


|

|
|
|
|
Introduction
The following sections provide an overview of the RosettaNet protocol:
About RosettaNet
This section introduces the RosettaNet standard for electronic business transactions. The RosettaNet Consortium is an independent, nonprofit consortium of major information technology, electronic component, and semiconductor manufacturing companies working to create and implement industry-wide, open e-business process standards. These processes are designed to standardize the electronic business interfaces used between participating supply chain partners. The RosettaNet Implementation Framework specification (available at http://www.rosettanet.org) is a guideline for applications that implement RosettaNet Partner Interface Processes (PIPs). These PIPs are standardized electronic business processes used between trading partners.
RosettaNet Architecture
BEA WebLogic Collaborate support for RosettaNet consists of the following components:
WebLogic Collaborate Architecture and RosettaNet
The following diagram shows how WebLogic Collaborate supports the RosettaNet architecture, and how WebLogic Collaborate interacts with other systems using RosettaNet.
Figure 1-1 WebLogic Collaborate RosettaNet Architecture
WebLogic Collaborate support for RosettaNet is designed to integrate RosettaNet seamlessly with the standard WebLogic Collaborate infrastructure. For more information about the remainder of the WebLogic Collaborate architecture, see Introducing BEA WebLogic Collaborate. RosettaNet Protocol Layer The RosettaNet protocol layer provides the ability to send and receive messages by way of the Internet according to the RNIF 1.1 and RNIF 2.0 specifications for transport, message packaging, and security. PIP Templates RosettaNet PIPs define the public processes in which trading partners participate while performing e-business transactions. For example, PIP 3A2 defines the process that a Customer trading partner performs with a Product Supplier trading partner to get information about the price and availability of goods that the Customer wants to buy and the Product Supplier wants to sell. Trading partners participating in PIPs need to implement the public process defined by their role in the PIP, and they need to connect their internal systems, as well as their private processes and workflows, to the public process. A key feature of the support for RosettaNet provided by WebLogic Collaborate is the set of WebLogic Process Integrator workflow PIP templates that trading partners can use to implement PIPs. Template sets are defined for the following PIPs: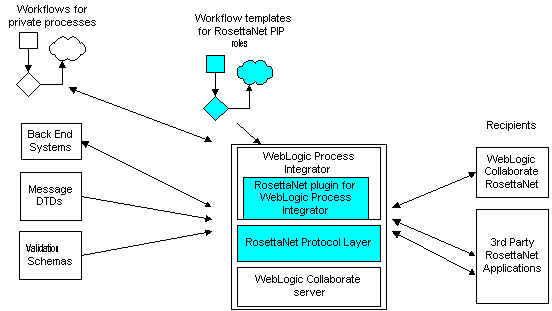
For further information about these and other PIPs, go to the RosettaNet Web site: http://www.rosettanet.org. For more information on the RosettaNet PIPs provided with this release of BEA WebLogic Collaborate, see RosettaNet PIP Templates.
Integration
BEA WebLogic Process Integrator models and executes workflows that implement RosettaNet PIPs. The RosettaNet protocol layer and WebLogic Process Integrator are integrated to provide workflows with the following capabilities:
Workflow Definition
To support the development of workflows for RosettaNet PIPs, WebLogic Collaborate provides the same tools used for modeling other WebLogic Collaborate workflow processes. All RosettaNet workflows use a common interface, based on WebLogic Process Integrator, to define workflow actions, events, and logic flows.
Digital Signatures
WebLogic Collaborate includes an out-of-the-box implementation of digital signatures, based on the RSA CertJ toolkit. For more information about implementing and configuring digital signatures, see Using BEA WebLogic Collaborate Security.
Message Validation
The RosettaNet PIP definitions contain detailed validation rules for messages exchanged in the PIP. These rules are significantly more stringent than the validation expressed within an XML Document Type Definition (DTD).
The required validation rules are expressed in XML schema documents (XSD), which are included with the PIP templates provided with BEA WebLogic Collaborate. For a more detailed description of message validation, see Using Workflows with RosettaNet.
Samples
BEA has developed several RosettaNet samples to demonstrate how RosettaNet functionality operates under WebLogic Collaborate. For more information on these samples, please visit the BEA Developer Center Web site:
http://developer.bea.com/index.jsp
Unsupported Items
Several RosettaNet-related features are not supported in this release of BEA WebLogic Collaborate:
RosettaNet Administration
Administrative support for RosettaNet on BEA Weblogic Collaborate is via the WLC Administation console. For more information on adminstration tasks, see Administering BEA WebLogic Collaborate.
The WebLogic Collaborate Administration Console requires RosettaNet-specific configuration of document exchanges. For more information see the BEA WebLogic Collaborate Administration Console Online Help.
Configuring Collaboration Agreements for RosettaNet
For RosettaNet, a collaboration agreement is defined between two trading partners. It can be deployed with or without a hub. The following sections describe how to configure RosettaNet collaboration agreements for both configurations.
Peer-to-Peer with No Hub
In a hubless configuration, you are assumed to be running RosettaNet strictly on a peer-to-peer basis.
In such a situation, you would configure a collaboration agreement similar to the one shown in the following listing. In this case, the collaboration agreement is represented as XML data, though in practice you will configure the collaboration agreement using the WebLogic Collaborate Administration Console.
Listing 1-1 RosettaNet Collaboration Agreement Configuration with No Hub
<collaboration-agreement
name="RN2|9.9|RosettaNet2|100"
global-identifier="RN2|9.9|RosettaNet2|RNBuyer|RNSeller|102"
version="1.0"
status="ENABLED"
conversation-definition-name="RN2"
conversation-definition-version="2.0">
<party
trading-partner-name="RNBuyer"
party-identifier-name="RNBuyerPID"
delivery-channel-name="RNBuyer"
role-name="Buyer"/>
<party
trading-partner-name="RNSeller"
party-identifier-name="RNSellerPID"
delivery-channel-name="RNSeller"
role-name="Seller"/>
</collaboration-agreement>
Peer-to-Peer with Hub
You can also run RosettaNet on WebLogic Collaborate using a hub. In this configuration, the hub acts as an intermediary for the RosettaNet traffic. The hub makes no modification to the message being routed.
From the RosettaNet messages routed through the hub, the information accessible by the hub to locate collaboration agreement information is very minimal. Therefore, the collaboration agreement definitions on the hub are not used. They must still be defined, however, to allow the lower level transport routines to provide the client connections.
Instead, the hub uses one of four possible delivery channels for RosettaNet messages:
These are the channel names the hub will use. The channels must be created and configured using the WebLogic Collaborate Administration Console.
When a message arrives on an insecure channel, the hub will route the message to the appropriate trading partner's insecure delivery channel for the specific protocol version. If the trading partner contains more than one insecure channel, then the WebLogic Collaborate run-time will randomly pick one to use.
When a message arrives on a secure channel, the hub will route the message to the appropriate trading partner's secure delivery channel for the specific protocol version. If the trading partner contains more than one secure channel, then WebLogic Collaborate will randomly pick one to use.
For example, suppose a trading partner contains the following delivery channels defined on the hub.
Listing 1-2 Trading Partner Delivery Channel Definitions
<delivery-channel
name="RNSellerSecureChannel"
status="ENABLED"
nonrepudiation-of-origin="true"
nonrepudiation-of-receipt="true"
secure-transport="true"
confidentiality="true"
transport-name="RNSellerTransport"
document-exchange-name="DOCEX-RosettaNet2"/>
<delivery-channel
name="RNSellerNonSecureChannel"
status="ENABLED"
nonrepudiation-of-origin="false"
nonrepudiation-of-receipt="false"
secure-transport="false"
confidentiality="false"
transport-name="RNSellerTransport"
document-exchange-name="DOCEX-RosettaNet2"/>
When a message arrives at the hub for the trading partner, it would be routed in one of two ways:
In either case, any collaboration agreement information defined in the hub for the RosettaNet protocol would be ignored.

|

|

|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2001 BEA Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
|