 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable Overview
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable Overview
This chapter discusses:
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable overview.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable business processes.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable integration.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable implementation.
 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable Overview
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable Overview
An accounts receivable department plays an important role in managing the cash flow of a business; it is responsible for processing invoices for goods and services sold to customers of an organization and applying payments from these same customers. In addition, the accounts receivable department might want to track payment information about their customers to gather statistical information about their paying habits. By understanding customers better, businesses can provide better customer support and manage their cash flow better.
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable system from Oracle helps you manage the cash flow with the flexibility that you need for effective cash management. It provides real-time information so that you can make immediate decisions about extending credit, forwarding collections, and applying cash.
With the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable system, you can streamline the day-to-day functions of the entire accounts receivable department. You can simplify and accelerate the process of applying receipts and you have up-to-date information that improves communication between the billing and the credit and collections department.
For organizations that have offices around the world, JD Edwards EnterpriseOne software provides the flexibility needed to operate in multiple countries, each with unique currency, language, and statutory requirements.
 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable Business Processes
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable Business Processes
This process flow illustrates the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable business processes:
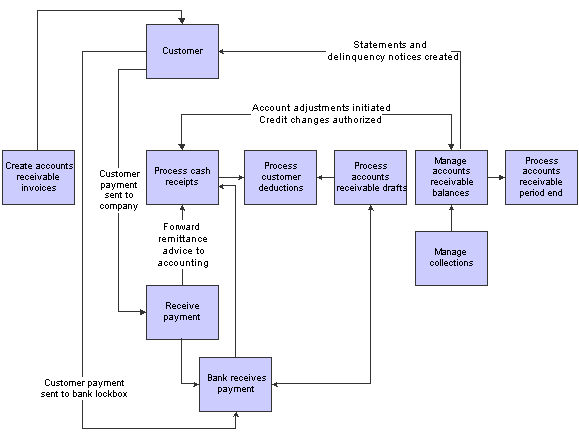
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable system flow
 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable Integrations
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable Integrations
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable system integrates with these JD Edwards EnterpriseOne systems from Oracle:
Contract and Service Billing.
General Accounting system
Real Estate Management system
Sales Order Management system
Service Management system
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable system works with other JD Edwards EnterpriseOne systems to ensure that all information is fully integrated into the general ledger and customer ledger. We discuss integration considerations in the implementation chapters in this implementation guide. Supplemental information about third-party application integrations is located on the Oracle | PeopleSoft Customer Connection website.
 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable Implementation
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable Implementation
This section provides an overview of the steps that are required to implement the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable system.
In the planning phase of the implementation, take advantage of all JD Edwards EnterpriseOne sources of information, including the installation guides and troubleshooting information. A complete list of these resources appears in the preface in the About This Documentation, with information about where to find the most current version of each.
When determining which electronic software updates (ESUs) to install for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable, use the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne and JD Edwards World Change Assistant. JD Edwards EnterpriseOne and JD Edwards World Change Assistant, a Sun Microsystems, Inc. Java-based tool, reduces the time required to search and download ESUs by 75 percent or more, and enables you to install multiple ESUs at one time.
See JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tools 8.98 Software Update Guide
For information about the Oracle Business Accelerator Solution for implementation of JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable, review the documentation available.
See http://www.peoplesoft.com/corp/en/iou/implement/rapid_start/rapid_start_prtr_notes.jsp

 Global Implementation Steps
Global Implementation Steps
This table lists the suggested global implementation steps for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable:
|
Step |
Reference |
|
1. Set up companies, fiscal date patterns, and business units. |
|
|
2. Set up accounts, and the chart of accounts. |
|
|
3. Set up the General Accounting constants. |
|
|
4. Set up multicurrency processing, including currency codes and exchange rates. |
|
|
5. Set up ledger type rules. |
|
|
6. Enter address book records. |

 Accounts Receivable Implementation Steps
Accounts Receivable Implementation Steps
This table lists the suggested implementation steps for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable:
|
Step |
Reference |
|
1. Set up Accounts Receivable constants, user–defined codes (UDCs), next numbers, automatic accounting instructions (AAIs), and payment terms. |
See Setting Up the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable System. |
|
2. Set up customer master information and customer bank information. |
|
|
3. (BRA) Set up electronic banking for Brazil. |
|
|
4. Set up algorithms, execution lists, and customer master records for automatic receipts processing. |
|
|
5. Set up date patterns, activity codes, delinquency policies, fee instructions, credit insurance policies, and credit and collection managers for credit and collections management processing. |
|
|
6. Set up batch approval and post security for invoices and receipts. Set up approved and secured users. |
|
|
7. Set up drafts and deduction processing. |
See Setting Up the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable System. |