


|

|
|
|
|
Introducing eLink Java Adapter for Mainframe WLS Edition
This section covers the following topics:
JAM Environment
The BEA eLink Java Adapter for Mainframe WLS Edition (JAM) environment is a set of software components that provides seamless bidirectional interactions between Java applications running on a WebLogic Server (WLS) platform and either Customer Information Control System (CICS) applications, or Information Management System (IMS) applications running on a mainframe. With CICS, the Java application request/response operations interact using Distributed Program Links (DPL). With IMS, the Java application request/response operations interact using IMS implicit Application Program-to-Program Communication (APPC) support.
This guide provides you with scenarios for developing and deploying applications by using the software components within the JAM environment. The scenarios depict specific tasks that work in conjunction with development and deployment procedures also provided in this guide. It is best to read and become familiar with the contents of Developing Java Applications and Deploying Applications before attempting the exercises in Programming Scenarios.
To learn more about how the System Network Architecture Communications Resource Manager (SNACRM) provides the emulation that enables CICS DPL protocols to flow into and out of the JAM environment, refer to the BEA eLink Adapter for Mainframe, SNACRM Administration Guide. This guide is accessible from the JAM documentation Web User Interface (WUI) in both HTML and PDF formats.
The JAM environment includes the following components:
Note: The WLS and third-party SNA stack are required as parts of the JAM environment, but are sold separately.
The WLS application server provides the environment for running Java Servlets and Enterprise Java Beans (EJB). The Java gateway is launched during the WLS startup using a startup class called gwboot. Configuration requirements for the server to start the gateway are limited to identifying the startup class along with any start-up arguments in the weblogic.properties file.
Note: Although JAM can be used with WebLogic Express (WLX), no EJB capability would be available because WLX does not support it.
System Network Architecture Communications Resource Manager
The SNACRM runs as a separate native process. It enables APPC conversations and DPL protocols to flow into and out of the Java environment and runs on the same platform as the SNA stack. The SNACRM obtains its configuration from the JCRMGW. If the Java gateway is running on a platform other than the one on which the SNACRM is running, the SNACRM should be started before the WLS is started so it is monitoring the address specified in the JCRMGW configuration.
The SNACRM supports non-transactional IMS programs using the implicit APPC support for IMS. Implicit APPC is similar to the CICS/ESA DPL. Any IMS program that sends and receives messages to and from the IMS message queue can be used without change as either a client or a server.
In order for the SNACRM to properly operate within the JAM environment, the CICS remote domain must be prepared to conduct operations with the local domain. This includes:
Refer to the BEA eLink Adapter for Mainframe, SNACRM Administration Guide for more detailed information. That guide is accessible from the JAM documentation WUI in both HTML and PDF formats.
Java Communications Resource Manager Gateway
The JCRMGW is a Java application that manages sessions providing access into and out of the Java environment. It is configured using a text file named jcrmgw.cfg residing in the WLS directory. Requests coming from the mainframe are mapped to an EJB which services the request while requests going to the mainframe are mapped to a mainframe program which can be executed using a CICS DPL or started from an IMS queue.
EgenCobol Code Generator
The EgenCobol code generator is a utility that generates Java source code from a COBOL copybook. A base Java application is provided on the JAM product CDROM so you can enhance it to create custom Java applications. The generated code is dependent on the generation model chosen:
The generated code provides for data accessors and conversions as well as miscellaneous functions. The generated servlet provides a basic form that matches the copybook. You can use this servlet for testing or proof of concept. For examples of using the EgenCobol code generator, refer to Developing Java Applications and Programming Scenarios.
Supported Third-Party SNA Stack
A properly configured SNA protocol stack is required for the SNACRM to communicate with a mainframe. (Refer to the BEA eLink Java Adapter for Mainframe WLS Edition Release Notes for a complete list of supported stacks.) The JCRMGW requires several parameters from the SNA stack configuration:
The local name of the SNACRM that is used by the mainframe CICS region.
An alias representing the mainframe partner application to be used by the SNACRM.
SNA mode definitions provide session characteristics for given local/remote LU pair.
Sessions are required for connections to be made between two LU. MAX sessions should be high enough to handled the expected gateway traffic.
This parameter is optional and determines priority of session activation.
Configuration Options
Figure 1-1 and Figure 1-2 show the component relationships of the JAM environment in two configurations, the combined configuration and the distributed configuration. This section contains the following topics:
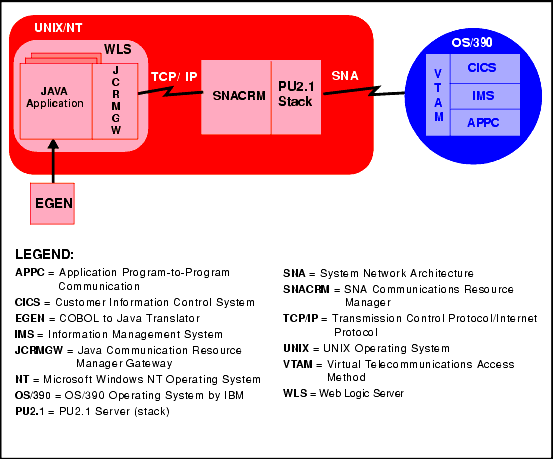
This configuration combines the Java application, JCRMGW, WLS, and the SNACRM with the stack (PU2.1 server) on the same UNIX or Windows NT platform. It employs the IBM proprietary SNA protocol for transactions with the mainframe via the stack (see Figure 1-1).
Figure 1-1 JAM Combined Configuration
The second configuration separates the Java applications and JCRMGW from the SNACRM on different UNIX or Windows NT platforms. It employs the widely used Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) connectivity between the Java applications platform and the SNACRM platforms, as well as the SNA connectivity to the mainframe environment(s). This configuration gives you the flexibility to deploy WLS separately from the SNACRM at installations that require WLS on a platform other than the one on which the SNA stack is running. Note that this configuration requires a one-to-one relationship between the local JCRMGW and the remote SNACRM (see Figure 1-2).
Figure 1-2 JAM Distributed Configuration
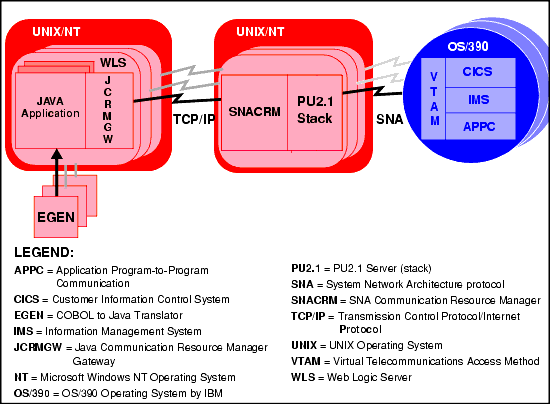
It is important to understand which of the configurations applies to your application development environment. During installation, you must enter the destinations for the two major JAM components, the SNACRM and the JCRMGW. Those destinations are determined by your configuration. If it is the combined configuration, both components are installed on the same platform. If it is the distributed configuration, the components are installed on different platforms; the JCRMGW must be on the platform with WLS and the SNACRM on the same platform with the SNA stack. Refer to "Pre-Installation Considerations" in the BEA eLink Java Adapter for Mainframe WLS Edition Installation Guide for additional information on this subject.

|
|

|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2000 BEA Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
|