
Attach supporting documentation for manual journal entries.
Approve journals.
Copy journals.
Run the Manual Journals Edit process.
Run the Recurring Journals process.

 Understanding Manual Journals
Understanding Manual Journals
Use the pages in the Manual Journal component to create, review, edit (validate), or copy manual journals. If you require journal approvals, use the Journal Approval page to update a journal's approval status. Journals are written to the journal fact table specified on the ledger template, (for example, GC_JRNL_MGT_F00), which is the source record for the various ledger posting processes.
Journal Balancing
When you save a journal, if the ledger with which it is associated is requires balancing, the system uses the balancing account type rule specified on the consolidation model to determine if the journal balances.
Journal Statuses
Journals can have the following statuses:
|
New |
The status when a journal has been created, but not edited (validated). |
|
Valid |
The status after a journal is edited (validated) and no errors are found. At this point the journal can be posted. |
|
Error |
The status when the manual journal cannot be edited (validated). |
|
Posted |
The status when the journal has been successfully posted. |
|
Unposted |
The status when the journal has been successfully unposted. |
Manual Journal Types
PeopleSoft Global Consolidations provides these three manual journal types:
Manual journals, used for one-time journal entries.
Recurring templates, used to define multiple journal entries that are scheduled on a recurring basis.
Recurring journals, which are the actual journals generated from recurring templates.
Defining Recurring Journal Entries
Global Consolidations enables you to create recurring journal entries that you can schedule in advance with a one-time setup.
For example, you might want to amortize a capital expenditure over the next twelve periods, and rather than entering the journal entry for the amortization each period, you can use a recurring template to setup the amortization schedule once. Your recurring template schedule could be the last day of the period for the next twelve periods. The system can create all twelve recurring journals at one time or you can run the Recurring Journal engine when you are ready to process each period.
There are two options for scheduling recurring journals:
Scheduling for sequential periods using the Every Period option, you can select either the first day or last day of the period for the Recurring Journal date.
Scheduling with the Specific Dates option lets you select a specific date for each recurring journal.
You can create all recurring journals immediately or you can run the recurring journals engine for each period at a later time. If the recurring template uses a currency other than the base currency, creating all of the recurring journals at one time will use the exchange rate from the recurring template, which may be incorrect for later periods. Running the recurring journal engine when you are ready to process each period will use the exchange rate appropriate for that period.
See Defining Recurring Journal Templates.
See Running the Recurring Journals Process.
Journal Copy
You can copy a manual journal or recurring template to:
Record the same journal entry to multiple scenarios.
(The journals must all use the same consolidation business unit.)
Duplicate a manual journal for another fiscal year or period.
Create a separate journal entry to reverse a manual journal entry.
You can copy any existing new, valid, or posted journal that was created from the Manual Journal Entries page.
Note. You can also copy a recurring template but not a recurring journal linked to a recurring template.
See Copying Journals.
Reversing Journal Entries
There are two methods for creating journal reversal entries :
Create a reversal batch.
Copy a manual journal with the reverse amount.
You can create a reversal batch by using the Journal Reversal page when creating a manual journal. The Create Reversal Batch option creates a separate batch linked to the original journal entry. Select this option to activate the journal reversal page and enter the setup information for your journal entry reversal. The only thing that you must specify for journal reversal setup is the period in which you want the reversal batch to be posted.
The reversal batch is created in a valid (edited) status that does not require performing journal edits. The reversal batch must be posted to the ledger. If you unpost the original journal batch that a posted reversal batch is linked to, you receive a warning to unpost the reversal batch. Similarly, if you try to post a reversal batch without posting the original journal batch, you receive a warning that the original journal batch has not yet been posted.
Alternatively, you can copy your original journal, select the reverse amount option, and designate the journal date to create a reversal journal. The Copy button on the Journal Entries page creates a separate manual journal that needs to be reviewed, edited, and posted to the ledger. When you copy a journal with reverse amount option, there are no post or unpost warnings because the two journals are not linked.
Attaching Supporting Documentation
You can attach supporting documentation to a Manual Journal. Use the Journal Attachments page and click the Add Attachments button to attach a document to the Manual Journal.

 Pages Used to Create, Copy, Edit, and Approve Manual Journals
Pages Used to Create, Copy, Edit, and Approve Manual Journals
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
PF_JOURNAL_TBL1 |
Global Consolidations, Manage Journals, Manual Journal Entry, select Journal Type Manual Journal, select Journal Entries tab |
Create, copy, or edit (validate) manual journals. |
|
|
PF_JOURNAL_TBL3 |
Global Consolidations, Manage Journals, Manual Journal Entry, Journal Reversal |
Reverse a journal entry by creating a journal reversal batch and specifying the fiscal year and accounting period in which to create the reversal. . |
|
|
GC_JOURNAL_RCRT |
Global Consolidations, Manage Journals, Manual Journal Entry, select Journal Type Recurring Journal, select Recurring Template tab |
Define the recurring journal template and specify schedule options. Create, edit, view, or delete recurring journals linked to a recurring template. |
|
|
GC_JOURNAL_RCRJ |
Global Consolidations, Manage Journals, Manual Journal Entry, select Journal Type Recurring Journal, select Recurring Journals tab |
View the recurring journal template that is used to create recurring journals. |
|
|
PF_JRNL_ATTACHMENT |
Global Consolidations, Manage Journals, Manual Journal Entry, Journal Attachments |
Attach documentation to support journal entries. |
|
|
PF_JOURNAL_TBL2 |
Global Consolidations, Manage Journals, Manual Journal Entry, Journal Approval |
View or edit the journal approval status. |
|
|
GC_JRNL_COPY |
Click the Copy button on the Journal Entries page. |
Copy a manual journal or recurring template. |
|
|
GC_JRNL_COPIED |
Click the OK button on the Copy Journals page. |
Review the results of the copy journal process. |
|
|
RUN_GC_JRNL_EDIT |
Global Consolidations, Manage Journals, Process Journals, Manual Journal Edit |
Run control page for editing (validating) manual journals. Runs the GC_JRNLEDT jobstream. |
|
|
RUN_GC_JRNL_EDIT2 |
Global Consolidations, Manage Journals, Process Journals, Manual Journal Edit, Manual Journal Selection |
Select manual journals for editing and posting. |
|
|
RUN_GC_JRNL_RCR |
Global Consolidations, Manage Journals, Process Journals, Recurring Journals |
Run control page for creating recurring journals for a specific period. Runs the GC_JRNLRCR jobstream. |
|
|
Journal Source |
PF_JRNL_SRC |
EPM Foundation, Data Enrichment Tools, Profit Manager, Performance Journals, Journal Source |
Enter journal source codes. |

 Creating and Reviewing Manual Journals
Creating and Reviewing Manual Journals
Access the Journal Entries page.
To create a new journal entry, access the Journal Entries page in Add mode, and specify a journal ID, journal date, business unit, scenario, and journal type. To review a journal entry, access the Journal Entries page in Update/Display mode, and enter the search parameters to view a list of journals that you can review.
Journal types are as follows: Manual Journal, Recurring Template, and Recurring Journal.
Note. In Add mode, only the Manual Journal and Recurring Template journal types are available. In Update/Display mode, all three journal types are available.
|
Status |
Displays the status of the manual journal entries. New is the default status when a manual journal is created.. |
|
Draft |
Select this option to create a draft journal. Draft journals are excluded from any additional processing. |
|
Hold Posting |
Select to prevent a journal from posting during the ledger post processing. This enables you to save the journal entry and continue to add information to it at a later time. When the journal is complete, clear the Hold Posting check box to enable the journal to post. |
|
Calculate |
Click to update the debit and credit totals in the Journal Information region and Journal Totals grid. The total debits and credits should be equal for each consolidation unit (such as ledger business unit). |
|
Copy |
Click to access the Copy Journals page, where you can copy the journal. This option is not available until you save the journal. |
|
Edit Journal |
Click to edit (validate) your journal. This checks for valid dimension values in the ChartFields that are specified on the journal entry. The total debits must equal the total credits for each consolidation unit (such as ledger business unit). Journals cannot be posted until they are valid. If there are errors on the journal, you can correct the errors, and then edit (validate) the journal again.. Alternatively, you can run journal edits for multiple journals by using the Manual Journal Edit application engine run control page. See Running the Edit Manual Journal Process. When you edit a journal, a batch ID is assigned and journals with valid line data are moved to the journal fact table defined in your Ledger Template (for example, GC_JRNL_MGT_F00) and journals with erroneous data reside in the journal error table (for example, GC_JRNL_MGT_E00) until you correct and edit the data. |
|
Post Journal |
After the journal is validated (edited) the Post Journal Link is active and you can click this link to take you to the Post Ledger run control page to post the journal. Alternatively, you can select the Post Journal option on the Manual Journal Edit run control page to validate and then post your manual journal entry after it is validated (edited). |
Journal Information
Expand the Journal Information region to complete or review these fields:
|
Journal Source Code |
Select the journal's source code. You define journal source codes on the Journal Source Code page in the Enterprise Performance Management Warehouse. This is an optional field. |
|
Description |
Enter a description for the journal entry. |
The system derives values in the Fiscal Year and Period fields from the scenario's calendar, based on the journal date. The system derives the value in the Base Currency field from the business unit definition. The amounts for Total Debits and Total Credits for the entire journal also appear in the Journal Information grid.
Journal Lines
To enter journal entries, add rows to the Journal Lines grid as needed. For each line, you must complete the consolidation dimension value (for example Ledger Unit), the Account field, and an Amount. If the transaction currency is not the same as the base currency, you must also specify the Currency, Amount, and Rate Type; the system uses the associated exchange rate and populates the Base Amount field.
The consolidation dimension field label varies depending on the consolidation dimension. For example, if the consolidation dimension is business unit, the field label that appears is Ledger Unit. The ledger template that is associated with the business unit for the journal entry determines the ChartFields that are available for the journal entry.
Note. You can customize the journal lines grid to show and hide the specific ChartFields that you want to see.
Journal Totals
Use the Journal Totals grid to view a summary of the journal entry. The information is grouped by consolidation dimension value (such as ledger business unit), listing the total number of lines and total debits and credits. If a journal is balanced, the Total Debits for each consolidation dimension should equal the Total Credits, based on the balancing rules specified for the consolidation model. If debits and credits do not balance, the system will let you save what has been entered, however the journal will not be valid until it is balanced.
See Defining Balancing Account Type Rules.

 Reversing Journal Entries
Reversing Journal Entries
Access the Journal Reversal page.
Select the Create Reversal Batch check box and specify the period in which you want the reversing journal entry to occur.
For the Journal Reversal Date, you can specify either the Next Period, which is based on your original journal date, or you can select Specific Period and enter a Fiscal Year and Accounting period.
You can create journal entry reversals at the same time that you create a manual journal or recurring journal template. Reversals created using this method are tied to your original journal by the journal ID. The only parameter that you need to specify for journal reversal setup is the period in which you want the reversal journal to be created. For manual journals, you can select either next Period or specific period. For recurring journal templates, you can only select next period.
The Create Reversal Batch option on the Journal Reversal page creates a separate batch that is linked to the original journal entry. The reversal batch is created in a valid (edited) status that does not require performing journal edits.
The original journal batch and the reversal batch will be posted separately to the ledger. If you unpost the original journal batch that a posted reversal batch is tied to, you receive a warning informing you that you have a posted reversal batch that you need to unpost. Similarly, if you try to post a reversal batch without posting the original journal batch, you receive a warning that the original journal batch (tied to the reversal by journal ID) has not yet been posted.
Alternatively, you can copy your original journal, select the reverse amount option, and designate the journal date to create the reversal journal. This creates a separate manual journal that needs to be reviewed and edited and batch posted to the ledger. Reversals created by copying the original journal entry are not linked to the original journal entry, so no warnings appear if you post or unpost the journals out of sequence.

 Defining Recurring Journal Templates
Defining Recurring Journal Templates
Access the Recurring Template page.
A recurring journal template provides the exact journal entry that you want to post periodically, including the accounts, amounts, and other dimensions. You create it exactly the same as a manual journal entry, except you select the Journal Type Recurring Template. On the Journal Entries page, you enter the line items including the accounts, amounts, and other dimensions for the journal entry and edit (validate) it. You can also select the Draft and Hold Posting options for the recurring template. When the recurring journals are generated, they will inherit the same options. If the recurring entry needs to be reversed in the next period, on the Journal Reversal page, enter the reversal information for the next period.
Note. The only option for reversing a recurring journal template is the next period.
On the Recurring Template page, you specify how frequently the recurring journal entry should be generated. You set up a recurring journal schedule by selecting one of the following Scheduling Options :
Note. The Recurring Template page is only visible when the journal type is Recurring Template.
|
Every Period |
Select to generate journals every period. You must also complete these fields:
The system uses the journal date that you specified when creating the recurring journal template as the begin period date. The Journal Date and the End Date fields are inclusive of the range of dates for processing. |
|
Specific Dates |
Select this option to schedule a recurring journal entry for the dates that you specify. In the Specific Dates grid, insert a row and enter each date the recurring journal should be generated. |
Journals Created
The Journals Created grid displays the journals that you have created by using either the Create Journals button or by using the recurring journals process.
|
Create Journal |
Click to create all of the journals that you specified with the Recurring Schedule. By default, any journals that are created are set to a status of New and must be edited (validated) before they can be posted. They will also inherit other options from the template, such as Hold Posting, Draft, or Create Reversal Batch. If the recurring journals use a currency other than the consolidation currency, all the recurring journals that you create at one time will use the current period translation rate. It is recommended that you only create recurring journal using a foreign currency for the current period to ensure that the currency is translated using the proper translation rate Alternatively, you can create a batch of recurring journals for a period by using the Create Recurring Journal run control page. The system picks up the recurring journal information from the recurring template data and creates all recurring journal entries for the period specified on the run control page that have not been previously created. On the run control page, you can also select options to edit and post the recurring journals that are generated by this process. See Running the Recurring Journals Process. Warning! After recurring journals are created, changes to the recurring template are not reflected in the recurring journals. If you want the template changes to be reflected in the recurring journals, you can delete the selected journals (if they have not been posted), then create the recurring journals again. |
|
Delete Selected Journals |
Select this check box to delete the recurring journal entries that are selected in the Journals Created grid. You cannot delete journals that are already posted. |
|
Select All |
Selects all created journals that haven't been previously posted. You can then click Delete Selected Journals to delete them. |
|
Clear All |
Unselects all journals that were previously selected. |

 Viewing a Recurring Journal
Viewing a Recurring Journal
Access the Recurring Journal page.
After a recurring journal entry is created, you can view it by selecting the Journal Type Recurring Journal when accessing the journal entries component. The journal ID is the same as the recurring template journal ID. On the Journal Entries page, if the journal has not been posted, you can change the line items, edit (validate) the journal, and select the link to post it. Select the Recurring Journal tab to view the Recurring Template ID and Template date.

 Attaching Supporting Documentation for Manual Journal Entries
Attaching Supporting Documentation for Manual Journal Entries
Access the Journal Attachments page.
You can use the Journal Attachments page to add supporting documentation for your manual journal.
Click the Add Attachment button to bring up a file browser dialog box. Click the Browse button to navigate to the location of the supporting documentation, select the file, and click Upload to attach the supporting documentation.
To view a document, click the file name link. To remove a document, click the Delete button.

 Approving Journals
Approving Journals
Access the Journal Approval page.
The system does not copy journal lines into the journal fact table until the journal status is set to Approved.
See Also
Understanding Journal Approval Processing

 Copying Journals
Copying Journals
Access the Journal Entries page and click the Copy button to access the Copy Journal Entry page.
Copy to Journal
The Copy From Journal region lists the values you are copying from the source journal.
Complete the fields within the Copy to Journal region to specify the journal ID, date, whether to reverse the copied amounts, and whether to hold posting.
Complete the fields within the Copy to Scenarios region to specify to which scenarios to copy the journal. You can only copy to scenarios that are linked to the same common consolidation business unit on the Warehouse Business Unit Scenario Definition page.
|
Journal ID and Journal Date |
Enter the journal ID and date. The default value appearing in this field is the same value as the journal you are copying. You can override this value. You must specify the journal date. The system uses the target journal date to derive the fiscal year and accounting period values. |
|
Reverse Amount |
Select to reverse the amount of the copied journal (credit to debit and debit to credit). This is one method to reverse a journal entry. You can also reverse a journal entry on the Journal Reversals page. |
|
Hold Posting |
Select to prevent the copied journal from posting to ledger. |
Copy to Scenarios
|
Copy |
Select this check box to copy the source journal to the scenario from this row. Only scenarios that are linked to the common consolidation business unit on the Warehouse Business Unit Scenario Definition page are listed. |
Click OK to copy the journal.
The Journal Copied page summarizes the scenarios to which the journal was copied. Any copied journals requiring approval (through workflow or security) initially have an approval status of None. Regardless of the source journal system, the target journal system source is set to SCG (meaning that the journal was system-generated and originated from the Journal Copy process).

 Running the Edit Manual Journal Process
Running the Edit Manual Journal Process
Access the Manual Journal Edit page.
You run the GC_JRNLEDT jobstream to identify any balance errors and check for valid dimension values in the ChartFields that are specified on the journal entry.
Use the Manual Journal Edit run control page to edit (validate) and optionally post selected manual journals or recurring journals with the status of New for the specified consolidation business unit, scenario ID, fiscal year, and accounting period. The journal edit process takes data from the Manual Journal Header table (PF_JRNL_HDR_TBL), and Line table (PF_JRNL_LN_TBL) and validates that data. The process creates a batch header (PF_BATCH_TBL) and moves the lines to the journal fact table (for example, GC_JRNL_MGT_F00) that is defined in the consolidation ledger template.
Note. You can also edit journals one at a time on the Journal Entries page.
|
Business Unit, Scenario ID, Fiscal Year, and Period |
Specify the consolidation business unit, scenario ID, fiscal year, and accounting period to process. |
|
Jobstream ID |
Accept the default value, GC_JRNLEDT, to use the delivered jobstream ID. |
|
Get Journal Data |
Select to get a list of all journals with the status of New or Valid for the specified consolidation business unit, scenario ID, fiscal year, and accounting period and display it on the Manual Journal Selection page. |
Selecting Manual Journals for Edit
Access the Manual Journal Selection page.
After selecting the Manual Journal Edit run control parameters, use the Manual Journal Selection page to select the manual and recurring journals that you want to edit. You can also select the option to post the journals on this page provided that the journals are valid after the manual journal edit process.
|
Journal ID |
Displays the journal Id. |
|
Journal Date |
Displays the journal date. |
|
Draft |
Displays whether Draft is selected for this journal on the Journal Entries page. |
|
Hold Posting |
Displays whether Hold Posting is selected for this journal on the Journal Entries page. |
|
Journal Status |
Displays the journal status. Only journals with the status of New or Valid are displayed. |
|
Edit Journal |
Select this check box to run the edit (validate) process for this journal. You can only select this check box for journals with the status of New. |
|
Post Journal |
Select this check box to run the post process for this journal. You can only select this check box for journals with the status of New. Only journals with the status of Valid after running the edit process will be posted. |

 Running the Recurring Journals Process
Running the Recurring Journals Process
Access the Recurring Journals run control page.
Use the Recurring Journals run control page to generate recurring journals for a specific fiscal year and period by running the GC_JRNLRCR jobstream. The system reviews each recurring journal template for the specified common consolidation business unit, scenario ID, fiscal year, and accounting period and creates all recurring journal entries that have not been previously created. You can also select Edit Journal to edit all of the journal entries created by this process, and Post Journal to post all of the journal entries created by this process.
Note. If you do not select the Edit Journal and Post Journal options, then the Recurring Journals are created with a status of New. You will need to select these journals and edit and post them.
|
Unit, Scenario ID, Fiscal Year, and Period |
Specify the common consolidation business unit, scenario ID, fiscal year, and accounting period to process. |
|
Jobstream ID |
Accept the default value, GC_JRNLRCR, to use the delivered jobstream ID. |
 Posting and Unposting Journals
Posting and Unposting Journals
This section provides an overview of journal posting and unposting and lists the pages used to post and unpost journals.

 Understanding Journal Posting and Unposting
Understanding Journal Posting and Unposting
To post or unpost journals to their respective ledgers, use the ledger posting or ledger unposting engines within PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Management Warehouse. When you run the consolidation application engines, if you choose the option to post, the system calls the appropriate PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Management Warehouse application engines.
You can post journals with the status Valid, meaning that they have been edited. You can unpost journals with the status Posted. When journals are unposted, their status is Unposted.
You can access and run the post ledger process by using any of these methods:
Access the ledger post engine in the Manage Journals, Process Journals folder or from the Performance Management Warehouse menu.
Select the Post Journal link on the Manual Journal Entries page or the Proforma Trial Balance page to access the Ledger Post run control page.
Select the Post Journal option when running the manual journal edit process.
Select the Post Journal Created option when running the elimination process.
Select the Post Journal Created option when running the equitization process.
Enter the consolidation business unit, scenario, fiscal year, and period for the journals that you want to post or unpost. To post journals, select the Job ID PF Ledger Post. To unpost journals, select the Job ID PF Ledger Post.
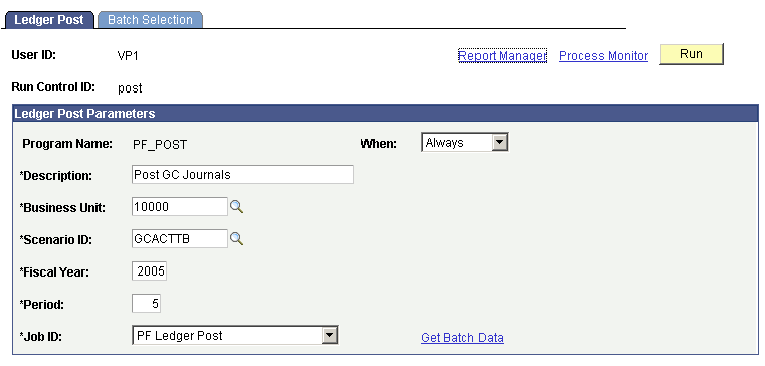
Ledger Post page
See Also
Processing and Posting Journals
Running the Edit Manual Journal Process

 Pages Used to Post and Unpost Journals
Pages Used to Post and Unpost Journals
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
RUN_PF_POST |
Global Consolidations, Manage Journals, Process Journals, Post Ledger or EPM Foundation, Data Enrichment Tools, Profit Manager, Performance Journals, Post Ledger, |
Enter the consolidation business unit, scenario, fiscal year, and period for the journals that you want to post and initiate the post ledger process. |
|
|
Batch Selection |
PF_POST_BATCH |
On the Ledger Post page select Get Batch Data. |
Select the journals that you want to post or unpost. |
|
RUN_PF_UNP |
Global Consolidations, Manage Journals, Process Journals, Unpost Ledger or EPM Foundation, Data Enrichment Tools, Profit Manager, Performance Journals, Unpost Ledger, PF Ledger Unpost |
Enter the consolidation business unit, scenario, fiscal year, and period for the journals that you want to unpost and initiate the unpost ledger process. |
 Publishing Journals
Publishing Journals This section provides overviews of journal publishing and PeopleSoft Enterprise Integration Broker and discusses how to:
Mapping journal publish rules.
Understanding PeopleSoft Enterprise Integration Broker.
Define journal publish target options.
Define journal publish source options.
Run journal publish.
Review journal publish history.

 Understanding Journal Publishing
Understanding Journal PublishingThe journal publish feature enables you to send journals that are generated in Global Consolidations back to source systems that subscribe to these messages. Journals are published as XML messages.
You set up data mapper rules that define which ChartFields the system publishes. Data mapper rules can also provide additional information not available in the in the journal data. For example, you can use data mapper rules to specify the values for the LEDGER_ID and AFFILIATE fields. Data Mapper also works in conjunction with ledger preparation. You can “reverse map” the changes done during the ledger preparation process.
You define journal publish rules that specify which journals the system publishes and which data mapper rules to use. You assign these rules to a consolidation model; therefore, different consolidation scenarios can use different publish rules.
The publish rules that you establish specify:
The data mapper rule to use.
The target ledger.
The format in which to publish the data.
Which journals to publish, based on the source process from the originating journal.
Note. The publish process cannot reverse map the consolidation ledger's chart of accounts if during the ledger preparation process, several source accounts were merged into one target account. The publish process cannot map changes done during calendar mapping or currency conversion process.
Data Flow
This diagram illustrates the data flow for publishing journals:
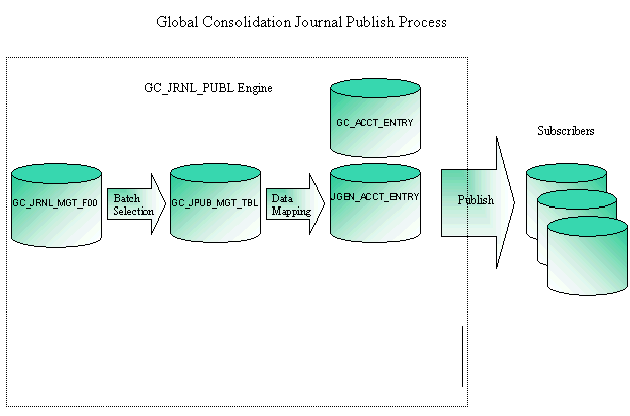
Journal publish data flow
The source record for the journals is GC_JRNL_MGT_F00. When you run the journal publish process, the system creates the accounting entries in the staging journal (GC_JPUB_MGT_TBL). You then use data mapper in conjunction with the journal publish process to move the data to either the Global Consolidation accounting entry table (GC_ACCT_ENTRY), the PS General Ledger accounting entry table (JGEN_ACCT_ENTRY), or both, depending on the options that you select. These tables are built from a ledger template, so you have the ability to customize their ChartFields.
You must process (edit and post) the published journals in the subscribing application; in PeopleSoft General Ledger, use Journal Generator.

 Mapping Journal Publish Rules
Mapping Journal Publish Rules
The Data Mapper provides a comprehensive ChartField mapping capability. Data Mapper is used with the Journal Publish process to set up “reverse mapping” rules for journal publish that map ChartFields in the staging journal to the target accounting entry table.
You follow these steps to map journal publish rules:
Define the journal record.
Define the staging journal.
Define target metadata.
Define data mapper rule sets and rule groups.
Define journal publish rules.
With the flexibility of data mapper rules, you can add constraints that filter input rows from GC_JRNL_MGT_TBL as needed. For example, you can populate data to the Global Consolidations account entry table for all ledger business units under the EMEA nodes of the GC_BUCONSL tree, and the General Ledger account entry table for other ledger business units. You can build filters and constraints for each situation and then specify the constraint to use with the appropriate data mapper rule.
Defining the Journal Record
Global Consolidations provides GC_JRNL_MGT_F00 as the journal record. If you are using a name other than GC_JRNL_MGT_F00 for your journal record, you must modify the GC_JRNL_PUB_VW SQL definition, or journal publish will not work.
To modify the GC_JRNL_PUB_VW SQL definition:
Using PeopleSoft Application Designer, open the GC_JRNL_PUB_VW SQL definition.
Locate this line:
From PS_GC_JRNL_MGT_F00 A.
Replace the GC_JRNL_MGT_F00 portion of the string with your journal record name, and save your changes.
Rebuild the view.
Defining the Staging Journal
The staging journal is a copy of the Global Consolidations journal fact table, with additional fields added that are required to properly load the data to the target accounting entry table. These additional fields include a unique transaction line number for each source row, as well as a few non-ChartFields that are common for either format of the accounting entry tables. The staging journal is used as the source record for the data mapper to perform ChartField mapping. After the staging journal is defined, it is specified on the consolidation Ledger Template - Consolidation Variables page. Global Consolidations provides the GCJRNLPUB staging journal, and it is specified on the GCCLEDMGT consolidation ledger template.
Note. Global Consolidations does not reverse engineer the rules used for ledger preparation and does not provide any embedded allocation processing.
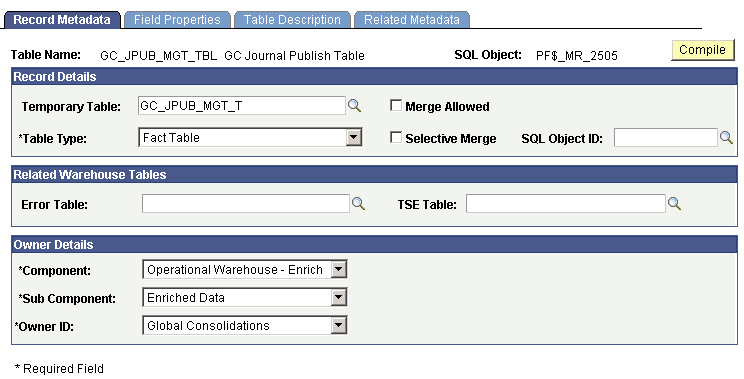
Record Metadata page
The following table lists the source metadata that is used with the staging journal table:
|
Metadata |
Metadata |
|
Record Metadata |
GC_JPUB_MGT_TBL |
|
Table Map |
GCJRNLPUB |
|
Source Data Map |
GCJRNLPUB |
|
Constraint |
GCJPUBNONE |
Defining the Target Metadata
You can publish the journals in these formats:
PeopleSoft GL Accounting Entry format.
This structure is in the format of the PeopleSoft General Ledger. You use data mapper to define rules that map the data back to the General Ledger and retain all of the detail. Each line in the journal is assigned a unique journal line number, preserving the journal detail. When publishing journals using the Journal Generator in General Ledger, the journal lines are aggregated into the journal that was created. The journals published using this format are stored in JGEN_ACCT_ENTRY.
Global Consolidation Accounting Entry format.
This structure retains all the detail in the journal. The BUSINESS_UNIT_LED field is mapped to the BUSINESS_UNIT field, and the GC_AFFLIATE field is mapped to the field that you specify. The journals published using this format are stored in GC_ACCT_ENTRY.
If you do any sort of many-to-one mapping in ledger preparation, you should either publish back to a single primary target value, or you must use additional dimensions to maintain the appropriate level of detail to support their reverse mapping needs. In order to use journal publish rules to move data directly to the PeopleSoft General Ledger, you must set up specific data mapper rules and supporting data.
Global Consolidations delivers the record metadata, tablemap, and datamap for GC_ACCT_ENTRY and for JGEN_ACCT_ENTRY. This table describes the delivered target metadata:
|
Metadata |
JGEN_ACCT_ENTRY |
GC_ACCT_ENTRY |
|
Record Metadata |
JGEN_ACCT_ENTRY |
GC_ACCT_ENTRY |
|
Tablemap |
JGENACCT |
GCACCTENT |
|
Datamap |
JGENACCT |
GCACCTENT |
This table lists the fields that are in each format. The fields are listed in alphabetical order so that you can easily compare the fields included for each format:
|
PeopleSoft GL Accounting Entry (JGEN_ACCT_ENTRY) Format Fields |
Global Consolidation Accounting Entry (GC_ACCT_ENTRY) Format Fields |
|
ACCOUNT |
ACCOUNT |
|
ACCOUNTING_DT |
ACCOUNTING_DT |
|
ACCOUNTING_PERIOD |
ACCOUNTING_PERIOD |
|
AFFILIATE |
AFFILIATE |
|
AFFILIATE_INTRA1 |
|
|
AFFILIATE_INTRA2 |
|
|
ALTACCT |
|
|
APPL_JRNL_ID |
APPL_JRNL_ID |
|
BATCH_STATUS |
BATCH_STATUS |
|
BOOK_CODE |
|
|
BUDGET_REF |
|
|
BUSINESS_UNIT |
BUSINESS_UNIT |
|
BUSINESS_UNIT_GL |
BUSINESS_UNIT_GL |
|
BUSINESS_UNIT_LED |
|
|
BUS_UNIT_E1 |
|
|
CHANNEL_ID |
|
|
CHARTFIELD1 |
|
|
CHARTFIELD2 |
|
|
CHARTFIELD3 |
|
|
CLASS_FLD |
|
|
CURRENCY_CD |
CURRENCY_CD |
|
CUST_ID |
|
|
DEPTID |
DEPTID |
|
DOC_SEQ_DATE |
|
|
DOC_SEQ_NBR |
|
|
DOC_TYPE |
|
|
FISCAL_YEAR |
FISCAL_YEAR |
|
FOREIGN_AMOUNT |
FOREIGN_AMOUNT |
|
FOREIGN_CURRENCY |
FOREIGN_CURRENCY |
|
FUND_CODE |
FUND_CODE |
|
GC_AFFILIATE |
|
|
GC_SOURCE |
GC_SOURCE |
|
GL_DISTRIB_STATUS |
GL_DISTRIB_STATUS |
|
IU_ANCHOR_FLG |
|
|
IU_SYS_TRAN_CD |
|
|
IU_TRAN_CD |
|
|
JOURNAL_DATE |
JOURNAL_DATE |
|
JOURNAL_ID |
JOURNAL_ID |
|
JOURNAL_LINE |
JOURNAL_LINE |
|
JRNL_LN_REF |
|
|
LEDGER |
LEDGER |
|
LEDGER_GROUP |
LEDGER_GROUP |
|
LINE_DESCR |
|
|
MONETARY_AMOUNT |
MONETARY_AMOUNT |
|
MOVEMENT_FLAG |
MOVEMENT_FLAG |
|
OPERATING_UNIT |
OPERATING_UNIT |
|
PF_BATCH_ID |
PF_BATCH_ID |
|
PF_EDIT_SEQ_NUM |
|
|
PF_SCENARIO_ID |
|
|
PROCESS_INSTANCE |
PROCESS_INSTANCE |
|
PRODUCT |
PRODUCT_ID |
|
PROGRAM_CODE |
|
|
PROJECT_ID |
PROJECT_ID |
|
RATE_DIV |
|
|
RATE_MULT |
|
|
RT_TYPE |
|
|
STATISTIC_AMOUNT |
STATISTIC_AMOUNT |
|
STATISTICS_CODE |
STATISTICS_CODE |
|
SUBLEDGER |
|
|
SUBLDGRTYPE |
|
|
SUBSIDIARY |
|
|
TRANSACTION_ID |
TRANSACTION_ID |
|
TRANSACTION_LINE |
TRANSACTION_LINE |
Defining Data Mapper Rule Sets and Rule Groups
PeopleSoft Global Consolidations provides the following data mapper rule sets to use with journal publishing:
GCJPUBR1 maps from GC_JPUB_MGT_TBL to JGEN_ACCT_ENTRY.
GCJPUBR2 maps from GC_JPUB_MGT_TBL to GC_ACCT_ENTRY.
You can use the provided rule sets and modify them as needed, or you can create your own. This is how the GCJPUBR1 data mapper rule set is delivered:
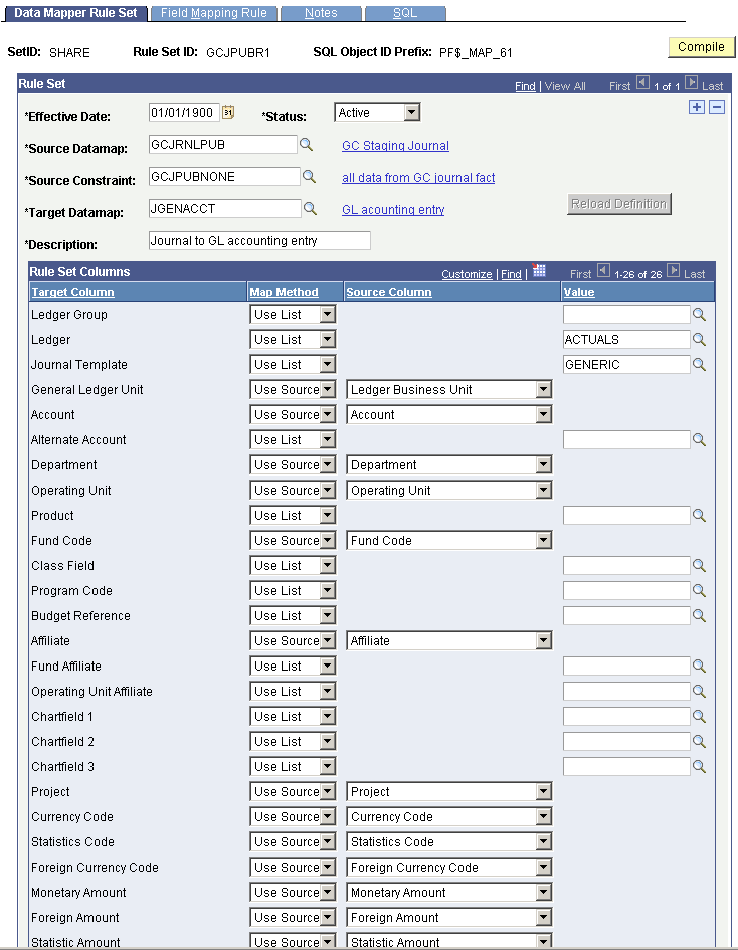
Data Mapper Rule Set page
The data mapper rule group is designed so that the source rows that are mapped by one rule set will be excluded from subsequent rule sets. The following shows that rule group GCJPUBG1 is created to include rule set GCJPUBR1.
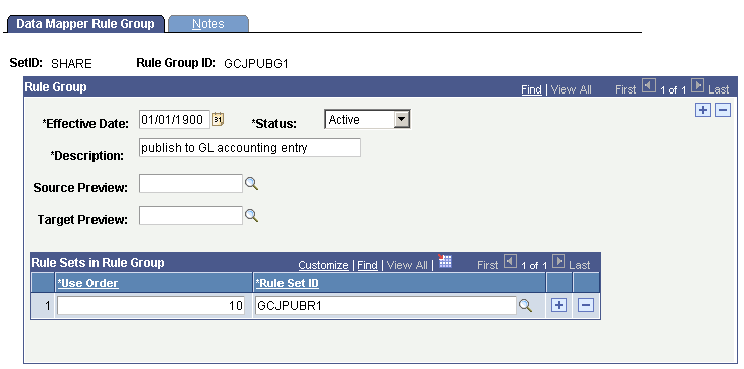
Data Mapper Rule Group page
Defining Journal Publish Rules
On the Journal Publish Rule page, you can create or select data mapper rule(s) to use with journal publish. When the Peoplesoft GL Accounting Entry check box is selected, the journal publish process picks up the associated data mapper rule to perform field mapping to JGEN_ACCT_ENTRY. When the Global Consolidation Accounting Entry check box is selected, the journal publish process picks up the associated data mapper rule to perform the field mapping to GC_ACCT_ENTRY.
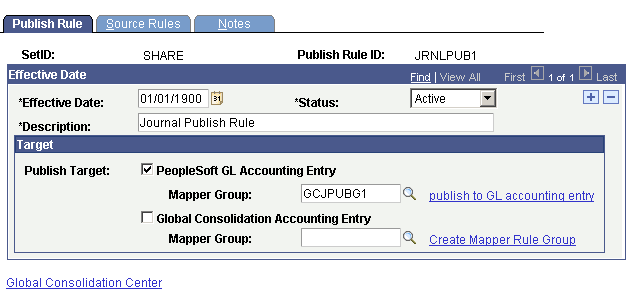
Journal Publish Rule page

 Understanding PeopleSoft Enterprise Integration Broker
Understanding PeopleSoft Enterprise Integration Broker
The journal publish feature uses enterprise integration points (EIPs), also known as data publish and subscribe, across applications. EIPs simplify cross-product integration and automate data transport by providing a predefined structure of the data message among involved parties. You must use PeopleSoft Enterprise Integration Broker to set up messages and message channels.
It is recommended that you read the following:
Enterprise PeopleTools PeopleBook: PeopleSoft Integration Broker, “Understanding Integration Broker,” Integration Broker Monitor.
Enterprise PeopleTools PeopleBook: PeopleCode Developer's Guide, “Using Methods and Built-in Functions,” Understanding File Attachment Architecture.
Setting Up PeopleSoft Integration Broker
To set up and use the Integration Broker Gateway:
Read Enterprise PeopleTools PeopleBook: PeopleSoft Integration Broker, “Understanding PeopleSoft Integration Broker” thoroughly.
Review theEnterprise PeopleTools PeopleBook: PeopleSoft Integration Broker chapters to learn how to set up the Integration Broker Gateway.
Point the Integration Broker Gateway to the PeopleSoft EPM and FDM databases following the instructions in the Enterprise PeopleTools PeopleBook: PeopleSoft Integration Broker.
Read Enterprise PeopleTools PeopleBook: PeopleSoft Integration Broker, “Managing Service Operations” thoroughly, and activate the GC_ACCT_ENTRY and JOURNAL_LOAD_TEMPLATE service operations.
Install any additional files required by the PeopleBook instructions.
To publish messages across applications, set up messages and message channels for both the publisher and the subscribers’ end.
You can use enterprise integration points (EIPs) to publish the journal accounting entries to subscribers. For the additional target record, you can use PeopleSoft Enterprise Integration Broker to set up messages and message channels for the data transport across applications. Similar setup should also be done on the subscribers’ side. The subscribing application must process (edit and post) the published journals; in PeopleSoft General Ledger, use Journal Generator.
Note. You set up the Integration Broker Gateway and point it to the PeopleSoft databases one time only.
Activating Relevant Service Options
To activate integration broker messages, use PeopleTools Integration Broker services options, and specify the service and the options. Both the GC_ACCT_ENTRY and JOURNAL_LOAD_TEMPLATE service operations are used with Global Consolidations journal publish. You must check the Active flag and select other options for each of them.
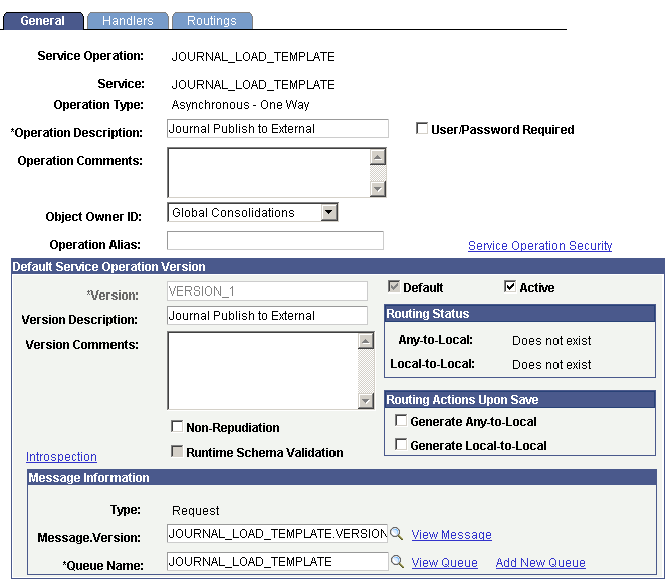
PeopleTools Integration Broker Service Options - General page
Review the Enterprise PeopleTools 8.48: Enterprise Integration PeopleBook and read the chapter “Managing Service Operations.”
Activate service operations that are initially delivered with an inactive status.
For the PeopleSoft EPM database to share information with the FDM database, you must activate the appropriate service operations in both databases.
Activate the following service operations:
|
Application Message Name |
Direction |
Remarks |
|
Service Operation = JOURNAL_LOAD_TEMPLATE |
||
|
JOURNAL_LOAD_TEMPLATE |
PeopleSoft EPM to PeopleSoft General Ledger |
PeopleSoft EPM sends PeopleSoft General Ledger accounting entries to PeopleSoft General Ledger. |
|
Service Operation = GC_ACCT_ENTRY |
||
|
GC_ACCT_ENTRY |
PeopleSoft EPM to PeopleSoft General Ledger |
PeopleSoft EPM sends Global Consolidation accounting entries to PeopleSoft General Ledger. |

 Pages Used to Publish Journals
Pages Used to Publish Journals
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GC_PUB_RULE_PG |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Common Definitions, Journal Publish Rule, Publish Rule |
Specify journal publish target options. |
|
|
GC_PUB_RULE_PG2 |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Common Definitions, Journal Publish Rule, Source Rules |
Specify which journals are available to publish on the Journal Publish run control page. |
|
|
GC_PUB_RULE_PG3 |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Common Definitions, Journal Publish Rule, Notes |
Enter notes to document the publish rule. |
|
|
RUN_GC_JRNLPUBLSH |
Global Consolidations, Manage Journals, Process Journals, Journal Publish |
Run the journal publish jobstream. |
|
|
GC_RUN_JPUBSEL_PG |
Global Consolidations, Manage Journals, Journal Publish, Batch Selection |
Select journal batches to publish. |
|
|
GC_JPUB_HIS_PG |
Global Consolidations, Consolidation Analysis, Consolidation Inquiries, Journal Publish History |
Review the history of published journal batches. |

 Defining Journal Publish Target Options
Defining Journal Publish Target OptionsAccess the Publish Rule page.
Specify the Publish Target by selecting one or both of the following check boxes:
|
PeopleSoft GL Accounting Entry |
Select to publish the journals using the PeopleSoft Enterprise General Ledger accounting entry structure. |
|
Global Consolidation Accounting Entry |
Select to publish the journals using the PeopleSoft Enterprise Global Consolidations accounting entry structure. This option retains all the details of the generated journals. |
For each selected Publish Target, specify the Mapper Group. To use pre-defined mapper groups, select the following:
|
GCJPUBG1 |
Select to map to JGENACCT (General Ledger accounts) as the target. |
|
GCJPUBG2 |
Select to map to GCACCTENT (Global Consolidations accounts) as the target. |

 Defining Journal Publish Source Options
Defining Journal Publish Source OptionsAccess the Source Rules page.
|
Source Process |
Lists each source process that generates journal batches. This is a display-only field. |
|
Publish Journals? |
Select whether to publish journal batches for this source process. Options are: Select: Select to include journal batches from this source process in the list of journals that you can opt to publish at runtime. Never: Select for sources that you do not want to publish. Always: Select to publish journal batches from this source process every time you run the journal publish process. |

 Running Journal Publish
Running Journal PublishAccess the Journal Publish run control page.
Specifying Run Control Parameters
|
Business Unit, Scenario ID, Fiscal Year, and Period |
Specify the common consolidation business unit, scenario ID, fiscal year, and accounting period to process. |
|
Jobstream ID |
The default value for this field is GC_JR_PUB. |
|
Republish Accounting Entries? |
Select to republish any journal batches that were previously published. |
Specifying Journal Batches to Publish
Access the Journal Publish - Batch Selection page.
|
Selected Flag |
Select to publish this journal batch. This field is active only for source processes that have the Publish Journals? field set to Select on the Source Rules page. |
|
Published |
If selected, indicates that published data for the batch already exists. |
|
Journal Publish Rule |
Click to access the Publish Rule page, where you can review the publish rule. |
|
View Publish History |
Click to access the Publish History page, where you can review the journal publish history. |
The only journals that the system will publish are:
Posted, unpublished journals.
Unposted journals, if their posted journals were previously published.

 Reviewing Journal Publish History
Reviewing Journal Publish HistoryAccess the Journal Publish History page.
This page displays the history of published journals, grouped by those that are set to always publish and those that are selectable.