









|
The following sections provide a high-level view of RMI over IIOP:
RMI over IIOP extends RMI to work across the IIOP protocol. This has two benefits that you can leverage. In a Java to Java paradigm, this allows you to program against the standardized Internet Interop-Orb-Protocol (IIOP). If you are not working in a Java-only environment, it allows your Java programs to interact with Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) clients and execute CORBA objects. CORBA clients can be written in a variety of languages (including C++) and use the Interface-Definition-Language (IDL) to interact with a remote object.
WebLogic Server provides its own ORB implementation which is instantiated by default when programs call ORB.init(), or when "java:comp/ORB" is looked up in JNDI. See CORBA Support for WebLogic Server for information how WebLogic Server complies with specifications for CORBA support in J2SE 1.4 .
The WebLogic Server implementation of RMI-IIOP allows you to:
How you develop your RMI-IIOP applications depends on what services and clients you are trying to integrate. See Programming Stand-alone Clients for more information on how to create applications for various clients types that use RMI and RMI-IIOP.
Figure 7-1 shows RMI Object Relationships for objects that use IIOP.
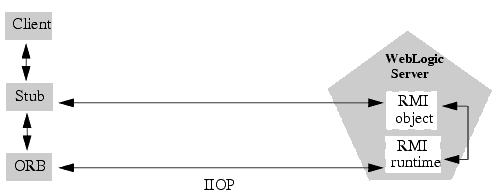
You can use RMI-IIOP with Java/RMI clients, taking advantage of the standard IIOP protocol. WebLogic Server provides multiple options for using RMI-IIOP in a Java-to-Java environment, including the new J2EE Application Client (thin client), which is based on the new small footprint client jar. To use the new thin client, you need to have the wlclient.jar (located in WL_HOME/server/lib) on the client side’s CLASSPATH. For more information on RMI-IIOP client options, see
Programming Stand Alone Clients.
WebLogic Server contains an implementation of the WebLogic Tuxedo Connector, an underlying technology that enables you to interoperate with Tuxedo servers. Using WebLogic Tuxedo Connector, you can leverage Tuxedo as an ORB, or integrate legacy Tuxedo systems with applications you have developed on WebLogic Server. For more information, see the WebLogic Tuxedo Connector Programmer’s Guide.
The developer community requires the ability to access J2EE services from CORBA/IDL clients. However, Java and CORBA are based on very different object models. Because of this, sharing data between objects created in the two programming paradigms was, until recently, limited to Remote and CORBA primitive data types. Neither CORBA structures nor Java objects could be readily passed between disparate objects. To address this limitation, the Object Management Group (OMG) created the Objects-by-Value specification . This specification defines the enabling technology for exporting the Java object model into the CORBA/IDL programming model--allowing for the interchange of complex data types between the two models. WebLogic Server can support Objects-by-Value with any CORBA ORB that correctly implements the specification.
Interoperability between WebLogic Server 9.x and WebLogic Server 7.0 and 8.1 is supported in the following scenarios:
The following table identifies supported options for achieving interoperability between two WebLogic Server instances.
|
RMI/IIOP1
|
RMI/IIOP2
Web Services3
|
RMI/IIOP4
Web Services5
|
|
|
RMI/IIOP6
Web Services7
|
|||
|
RMI/IIOP8
Web Services9
|
|||
Sun JDK ORB client10
|
RMI/IIOP11
|
RMI/IIOP12
|
RMI/IIOP13
|
1 No support for clustered URLs 2 No support for clustered URLs 3 Must use portable client stubs generated from the “To Server” version 4 No support for clustered URLs 5 Must use portable client stubs generated from the “To Server” version 6No support for clustered URLs and no transaction propagation 7 Must use portable client stubs generated from the “To Server” version 8No support for clustered URLs and no transaction propagation 9 Must use portable client stubs generated from the “To Server” version 10This option involves calling directly into the JDK ORB from within application hosted on WebLogic Server. 11 JDK 1.3.x or 1.4.1. No clustering. No transaction propagation 12 JDK 1.3.x or 1.4.1. No clustering. No transaction propagation 13 JDK 5.0. No clustering. No transaction propagation |
The following table identifies supported options for achieving interoperability between a stand-alone Java client application and a WebLogic Server instance.
|
RMI/IIOP1
|
RMI/IIOP2
Web Services3
|
RMI/IIOP4
Web Services5
|
|
|
RMI/IIOP6
Web Services7
|
|||
|
RMI/IIOP8
Web Services9
|
|||
Sun JDK ORB client10
|
RMI/IIOP11
|
RMI/IIOP12
|
RMI/IIOP13
|
1 No Cluster or Failover support 2 No Cluster or Failover support 3 Must use portable client stubs generated from the “To Server” version 4 No Cluster or Failover support 5 Must use portable client stubs generated from the “To Server” version 6 No Cluster or Failover support and no transaction propogation. Known problems with exception marshalling 7 Must use portable client stubs generated from the “To Server” version 8 No Cluster or Failover support and no transaction propogation. Known problems with exception marshalling 9 Must use portable client stubs generated from the “To Server” version 10 This option involved calling directly into the JDK ORB from within a client application. 11 JDK 1.3.x or 1.4.1. No clustering. No transaction propagation 12 JDK 1.3.x or 1.4.1. No clustering. No transaction propagation 13 JDK 5.0. No clustering. No transaction propagation |


|