| Oracle® Identity Manager Connector Guide for SAP User Management Release 9.1.2 E11212-14 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle® Identity Manager Connector Guide for SAP User Management Release 9.1.2 E11212-14 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
Oracle Identity Manager automates access rights management, security, and provisioning of IT resources. Oracle Identity Manager connectors are used to integrate Oracle Identity Manager with external, identity-aware applications. This guide discusses the connector that enables you to use SAP R/3 and SAP CUA systems as managed (target) resources of Oracle Identity Manager.
In the account management (target resource) mode of the connector, data about users created or modified directly on the target system can be reconciled into Oracle Identity Manager. This data is used to provision (allocate) new resources or update resources already assigned to OIM Users. In addition, you can use Oracle Identity Manager to provision or update SAP R/3 or SAP CUA resources assigned to OIM Users. These provisioning operations performed on Oracle Identity Manager translate into the creation of or updates to target system accounts.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Section 1.3, "Connector Architecture and Supported Deployment Configurations"
Section 1.5, "Lookup Definitions Used During Connector Operations"
Section 1.8, "Roadmap for Deploying and Using the Connector"
Table 1-1 lists certified components for the connector.
Table 1-1 Certified Components
| Component | Requirement |
|---|---|
|
You can use one of the following releases of Oracle Identity Manager:
The connector does not support Oracle Identity Manager running on Oracle Application Server. For detailed information about certified components of Oracle Identity Manager, see the certification matrix on Oracle Technology Network at
|
|
|
JDK |
The JDK requirement is as follows: Note: JRockit is not supported because it is incompatible with the SAP JCo libraries.
|
|
The target system can be any one of the following:
Note: From version 6.40 onward, SAP WAS is also known as "SAP NetWeaver." In general:
|
|
|
If you want to configure and use the SoD feature of Oracle Identity Manager with this target system, then install the version of SAP GRC that is supported by Oracle Identity Manager: SAP GRC versions 5.2 SP4 or later and 5.3 SP5 or later |
|
|
If you want to configure and use the Compliant User Provisioning feature of the connector, then you must also configure the Compliant User Provisioning module included in SAP GRC versions 5.2 SP4 or later and 5.3 SP5 or later. |
|
|
The connector works with SAP JCo 3.0. The following SAP custom code files are required:
Note: There are different distribution packages (JCo) 3.0 available for various supported platforms and processors. See, JCo documentation for more information about using JCo 3.0 packages as per your environment. |
The connector supports the following languages:
Arabic
Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Traditional)
Danish
English
French
German
Italian
Japanese
Korean
Portuguese (Brazilian)
Spanish
|
See Also: For information about supported special characters supported by Oracle Identity Manager, see one of the following guides:
|
In its basic mode of operation, the connector sets up Oracle Identity Manager as the front end for sending account creation or modification provisioning requests to either SAP R/3 or SAP CUA. While deploying the connector, you can opt for enabling either direct provisioning or request-based provisioning in Oracle Identity Manager. In direct provisioning, only Oracle Identity Manager administrators can create and manage target system resources. In request-based provisioning, users can raise requests for creating and managing their accounts. Other users designated as administrators or approvers act upon these requests.
An access policy change is the third form of provisioning operation supported by the connector. If a change in an access policy requires corresponding changes in resources provisioned to a set of users, then the required provisioning operations on the target system are automatically initiated from Oracle Identity Manager.
Account data added or modified through provisioning operations performed directly on the target system can be reconciled into Oracle Identity Manager.
Figure 1-1 shows the connector integrating SAP R/3 with Oracle Identity Manager.
Figure 1-1 Connector Integrating SAP R/3 with Oracle Identity Manager
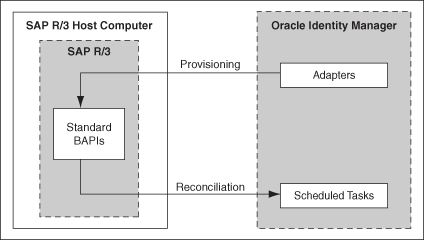
Figure 1-2 shows the connector integrating SAP CUA with Oracle Identity Manager.
Figure 1-2 Connector Integrating SAP CUA with Oracle Identity Manager
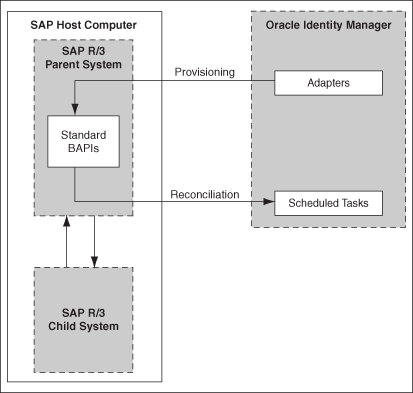
As shown in these figures, either SAP R/3 or SAP CUA is configured as a target resource of Oracle Identity Manager. Through provisioning operations performed on Oracle Identity Manager, accounts are created and updated on the target system for OIM Users. Through reconciliation, account data that is created and updated directly on the target system is fetched into Oracle Identity Manager and stored against the corresponding OIM Users.
|
Note: The connector does not support direct administration of accounts on child systems in SAP CUA. As shown in Figure 1-2, all connector operations are performed between Oracle Identity Manager and the SAP R/3 parent system. When required, user data changes resulting from these connector operations are propagated from the parent system to the child system. |
During provisioning, adapters carry provisioning data submitted through the process form to the target system. Standard BAPIs on the target system accept provisioning data from the adapters, carry out the required operation on the target system, and return the response from the target system to the adapters. The adapters return the response to Oracle Identity Manager.
During reconciliation, a scheduled task establishes a connection with the target system and sends reconciliation criteria to the BAPIs. The BAPIs extract user records that match the reconciliation criteria and hand them over to the scheduled task, which brings the records to Oracle Identity Manager.
Each record fetched from the target system is compared with SAP UM resources that are already provisioned to OIM Users. If a match is found, then the update made to the SAP record from the target system is copied to the SAP UM resource in Oracle Identity Manager. If no match is found, then the user ID of the record is compared with the user ID of each OIM User. If a match is found, then data in the target system record is used to provision an SAP UM resource to the OIM User.
Besides enabling direct integration with the target system, the connector can also be used to act as an interface with the Risk Analysis and Remediation and Compliant User Provisioning modules of SAP GRC. The target system (SAP R/3 or SAP CUA) and these two modules of SAP GRC together provide various deployment configurations. The following sections provide information about the supported deployment configurations of the connector:
Section 1.3.3, "User Management with Compliant User Provisioning"
Section 1.3.4, "User Management with Both SoD and Compliant User Provisioning"
Section 1.3.5, "Guidelines on Using a Deployment Configuration"
Section 1.3.6, "Considerations to Be Addressed When You Enable Compliant User Provisioning"
When you configure the connector for basic user management, the connector accepts provisioning data submitted through Oracle Identity Manager and propagates this data to the target system. For example, when a Create User provisioning operation is performed on Oracle Identity Manager, the outcome is the creation of an account on the target system.
Account data added or modified through provisioning operations performed directly on the target system can be reconciled into Oracle Identity Manager.
Figure 1-1 and Figure 1-2 show the architecture of the connector in this deployment configuration.
The steps performed during a provisioning operation can be summarized as follows:
The provisioning operation is initiated through direct provisioning, request-based provisioning, or an access policy change.
Provisioning data is sent to the target system.
The required change is made on the target system, and the outcome of the operation is sent back to and stored in Oracle Identity Manager.
You might have the Risk Analysis and Remediation module of SAP GRC configured to implement segregation of duties (SoD) in your SAP operating environment. In this scenario, the connector can be used as the interface between Oracle Identity Manager and the SoD module. You can configure the connector so that provisioning requests sent from Oracle Identity Manager are first run through the SoD validation process of SAP GRC Risk Analysis and Remediation. Provisioning requests that clear this validation process are then propagated from Oracle Identity Manager to the target system.
Reconciliation does not involve SAP GRC Risk Analysis and Remediation. Account data added or modified through provisioning operations performed directly on the target system can be reconciled into Oracle Identity Manager.
In this guide, the phrase configuring SoD is used to mean configuring the integration between Oracle Identity Manager and SAP GRC Risk Analysis and Remediation.
Figure 1-3 shows data flow in this mode of the connector.
Figure 1-3 Data Flow During the SoD Validation Process
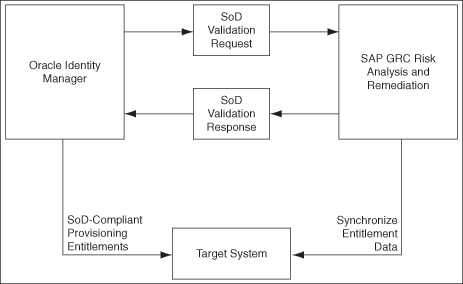
The steps performed during a provisioning operation can be summarized as follows:
|
See Also: The "Segregation of Duties (SoD) in Oracle Identity Manager" chapter in Oracle Identity Manager Tools Reference for detailed information about the provisioning process flow |
The provisioning operation is initiated through direct provisioning, request-based provisioning, or an access policy change.
The resource approval workflow of Oracle Identity Manager sends this request to the SoD engine (SAP GRC Risk Analysis and Remediation).
The SoD engine uses predefined rules to check if the entitlement assignment would lead to SoD violations. The outcome of this check is then sent back to Oracle Identity Manager.
If the request fails SoD validation, then the approval workflow can be configured to take remediation steps. If the request passes SoD validation and if the approver in Oracle Identity Manager approves the request, then the resource provisioning workflow is initiated.
This resource provisioning workflow can be configured to perform the SoD validation again. This is to ensure SoD compliance of the entitlement assignment immediately before the entitlement assignment is provisioned to the target system. You can also configure the SoD validation check in the resource provisioning workflow to be bypassed if this validation has been passed in the resource approval workflow.
The resource provisioning workflow performs the required change on the target system, and the outcome of the operation is sent back to and stored in Oracle Identity Manager.
Compliant User Provisioning (CUP) is a module in the SAP GRC suite. In an SAP environment, you can set up Compliant User Provisioning as the front end for receiving account creation and modification provisioning requests. In Compliant User Provisioning, workflows for processing these requests can be configured and users designated as approvers act upon these requests.
|
Note: In this guide, the phrase configuring Compliant User Provisioning has been used to mean configuring the integration between Oracle Identity Manager and SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning. |
In your operating environment, the Compliant User Provisioning module might be directly linked with the Risk Analysis and Remediation module. In other words, provisioning requests are first sent from Compliant User Provisioning to Risk Analysis and Remediation for SoD validation. Only requests that clear the validation process are implemented on the target system. In this scenario, it is recommended that you do not configure the SoD feature of the connector.
Reconciliation does not involve SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning. Scheduled tasks on Oracle Identity Manager fetch data from the target system to Oracle Identity Manager.
Figure 1-4 shows data flow in this mode of the connector.
Figure 1-4 Connector Integrating SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning with Oracle Identity Manager and the Target System
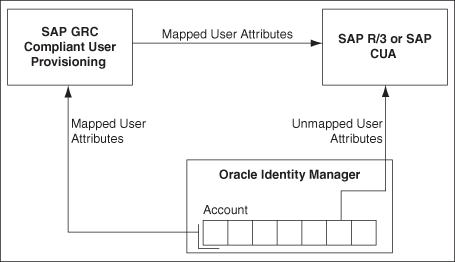
The following is the detailed sequence of steps performed during a provisioning operation:
The provisioning operation is initiated through direct provisioning, request-based provisioning, or an access policy change.
A BAPI is run on the target system to determine one of the following:
For a Create User operation, if the BAPI determines that the user exists on the target system, then an error message is displayed. If the user does not exist, then a request is created out of the provisioning data and sent to SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning.
For a Modify User operation, if the BAPI determines that the user does not exist on the target system, then an error message is displayed. If the user exists, then a request is created out of the provisioning data and sent to SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning.
The connector sends requests and receives responses through the following Web services of SAP GRC:
SAPGRC_AC_IDM_SUBMITREQUEST: This Web service is used to submit requests.
SAPGRC_AC_IDM_REQUESTSTATUS: This Web service is used to fetch request statuses.
SAPGRC_AC_IDM_AUDITTRAIL: This Web service is used to check if there are error messages in the SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning logs.
The process form holds fields for both basic user management and Compliant User Provisioning. However, for a Create User operation, only the Compliant User Provisioning fields (attributes) on the process form are used. Mappings for these fields are stored in the Lookup.SAP.CUP.ProvisionAttrMap and Lookup.SAP.CUP.ProvisionRoleAttrMap lookup definitions. If you specify values for any attribute that is not present in these lookup definitions, then the connector ignores those attributes during the Create User operation.
|
Note: SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning does not process passwords. Therefore, any value entered in the Password field is ignored during Create User provisioning operations.See Section 3.6, "Guidelines on Performing Provisioning" for information about setting passwords when you configure Compliant User Provisioning. |
For a Modify User operation, a request is created only for attributes whose mappings are present in these lookup definitions. If you specify values for attributes that are not present in these lookup definitions, then the connector directly sends them to the target system.
|
Note: In a Modify User operation, you can specify values for attributes that are mapped with SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning and attributes that are directly updated on the target system. |
When the request is created on SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning, data sent back by Compliant User Provisioning is stored in the following read-only fields in Oracle Identity Manager:
Request ID: This field holds the request ID that is generated on SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning. The request ID does not change during the lifetime of the request.
Request Status: This field holds the status of the request on SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning. You configure and run the SAP CUP Status Update Recon scheduled task to fetch the latest status of the request from the target system. Section 3.4.3.3, "SAP CUP Status Update Recon" describes this scheduled task.
CUP Requestor ID
CUP Requestor First Name
CUP Requestor Last Name
CUP Requestor Email
The request is passed through the workflow defined in SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning. The outcome is one of the following:
If Compliant User Provisioning clears the request, then the outcome is the creation or modification of a user's account on the target system (SAP R/3 or SAP CUA). The status of the request is set to Closed and a message is recorded in the Oracle Identity Manager logs.
If Compliant User Provisioning rejects the provisioning request, then the status of the request is set to Reject and a message is recorded in the Oracle Identity Manager logs.
If an error occurs during communication between Compliant User Provisioning and the target system, then the request remains in the Open state. A message stating that the operation has failed is recorded in the audit log associated with the request. An error message is displayed on the console.
You might have both SAP GRC Risk Analysis and Remediation and Compliant User Provisioning configured in your SAP operating environment. You should configure the connector features for both SoD and Compliant User Provisioning at the same time only if the Risk Analysis and Remediation and Compliant User Provisioning modules are discretely configured (that is, not linked) modules in your operating environment.
|
Note: If SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning is configured to send provisioning requests to SAP GRC Risk Analysis and Remediation for SoD validation, then you must not configure the SoD feature of the connector. |
When you integrate Oracle Identity Manager with your SAP operating environment, you might have one of the following requirements in mind:
Use Oracle Identity Manager as the provisioning source for account management on SAP resources.
Leverage workflows and access policies configured in SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning, with Oracle Identity Manager as the provisioning source for account management on SAP resources.
Use SAP GRC Risk Analysis and Remediation for SoD enforcement and SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning for user approval of provisioning requests sent through Oracle Identity Manager. Overall account management on SAP resources is performed through Oracle Identity Manager.
The following sections describe guidelines on the supported deployment configurations:
|
Note: There are no special guidelines for the Basic User Management configuration and the User Management with SoD configuration. |
User Management with SoD and Compliant User Provisioning
The following are deployment guidelines that you must apply for a scenario in which SAP GRC Risk Analysis and Remediation and SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning are enabled and discretely configured modules:
Configure both SoD and Compliant User Provisioning features of the connector.
On SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning, configure the no-stage approval for account creation. In other words, account creation requests must be auto-approved on Compliant User Provisioning.
If a role or profile is provisioned on Oracle Identity Manager but rejected on SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning, then the role or profile is revoked from Oracle Identity Manager at the end of the next user reconciliation run. Therefore, you can have approval workflows defined for role and profile provisioning requests on SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning.
Summary of the account management process:
Data from a provisioning operation on Oracle Identity Manager is first sent to the SAP GRC Risk Analysis and Remediation module for SoD validation.
After the SoD validation checks are cleared, the provisioning request is sent to SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning.
After the SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning workflow clears the request, the provisioning request is implemented on the target system.
Scheduled tasks run from Oracle Identity Manager reconcile the outcome of the operation from the target system into Oracle Identity Manager.
User Management with Compliant User Provisioning
The following are deployment guidelines that you must apply for a scenario in which SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning is configured and enabled in your SAP operating environment:
On SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning, configure the no-stage approval for account creation. In other words, account creation requests must be auto-approved on Compliant User Provisioning.
The scenario described earlier in this section explains this guideline.
Configure the Compliant User Provisioning feature of the connector.
Do not configure the SoD feature of the connector.
Summary of the account management process:
Data from a provisioning operation on Oracle Identity Manager is sent to SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning.
The workflow defined in SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning sends the request to the SAP GRC Risk Analysis and Remediation module for SoD validation.
After the SoD validation checks are cleared, the provisioning request is implemented on the target system.
Scheduled tasks run from Oracle Identity Manager reconcile the outcome of the operation from the target system into Oracle Identity Manager.
Keep in mind the following considerations when you enable the Compliant User Provisioning feature of the connector:
Multiple requests are generated from Oracle Identity Manager in response to some provisioning operations. For example, if you assign multiple roles to a user in a particular provisioning operation, then one request is created and sent to Compliant User Provisioning for each role.
For a particular account, Oracle Identity Manager keeps track of the latest request only. This means, for example, if more than one attribute of an account has been modified in separate provisioning operations, then Oracle Identity Manager keeps track of data related to the last operation only.
A Modify User operation can involve changes to multiple process form fields or child form fields. For each field that is modified, one request is created and sent to SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning. Only information about the last request sent to Compliant User Provisioning is stored in Oracle Identity Manager.
Only parent or child form requests can be submitted in a single operation. You cannot submit both parent and child form requests at the same time.
Enable linking of SAP HRMS and SAP R/3 or SAP CUA accounts only if a no-stage workflow has been defined for the Create User provisioning operations.
Section 1.4.9, "Linking of SAP HRMS and SAP R/3 or SAP CUA Accounts" describes the feature of the connector that stores the link between an SAP HRMS account created for an individual and the corresponding SAP R/3 or SAP CUA account created for the same individual. When you configure the Compliant User Provisioning feature, you should enable linking only if a no-stage approval has been defined for the Create User request type in SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning. A no-stage approval is one in which no approvers are involved. All requests sent through a no-stage approval are automatically approved.
The following are features of the connector:
Section 1.4.2, "Mapping Standard and Custom Attributes for Reconciliation and Provisioning"
Section 1.4.4, "Routing of Provisioning Requests Through SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning"
Section 1.4.9, "Linking of SAP HRMS and SAP R/3 or SAP CUA Accounts"
Section 1.4.10, "SNC Communication Between the Target System and Oracle Identity Manager"
Section 1.4.11, "Specifying Accounts to Be Excluded from Reconciliation and Provisioning Operations"
Section 1.4.12, "Configuring Password Changes for Newly Created Accounts"
Section 1.4.15, "Specifying the Use of a Logon Group on the Target System for Connector Operations"
Section 1.4.16, "Transformation and Validation of Account Data"
Section 1.4.18, "Support for Both Unicode and Non-Unicode Modes"
The connector can be used to integrate Oracle Identity Manager with either or both SAP R/3 and SAP CUA. From release 9.1.1 onward, this connector replaces release 9.1.0 of both the SAP User Management and SAP CUA connectors.
Most of the features of the connector are the same for both target systems. Where there are differences, these differences have been called out in this guide.
You can create mappings for attributes that are not included in the list of default attribute mappings. These attributes can be part of the standard set of attributes provided by the target system or custom attributes that you add on the target system.
See Chapter 4, "Extending the Functionality of the Connector" for more information.
The connector supports the SoD feature introduced in Oracle Identity Manager release 9.1.0.2. The following are the focal points of this software update:
The SoD Invocation Library (SIL) is bundled with Oracle Identity Manager. The SIL acts as a pluggable integration interface with any SoD engine.
The SAP User Management connector is preconfigured to work with SAP GRC as the SoD engine. To enable this, changes have been made in the approval and provisioning workflows of the connector.
|
Note: The default approval workflow and associated object form are configured for the SoD validation capabilities of SAP GRC. You can use them to develop your own approval workflows and object forms.In Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.1, object forms have been replaced by request datasets. A request dataset is an XML file that specifies information to be submitted by the requester during a provisioning operation. Predefined request datasets are shipped with this connector. The default approval workflow and associated request dataset are configured for the SoD validation capabilities of SAP GRC. You can use them to develop your own approval workflows and request datasets. See Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle Identity Manager for more information about request datasets. |
The SoD engine processes role and profile entitlement requests that are sent through the connector. This preventive simulation approach helps identify and correct potentially conflicting assignment of entitlements to a user, before the requested entitlements are granted to users.
|
See Also: Oracle Identity Manager Tools Reference for detailed information about the SoD feature Section 2.3.12, "Configuring SoD" in this guide |
You can configure the connector to work with SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning. See Section 1.3.3, "User Management with Compliant User Provisioning" for detailed information about this feature.
In full reconciliation, all records are fetched from the target system to Oracle Identity Manager. In incremental reconciliation, only records that are added or modified after the last reconciliation run are fetched into Oracle Identity Manager.
At the end of a reconciliation run, an attribute of the scheduled task holds the time stamp at which the reconciliation run began. If that attribute is set to 0, then full reconciliation is performed. If that attribute holds a non-zero value, then incremental reconciliation is performed.
During full reconciliation, a single reconciliation event is generated for a particular target system account. However, during incremental reconciliation, two reconciliation events are generated for each account:
The first reconciliation event contains all account data other than the Locked/Unlocked status.
The second reconciliation event contains the Locked/Unlocked status.
You can switch from incremental to full reconciliation at any time after you deploy the connector. See Section 3.1, "Performing Full Reconciliation" for more information.
To limit or filter the records that are fetched into Oracle Identity Manager during a reconciliation run, you can specify the subset of added or modified target system records that must be reconciled.
See Section 3.4.2, "Limited Reconciliation" for more information.
You can break down a reconciliation run into batches by specifying the number of records that must be included in each batch.
See the description of the Batch Size attribute in Section 3.4.3, "Reconciliation Scheduled Tasks" for more information.
Valid From and Valid Through are two user attributes on the target system. For a particular user in SAP, if the Valid Through date is less than the current date, then the account is in the Disabled state. Otherwise, the account is in the Enabled state. The same behavior is duplicated in Oracle Identity Manager through reconciliation. In addition, you can set the value of the Valid Through date to a current date or a date in the past through a provisioning operation.
|
Note: The Enabled or Disabled state of an account is not related to the Locked or Unlocked status of the account. |
An SAP HRMS account created for an individual can be linked with the SAP R/3 or SAP CUA account created for the same user. For a particular user, an attribute of SAP HRMS holds the user ID of the corresponding SAP R/3 or SAP CUA account.
You can duplicate this link in Oracle Identity Manager by using the following entries of the Lookup.SAP.UM.Configuration lookup definition:
Support HRMS 0105 Infotype Linking
Validate Personnel Number before Linking
Overwrite Link
See Section 2.3.3.1, "Linking of SAP HRMS and SAP R/3 or SAP CUA Accounts" for more information.
You can configure Secure Network Communication (SNC) to secure communication between Oracle Identity Manager and the target system.
See Section 2.3.13, "Configuring SNC to Secure Communication Between Oracle Identity Manager and the Target System" for more information.
You can specify a list of accounts that must be excluded from all reconciliation and provisioning operations. Accounts whose user IDs you specify in the exclusion list are not affected by reconciliation and provisioning operations.
See Section 2.3.8, "Setting Up the Lookup.SAP.UM.ExclusionList Lookup Definition" for more information.
When you log in to SAP by using a newly created account, you are prompted to change your password at first logon. For accounts created through Oracle Identity Manager, password management can be configured using one of the following approaches:
Configure the connector so that users with newly created accounts are prompted to change their passwords at first logon.
Configure the connector so that the password set while creating the account on Oracle Identity Manager is set as the new password on the target system. The user is not prompted to change the password at first logon.
This feature is configured using the Dummy password parameter of the IT resource and the Change Password entry of the Lookup.SAP.UM.Configuration lookup definition. In addition, the Password Disabled entry of this lookup definition allows you to specify whether or not the password must be optional during Create User provisioning operations.
The connector uses the SAP JCo for reconciliation and provisioning operations. The JCo trace level is a numeric specification of the level of trace data that must be logged when the SAP JCo is used. You can specify the trace level as a parameter of the IT resource.
See Table 2-12, "Parameters of the IT Resource" for more information.
A connection pool is a cache of objects that represent physical connections to the target system. Oracle Identity Manager connectors can use these connections to communicate with target systems. At run time, the application requests a connection from the pool. If a connection is available, then the connector uses it and then returns it to the pool. A connection returned to the pool can again be requested for and used by the connector for another operation. By enabling the reuse of connections, the connection pool helps reduce connection creation overheads like network latency, memory allocation, and authentication.
One connection pool is created for each IT resource. For example, if you have three IT resources for three installations of the target system, then three connection pools are created, one for each target system installation.
The configuration properties of the connection pool are part of the IT resource definition. Section 2.3.14, "Configuring the IT Resource" provides information about setting up the connection pool.
In SAP, a logon group is used as a load-sharing mechanism. When a user logs in to a logon group, the system internally routes the connection request to the logon group member with the least load. You can configure the connector to use a logon group for logging in to the target system for reconciliation and provisioning operations.
See Section 2.3.14.1, "Parameters for Enabling the Use of a Logon Group" for more information.
You can configure validation of account data that is brought into or sent from Oracle Identity Manager during reconciliation and provisioning. In addition, you can configure transformation of account data that is brought into Oracle Identity Manager during reconciliation. The following sections provide more information:
You can configure transformation of lookup field data that is brought into Oracle Identity Manager during lookup field synchronization. Section 4.11, "Configuring Transformation of Data During Lookup Field Synchronization" for more information.
An SAP application can be run in either Unicode or non-Unicode mode. The connector supports both modes.
Lookup definitions used during connector operations can be categorized as follows:
During a provisioning operation, you use a lookup field on the process form to specify a single value from a set of values. For example, you use the Date Format lookup field to select a date format from the list of supported date formats. When you deploy the connector, lookup definitions corresponding to the lookup fields on the target system are automatically created in Oracle Identity Manager. Lookup field synchronization involves copying additions or changes made to the target system lookup fields into the lookup definitions in Oracle Identity Manager.
|
Note: The target system allows you to use special characters in lookup fields. However, in Oracle Identity Manager, special characters are not supported in lookup definitions. |
The Lookup.SAP.UM.LookupMappings and Lookup.SAP.CUA.LookupMappings lookup definitions are used to map each lookup definition with the BAPI that is used to fetch values for the lookup definition from the target system. The Code Key column of these lookup definitions contains names of the lookup definitions that are synchronized with the target system. The Decode column contains the name and parameters of the corresponding BAPIs.
Table 1-2 lists the entries in these lookup definitions. The Decode column holds a list of the parameters required to fetch lookup field values from the target system.
Table 1-2 Entries in the Lookup.SAP.UM.LookupMappings and Lookup.SAP.CUA.LookupMappings Lookup Definitions
| Code Key | Decode |
|---|---|
|
BAPI_HELPVALUES_GET;GETDETAIL;ADDRESS;COMM_TYPE;COMM_TYPE;COMM_TEXT |
|
|
BAPI_HELPVALUES_GET;GETDETAIL;COMPANY;COMPANY;COMPANY;COMPANY;USCOMPANY_ADDR;SH |
|
|
BAPI_HELPVALUES_GET;GETDETAIL;UCLASSSYS;LIC_TYPE;USERTYP;UTYPTEXT;LANGU;I;EQ;EN |
|
|
BAPI_HELPVALUES_GET;GETDETAIL;DEFAULTS;DATFM;_LOW;_TEXT |
|
|
BAPI_HELPVALUES_GET;GETDETAIL;DEFAULTS;DCPFM;_LOW;_TEXT |
|
|
BAPI_HELPVALUES_GET;GETDETAIL;ADDRESS;LANGU_P;SPRAS;SPTXT |
|
|
BAPI_HELPVALUES_GET;GETDETAIL;PARAMETER;PARID;PARAMID;PARTEXT |
|
|
BAPI_HELPVALUES_GET;GETDETAIL;PROFILES;BAPIPROF;PROFN;PTEXT For SAP CUA: RFC_READ_TABLE;USRSYSPRFT;PROFN;PTEXT;SUBSYSTEM;USRSYSPRF;LANGU = 'EN' |
|
|
BAPI_HELPVALUES_GET;GETDETAIL;ACTIVITYGROUPS;AGR_NAME;AGR_NAME;TEXT;AGR_COLL;SH For SAP CUA: RFC_READ_TABLE;USRSYSACTT;AGR_NAME;TEXT;SUBSYSTEM;USRSYSACT;LANGU = 'EN' |
|
|
SYSTEMNAME For SAP CUA: RFC_READ_TABLE;USZBVLNDRC;RCVSYSTEM;RCVSYSTEM |
|
|
BAPI_HELPVALUES_GET;CHANGE;ADDRESS;TIME_ZONE;TZONE;DESCRIPT |
|
|
BAPI_HELPVALUES_GET;GETDETAIL;GROUPS;USERGROUP;USERGROUP;TEXT |
|
|
BAPI_HELPVALUES_GET;GETDETAIL;ADDRESS;TITLE_P;TITLE_MEDI;TITLE_MEDI;ADDR2_SH_TITLE;SH |
The following is the format of entries in each lookup definition listed in this table:
Code Key format: IT_RESOURCE_KEY~LOOKUP_FIELD_ID
|
Note: For multivalued attributes (roles and profiles), the format is as follows:
IT_RESOURCE_KEY~SYSTEM_NAME~LOOKUP_FIELD_ID
|
In this format:
IT_RESOURCE_KEY is the numeric code assigned to the IT resource in Oracle Identity Manager.
LOOKUP_FIELD_ID is the target system code assigned to the lookup field entry.
Sample value: 1~PRT
Decode format: IT_RESOURCE_NAME~LOOKUP_FIELD_ENTRY
In this format:
IT_RESOURCE_NAME is the name of the IT resource in Oracle Identity Manager.
LOOKUP_FIELD_ENTRY is the value or description of the lookup field entry on the target system.
Sample value: SAP IT~Printer
The SAP User Management Lookup Recon scheduled task is used to synchronize values of these lookup definitions with the target system. Section 3.2, "Scheduled Task for Lookup Field Synchronization" provides more information about this scheduled task.
While performing a provisioning operation on the Administrative and User Console, you select the IT resource for the target system on which you want to perform the operation. When you perform this action, the lookup definitions on the page are automatically populated with values corresponding to the IT resource (target system installation) that you select.
During lookup field synchronization, new entries are appended to the existing set of entries in the lookup definitions. You can switch from an SAP R/3 target to a SAP CUA target, or you can switch between multiple installations of the same target system. Because the IT resource key is part of each entry created in each lookup definition, only lookup field entries that are specific to the IT resource you select during a provisioning operation are displayed.
Table 1-3 describes the other lookup definitions that are created in Oracle Identity Manager when you deploy the connector. These lookup definitions are either prepopulated with values or values must be manually entered in them after the connector is deployed.
Table 1-3 Preconfigured Lookup Definitions
| Lookup Definition | Description of Values | Method to Specify Values for the Lookup Definition |
|---|---|---|
|
This lookup definition holds connector configuration entries that are used during reconciliation and provisioning. |
Some of the entries in this lookup definition are preconfigured. See Section 2.3.3, "Setting Up the Configuration Lookup Definition in Oracle Identity Manager" for information about the entries for which you can set values. |
|
|
This lookup definition holds connector configuration entries that are used during reconciliation and provisioning by the Compliant User Provisioning feature. Note: This lookup definition is created only after you configure the Compliant User Provisioning feature. |
Some of the entries in this lookup definition are preconfigured. See Section 2.3.11.7, "Setting Values in the Lookup.SAP.CUP.Configuration Lookup Definition" for information about the entries for which you can set values. |
|
|
This lookup definition stores values that are used internally by the connector. The connector development team can use this lookup definition to make minor configuration changes in the connector. |
You must not modify the entries in this lookup definition. |
|
|
This lookup definition stores values that are used internally by the Compliant User Provisioning feature of the connector. The connector development team can use this lookup definition to make minor configuration changes in the connector. Note: This lookup definition is created only after you configure the Compliant User Provisioning feature. |
You must not modify the entries in this lookup definition. |
|
|
This lookup definition holds user IDs of target system accounts for which you do not want to perform reconciliation and provisioning. |
You can enter user IDs in this lookup definition. See Section 2.3.8, "Setting Up the Lookup.SAP.UM.ExclusionList Lookup Definition" for more information. |
|
|
The IT resource is a set of the connection properties required to establish a connection with the target system. The entries listed in this lookup definition are mappings between: |
See Table 2-11 for a listing of the entries in this lookup definition. If you want to add more SAP JCo parameters for establishing a connection between Oracle Identity Manager and the target system installation, then see Section 2.3.14.4, "Mapping New Connection Properties" for information. |
|
|
Lookup.SAP.CUA.LookupMappings and Lookup.SAP.UM.LookupMappings |
These lookup definitions hold data required to synchronize other lookup definitions with the target system. |
These lookup definitions are preconfigured. You can add entries in this lookup definition, but you must not modify existing entries. See the earlier section for a listing of the entries in these lookup definitions. See Section 4.12, "Configuring Synchronization of New Lookup Definitions with the Target System" for more information about adding entries. |
|
This lookup definition is used to configure transformation of data during lookup field synchronization. |
See Section 4.11, "Configuring Transformation of Data During Lookup Field Synchronization" for more information about adding entries in this lookup definition. |
|
|
This lookup definition holds mappings between process form fields and single-valued target system attributes. |
This lookup definition is preconfigured. Table 1-8 lists the default entries in this lookup definition. You can add entries in this lookup definition if you want to map new target system attributes for provisioning. See Section 4.4, "Adding New Standard Attributes for Provisioning" for more information. |
|
|
This lookup definition holds mappings between process form fields and single-valued attributes on SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning. Note: This lookup definition is created only after you configure the Compliant User Provisioning feature. |
This lookup definition is preconfigured. Table 1-10 lists the default entries in this lookup definition. You can add entries in this lookup definition if you want to map new attributes for provisioning. See Section 4.5, "Adding New Standard SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning Attributes for Provisioning" for more information. |
|
|
This lookup definition holds mappings between process form fields and multivalued target system attributes. |
This lookup definition is preconfigured. Table 1-9 lists the default entries in this lookup definition. You can add entries in this lookup definition if you want to map new multivalued target system attributes for provisioning. See Section 4.6, "Adding New Standard Multivalued Attributes for Provisioning" for more information. |
|
|
This lookup definition holds mappings between process form fields and multivalued attributes on SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning. Note: This lookup definition is created only after you configure the Compliant User Provisioning feature. |
This lookup definition is preconfigured. Table 1-9 lists the default entries in this lookup definition. |
|
|
This lookup definition is used to map check box attributes of the target system with their values when selected and deselected. It is used during provisioning. |
By default, there are no entries in this lookup definition. You must add entries only if you want to add a check box attribute on the target system for provisioning. See Step 4 in Section 4.4, "Adding New Standard Attributes for Provisioning" for more information. |
|
|
This lookup definition is used to configure validation of attribute values entered on the process form during provisioning operations. |
You manually create entries in this lookup definition. See Section 4.9, "Configuring Validation of Data During Reconciliation and Provisioning" for more information. |
|
|
This lookup definition holds mappings between resource object fields and single-valued target system attributes. |
This lookup definition is preconfigured. Table 1-4 lists the default entries in this lookup definition. You can add entries in this lookup definition if you want to map new target system attributes for reconciliation. See Section 4.2, "Adding New Attributes for Reconciliation" for more information. |
|
|
This lookup definition holds mappings between resource object fields and multivalued target system attributes. |
This lookup definition is preconfigured. Table 1-5 lists the default entries in this lookup definition. You can add entries in this lookup definition if you want to map new target system attributes for reconciliation. See Section 4.3, "Adding New Standard and Custom Multivalued Attributes for Reconciliation" for more information. |
|
|
This lookup definition holds mappings between resource object fields and custom multivalued target system attributes. |
You can add entries in this lookup definition if you want to map custom target system attributes for reconciliation. See Section 4.3, "Adding New Standard and Custom Multivalued Attributes for Reconciliation" for more information. |
|
|
Code Key: Dummy role child form attribute name Decode: Corresponding actual role child form attribute name This lookup definition is used during SoD validation of entitlement requests. |
This lookup definition is preconfigured. Table 2-9 lists the entries in this lookup definition. |
|
|
This lookup definition maps check box attributes of the target system with their values when selected and deselected. It is used during reconciliation. |
By default, there are no entries in this lookup definition. You must add entries only if you want to add a check box attribute on the target system for reconciliation. See Step 7 in Section 4.2, "Adding New Attributes for Reconciliation" for more information. |
|
|
This lookup definition is used to configure transformation of attribute values that are fetched from the target system during user reconciliation. |
You manually create entries in this lookup definition. See Section 4.10, "Configuring Transformation of Data During User Reconciliation" for more information. |
|
|
This lookup definition is used to configure validation of attribute values that are fetched from the target system during reconciliation. |
You manually create entries in this lookup definition. See Section 4.9, "Configuring Validation of Data During Reconciliation and Provisioning" for more information. |
|
|
Code Key: Dummy profile child form attribute name Decode: Corresponding actual profile child form attribute name This lookup definition is used during SoD validation of entitlement requests. |
This lookup definition is preconfigured. Table 2-8 lists the entries in this lookup definition. |
|
|
This lookup definition holds configuration values that are used by the connector during SoD operations. |
See Section 2.3.12.2, "Specifying Values for SoD-Related Entries in the Lookup.SAP.UM.SoDConfiguration Lookup Definition" for information about specifying values for the entries in this lookup definition. |
|
|
This lookup definition holds details of custom attributes that you want to include for reconciliation. |
See Step 6 in Section 4.2, "Adding New Attributes for Reconciliation" for information about creating entries in this lookup definition. |
The SAP User Management User Recon scheduled task is used to initiate a reconciliation run. This scheduled task is discussed in Section 3.4.3, "Reconciliation Scheduled Tasks".
|
See Also: The "Reconciliation" section in Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Identity Manager for conceptual information about reconciliationOracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Identity Manager |
This section discusses the following topics:
The Lookup.SAP.UM.ReconAttrMap lookup definition maps resource object fields and target system attributes. The Code Key column stores the names of resource object fields. The format of the Decode column is as follows:
FIELD_TYPE;FIELD_NAME;STRUCTURE_NAME
In this format, FIELD_TYPE can be TEXT, LOOKUP, CHECKBOX, or DATE.
Table 1-4 lists entries in this lookup definition.
Table 1-4 Entries in the Lookup.SAP.UM.ReconAttrMap Lookup Definition
| Resource Object Field | Target System Attribute |
|---|---|
|
Accounting Number |
TEXT;ACCNT;LOGONDATA |
|
Alias |
TEXT;USERALIAS;ALIAS |
|
Building |
TEXT;BUILDING_P;ADDRESS |
|
Communication Type |
LOOKUP;COMM_TYPE;ADDRESS |
|
Company |
LOOKUP;COMPANY;COMPANY |
|
Contractual User Type |
LOOKUP;LIC_TYPE;UCLASS|UCLASSSYS |
|
Cost Center |
TEXT;KOSTL;DEFAULTS |
|
Date Format |
LOOKUP;DATFM;DEFAULTS |
|
Decimal Notation |
LOOKUP;DCPFM;DEFAULTS |
|
Department |
TEXT;DEPARTMENT;ADDRESS |
|
E Mail |
TEXT;E_MAIL;ADDRESS |
|
Fax Extension |
TEXT;FAX_EXTENS;ADDRESS |
|
Fax Number |
TEXT;FAX_NUMBER;ADDRESS |
|
First Name |
TEXT;FIRSTNAME;ADDRESS |
|
Floor |
TEXT;FLOOR_P;ADDRESS |
|
Function |
TEXT;FUNCTION;ADDRESS |
|
Lang Communication |
LOOKUP;LANGU_P;ADDRESS |
|
Last Name |
TEXT;LASTNAME;ADDRESS |
|
Logon Language |
LOOKUP;LANGU;DEFAULTS |
|
Room Number |
TEXT;ROOM_NO_P;ADDRESS |
|
Start Menu |
TEXT;START_MENU;DEFAULTS |
|
Telephone Extension |
TEXT;TEL1_EXT;ADDRESS |
|
Telephone Number |
TEXT;TEL1_NUMBR;ADDRESS |
|
Time Zone |
LOOKUP;TZONE;LOGONDATA |
|
Title |
LOOKUP;TITLE_P;ADDRESS |
|
User Group |
LOOKUP;CLASS;LOGONDATA |
|
User Type |
TEXT;USTYP;LOGONDATA |
|
Valid From |
DATE;GLTGV;LOGONDATA |
|
Valid Through |
DATE;GLTGB;LOGONDATA |
The Lookup.SAP.UM.ReconChildAttrMap lookup definition maps resource object fields and multivalued target system attributes. Table 1-5 lists entries in this lookup definition.
The format of Decode entries in this lookup definition is as follows:
FIELD_TYPE;FIELD_NAME;TABLE_NAME;OIM_CHILD_TABLE_NAME
In this format, FIELD_TYPE can be TEXT, LOOKUP, CHECKBOX, or DATE.
Table 1-5 Entries in the Lookup.SAP.UM.ReconChildAttrMap Lookup Definition
| Child Form Field | Target System Attribute |
|---|---|
|
End Date |
DATE;TO_DAT;ACTIVITYGROUPS;User Role |
|
Profile Name |
LOOKUP;PROFILE|BAPIPROF;PROFILES;User Profile |
|
Profile System Name |
LOOKUP;SUBSYSTEM;PROFILES;User Profile |
|
Role Name |
LOOKUP;AGR_NAME;ACTIVITYGROUPS;User Role |
|
Role System Name |
LOOKUP;SUBSYSTEM;ACTIVITYGROUPS;User Role |
|
Start Date |
DATE;FROM_DAT;ACTIVITYGROUPS;User Role |
|
See Also: Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Identity Manager for generic information about reconciliation matching and action rules |
The following sections provide information about the reconciliation rules for this connector:
The following is the process-matching rule:
Rule name: SAP UM Recon Rule
Rule element: User Login Equals User ID
In this rule element:
User Login is the User ID field of the OIM User form.
User ID is the user ID of the SAP account.
After you deploy the connector, you can view the reconciliation rule for reconciliation by performing the following steps:
|
Note: Perform the following procedure only after the connector is deployed. |
Log in to the Oracle Identity Manager Design Console.
Expand Development Tools.
Double-click Reconciliation Rules.
Search for and open SAP UM Recon Rule. Figure 1-5 shows this reconciliation rule.
|
Note: No action is performed for rule conditions that are not predefined for this connector. You can define your own action rule for such rule conditions. For information about modifying or creating reconciliation action rules, see one of the following guides:
|
The following sections provide information about the reconciliation rules for this connector:
Section 1.6.3.1, "Reconciliation Action Rules for Reconciliation"
Section 1.6.3.2, "Viewing Reconciliation Action Rules in the Design Console"
Table 1-6 lists the action rules for reconciliation.
After you deploy the connector, you can view the reconciliation action rules for reconciliation by performing the following steps:
Log in to the Oracle Identity Manager Design Console.
Expand Resource Management, and double-click Resource Objects.
If you want to view the reconciliation action rules for reconciliation, then search for and open the SAP UM Resource Object resource object.
Click the Object Reconciliation tab, and then click the Reconciliation Action Rules tab. The Reconciliation Action Rules tab displays the action rules defined for this connector. Figure 1-6 shows the reconciliation action rules for reconciliation.
Provisioning involves creating or modifying user data on the target system through Oracle Identity Manager.
|
See Also: The "Provisioning" section in Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Identity Manager for conceptual information about provisioning |
This section discusses the following topics:
Table 1-7 lists the supported user provisioning functions and the adapters that perform these functions. The functions listed in the table correspond to either a single or multiple process tasks.
|
See Also: Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Identity Manager for generic information about process tasks and adapters |
Table 1-7 User Provisioning Functions
| Function | Adapter |
|---|---|
|
Create a user account |
SAPU Create User |
|
Update a user account |
SAPU Modify User |
|
Update the user ID of an account |
SAPU Update User ID |
|
Delete a user account |
SAPU Delete User |
|
Lock or unlock a user account |
SAPU Lock UnLock User |
|
SAPU Enable User |
|
|
SAPU Disable User |
|
|
SAPU Create Link |
|
|
SAPU Modify Password |
|
|
Add (provision) a multivalued attribute (for example, role or profile) |
SAPU Add Multivalue Data |
|
Add (provision) a custom multivalued attribute |
SAPU Add Custom Multivalue Data |
|
Remove (revoke) a multivalued attribute (for example, role or profile) |
SAPU Remove Multivalue Data |
|
Update a multivalued attribute (for example, role or profile) |
SAPU Update Multivalue Data |
|
Remove (revoke) a multivalued attribute |
SAPU Remove Custom Multivalue Data |
|
Update a custom attribute added on the target system |
SAPU Custom Attr Modify |
The Lookup.SAP.UM.ProvAttrMap lookup definition maps process form fields with single-valued target system attributes. The Code Key column holds the names of process form fields. The format of values in the Decode column is as follows:
FIELD_TYPE;FIELD_NAME;STRUCTURE_NAME;FIELD_NAME_X;STRUCTURE_NAME_X
In this format:
FIELD_TYPE can be TEXT, DATE, CHECKBOX, or LOOKUP.
FIELD_NAME is the name of the field.
STRUCTURE_NAME is the name of the structure.
FIELD_NAME_X is the name of the field used to indicate whether or not the value in FIELD_NAME must be applied.
STRUCTURE_NAME_X is the name of the structure that holds FIELD_NAME_X.
Table 1-8 lists the entries in this lookup definition.
Table 1-8 Entries in the Lookup.SAP.UM.ProvAttrMap Lookup Definition
| Process Form Field | Target System Attribute |
|---|---|
|
Accounting Number |
TEXT;ACCNT;LOGONDATA;ACCNT;LOGONDATAX |
|
Alias |
TEXT;USERALIAS;ALIAS;BAPIALIAS;ALIASX |
|
Building |
TEXT;BUILDING_P;ADDRESS;BUILDING_P;ADDRESSX |
|
Communication Type |
LOOKUP;COMM_TYPE;ADDRESS;COMM_TYPE;ADDRESSX |
|
Company |
LOOKUP;COMPANY;COMPANY;COMPANY;COMPANYX |
|
Contractual User Type |
LOOKUP;LIC_TYPE;UCLASS;UCLASS;UCLASSX |
|
Cost Center |
TEXT;KOSTL;DEFAULTS;KOSTL;DEFAULTSX |
|
Date Format |
LOOKUP;DATFM;DEFAULTS;DATFM;DEFAULTSX |
|
Decimal Notation |
LOOKUP;DCPFM;DEFAULTS;DCPFM;DEFAULTSX |
|
Department |
TEXT;DEPARTMENT;ADDRESS;DEPARTMENT;ADDRESSX |
|
E Mail |
TEXT;E_MAIL;ADDRESS;E_MAIL;ADDRESSX |
|
Fax Extension |
TEXT;FAX_EXTENS;ADDRESS;FAX_EXTENS;ADDRESSX |
|
Fax Number |
TEXT;FAX_NUMBER;ADDRESS;FAX_NUMBER;ADDRESSX |
|
First Name |
TEXT;FIRSTNAME;ADDRESS;FIRSTNAME;ADDRESSX |
|
Floor |
TEXT;FLOOR_P;ADDRESS;FLOOR_P;ADDRESSX |
|
Function |
TEXT;FUNCTION;ADDRESS;FUNCTION;ADDRESSX |
|
Language Communication |
LOOKUP;LANGU_P;ADDRESS;LANGU_P;ADDRESSX |
|
Last Name |
TEXT;LASTNAME;ADDRESS;LASTNAME;ADDRESSX |
|
Logon Language |
LOOKUP;LANGU;DEFAULTS;LANGU;DEFAULTSX |
|
TEXT;BAPIPWD;PASSWORD;BAPIPWD;PASSWORDX |
|
|
Room Number |
TEXT;ROOM_NO_P;ADDRESS;ROOM_NO_P;ADDRESSX |
|
Start Menu |
TEXT;START_MENU;DEFAULTS;START_MENU;DEFAULTSX |
|
Telephone Extension |
TEXT;TEL1_EXT;ADDRESS;TEL1_EXT;ADDRESSX |
|
Telephone Number |
TEXT;TEL1_NUMBR;ADDRESS;TEL1_NUMBR;ADDRESSX |
|
Time Zone |
LOOKUP;TZONE;LOGONDATA;TZONE;LOGONDATAX |
|
Title |
LOOKUP;TITLE_P;ADDRESS;TITLE_P;ADDRESSX |
|
User Group |
LOOKUP;CLASS;LOGONDATA;CLASS;LOGONDATAX |
|
User ID |
TEXT;USERNAME;NONE;NONE;NONE |
|
User Type |
TEXT;USTYP;LOGONDATA;USTYP;LOGONDATAX |
|
Valid From |
DATE;GLTGV;LOGONDATA;GLTGV;LOGONDATAX |
|
Valid Through |
DATE;GLTGB;LOGONDATA;GLTGB;LOGONDATAX |
The Lookup.SAP.UM.ProvChildAttrMap lookup definition maps process form fields with multivalued target system attributes. The Code Key column holds the names of the child form fields. The format of the Decode column is the same as that for the Lookup.SAP.UM.ProvAttrMap lookup definition.
Table 1-9 lists the entries in this lookup definition.
Table 1-9 Entries in the Lookup.SAP.UM.ProvChildAttrMap Lookup Definition
| Child Form Field | Target System Attribute |
|---|---|
|
End Date |
TEXT;TO_DAT;ACTIVITYGROUPS |
|
Profile Name |
LOOKUP;PROFILE|BAPIPROF;PROFILES |
|
Profile System Name |
LOOKUP;SUBSYSTEM;PROFILES |
|
Role Name |
LOOKUP;AGR_NAME;ACTIVITYGROUPS |
|
Role System Name |
LOOKUP;SUBSYSTEM;ACTIVITYGROUPS |
|
Start Date |
TEXT;FROM_DAT;ACTIVITYGROUPS |
In the Compliant User Provisioning feature, the Lookup.SAP.CUP.ProvAttrMap lookup definition maps process form fields with single-valued attributes in SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning. Table 1-10 lists entries in this lookup definition.
Table 1-10 Entries in the Lookup.SAP.CUP.ProvAttrMap Lookup Definition
| Process Form Field | Target System Attribute |
|---|---|
|
CUP Requestor ID |
requestorId;TEXT;STANDARD;NONE;MANDATORY |
|
CUP Requestor First Name |
requestorFirstName;TEXT;STANDARD;NONE;MANDATORY |
|
CUP Requestor Last Name |
requestorLastName;TEXT;STANDARD;NONE;MANDATORY |
|
CUP Requestor Email |
requestorEmailAddress;TEXT;STANDARD;NONE;MANDATORY |
|
E Mail |
emailAddress;TEXT;STANDARD;E_MAIL;MANDATORY |
|
First Name |
firstName;TEXT;STANDARD;FIRSTNAME;MANDATORY |
|
Last Name |
lastName;TEXT;STANDARD;LASTNAME;MANDATORY |
|
User ID |
userId;TEXT;STANDARD;NONE;MANDATORY |
|
Valid From |
validFrom;DATE;STANDARD;GLTGV;NONE |
|
Valid Through |
validTo;DATE;STANDARD;GLTGB;MANDATORY |
In the Compliant User Provisioning feature, the Lookup.SAP.CUP.ProvisionRoleAttrMap lookup definition maps process form fields with multivalued attributes (roles and profiles) in SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning. Table 1-10 lists entries in this lookup definition.
The following is the organization of information in the rest of this guide:
Chapter 2, "Deploying the Connector" describes procedures that you must perform on Oracle Identity Manager and the target system during each stage of connector deployment.
Chapter 3, "Using the Connector" describes guidelines on using the connector and the procedure to configure reconciliation runs and perform provisioning operations.
Chapter 4, "Extending the Functionality of the Connector" describes the procedures to perform if you want to extend the functionality of the connector.
Chapter 5, "Known Issues" lists known issues associated with this release of the connector.