14 Managing Customers' Subscription-Level Services
This chapter describes Oracle Communications Billing and Revenue Management (BRM) subscription service management, including setting up services to track and rate usage and create bills for customers' subscriptions.
Before reading this document, you should be familiar with managing customers. See "About Managing Customers".
About Grouping Services by Subscription
BRM allows you to group services by subscription. A subscription is a service or group of services, such as telephony, email, and data transfer, that customers purchase for a particular device, such as a wireless phone. Customers might have several subscriptions, such as a wireless phone and Internet access or two wireless phones with different phone numbers.
Grouping services by subscription allows you to rate and bill for services according to the customer's subscription rather than by account. When services are grouped by subscription, you can:
-
Keep separate balances for the subscription.
-
Create a separate bill for the subscription.
-
Offer subscription-level discounts.
-
Specify subscription-level credit limits.
Subscription service management can be applied to various types of customers; for example:
-
A single customer owns one wireless handset.
-
A family in which one account owns multiple handsets.
-
A corporate customer in which a sponsored account and subscription is set up for each employee.
You use Pricing Center to configure your subscription groups and Customer Center to purchase the subscription services and member services.
About Subscription Services
To group services by subscription, you configure a subscription group in Pricing Center, which includes a subscription service, and assign member services:
-
A subscription service represents a customer's subscription, such as a wireless phone line, and includes member services. You can associate the subscription service with the customer's device, such as the SIM card in a wireless handset.
-
Member services are related to the subscription service. To purchase member services in Customer Center, you must also purchase its subscription service. You assign the devices associated with the subscription service to the member services when registering customers. For more information, see "Associating a Device with a Subscription Service".
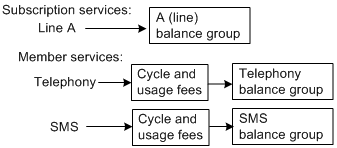
For example, a subscription might consist of the following services as shown in Figure 14-1:
Figure 14-1 Services for a Subscription (Example)

Description of ''Figure 14-1 Services for a Subscription (Example)''
For example, a customer owns two wireless handsets, each with a unique phone number. You set up two subscription groups in the customer's account, one for each phone line as shown in Figure 14-2:
Figure 14-2 Multiple Subscriptions for an Account

Description of ''Figure 14-2 Multiple Subscriptions for an Account''
About Subscription Service Dependencies
A service instance cannot be a member of two different subscription services.
A subscription service cannot be a member of another subscription service.
However, a subscription service, a member service, or both can sponsor charges or share discounts with services in another subscription's group. For more information, see "About Sharing Discounts and Sponsoring Charges for Subscription Services".
How Resources Are Tracked and Shared for Subscription Services
When a customer uses the services included in the subscription, the usage fees are stored in a balance group. You create balance groups to track balances for one or more specific services. A service in a subscription group can also include resources that can be distributed among one or more member services. How usage fees are tracked and resources are distributed is determined partly by the balance groups that you create for the services.
For more information on balance groups, see "About Accounts Receivable" in BRM Configuring and Running Billing.
Tracking a Subscription's Currency Resources
When you define the services for a subscription, you create one or more balance groups. To track resources at the subscription level, you define a balance group for the subscription service and associate all member services with that balance group.
While it is possible for a subscription service to use the account's balance group, it is much easier to track usage for a subscription when the subscription service has its own balance group. This is relevant when a customer's account includes both a subscription service, such as a handset with multiple services, and a standalone service such as an Internet connection.
Note:
You cannot transfer a subscription service that uses the account's balance group to another subscriber's account. If you want to be able to transfer the subscription service, define service-level balance groups or define a balance group for the subscription service and associate all the member services with that balance group. See "About Transferring a Subscription Service to Another Subscriber".Typically, you also create a balance group for each member service. This makes it possible to set up shared discounts, set credit limits on service resources, and limit resource consumption to the specified service. When services have their own balance groups, cycle and usage fees for each service are tracked in the service's balance group as shown in Figure 14-3:
You can associate all services with the subscription service's balance group. When customers use member services, the cycle and usage fees are stored in the subscription service's balance group as shown in Figure 14-4:
Figure 14-4 Storage of Cycle and Usage Fee
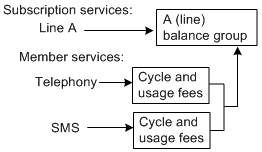
Description of ''Figure 14-4 Storage of Cycle and Usage Fee ''
A member service can also be associated with another member service's balance group to track usage for those services together. However, member services cannot use the balance group of a service that is not in the same subscription group.
Sharing a Subscription's Non-Currency Resources
When all member services use the subscription service's balance group, all non-currency resources, such as free minutes and frequent flyer miles, are shared by all services in the group.
For example, a telephony service includes 360 free minutes of usage per month and a data service includes 30 free minutes per month. At the beginning of the month, a balance of 390 free minutes is stored in the subscription service's balance group, and all services have access to the 390 free minutes as shown in Figure 14-5:
Figure 14-5 Sharing of Non-Currency Resources
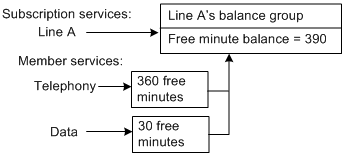
Description of ''Figure 14-5 Sharing of Non-Currency Resources''
When you create a balance group for a member service, any non-currency resources included with that service can be consumed by only that service.
In Figure 14-6, the data service includes 30 free minutes that can be applied only to the data service. The data service has access only to its own resources; it cannot use the free minutes included with any other service.
Figure 14-6 Non-Currency Services with Multiple Balance Groups
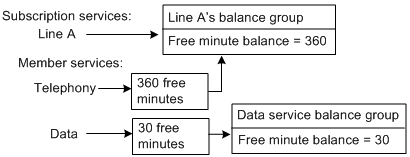
Description of ''Figure 14-6 Non-Currency Services with Multiple Balance Groups''
You might want some types of non-currency resources to be tracked at the subscription level (for example, the number of months users have been subscribers regardless of whether they have changed the services on their lines).
To track these non-currency resources at the subscription level, you configure a counting sub-balance for the subscription service. For more information, see "About Tracking Resources in Account Sub-Balances" in BRM Setting Up Pricing and Rating.
How Products and Discounts Are Selected for Rating Subscription Service Usage
Products and discounts can be owned by the subscription service, a member service, or both:
-
When the subscription service owns products and discounts, those products and discounts are used to rate member service usage.
-
When the subscription service and member service both own a product, the product used for rating (the member's or the subscription service's) is determined by the product's priority.
-
When the subscription service and member service both own discounts, the order in which the discounts are distributed is determined by the discount's priority.
If a member service owns a discount but does not have its own balance group, its discount adjustment is applied to the subscription service's balance group.
You specify product and discount priority when you create products and discounts in Pricing Center. For more information, see the Pricing Center Help.
About Distributing Discounts in a Subscription Service Group
You can apply the same types of discounts to a subscription service as you can to a standalone service; for example:
-
Cycle discounts, such as a 10% discount for certain months.
-
Billing-time discounts, such as 10% off when the total usage fee exceeds $100.
-
System discounts, such as 15% off on certain holidays for all customers.
-
Shared discounts, such as free minutes that are distributed to services based on the service's usage amount.
For more information on discounts, see "About Implementing Discounts" in BRM Configuring Pipeline Rating and Discounting.
There are two ways that discounts owned by a subscription service can be distributed to member services in a subscription group:
-
Through inheritance: When a member service shares the subscription service's balance group, any discount purchased by the subscription service is automatically inherited by the member service. The discount balance impact is applied to the subscription service's shared balance group.
-
Through a discount sharing group: When the subscription service and a member service have separate balance groups, the subscription service can share its discounts with the member service through a discount sharing group. The discount balance impact can be applied to a balance in the subscription service's balance group or in the member service's balance group. For more information, see "About Sharing Discounts and Sponsoring Charges for Subscription Services".
Note:
When a billing-time discount is inherited, it is applied to the subscription service and every member service that inherits it. If the discount grants a percentage off of currency charges based on the total usage of all services in the group, the total discount granted can be greater than intended. If you do not want billing-time discounts to be inherited, purchase them at the member service level instead of the subscription service level. You can also configure BRM to disallow inheritance for billing-time discounts. For more information, see "Specifying Whether Billing-Time Discounts Are Inherited by Member Services in Subscription Groups" in BRM Configuring Pipeline Rating and Discounting.
About Sharing Discounts and Sponsoring Charges for Subscription Services
To apply subscription-level cycle, billing-time, and system discounts, you create the discounts and assign them to the subscription service. To apply shared discounts, you create a discount sharing group.
Charges can also be sponsored among a subscription's services. To sponsor charges, you create a charge sharing group.
Discount and charge sharing groups are groups of services that share resources. These resource sharing groups consist of group owners and group members. An owner can be any one of the following, and the members can include any combination of these:
-
An account
-
A subscription service
-
A subscription's member service
-
A service outside the subscription's group in the same or another account
To create subscription-level resource sharing (for example, to distribute 300 free minutes to all services on a phone line), make the subscription service the owner of the sharing group and make the member services the members of the sharing group.
The service type of the subscription service must match the type of service to which the shared discount applies.
Important:
All services in a resource sharing group must have their own balance groups so that BRM can track the resources that they use and share.For more information on discount and charge sharing groups, see "About Resource Sharing Groups" in BRM Configuring Pipeline Rating and Discounting.
How Sharing Group Resources Are Distributed to Subscription Service Members
Members in discount and charge sharing groups have an ordered balance group. For more information, see "About Ordered Balance Groups" in BRM Configuring Pipeline Rating and Discounting.
When a subscription service is a member in a resource sharing group, the member services may or may not share the subscription service's ordered balance group:
-
A member service that is not itself a resource sharing group member (that is, it does not have its own ordered balance group), uses the ordered balance group of the subscription service. By default, the member service inherits member status in the resource sharing group from the subscription service, and the member service has access to the sharing group's resources as illustrated in Figure 14-7:
Figure 14-7 Member Service Using Group's Resources
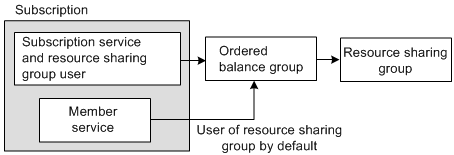
Description of ''Figure 14-7 Member Service Using Group's Resources''
-
A member service that has its own ordered balance group does not use the subscription service's ordered balance group. This is true even when the member service and subscription service belong to the same resource sharing group as illustrated in Figure 14-8:
Figure 14-8 Member Service Using Own Ordered Balance Group
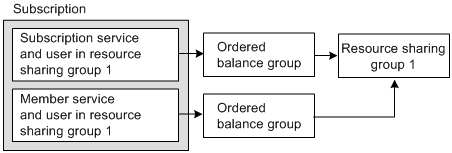
Description of ''Figure 14-8 Member Service Using Own Ordered Balance Group''
-
If a member service and the subscription service belong to different resource sharing groups, the services have access only to the shared resources in the sharing group to which they belong as illustrated in Figure 14-9:
Figure 14-9 Restrictions for Services Using Different Resource Sharing groups
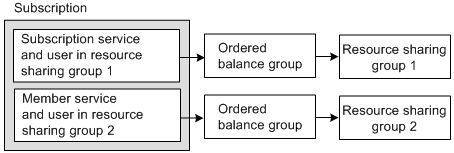
Description of ''Figure 14-9 Restrictions for Services Using Different Resource Sharing groups''
When the subscription service and a member service are both discount sharing group owners and have members in common, the sequence of the ordered balance group list for each discount sharing group member determines whether the member service's discounts or the subscription service's discounts are applied first.
If a service is a member of both a discount and charge sharing group, the discounts are used before charges are applied.
You set up discounts in Pricing Center.
You define how charges are shared in Pricing Center.
To create discount and charge sharing groups, you implement BRM opcodes in your customer relationship management (CRM) system.
How Pipeline Manager Chooses a Rate Plan for Subscription Services
Member services use the rate plan associated with the products and discounts owned by the subscription service. If the subscription service and a member service both have products and discounts, the member service's products and discounts are used to rate the member service usage.
For more information, see "How Pipeline Manager Chooses a Rate Plan" in BRM Configuring Pipeline Rating and Discounting.
How Service Status Changes Affect Subscription Services
The status of the subscription service or any member service can be active, inactive, or closed. Changing the status of the subscription service changes the status of all the subscription's member services unless the status of a member service was previously changed independently.
-
When you inactivate a subscription service, all of its member services are inactivated.
-
When you close a subscription service, all of its member services are closed.
-
When you reactivate a subscription service that has been inactivated or closed, all of its member services are reactivated.
Changing the status of a member service affects only that service. If you close a member service and then close the subscription service, reactivating the subscription service does not reactivate the previously closed member service.
Closing a service cancels all products and discounts owned by that service. If you reactivate a service and want to restore canceled products and discounts, you must repurchase those products and discounts for the service.
About Setting Up Corporate Accounts That Use Subscription Services
When setting up a corporate account that uses subscription services, rating performance is affected if the company has many employees whose services share account balances.
For corporate accounts, it is better to set up an account hierarchy in which the company account is the parent account and the employees own child account that include their own subscription and member services. This way, the charges are rolled up to the corporate account at billing time, so rating performance is less affected.
About Creating and Managing Subscription Services
A subscription consists of a set of services that you group together by assigning the subscription service and adding any number of member services. Setting up subscription service groups includes these tasks:
About Setting Up a Subscription Service
A subscription service is a /service storable object in the BRM database. You can create a new storable class to represent a subscription service, or you can use an existing storable class. Member services can be a subclass of the subscription service or a different service type.
For example, to use subclasses for member services, you might use the /service/telco/gsm storable object as the subscription service and /service/telco/gsm/telephony and /service/telco/gsm/sms objects as member services.
To create custom storable objects that represent subscription services, see "Creating Custom Fields and Storable Classes" in BRM Developer's Guide.
About Configuring a Subscription Service Group
A service instance can be either a subscription service or a member service, but not both. After a service is selected as a subscription service, it cannot be used again as a member service in the same subscription group.
Note:
Although you can create a subscription group with optional member services, the optional member services cannot be purchased separately.You can configure a subscription service group by using only the services included in the plan.
You can create subscription services in two ways:
-
When creating a plan in Pricing Center. When customers purchase the plan, the member service objects are created and associated with the subscription service object. Additional member services can be added during customer registration.
To create subscription services by using Pricing Center, see "Creating a Subscription Service Group".
Subscription groups are configured in Pricing Center; the deals associated with the subscription and member services can be purchased in Customer Center.
-
If you implement your own customer relationship management (CRM) system, customer service representatives (CSRs) can dynamically set up subscription services or add member services to an existing subscription service when registering customers. To create subscription service groups when registering customers, you implement BRM opcodes in your CRM system.
About Adding Deals to Subscription Services
You can add deals to the subscription service and to member services. A deal owned by the subscription service is a subscription-level deal. That is, the products in the deal are available for rating all services in the subscription group.
You associate deals with subscription services when you add deals to plans in Pricing Center.
A CSR can also add a deal to a subscription service or member service that a customer has purchased in Customer Center.
About Setting Up Balance Groups for Subscription Services
When using Pricing Center to create subscription services in plans, you can assign all member services to the subscription service's balance group, create a balance group for each individual service in the group, or associate groups of services with different balance groups.
When you create a balance group for each member service in Pricing Center, if you have set up any credit limits, credit floors, and credit thresholds for the subscription's service, those values will be set in the balance group of each member service. You can later change these in the service.
When setting up subscription services during customer registration, you specify which balance group each service in the group should use.
You can change the credit limit on a balance group for a subscription service in Customer Center.
About Setting Up Subscription-Level ERAs
To set up a subscription-level extended rating attributes (ERAs), you configure a service-level ERA for the subscription service. You set up service-level ERAs for a subscription service the same way that you set up service-level ERAs for an account. See "About Provisioning Tags for Telco Services" in BRM Telco Integration.
Any member service that does not have its own ERA uses the subscription service's ERA. If the subscription service and member service both have an ERA, the member service's ERA is used to rate the member service usage.
After setting up ERAs, you configure them for a specific customer during customer registration.
About Modifying Subscription Services
You can perform the following actions to modify an existing subscription's services:
-
Add a member service to a subscription group.
-
Add deals to a service in a subscription group.
-
Change the status of a service in a subscription group.
To modify a subscription's services when setting up services in Pricing Center, see the Pricing Center Help.
To modify the subscription and member services that a customer has purchased in Customer Center, see "Managing Services". Otherwise, to modify a subscription's services after customers have purchased them, you implement BRM opcodes in your CRM system.
About Canceling a Subscription Service
A subscription service can be canceled at any time during the billing cycle. You can also specify to bill the account for the service immediately upon cancellation.
In BRM, a subscription service is canceled when:
-
The account that owns the subscription service is closed.
-
The subscription service has expired.
-
The subscription service is canceled by a CSR; for example, in Customer Center.
To perform a subscription service cancellation, BRM does the following:
-
Closes the subscription service and all of its member services. See "About Service Status When a Subscription Service Is Canceled".
-
Cancels the products and discounts associated with the subscription service and its member services. See "Effect of Canceling a Subscription Service on Products and Discounts Owned by the Service".
-
Deletes the sharing groups owned by the subscription service and its member services, and removes the services from any sharing groups of which they are members. See "Effect of Canceling a Subscription Service on Resource Sharing Groups Owned by the Service".
-
Bills the account, if specified. See "About Billing on Subscription Service Cancellation".
Your CSRs can use Customer Center to cancel subscription services as they cancel other services. To cancel subscription services with your client application, you implement BRM opcodes. For more information, see "Canceling a Subscription Service".
About Service Status When a Subscription Service Is Canceled
When a subscription service is canceled, all of its member services are canceled as well. The status of the subscription service and its member services are set to closed.
-
The status-flag value of the subscription service is set to PIN_STATUS_FLAG_CANCEL_LINE, and the status-flag value of the member services are set to PIN_STATUS_FLAG_DUE_TO_SUBSCRIPTION_SERVICE, which specifies that the member service's status was changed due to the status change of the subscription service.
-
The purchase, usage, and cycle end dates for the subscription service and all of its member services are set to the cancellation date.
For more information, see "How Service Status Changes Affect Subscription Services".
Effect of Canceling a Subscription Service on Products and Discounts Owned by the Service
Canceling a subscription service cancels all the product and discount instances owned by the service and its member services.
-
The status of the product and discount instances owned by the subscription service and its member services are set to canceled.
-
The purchase, usage, and cycle end dates for the canceled product and discount instances are set to the subscription service cancellation date.
Effect of Canceling a Subscription Service on Resource Sharing Groups Owned by the Service
A subscription service and its member services can own a resource sharing group, be members of a resource sharing group, or both.
When a subscription service is canceled, BRM does the following:
-
For each sharing group member, it deletes the sharing group's balance group from the group member's ordered balance group list.
-
Removes the subscription service and its member services from any sharing groups in which they are members.
For more information on sharing groups, see "About Resource Sharing Groups" in BRM Managing Accounts Receivable.
About Transferring a Subscription Service to Another Subscriber
You can transfer a subscription service from one subscriber to another at any time during the billing cycle.
Transferring a subscription service also transfers all member services to the new subscriber's account. The member service objects are updated to reference the new subscriber's account object.
Important:
When you transfer a subscription service from one account to another, its balance group is also transferred. If the subscription service (or one of its member services) uses an account-level balance group, however, that balance group cannot be transferred. (Transferring the account-level balance group would leave the original account without a balance group, which is not allowed.) As a result, the subscription service itself cannot be transferred. To avoid this problem, the subscription service and member services should use service-level balance groups. You can define a balance group for the subscription service and associate all the member services with that balance group. See "About Creating and Managing Subscription Services".The following functions are not supported for subscription service transfer:
-
Transferring a subscription service across different brands.
-
Backdating of a subscription service transfer.
Each time a subscription service is transferred, BRM stores information about the old account and the date and time when the transfer occurred in a transfer list.
The transfer list is stored in the /service object. Information stored in the transfer list is used by BRM to rate and record any delayed events and call details records (CDRs) and to bill for usage created prior to the service transfer for the old subscriber's account.
To transfer subscription services, you implement BRM opcodes in your client application.
Transferring Subscription Services Between Accounts with Different Statuses
You can transfer a subscription service from a closed account to an account that is active, as well as transfer a subscription service from an active account to an account that is closed. When a subscription service is transferred from a closed account to an active account, the subscription service's status remains closed after the transfer. You must manually activate the subscription service. When a subscription service is transferred from an active account to a closed account, the subscription service's status remains active after the transfer. In this case, you must manually activate the closed account.
You can transfer pending scheduled actions associated with an existing subscription when you transfer the subscription to a different account. All the /schedule objects corresponding to the member services (including the parent service) are transferred to the target account. Completed actions (that is, /schedule objects with Done status) are not transferred.
If you want to disallow the transfer of a subscription service to an account that is closed, you can do this by using event notification and writing a custom opcode to generate an error when the subscription service transfer event occurs. For more information on using event notification, see "Using Event Notification" in BRM Developer's Guide.
About Transferring Subscription Services Between Schemas
To transfer a a subscription service between accounts stored in multiple schemas, you can do one of the following:
-
Migrate the accounts to the same schema and then transfer the service.
For example, if you have:
-
Account A stored in Schema 1
-
Account B stored in Schema 2
To transfer a subscription service from Account B to Account A, you must move Account B to Schema 1, and then transfer the subscription service to Account A.
See "Transferring Subscription Services Between Accounts in the Same Schema" for information about transferring subscriptions services in the same schema.
BRM provides the Account Migration Manager (AMM), which can be used to migrate accounts between database schemas.
Important:
AMM is an optional feature. Contact your BRM account manager for more information on using AMM. -
-
If you do not want to migrate the accounts to the same schema, enable the RecreateDuringSubscriptionTransfer business parameter. See "Transferring Subscription Services Between Accounts in Multiple Schemas" for more information.
About Transferring Objects Associated with a Subscription Service
When a subscription service is transferred, objects associated with the service and member services are transferred to the new subscriber's account.
In BRM, a service can be associated with the following objects:
-
Service profiles. See "About Transferring Service Profiles Associated with a Subscription Service".
-
Devices and associated phone numbers for the service. See "About Transferring Devices Associated with a Subscription Service".
-
Products and discounts. See "About Transferring Products and Discounts Associated with a Subscription Service".
-
Service resource sub-balances and billing information. See "About Transferring Service-Level Balance Groups during Subscription Service Transfer".
-
Service groups. See "How a Subscription Service Transfer Affects Charge and Discount Sharing Groups Owned by the Service".
About Transferring Service Profiles Associated with a Subscription Service
In BRM, you can create service profiles to store additional information about the service. A service profile object is associated with a service and the account that the service belongs to. When a subscription service is transferred to a new subscriber's account, the profile objects associated with the subscription service and the member services are updated to reference the new subscriber's account object.
For more information on profiles, see "About Collecting Nonstandard Account Information".
About Transferring Devices Associated with a Subscription Service
In BRM, devices such as a mobile phone are associated with services. A device object is associated with a service and the account that the service belongs to. When a subscription service is transferred to a new subscriber's account, the devices associated with the subscription service and the member services are updated to reference the new subscriber's account object.
For more information on devices, see "Managing Devices with BRM" in BRM Developer's Guide.
About Transferring Products and Discounts Associated with a Subscription Service
BRM rates events by using the product and discount information associated with the service for which the events are generated. The purchase, cycle, and usage start and end dates define the validity periods during which a product or a discount can be purchased and cycle fees and usage charges can be applied.
When a subscription service is transferred, BRM cancels the products and discounts associated with the subscription service and member services for the old subscriber account by setting the end dates to the transfer date. When delayed billing is enabled, delayed events and CDRs are rated and discounted by using the canceled products and discounts for the old subscriber's account.
Important:
For delayed events to be rated and discounted for the old subscriber's account, the canceled product and discount instances must persist in the account. For more information, see "Rating Delayed Events for Canceled Products" and "Rating Delayed Events for a Canceled Discount".Another instance of the products and discounts associated with the subscription service and member services is added to the new subscriber's account with the purchase, cycle, and usage start dates set to the transfer date. The end dates are set to the old end dates. Events generated by the subscription service after the transfer date are then rated and discounted for the new subscriber's account.
Note:
-
To discount any charges associated with the products, such as the prorated cycle fee amount, the discount instances are added to the new subscriber's account before the product instance.
-
When a subscription service is transferred, the subscriber accounts are not charged with any purchase or cancellation fees that are generally applied when a product or discount is purchased or canceled.
-
When a subscription service is transferred, customized products are transferred along with their base product.
For more information on customer's products and discounts, see "Managing Customers' Services and Products".
About Transferring Sponsored Products
When a subscriber's account owns sponsored products, the sponsored products are associated with the sponsor group that the subscriber is a member of. The balance impacts for the sponsored products are applied to the sponsor group owner account.
When a subscription service is transferred, one of the following occurs for sponsored products:
-
If the new subscriber account is not a member of any sponsor group, reference to the sponsor group is removed from the product instance.
-
If the new subscriber account is a member of another sponsor group and the same product is sponsored, reference to the sponsor group is changed to the new sponsor group in the product instance.
-
If the product was not sponsored for the old subscriber account but is sponsored for the new subscriber account, a reference to the new sponsor group is added to the product instance.
For more information on sponsorship, see "About Resource Sharing Groups" in BRM Managing Accounts Receivable.
How a Subscription Service Transfer Affects Charge and Discount Sharing Groups Owned by the Service
Charge sharing and discount sharing groups associated with the subscription service or member services are not transferred when the subscription service is transferred to a new subscriber's account.
When a subscription service or member service owns a discount sharing or charge sharing group, the group is deleted when the service is transferred, and the group's balance group is deleted from the ordered balance group list for each member in the group. You need to re-create the groups for the service after the service has been transferred into the new subscriber's account.
When a subscription service or member service is a member of a charge sharing or discount sharing group, the service is deleted from the group when it is transferred, and the group's balance group is deleted from the ordered balance group list for the service. The service must be added back to the group after the service has been transferred.
For more information on deleting a sharing group or deleting a sharing group member, see "About Sponsor Groups" in BRM Developer's Guide.
About Transferring Service-Level Balance Groups during Subscription Service Transfer
A subscription service can have its own service-level balance group. Each member service can also have its own balance group. The balance group is associated with the subscriber account's bill units.
When a subscription service is transferred, the balance groups associated with the subscription service and the member services are transferred to the new subscriber's account. Either the balance groups are added to an existing bill unit in the new subscriber's account or a new bill unit is created for the service only.
Note:
-
You cannot transfer subscription services that use account-level balance groups. When you transfer a subscription service from one account to another, its balance group is also transferred. If the subscription service (or one of its member services) uses the account-level balance group, however, that balance group cannot be transferred. (Transferring the account-level balance group would leave the original account without a balance group, which is not allowed.) As a result, the subscription service itself cannot be transferred. To avoid this problem, subscription services should use service-level balance groups. See "About Creating and Managing Subscription Services".
-
BRM does not allow movement of a balance group from one bill unit to another when the balance group's bill unit has unallocated payments or adjustments, open refunds, or unresolved disputes. However, this restriction does not apply when a balance group is moved to another account as a result of a subscription service transfer.
How Events Are Assigned to Bill Items after a Subscription Service Transfer
Each billable event generated by a subscription service is assigned to a bill item (/item). During billing, charges from all the bill items are collected in a bill for the subscriber's account.
When a subscription service is transferred, BRM creates new bill items for the new subscriber's account by using item configurations (/config/items). Events generated after the transfer date are assigned to the new bill items. The new bill items are tied to the bill unit (/billinfo) that is referenced by the service's balance group in the new subscriber's account. As a result, charges for the new events are applied to the new subscriber's account.
Delayed events and CDRs are assigned to the bill items in the old subscriber's account. The bill items are associated with the old subscriber's bill unit; therefore, charges for the bill items are applied to the old subscriber's account.
About Transferring Non-Currency Resources during Subscription Service Transfer
When a subscription service is transferred from one subscriber's account to another, available non-currency resources that were granted by cycle forward fees are prorated and stored in two sub-balances with different validity periods.
-
Original sub-balance: By default, resources in this sub-balance are valid from the start of the original account's current billing cycle to the transfer date.
-
New sub-balance: By default, resources in this sub-balance are valid from the transfer date to the end of the new account's current billing cycle.
Before a subscription service is transferred, a resource is stored in a single sub-balance. After a subscription service is transferred, each resource is prorated and stored in two sub-balances: the original sub-balance and a new sub-balance.
Note:
To create separate sub-balances with different validity periods, the balance impact that grants the free resource must have a non-zero relative cycle start date. If the balance impact's relative cycle offset in the cycle forward or cycle arrears rate plan is set to 0, a new sub-balance is not created. Instead, the resources are added to the original sub-balance and are valid forever.Rating and discounting impact the resources in the original sub-balance for delayed events generated by the service prior to the transfer date. Resources in the new sub-balance are consumed for new events generated by the subscription service after the transfer date.
By default, the original sub-balance always expires on the transfer date. Because events generated by the new account occur after the transfer date, the new account cannot consume free resources from the original sub-balance. You can extend the validity period of the original sub-balance so that its free resources can be consumed by the new account. See "About Extending Sub-Balance Validity When a Subscription Service Is Transferred".
About Extending Sub-Balance Validity When a Subscription Service Is Transferred
When a subscription service is transferred from one account to another, non-currency resources are prorated and stored in sub-balances with different validity periods. See "About Transferring Non-Currency Resources during Subscription Service Transfer".
To extend the validity period of the original sub-balance, you set the sub_bal_validity business configuration parameter to one of the following options:
-
Cut: This is the default. This option sets the validity period from the start of the original account's current billing cycle to the service transfer date.
-
Maintain: This option retains the original end date of the bucket. This is true even in the case of a product cancellation or line transfer.
-
Align: This option sets the validity period from the start of the original account's current billing cycle to the end of the new account's current billing cycle.
Note:
-
Setting the sub_bal_validity business configuration parameter extends the validity period of the original sub-balance only. The resources in the new sub-balance are always valid from the service transfer date to the end of the new account's billing cycle.
-
Extending the validity period of the original sub-balance extends only the time the free resources in the bucket are accessible and does not change the resource proration. The free resources are prorated based on the service transfer date. For more information, see "How Cycle Fees Are Prorated When a Subscription Service Is Transferred".
-
If you do not configure the sub_bal_validity parameter, BRM sets the original sub-balance to expire on the service transfer date, and the new account cannot access this sub-balance.
To configure sub-balance validity, see "Configuring Sub-Balance Validity for Subscription Service Transfer".
How Non-Currency Resources Are Consumed When a Subscription Service Is Transferred
When a subscription service is transferred from one account to another, non-currency resources are prorated and stored in sub-balances with different validity periods. See "About Transferring Non-Currency Resources during Subscription Service Transfer".
The original account always consumes free resources from the original sub-balance because the events for this account occur before the service transfer date. The new account, however, can consume resources from both the original sub-balance and the new sub-balance when the validity period for the original sub-balance is extended beyond the service transfer date. See "About Extending Sub-Balance Validity When a Subscription Service Is Transferred".
The following examples demonstrate how non-currency resources are consumed after a subscription service is transferred.
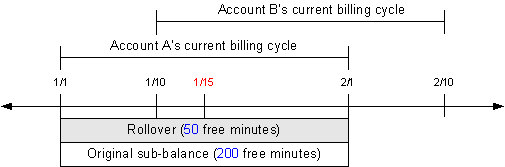
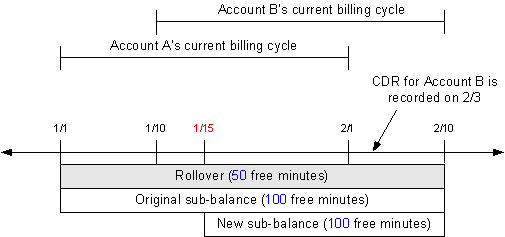
On January 1, Account A has a rollover balance of 50 free minutes, rolled over from the previous cycle, and a new grant of 200 free minutes. Subscription service A is later transferred from Account A to Account B on January 15. A timeline for the subscription transfer, including, free minute balances, is shown in Figure 14-10:
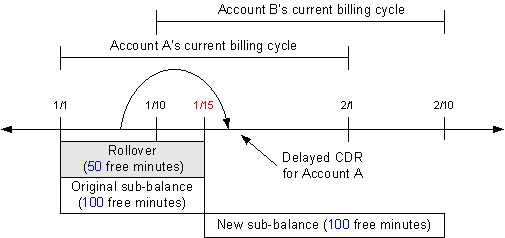
When sub_bal_validity is set to Cut, the rollover and original sub-balance buckets' valid_to dates are set to the transfer date. The resources in the original sub-balance are prorated and a new sub-balance is created with 100 free minutes.
A delayed CDR for Account A is recorded on January 17 for 200 minutes. When the CDR is rated, 50 minutes are consumed from the rollover sub-balance and 100 minutes are consumed from the original sub-balance. The balance in these two sub-balances becomes 0. Because the CDR occurred before January 15, it cannot consume minutes from the new sub-balances, and Account A is charged for the remaining 50 minutes of usage. Figure 14-11 illustrates this example.
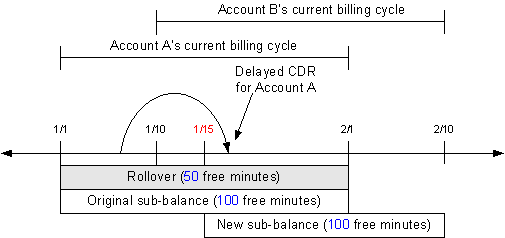
When sub_bal_validity is set to Maintain, the rollover and original sub-balance buckets' valid_to dates are extended to the end of Account A's billing cycle.
A delayed CDR for Account A is recorded on January 17 (after the service transfer date) for 200 minutes. When the CDR is rated, 50 minutes are consumed from the rollover sub-balance and 100 minutes are consumed from the original sub-balance. The balance in these two sub-balances becomes 0. Because the CDR occurred before January 15, it cannot consume minutes from the new sub-balance, and Account A is charged for the remaining 50 minutes of usage. Figure 14-12 illustrates this example.
When sub_bal_validity is set to Align, the rollover and original sub-balance buckets' valid_to dates are extended to the end of Account B's billing cycle.
A CDR for Account B is recorded on February 3 for 200 minutes. Because the validity period of the rollover and original sub-balance is extended until February 10, 50 minutes are consumed from the rollover sub-balance and 100 minutes are consumed from the original sub-balance. The remaining 50 minutes are consumed from the new sub-balance. The balance in the rollover and original sub-balance buckets becomes 0, and the balance in the new sub-balance becomes 50. Figure 14-13 illustrates this example.
How Non-Currency Resources Are Rolled Over When a Subscription Service Is Transferred
You can configure rollover so that non-currency resources associated with cycle forward fees are rolled over for use in future cycles. For more information, see "About Rollovers" in BRM Setting Up Pricing and Rating.
When a subscription service is transferred, the free resources in the rollover and original sub-balance buckets are rolled over when sub_bal_validity is set to Maintain or Align.
Note:
The rollover and original sub-balance buckets are not rolled over when sub_bal_validity is set to Cut.The following example demonstrates how unused resources are rolled over when a subscription service is transferred to another account. In this example:
-
The subscription service grants 200 free minutes valid from January 1.
-
The subscription service is transferred to the new subscriber's account on January 15.
-
The billing cycle for the original account starts on the first of each month.
-
The billing cycle for the new account starts on the 15th of each month.
-
The sub_bal_validity business configuration parameter is set to Maintain.
-
Rollover minutes from the previous cycle are 50.
The rollover rules are:
-
A maximum of 50 free minutes can be rolled over to the next cycle.
-
The maximum number of rollover cycles is 1.
-
The maximum number of free minutes that can be rolled over from previous months is 100.
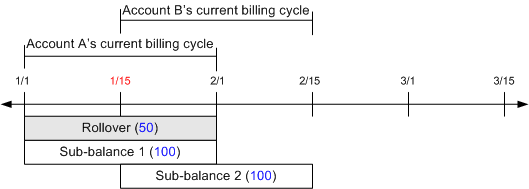
On January 1, the old subscriber's account is granted 200 free minutes for the month of January. On January 15, the subscription service is transferred to the new subscriber's account. The 200 minutes are prorated and put in two buckets with different validity dates: the original bucket (Sub-balance 1) and a new bucket (Sub-balance 2). Figure 14-14 illustrates this example.
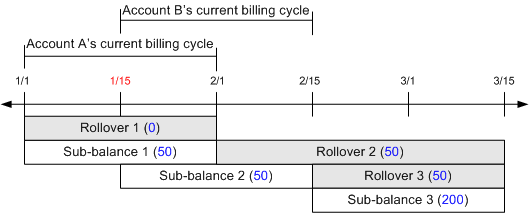
When pin_bill_day is run on February 1, 50 minutes from Sub-balance 1 are rolled over. Because Sub-balance 1 is valid for a partial cycle (from January 15 to February 1 instead of January 15 to February 15), the resources are rolled over for one entire cycle. As a result, the Rollover 2 bucket is valid until March 15, which is the next accounting cycle end date for Account B.
When pin_bill_day is run on February 15, 50 minutes from Sub-balance 2 are rolled over into a new bucket (Rollover 3) and are valid until March 15. The new account is granted an additional 200 minutes for the new cycle (Sub-balance 3).
Figure 14-15 illustrates the billing timeline associated with this example.
Because the Rollover 2 and Rollover 3 buckets are valid after the transfer date, only the new account can access the resources in these buckets. The old account cannot consume the free minutes from these buckets.
How Cycle Fees Are Prorated When a Subscription Service Is Transferred
Typically, cycle fees are applied at the beginning of a billing cycle for services provided during that cycle and are prorated when a service is purchased or canceled during a billing cycle.
However, a subscription service transfer is not the same as canceling the product in the old account and purchasing it for the new account. Instead, a service transfer moves the service from one account to another. When a subscription service is transferred, the subscriber accounts are not charged with the product purchase or cancellation fees and therefore the purchase and cancellation proration are also not applied that are generally applied when a product or discount is purchased or canceled.
Consequently, when a subscription service is transferred during a billing cycle, cycle fee proration is enforced based on the transfer date to charge the old account for the fees before the transfer and the new account for the fees after the transfer. The prorated cycle fees from the start of the billing cycle to the transfer date are applied to the old subscriber's account, and the prorated cycle fees from the transfer date to the end of the billing cycle are applied to the new subscriber's account.
For more information on how cycle fees are prorated, see "About Proration" in BRM Configuring and Running Billing.
How Billing Time Discounts and Folds Are Applied When a Subscription Service Is Transferred
Billing time discounts and folds are applied at the end of the accounting cycle and are based on resources used during the cycle. In BRM, resource balances are stored and tracked in account-level or service-level balance groups.
When a subscription service is moved to a new subscriber's account, the service-level balance group is transferred to the new subscriber's account. As a result, billing-time folds and discounts are applied to the new subscriber's account. See "About Transferring Service-Level Balance Groups during Subscription Service Transfer".
For more information on billing time discounts, see "About Implementing Discounts" in BRM Configuring Pipeline Rating and Discounting.
About Rating Delayed Events When a Subscription Service Is Transferred
Delayed events generated by a subscription service that occur prior to the subscription service transfer are billed to the old subscriber's account. See "How Events Are Assigned to Bill Items after a Subscription Service Transfer".
BRM rates events by using the product and discount information associated with the service for which the events are generated. When a subscription service is transferred, BRM stores the original account's products and discounts to rate and discount delayed events generated by that account. See "About Transferring Products and Discounts Associated with a Subscription Service".
When rating delayed CDRs for the original account, the original account can be charged for usage when all of the free resources have been consumed by the new account. This can occur when the validity period of the original sub-balance is extended beyond the subscription service transfer date. See "How Non-Currency Resources Are Consumed When a Subscription Service Is Transferred".
Important:
To achieve correct rating results when rating delayed events, you must rerate the events for both the original and new account in the correct sequence. For more information on rerating, see "About Rerating Events" in BRM Setting Up Pricing and Rating.How a Subscription Service Transfer Affects Account Migration
When an account selected for rerating is associated with a subscription service transfer, rerating requires both the original account and the account to which the service was transferred to reside in the same database schema. For this reason, the Account Migration Manager (AMM) does not allow the original account or the account to which a service was transferred to be migrated to another schema.
For example:
-
Account A is stored in Schema A.
-
Account B is stored in Schema B.
-
Account C is stored in Schema C.
To transfer a subscription service from Account A to Account B, both accounts must reside in the same schema. You must move Account B to Schema A or Account A to Schema B, and then transfer the service to Account B.
If, after the service transfer, you want to migrate Account A or Account B to Schema C, AMM does not allow the migration because rerating requires the original account and the account to which the service was transferred to reside in the same schema. If you want to transfer the service again to Account C, you must move Account C to Schema A, and then transfer the service.
Configuring Sub-Balance Validity for Subscription Service Transfer
To extend the validity period of the original sub-balance when a subscription service is transferred, you change the sub_bal_validity business configuration parameter. This parameter takes one of the following values:
-
Cut
-
Maintain
-
Align
sub_bal_validity is a system-wide parameter. By default, this parameter is set to Cut. Changing the value of this parameter affects the sub-balance validity period for any subscription service transfer that occurs after the change. For more information, see "About Extending Sub-Balance Validity When a Subscription Service Is Transferred".
Caution:
If you change the sub_bal_validity parameter (for example, from Align to Maintain), BRM does not keep a record of the original setting. BRM uses the new setting for any subscription service transfers that occur after the change.Note:
If you do not configure the sub_bal_validity parameter, BRM follows the default implementation by setting the original sub-balance to expire on the service transfer date.To extend the validity period of the original sub-balance, you modify a field in the /config/business_params object created during BRM installation. You modify the /config/business_params object by using the pin_bus_params utility. For more information on this utility, see "pin_bus_params" in BRM Developer's Guide.
-
Go to the BRM_Home/sys/data/config directory, where BRM_Home is the directory in which you installed BRM.
-
Run the following command, which creates an editable XML file from the billing instance of the /config/business_params object:
pin_bus_params -r BusParamsBilling bus_params_billing.xmlThis command creates the XML file named bus_params_billing.xml.out in your working directory. To place this file in a different directory, specify the path as part of the file name.
-
Open the bus_params_billing.xml.out file.
-
Search the XML file for the following line:
<SubBalValidity>Cut</SubBalValidity> -
Change Cut to one of the following:
-
Maintain if you want to extend the validity of the original sub-balance to the end of the original account's current billing cycle.
-
Align if you want to extend the validity of the original sub-balance to the end of the new account's current billing cycle.
-
-
Save the file as bus_params_billing.xml.
-
Run the following command, which loads this change into the /config/business_params object:
pin_bus_params PathToWorkingDirectory/bus_params_billing.xml
where PathToWorkingDirectory is the directory in which the bus_params_AR.xml file resides.
Caution:
BRM uses the XML in this file to overwrite the existing billing instance of the /config/business_params object. If you delete or modify any other parameters in the file, these changes affect the associated aspects of the BRM billing configuration.Note:
To run this command from a different directory, see "pin_bus_params" in BRM Developer's Guide. -
Read the object with the testnap utility or Object Browser to verify that all fields are correct.
See "Using testnap" in BRM Developer's Guide for general instructions on using the testnap utility. See "Reading Objects by Using Object Browser" in BRM Developer's Guide for information on how to use Object Browser.
-
Stop and restart the Connection Manager (CM). For more information, see "Starting and Stopping the BRM System" in BRM System Administrator's Guide.
-
(Multischema systems only) Run the pin_multidb script with the -R CONFIG parameter. For more information, see "pin_multidb" in BRM System Administrator's Guide.
Mapping Subscription Services in the Pipeline Manager Database
To rate subscription services in a pipeline, the data that defines the subscription service object must be mapped in the Pipeline Manager database. Sample mapping is provided by BRM for some service objects. However, if you set up a service object for the subscription service that is not already configured in the Pipeline Manager database, you must map that service to the data that defines it.
Use Pricing Center to map the subscription service in the following Pipeline Manager database tables:
-
IFW_SERVICE specifies the pipeline rating service code to real-time rating service code mapping; for example, map GSM to /service/telco/gsm.
-
IFW_SERVICE_MAP specifies the external data used to determine the internal service code. You define the mapping when you set up service code mapping.
-
IFW_REF_MAP specifies the service-type-to-event-type mapping so that the services in your price list are associated with usage events. This database table also specifies the prefix for the data that identifies an account; for example, MSISDN or IMSI.
Important:
Be sure to map a corresponding delayed event type to your subscription service object. For example, if you map to the usage event type /event/session/telco/gsm, also map to /event/delayed/session/telco/gsm. The delayed event type is used by Rated Event (RE) Loader when loading the rated events into the BRM database. For more information, see "Understanding Rated Event Loader" in BRM Configuring Pipeline Rating and Discounting.If the delayed event type does not exist in the BRM database, you must create one. See "Adding New Event Types for RE Loader to Load" in BRM Configuring Pipeline Rating and Discounting.
-
IFW_ALIAS_MAP specifies which data to use for looking up an account in order to get the parameters for rating usage. You define the alias mapping when you set up EDR container fields. For more information, see "Modifying and Loading the EDR Container Description" in BRM Configuring Pipeline Rating and Discounting.
To define the alias mapping by using Pricing Center:
-
From the Pipeline Setup Toolbox, select EDR - EDR Container Description.
-
In the EDR Container Description dialog box, select the ALL_RATE sample container description and click Edit.
-
Click the Alias Map tab and enter the alias data information for the subscription service.
-
For more information on mapping pipeline data, see "Setting Up Pipeline Price List Data" in BRM Configuring Pipeline Rating and Discounting.
About Billing for Subscription Service Usage
To bill for a subscription, all balance groups in the subscription group must be associated with a bill unit (/billinfo object). A bill is produced for each bill unit.
Important:
If a member service's balance group is not associated with a bill unit, charges for that service are not billed.You can create a bill unit for a subscription or use the account's bill unit (the AR bill unit). If you use the account's bill unit, charges for any service owned by the account that are not part of the subscription are also included in the bill.
You use Customer Center to create bill units and associate them with balance groups.
You can also create and manage bill units by using the BRM API. See "Managing Bill Units with Your Custom Application" in BRM Configuring and Running Billing.
About Creating Multiple Bills for a Subscription
When a member service has its own balance group, you can create a separate bill for that service by associating it with a new bill unit. You can also associate several member services with a single bill unit, if each member service has a balance group.
When member services have their own balance groups, you can create separate bills for those services by associating them with a new bill unit. Charges for any member service that does not have its own balance group are rolled up to the subscription service's bill unit and are included in the subscription service's bill.
About Billing for Multiple Subscriptions
When a customer owns multiple subscriptions, you can bill for each subscription separately or include charges for all subscriptions in the same bill. To create one bill for all subscriptions, associate the balance groups in all the subscription groups with the same bill unit.
About Billing on Subscription Service Cancellation
Normally, you bill a subscriber's account on its regularly scheduled billing day at the end of the billing cycle. You can also bill the account immediately upon a subscription service cancellation.
To bill the subscriber's account immediately, you specify the Bill Now option when cancelling the subscription. See "About Bill Now" in BRM Configuring and Running Billing.
Note:
If the Bill Now option is not specified, the service is billed during the regularly scheduled billing time.When the Bill Now option is specified, the subscriber's account is billed for all current charges generated by the subscription service until the cancellation date.
Delayed events for the service recorded after the cancellation date are billed on the next regularly scheduled billing date.
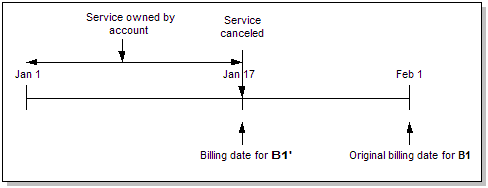
In Figure 14-16, the subscription service is canceled on January 17 with the Bill Now option specified. Bill B1' includes all current charges between January 1 and January 17. Bill B1 includes all delayed charges for the service recorded after the cancellation date.
When the Bill Now option is specified, BRM bills the bill units (/billinfo objects) associated with the subscription service. Typically, all the member services are associated with the subscription service's bill unit. However, a member service can have its own bill unit.
By default, any other service belonging to the same bill unit as the canceled subscription service or its member service's bill unit are also billed.
If you do not want other services in the bill unit to be billed immediately, do one of the following:
-
Wait for the regular billing day, and bill the canceled subscription service along with the other services in the bill unit.
-
Customize the PCM_OP_BILL_POL_GET_PENDING_ITEMS policy opcode to include only the pending bill items for the subscription service that was canceled.
You can extend your customer management application to create a Bill Now for a specific service. For more information, see descriptions of the following opcodes:
-
PCM_OP_BILL_CREATE_SPONSORED_ITEMS
-
PCM_OP_BILL_MAKE_BILL_NOW
-
PCM_OP_BILL_POL_GET_PENDING_ITEMS
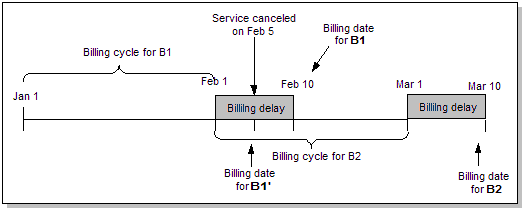
How an Account Is Billed When a Subscription Service Is Canceled during the Billing Delay Period
When a subscription service is canceled during the billing delay period with the Bill Now option specified, the subscriber's account is billed immediately for all current charges that includes charges from the current billing cycle and the previous billing cycle.
Delayed events recorded after the cancellation date are billed on the regularly scheduled billing date.
In Figure 14-17, the subscription service is canceled during the billing delay period on February 5. Bill B1' includes all current charges from January 1 to February 5 for both billing cycle B1 and billing cycle B2. Delayed events for billing cycle B1 recorded after February 5 are billed on February 10. Events generated for billing cycle B2 after February 5 are billed on March 10.
About Billing a Subscription Service after It Is Transferred to Another Subscriber
A subscription service can be transferred at any time during the billing cycle.
At the time of billing, any cycle fees associated with the service are prorated. The old subscriber's account is billed for the prorated amount until the transfer date. The new subscriber's account is billed for the remainder of the cycle. See "How Cycle Fees Are Prorated When a Subscription Service Is Transferred".
The old subscriber's account is billed for usage charges associated with the service that was incurred during the time the service was owned by the old subscriber's account, including delayed events that occurred prior to the transfer of the service. Events generated after the transfer are billed to the new subscriber's account.
Any remaining non-currency grants, such as free minutes, are transferred to the new subscriber's account. See "About Transferring Non-Currency Resources during Subscription Service Transfer".
Managing Subscription Services in Your Custom Application
For more information on subscription services, see "About Subscription Services".
Creating a Subscription Service Group
You can create subscription service groups when creating price plans or when registering customers.
Creating Subscription Services in a Price Plan
To create a subscription service in a price plan, use the PCM_OP_PRICE_SET_PRICE_LIST opcode and set the following subscription group fields in the input flist:
-
Add a PIN_FLD_SERVICES array for each service in the subscription.
Important:
The service arrays must start with array element 1. -
In each service array, set the PIN_FLD_SUBSCRIPTION_INDEX field to specify the index of the array that contains the subscription service.
Note:
When you add standalone services to a price plan, you set the PIN_FLD_SUBSCRIPTION_INDEX field to 0. This value indicates that the service is not a member of a subscription group. -
Add a PIN_FLD_BAL_INFO array to create a balance group for the subscription service. Optionally, specify any subscription-level credit limits or thresholds.
-
Add an additional PIN_FLD_BAL_INFO array for each member service that should have its own balance group, and set credit limits and thresholds, if any. A member service that does not have a balance group uses the subscription service's balance group.
-
In each PIN_FLD_SERVICES array, set the PIN_FLD_BAL_INFO_INDEX field to specify the index of the array that contains the balance group for that service.
PCM_OP_PRICE_SET_PRICE_LIST validates that:
-
The PIN_FLD_SUBSCRIPTION_INDEX field specifies an existing element ID of the PIN_FLD_SERVICES array. If the element ID does not exist, the PIN_PRICE_ERR_INVALID_SUBSCRIPTION_INDEX error is returned.
-
Member services from different subscription groups do not share the same balance group. If the PIN_FLD_BAL_INFO_INDEX field for two services that belong to different subscription groups specify the same balance group index array element, the PIN_PRICE_ERR_INVALID_BAL_INFO_INDEX error is returned.
The following example shows an flist with the fields that pertain to subscription service groups. The plan includes three services in a subscription group, one subscription service, and two member services. All services use the subscription service's balance group:
. . .
0 PIN_FLD_BAL_INFO ARRAY [1] allocated 2, used 2 //the subscription service's balance group
1 PIN_FLD_NAME STRING [0] subscription
1 PIN_FLD_LIMIT ARRAY [840] allocated 3, used 3
2 PIN_FLD_CREDIT_FLOOR DECIMAL [0] 0.0
2 PIN_FLD_CREDIT_LIMIT DECIMAL [0] 500.0
2 PIN_FLD_CREDIT_THRESHOLDS INT [0] 0
0 PIN_FLD_SERVICES ARRAY [1] allocated 3, used 3 // Array of the subscription service
1 PIN_FLD_SERVICE_OBJ POID [0] 0.0.0.1 /service/telco/gsm -1 0 //The subscription service object.
1 PIN_FLD_SUBSCRIPTION_INDEX INT [0] 1 //The index of the subscription service. Note that it references itself.
1 PIN_FLD_BAL_INFO_INDEX INT [0] 1 //The index of the subscription service's balance group array.
. . .
0 PIN_FLD_SERVICES ARRAY [2] allocated 3, used 3
1 PIN_FLD_SERVICE_OBJ POID [0] 0.0.0.1 /service/telco/gsm/telephony -1 0 // Member service.
1 PIN_FLD_SUBSCRIPTION_INDEX INT [0] 1
1 PIN_FLD_BAL_INFO_INDEX INT [0] 1
. . .
0 PIN_FLD_SERVICES ARRAY [3] allocated 3, used 3
1 PIN_FLD_SERVICE_OBJ POID [0] 0.0.0.1 /service/telco/gsm/sms -1 0 // Member service.
2 PIN_FLD_SUBSCRIPTION_INDEX INT [0] 1
3 PIN_FLD_BAL_INFO_INDEX INT [0] 1
. . .
Creating Subscription Services When Registering Customers
The /service objects for subscription services are created when plans are purchased. This can occur at two times:
-
When registering customers, use the PCM_OP_CUST_COMMIT_CUSTOMER opcode.
-
When customers purchase a plan for an existing account, use the PCM_OP_CUST_MODIFY_CUSTOMER opcode.
These opcodes call other opcodes to set up a customer's services and create the /service objects.
These opcodes set the subscription group relationship fields in the /service objects that they create. Services are created in the following order: account-level services, the subscription service, and member services in the subscription group.
To create a subscription service group, set the following fields in the input flist of PCM_OP_CUST_CREATE_CUSTOMER and PCM_OP_CUST_MODIFY_CUSTOMER:
-
Add a PIN_FLD_SERVICES array for each service in the subscription group.
Important:
The service arrays must start with array element 1. -
In each service array, set the PIN_FLD_SUBSCRIPTION_OBJ field to specify the Portal object ID (POID) of the subscription service. If the service being created is the subscription service, this field and the PIN_FLD_POID field specify the same value.
-
Add a PIN_FLD_BAL_INFO array to create a balance group for the subscription service. Optionally, specify any subscription-level credit limit or threshold.
-
Add an additional PIN_FLD_BAL_INFO array for each member service that should have its own balance group, and optionally set the credit limit and threshold. A member service that does not have a balance group uses the subscription service's balance group.
-
In each PIN_FLD_SERVICES array, set the PIN_FLD_BAL_INFO_INDEX field to specify the index of the array that contains the balance group for that service.
Configuring ERAs for a Subscription Service
After setting up system-wide ERAs, you assign an ERA to a customer's service and specify customer-specific information; for example, the customer's birthday for a birthday discount ERA.
Service-level ERAs are stored in /profile/serv_extrating objects. These objects are typically associated with customer accounts at two times:
-
When registering customers, use PCM_OP_CUST_COMMIT_CUSTOMER.
-
When customers purchase a plan for an existing account, use PCM_OP_CUST_MODIFY_CUSTOMER.
These opcodes call other opcodes to create or modify the /profile objects.
To configure a subscription-level ERA for a specific customer, add a PIN_FLD_PROFILES array to the subscription service's PIN_FLD_SERVICES array on the input flist of the *_CUSTOMER opcodes. In the profiles array, set the POID of the /profile/serv_extrating object owned by the service.
To configure the ERA with customer-specific data, write custom code that sets the customer's information in the PIN_FLD_DATA array of the /profile/serv_extrating object.
To validate the customer's profile information, you must modify the PCM_OP_CUST_POL_VALID_PROFILE policy opcode. See the opcode documentation for more information.
You can also use the Customer profile opcodes to create and modify /profile objects directly. See "Managing and Customizing Profiles".
Associating a Device with a Subscription Service
Customers use devices, such as a wireless handset, to access their subscription services. The device information, such as device ID, manufacturer, and associated account and service, are stored in a /device object. You associate /device objects with subscription /service objects when you register customers or add plans to customer accounts:
-
When registering customers, use PCM_OP_CUST_COMMIT_CUSTOMER.
-
When customers purchase a plan for an existing account, use PCM_OP_CUST_MODIFY_CUSTOMER.
These opcodes call other opcodes to create or modify the /device objects.
To create a /device object and associate it with a subscription service, set the following fields in the subscription service's PIN_FLD_SERVICES array on the input flist of the customer opcodes:
-
Specify the POID of the /device object in the PIN_FLD_DEVICE_OBJ field of the PIN_FLD_DEVICES array.
-
Specify the number associated with the device (such as the IMSI or MSISDN) in the PIN_FLD_ALIAS_LIST array.
You can also use the PCM_OP_CUST_UPDATE_SERVICES opcode to modify /device objects. This opcode calls the PCM_OP_DEVICE_ASSOCIATE opcode to associate or disassociate a device with a service.
To directly create or modify /device objects, use the PCM_OP_DEVICE* opcodes.
Adding a Service to an Existing Subscription Service Group
You add a service to a subscription group in the same way that you create a service in a subscription group. Use PCM_OP_CUST_MODIFY_CUSTOMER and set the service information on the input flist. See "Creating a Subscription Service Group".
Canceling a Subscription Service
For general information about subscription service cancellation, see "About Canceling a Subscription Service".
You can use Customer Center to cancel a subscription service.
For customizations, you can use the PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_CANCEL_SUBSCRIPTION opcode directly. This opcode is used to cancel a subscription service and all the member services and to bill the service upon cancellation.
Specify the following information in the PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_CANCEL_SUBSCRIPTION input flist:
-
Set PIN_FLD_POID to the POID of the account object that owns the subscription service.
-
Set PIN_FLD_SUBSCRIPTION_OBJ to the POID of the subscription service to be canceled.
-
Set the input flag PIN_FLD_FLAGS to PIN_BILL_FLG_BILL_NOW, to bill the account immediately upon service cancellation.
Note:
If the input flag is not set, the account is billed for the service on the regularly scheduled billing date.
PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_CANCEL_SUBSCRIPTION performs the following tasks:
-
If the PIN_BILL_FLG_BILL_NOW flag is passed in the input flist, calls the PCM_OP_BILL_MAKE_BILL_NOW opcode for each bill unit (/billinfo object) associated with the subscription service.
Note:
Typically, all the member services are associated with the subscription service's bill unit. However, it is possible for member services to be associated with different bill units. -
Calls the PCM_OP_CUST_UPDATE_SERVICES opcode to update the status of the subscription service and member services. PCM_OP_CUST_UPDATE_SERVICES does the following:
-
Updates the status of the subscription service and all of its member services to closed.
-
Updates the status of all discounts and products associated with the subscription service and member services to canceled.
-
Deletes any resource sharing groups owned by the subscription service and the member services, and updates the ordered balance group (/ordered_balgrp object) of the group members.
-
Removes the subscription service and member services from any resource sharing group of which they are members.
-
-
Generates the /event/audit/subscription/cancel audit event to record the service cancellation.
If the PIN_BILL_FLG_BILL_NOW flag is specified in the input flist, the service is billed upon cancellation. Otherwise, the service is billed during the regularly scheduled billing time.
If successful, PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_CANCEL_SUBSCRIPTION returns the following:
-
The POID of the subscription service that was canceled.
-
The POID of the /event/audit/subscription/cancel audit event that was created to record the cancellation.
Transferring Subscription Services Between Accounts in the Same Schema
For general information about subscription service transfer, see "About Transferring a Subscription Service to Another Subscriber".
To transfer a subscription service to another subscriber's account, use PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION.
Specify the following information in the PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION opcode input flist:
-
The POID of the account object from which the service is transferred.
-
The POID of the account object to which the service is transferred.
-
The POID of the subscription service to transfer.
-
The POID of a bill unit (/billinfo object) and the POID of a /payinfo object (/payinfo):
-
If the service is to be associated with an existing bill unit in the new subscriber's account, specify the POIDs of any existing bill unit and /payinfo objects.
-
If the service is to be associated with a new bill unit created for the service only, specify the POIDs of the new bill unit and payinfo objects.
-
-
The POID of an existing payment object (/payinfo) for the new subscriber or the POID of a new payment object created for the service only.
To transfer the services, PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION does the following for each member service:
-
Sets the account object POID to the new subscriber's account object POID.
-
Creates a transfer list array element and adds it to the service objects.
-
Creates the audit event /event/audit/subscription/transfer to record the service transfer.
To transfer the devices, PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION does the following for each member service:
-
Finds all the devices owned by the service and sets each device's account object POID to the new subscriber's account object POID.
-
Creates the /event/audit/subscription/transfer audit event to record the device transfer.
To transfer the products and discounts, PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION cancels the products and discounts owned by the old subscriber's account and creates copies for the new subscriber's account. To do this, it does the following for each member service:
-
Finds all products and discounts associated with the service owned by the existing subscriber's account.
-
For each product instance:
-
Calls the PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_SET_PRODINFO opcode to set the purchase, cycle, and usage end dates to the transfer date for the old subscriber's account and to apply cycle forward fees.
-
Creates another instance of the product and assigns it to the new subscriber's account with purchase, cycle, and usage start dates set to the transfer date.
Note:
For customized products, the opcode does not separately set end dates in the old account and start dates in the new account. The start and end dates of customized products are adjusted automatically when the dates for their base products are set. -
Creates the /event/billing/product/action/purchase event to record the product instance transfer.
Note:
If the product is sponsored, and the new subscriber's account is not a member of the same sponsor group as the old subscriber's account, the POID of the sponsor group account object is deleted from the product instance.
-
-
For each discount instance:
-
Calls the PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_SET_DISCOUNTINFO opcode to set the purchase, cycle, and usage end dates to the transfer date for the existing subscriber's account and to apply cycle forward fees.
-
Creates another instance of the discount and assigns it to the new subscriber's account with purchase, cycle, and usage start dates set to the transfer date.
-
Creates the /event/billing/discount/action/purchase event to record the discount instance transfer.
-
To transfer the subscription service billing information, PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION associates the service balance groups with an existing bill unit in the new subscriber's account or with a new bill unit created for the service. To do this, it does the following:
-
If a /billinfo object is specified in the input flist, it sets the PIN_FLD_BILLINFO_OBJ field in the service's /balance_group object to reference the /billinfo object.
-
If a /payinfo object is specified in the input flist, it sets the PIN_FLD_PAYINFO_OBJ field in the service's /balance_group object to reference the /payinfo object.
-
If a /billinfo object is not specified, it calls the PCM_OP_CUST_SET_BILLINFO opcode to create a new /billinfo object and sets the PIN_FLD_BILLINFO_OBJ field in the service's /balance_group object to the newly created /billinfo object.
-
If a /payinfo object is not specified, it calls the PCM_OP_CUST_SET_PAYINFO opcode to create a new /payinfo object and sets the PIN_FLD_PAYINFO_OBJ field in the service's /balance_group object to the newly created /payinfo object.
To transfer the subscription service's resource sub-balances, PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION does the following:
-
Modifies the service's /balance_group object to reference the /billinfo object in the subscriber's account.
-
Sets the sub-balance validity based on the sub_bal_validity parameter in /config/business_params.
-
Creates the /event/audit/subscription/transfer audit event to record the balance group transfer.
To transfer pending scheduled actions for a specific service associated with an existing subscription when transferring the subscription to a different account, PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION calls the PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_POL_POST_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION policy opcode.
The TransferScheduledActions business parameter must be enabled in order for PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION to call the PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_POL_POST_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION policy opcode. See "Enabling Transfer of Pending Scheduled Actions during Subscription Transfers".
When a subscription service is transferred to a new subscriber's account, it is deleted from any group of which it is a member. PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION does the following for each member service:
-
Finds the charge sharing or discount sharing groups that the service is a member of and deletes the service from the group.
-
Deletes any ordered balance group associated with the service.
When a subscription service is transferred to a new subscriber's account, any group that it owns is deleted. PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION finds the charge sharing group or discount sharing group that it owns and deletes the group for each member service.
Enabling Transfer of Pending Scheduled Actions during Subscription Transfers
To enable the transfer of pending scheduled actions during subscription transfers, enable the TransferScheduledActions business parameter by doing the following:
-
Go to the BRM_Home/sys/data/config directory.
-
Run the following command, which creates an editable XML file from the subscription instance of the /config/business_params object:
pin_bus_params -r BusParamsSubscription bus_params_subscription.xmlThis command creates the XML file named bus_params_subscription.xml.out in your working directory. To place this file in a different directory, specify the path as part of the file name.
-
Open the bus_params_subscription.xml.out file.
-
Search for the following line:
<TransferScheduledActions>disabled</TransferScheduledActions> -
Change disabled to enabled.
-
Save the file as bus_params_subscription.xml.
-
Go to the BRM_Home/sys/data/config directory, which includes support files used by the pin_bus_params utility.
-
Run the following command, which loads this change into the /config/business_params object:
pin_bus_params PathToWorkingDirectory/bus_params_subscription.xml
where PathToWorkingDirectory is the directory in which bus_params_subscription.xml resides.
Caution:
BRM uses the XML in this file to overwrite the existing Subscription instance of the /config/business_params object. If you delete or modify any other parameters in this file, your changes affect the associated aspects of the BRM subscription configuration.Note:
To run this command from a different directory, see "pin_bus_params" in BRM Developer's Guide. -
Read the object with the testnap utility or Object Browser to verify that all fields are correct.
See "Using testnap" in BRM Developer's Guide for general instructions on using the testnap utility. See "Reading Objects by Using Object Browser" in BRM Developer's Guide for information on how to use Object Browser.
-
Stop and restart the CM. For more information, see "Starting and Stopping the BRM System" in BRM System Administrator's Guide.
-
(Multischema systems only) Run the pin_multidb script with the -R CONFIG parameter. For more information, see "pin_multidb" in BRM System Administrator's Guide.
Transferring Subscription Services Between Accounts in Multiple Schemas
To transfer a subscription service between accounts stored in multiple schemas, you enable the RecreateDuringSubscriptionTransfer business parameter.
Note:
When the RecreateDuringSubscriptionTransfer business parameter is enabled, PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION recreates all the objects in the schema to which the subscription services are transferred.Enabling Transfer of Subscription Services Between Accounts in Multiple Schemas
To enable transfer of subscription services of an account in a schema to another account in a different schema, enable the RecreateDuringSubscriptionTransfer business parameter in the following way:
-
Go to the BRM_Home/sys/data/config directory.
-
Run the following command, which creates an editable XML file from the subscription instance of the /config/business_params object:
pin_bus_params -r BusParamsSubscription bus_params_subscription.xmlThis command creates the XML file named bus_params_subscription.xml.out in your working directory. To place this file in a different directory, specify the path as part of the file name.
-
Open the bus_params_subscription.xml.out file.
-
Search for the following line:
<RecreateDuringSubscriptionTransfer>disabled</RecreateDuringSubscriptionTransfer> -
Change disabled to enabled.
-
Save the file as bus_params_subscription.xml.
-
Go to the BRM_Home/sys/data/config directory, which includes support files used by the pin_bus_params utility.
-
Run the following command, which loads this change into the /config/business_params object:
pin_bus_params PathToWorkingDirectory/bus_params_subscription.xml
where PathToWorkingDirectory is the directory in which bus_params_subscription.xml resides.
Caution:
BRM uses the XML in this file to overwrite the existing Subscription instance of the /config/business_params object. If you delete or modify any other parameters in this file, your changes affect the associated aspects of the BRM subscription configuration.Note:
To run this command from a different directory, see "pin_bus_params" in BRM Developer's Guide. -
Read the object with the testnap utility or Object Browser to verify that all fields are correct.
See "Using testnap" in BRM Developer's Guide for general instructions on using the testnap utility. See "Reading Objects by Using Object Browser" in BRM Developer's Guide for information on how to use Object Browser.
-
Stop and restart the CM. For more information, see "Starting and Stopping the BRM System" in BRM System Administrator's Guide.
-
(Multischema systems only) Run the pin_multidb script with the -R CONFIG parameter. For more information, see "pin_multidb" in BRM System Administrator's Guide.
To transfer a subscription service, PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION does the following:
-
Finds all the related services. If the service to be transferred is a subscription service, this opcode finds all the member services and groups.
-
Updates the status of the services to CANCELLED and recalculates charges for all service-level purchased offerings that use PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_SET_PRODINFO or PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_SET_DISCOUNTINFO.
-
Creates a flist of all the services to be transferred and saves login information, profiles, and devices.
-
Adds login information to the source services by pre pending the login details with the service POID and generates the /event/customer/login event.
-
Calls PCM_OP_CUST_MODIFY_CUSTOMER to create all new service instances in the account in the target schema.
-
Creates the /billinfo, /payinfo, and /balance_group objects if the source objects do not already have these.
Note:
The /billinfo object passed in the input must belong to the account in the target schema. -
Fetches the encrypted password from the service in the source schema and sets it in the service in the target schema and generates the /event/customer/status and /event/customer/login events.
-
If called from PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_SERVICE_BALGRP_TRANSFER, saves the /service, /balance_group, and /billinfo objects in the NAMED_TRANS_FLIST array.
-
Updates SUBSCRIPTION_OBJ of the newly created instance of the member services in the target schema with the POID of the parent service created in the target schema.
-
Updates the /device object with the service and the account in the target schema.
Note:
Devices associated with the services to be transferred must not be associated with any other services that are not transferred. -
Recreates the /profile objects in the target schema using CREATE_OBJ that has effective_t set to the transfer time.
Note:
To cancel the source service instances, the opcode deletes the /ordered_balgrp and /group/sharing/* relationships and saves the audit copies on the source service instances for processing late CDRs. Sharing group relationships are terminated on the transfer date and the new service instances will not participate in any sharing relationships. -
Calls PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_SHARING_GROUP_DELETE to delete all sharing groups in which the service is a parent or a member.
-
Creates the /purchased_discount and /purchased_product objects and CYCLE_FORWARD events. For cycle arrears events, calls PRO_FORCED in CYCLE_FEE_FLAGS.
-
Regenerates a package ID for the offerings created in the target schema.
-
Calls PCM_OP_CUST_UPDATE_SERVICES to close the service on the source schema.
-
Sets the status flag of the source parent service to PIN_STATUS_FLAG_DUE_TO_SERVICE_TRANSFER and sets the status to Closed.
-
Sets the status flag of the source member services with PIN_STATUS_FLAG_DUE_TO_SUBSCRIPTION_SERVICE and sets the status to Closed.
-
Generates the /event/customer/status event.
-
Creates the /event/audit/subscription/transfer audit event to record the service transfer. The /event/audit/subscription/transfer event contains PIN_FLD_TO_SERVICE_OBJ, PIN_FLD_TO_BAL_GRP_OBJ, and PIN_FLD_TO_PROFILE_OBJ.
-
Calls the PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_POL_POST_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION policy opcode if the TransferScheduledActions business parameter is enabled.
If the source and target balance groups of the services transferred are in different schemas, PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_SERVICE_BALGRP_TRANSFER does the following:
-
Calls PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION, which finds all the services and their new service references and uses the references to purchase deals on the services in PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_SERVICE_BALGRP_TRANSFER.
Note:
For PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_SERVICE_BALGRP_TRANSFER to call PCM_OP_SUBSCRIPTION_TRANSFER_SUBSCRIPTION:-
Either PIN_FLD_FROM_BAL_GRP_OBJ or the /service object must be present in the input flist.
-
Either the /billinfo object or the /billinfo array must be present in the input flist.
-
-
Creates the /event/audit/service_balgrp_transfer audit event to record the balance group transfer. The /event/audit/service_balgrp_transfer audit event contains PIN_FLD_TO_SERVICE_OBJ.