| SIP Servlet Engine© Documentations |
| Top > System Administration > Configuration > Security Management |
Security Management
This document describes an overview of the security capabilities provided by SIP Servlet Engine.
Digest Authentication
SIP Servlet Engine supports the digest authentication when receiving a request from an SIP client. This digest authentication provides the same behavior as the HTTP digest authentication. (Refer to http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2617.txt, http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3261.txt.)
Security Structure
Basic Structure and Process Flow
The security capabilities of SIP Servlet Engine are broadly divided into two processes : authentication and authorization. The following section describes each process flow.
Overview of the Authentication and Authorization Processes
The following shows the structure and steps of the authentication and authorization processes when SIP Servlet Engine receives an SIP request.
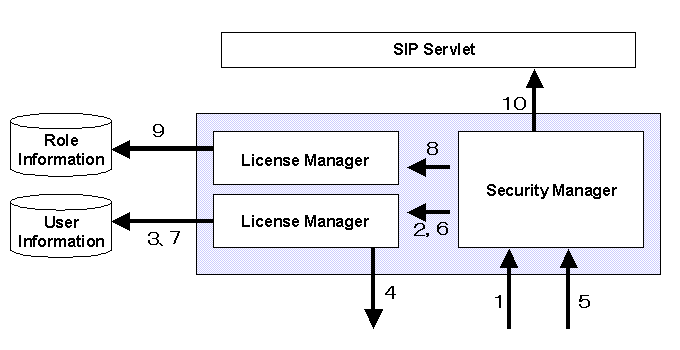
- SIP Servlet Engine passes the SIP request sent from the SIP client to Security Manager.
- Security Manager passes the SIP request to Authentication Manager and delegates authentication.
- For an unauthenticated SIP request, Authentication Manager creates the authentication header for the 401 or 407 response.
- Authentication Manager returns the 401 or 407 response to the SIP client.
- The SIP client sends the SIP request dealt with the 401 or 407 response.
- SecurityManager passes the SIP request to Authentication Manager and delegates authentication again.
- Authentication Manager checks on the user information and determines whether it is an authenticated request or not. if authentication fails, it returns a 403 response.
- After Authentication Manager determines that it is an authenticated request, SecurityManager passes the SIP request to Authorization Manager and delegates authorization.
- Authorization Manager reads the role information of the user corresponding to the SIP request and determines whether it is an authorized user or not. If Authorization Manager determines that it is not authorized, a 403 response is returned.
- After Authorization Manager determines that the request sent from the user is an authorized request, Security Manager passes the SIP request to the SIP servlet.
These steps are all the authentication and authorization processes for the SIP request.
Also, in the Authentication Manager provided by default, SPI are used.
Overview of the User Authentication via Web
SIP Servlet Engine supports the authentication for the users registered on SIP Servlet Engine using the FORM authentication through the authentication mechanism provided by each J2EE component.
WebLogic Server 8.1 SP3 provides various types of security providers to use in SIP Servlet Engine for user authentication. Using these various security providers enables the authentication with the user information used by SIP Servlet Engine.
Security Providers in WebLogic
The authenticated and authorized information in SIP Servlet Engine is passed to WebLogic Server by using the security providers in WebLogic. For more information about the WebLogic security architecture, see WebLogic Security Service Architecture.
The following describes the security providers provided by SIP Servlet Engine.
Authentication provider
- SipAuthenticator
- The authentication provider used when authenticating the SIP request. It is invoked from the Authentication Manager and checks that the user who sent an SIP message is a user registered in SIP Servlet Engine.
- FormAuthenticator
- The authentication provider used when performing the FORM authentication via Web. It checks and authenticates that the user name sent via FORM authentication is a user registered in SIP Servlet Engine.
- DefaultAuthenticator
- The default authentication provider provided by WebLogic. It is used for managed user authentication used in Administration Console, etc.
Authorization provider
- DefaultAuthorizer
- The default authorization provider provided by WebLogic. It grants permission to users authenticated by the authentication provider to access the WebLogic resource.
Roll Mapping Provider
- SipRoleMapper
- The role mapping provider which maps the role to the SIP request. It grants the role assigned by Authorization Manager on SIP Servlet Engine to the user who sent the SIP message.
- DefaultRoleMapper
- The default role mapping provider provided by WebLogic.
Also, in order to authenticate the SIP message, the LoginConfig with the following settings is specified for "java.security.auth.login.config" system property.
equips-sip {
com.oki.sip.bea.wls81.security.authentication.EngineLoginModule required debug=true;
};
This LoginModule is invoked from the Authentication Manager of SIP servlet engine and specifies user information and role information to Subject, using the SPI.
Data Structure
The database used by SIP Servlet Engine contains the user information and the role information assigned to the user.
The following shows the basic data structure.
Data structure about the user information
| userid | The ID assigned to the user. |
|---|---|
| subscriber | The user name used by SipURI. |
| host | The host name used by SipURI. |
| alias | The alias which can be assigned to the user. |
In addition, each table contains the hash value used by the digest authentication, the number of times the user authentication failed, and so on. These data are used by Authentication Manager when authenticating the user.
Data structure about the role information
| roleid | The ID assigned to the role. |
|---|---|
| rolename | The name of the role. |
| description | The description of the role. |
Data structure about the role assigned to the user
| userid | The ID assigned to the user. |
|---|---|
| roleid | The ID assigned to the role. |
These data about the role are used by Authorization Manager when granting the role to the authenticated user.
To manipulate these data, use the SIP Servlet Engine management tool. (See sip-admin Users Guide.)
APIs for Managing the Roles
The component for managing the roles is deployed as EJB. You can use the RoleMapper interface to add or remove the role and add or remove the user to/from the role.
The following shows the APIs for managing the roles.
- RoleMapper Interface
- RoleMapInfo Class
RoleMapper Interface
The interface for managing the roles.
public interface RoleMapper extends EJBObject {
boolean isUserInRole(SipURI subscriber, String role) throws RemoteException;
void addRole(String role, String desc) throws RemoteException;
void removeRole(String role) throws RemoteException;
Set getAllRoles() throws RemoteException;
void addMemberToRole(SipURI subscriber, String role) throws RemoteException;
void removeMemberFromRole(SipURI subscriber, String role) throws RemoteException;
Set getMembersRole(SipURI subscriber) throws RemoteException;
}
isUserInRole is the method to determine whether the user is included in the role or not. The argument subscriber specifies the SipURI of the target user and the argument role specifies the role name to determine. If the subscriber is included in the role, this method returns true. Otherwise, it returns false.
addRole is the method to add the new role. The argument role specifies the name of the role to add and the argument desc specifies the description of the role.
removeRole is the method to remove the role. The argument role specifies the name of the role to remove.
getAllRoles is the method to get the Set which contains the information of all the roles. The returned Set includes the RoleMapInfo.
addMemberToRle is the method to add the user to the role. The argument subscriber specifies the SipURI of the target user and the argument role specifies the role name.
removeMemberFromRole is the method to remove the user from the role. The argument subscriber specifies the SipURI of the target user and the argument role specifies the role name.
getMembersRole is the method to get the Set which contains the information of the role which includes the user. The argument subscriber specifies the SipURI of the target user.
RoleMapInfo Class
The class for containing the information about the roles.
public class RoleMapInfo implements Serializable {
public RoleMapInfo(String rolename,
String desc);
public String getRoleName();
public String getDesc();
public int hashCode();
public boolean equals(Object obj);
public String toString();
}
The argument rolename specifies the name of the role for the role information and the argument desc specifies the description for the role information.
getRoleName can get the name of the role for the role information.
getDesc can get the description for the role information.
Limitations on Using
There are two ways to use the user information managed by the existing application:
- Copy the existing user information to the database schema managed by SIP Servlet Engine 3.0.
- Change the implementation of the SPI by adding the SIP information managed by SIP Servlet Engine 3.0 to the existing user information.
Each has its advantages and disadvantages:
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|
| When copying the existing user information | You do not need to change the implementation of the SPI. | The user information will be managed doubly. |
| When implementing the SPI | You can unify the user information management. | SIP Servlet Engine requests only com.oki.sip.spi.Authenticator.You need to perform this implementation. |
Last Modified:Tue Dec 28 15:19:23 JST 2004
| Copyright © 2003, 2004 Oki Electric Industry Co.,Ltd. All rights reserved. |