1 Introduction to JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting
This chapter contains the following topics:
-
Section 1.1, "JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting Overview"
-
Section 1.2, "JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting Business Processes"
-
Section 1.3, "JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting Integrations"
-
Section 1.4, "JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting Implementation"
1.1 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting Overview
Typically, a company uses some type of general ledger application to successfully manage its financial activities. The financial activities might include allocating revenue and expenses among various departments within the company, eliminating intercompany transactions, reconciling account balances, and projecting budgets for future periods and reviewing them against the actual activity.
With the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting system from Oracle, you can organize, maintain, record, and analyze financial information. For example, you can:
-
Access account balances and consolidated information at any time during an accounting period.
-
Create high-level budget projections or detail-level budgets and compare your budget-to-actual figures online by using any time frame.
-
Forecast revenue and expense budget amounts up to 15 years in the future.
-
Project future cash requirements and effectively manage your cash accounts.
-
Produce cash flow statements that show the historical changes in cash and cash equivalents during a specified period of operations.
-
Create intercompany settlements automatically for transactions between companies.
1.2 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting Business Processes
This process flow illustrates the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting business processes:
Figure 1-1 General Accounting process flow
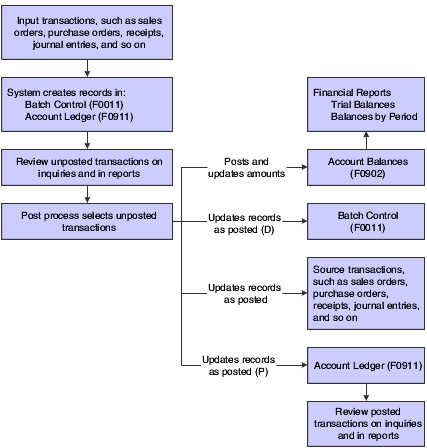
Description of ''Figure 1-1 General Accounting process flow''
We discuss these business processes in the business process chapters in this implementation guide.
1.3 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting Integrations
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting system integrates with these JD Edwards EnterpriseOne systems:
-
Payroll
-
Fixed Assets
-
Plant and Equipment Management
-
Accounts Receivable
-
Accounts Payable
-
Job Cost
-
Multi-currency processing
-
Service billing
-
Tax Processing
-
Inventory Management
-
Warehouse Management
-
Sales Order Management
-
Procurement and Subcontract Management
-
EDI Processing
-
Transportation Management
-
Advanced Stock Valuation
-
Homebuilder Management
-
Real Estate Management
-
Service Management
-
Product Data Management
-
Shop Floor Management
-
Work Orders
For localizations, the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting system integrates with following areas:
-
Asia Pacific
-
Latin American
-
Central America
-
Europe
-
Middle East
-
Asia
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting system works with other JD Edwards EnterpriseOne systems to ensure that all information is fully integrated into the general ledger. We discuss integration considerations in the implementation chapters in this implementation guide. Supplemental information about third-party application integrations is located on the My Oracle Support website.
1.3.1 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Workforce Management
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Payroll system from Oracle creates general ledger transactions for labor, labor billing distribution, disbursements, and so on during the payroll cycle.
1.3.2 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Financial Management
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Financial Management systems from Oracle create general ledger transactions for invoices and vouchers, receipt and payment processing, and so on.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting also integrates with the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Contract Billing system by enabling you to include burdening transactions in the Billing Detail Workfile table (F4812).
1.3.3 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Localization
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Localization systems from Oracle create general ledger transactions for journal entries with taxes that are used by certain countries.
1.3.4 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Capital Asset Management
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Capital Asset Management systems from Oracle create general ledger transactions for depreciation, asset transfers, vouchers, equipment, billing, and so on.
1.3.5 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Logistics Management
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Logistics Management systems from Oracle create general ledger transactions during the processes for sales order update, purchase order receipt, voucher match, and so on.
1.3.6 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Multi-mode Manufacturing
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Multi-mode Manufacturing systems from Oracle create general ledger transactions for material issues, completions, labor hours, variances, and so on during the manufacturing accounting process.
1.3.7 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Homebuilder Management
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Homebuilder Management system from Oracle creates general ledger transactions for lot closes and progress payments.
1.3.8 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Real Estate Management
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Real Estate Management system from Oracle creates general ledger transactions during invoice and voucher entry.
1.3.9 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Service Management
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Service Management system from Oracle creates general ledger transactions for inventory costs.
1.4 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting Implementation
This section provides an overview of the steps that are required to implement the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting system.
In the planning phase of your implementation, take advantage of all JD Edwards EnterpriseOne sources of information, including the installation guides and troubleshooting information.
When determining which electronic software updates (ESUs) to install for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting, use the EnterpriseOne and World Change Assistant. EnterpriseOne and World Change Assistant, a Java-based tool, reduces the time required to search and download ESUs by 75 percent or more and enables you to install multiple ESUs at one time.
See JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tools Software Updates Guide.
For information about the Oracle Business Accelerator solution for implementation of JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting, review the documentation at http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E24705_01/index.htm.
1.4.1 Global Implementation Steps
The suggested implementation steps for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting system:
-
Set up fiscal date patterns, companies, and business units.
-
Create the chart of accounts and set up accounts and subledgers.
-
Set up the General Accounting constants.
-
Set up multicurrency processing.
-
Set up ledger type rules.
-
Enter address book records.
1.4.2 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting Implementation Steps
The suggested application-specific implementation steps for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting:
-
Set up user-defined codes (UDCs), ledger types, automatic accounting instructions (AAIs), and business unit supplemental data.
See Setting Up User-Defined Codes for General Accounting.
See Setting Up the General Accounting System.
-
Set up next numbers by system and by company and fiscal year.
-
Set up batch approval and post security for journal entries. Set up approved and secured users.
-
Set up AAIs for account reconciliation and reconciliation codes.
-
Set up UDCs, bank account cross-references, automatic bank statement accounts, and automatic reconciliation rules and groups.
-
Set up growth patterns and assign them to business units.
-
Set up cash type rules for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable, JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable, and JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting systems and define a cash forecast report structure.
-
Set up cash flow activity codes, normal balance codes, and cash flow rules.
-
Set up document types for cash basis entries, assign the document types to the actual amounts (AA) ledger, and set up AAIs for unapplied receipts and accounts payable and accounts receivable balance accounts.
-
Set up 52-period fiscal date patterns and assign the dates to a company.
-
Set up sales tax using Vertex Sales Tax Q Series.
1.5 Business Interface Integration Objects
A business interface is a set of components that implementation teams can use to create an integration between JD Edwards EnterpriseOne and an external system. Business interfaces can include one or more of these business interface components:
-
Business Services
-
Real-Time Events
-
Batch Import and Export Programs
For additional information about business interfaces, and the business objects available for this product area, see these topics in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Applications Business Interface Reference Guide: