Unit of Measure
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Overview of Units of Measure
- Defining Unit of Measure Classes
- Examples of Unit of Measure Classes
- Defining Units of Measure
- Examples of Units of Measure
- Defining Unit of Measure Conversions
- Examples of Unit of Measure Conversions
- Lot-Specific Unit of Measure Conversions
Overview of Units of Measure
Oracle Inventory provides you with powerful methods for defining and manipulating units of measure. You can easily convert between the units of measure you define. This enables you to manufacture, order, or receive items in any unit of measure. With units of measure you can:
Defining Unit of Measure Classes
Unit of measure classes represent groups of units of measure with similar characteristics. Creating unit of measure classes is the first step in unit of measure management. Each unit of measure you define must belong to a unit of measure class.
Each class has a base unit of measure. The base unit of measure is used to perform conversions between units of measure in the class. For this reason, the base unit of measure should be representative of the other units of measure in the class, and generally one of the smaller units. For example, you could use CU (cubic feet) as the base unit of a class called Volume.
Unit of measure classes are not organization-specific. Default unit of measure classes are not provided.
To define a unit of measure class
-
Navigate to the Unit of Measure Classes window.
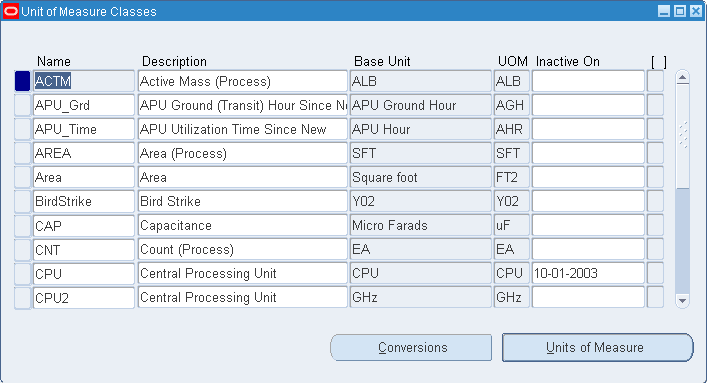
Important: You should use the Oracle Assets or Oracle Order Management versions of this window only when you use those products without Oracle Inventory or Oracle Purchasing. If you use Inventory or Purchasing, you should use their Unit of Measure Classes windows.
When using Oracle Assets, you need to set up units only if you use the units of production depreciation method.
-
Enter a unique name for the unit of measure class.
-
Define the base unit of measure for this class.
-
Define a unique abbreviation for the base unit of measure.
For example, EA for each or HRS for hours.
-
Save your work.
To make a unit of measure class inactive
-
Enter the date on which the unit of measure class becomes inactive.
As of this date, you can no longer define new units of measure for this class.
Related Topics
Examples of Unit of Measure Classes
Examples of Unit of Measure Classes
| Unit | Base Unit of Measure | Other Units Measure |
|---|---|---|
| Quantity | each | dozen, box |
| Weight | gram | pound, kilogram |
| Time | second | minute, hour |
| Volume | cubic inches | cubic feat, cubic centimeters |
Defining Units of Measure
Units of measure are used by a variety of functions and transactions to express the quantity of items. Defining units of measure is the second step in unit of measure management.
The values defined in the Units of Measure window provide the list of values available in unit of measure fields in other windows.
Units of measure are not organization-specific.
Primary Unit of Measure
Theprimary unit of measure is the stocking unit of measure for an item in a particular organization. The primary unit of measure is an item attribute that you specify when defining each item.
Prerequisites
- You must define at least one unit of measure class. See: Defining Unit of Measure Classes
To define a unit of measure
-
Navigate to the Units of Measure window.
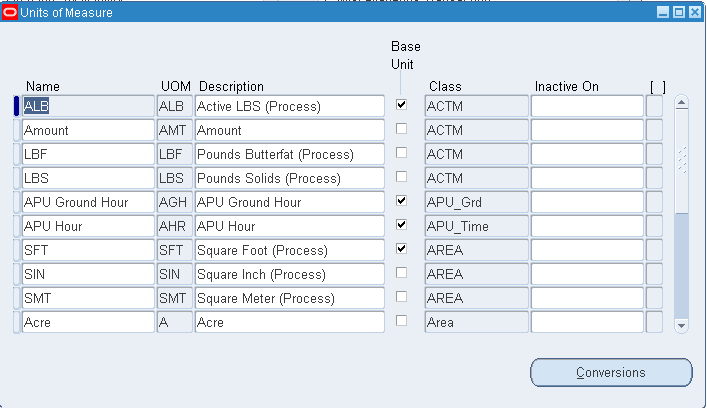
Important: You should use the Oracle Assets or Oracle Order Management versions of this window only when you use those products without Oracle Inventory or Oracle Purchasing. If you use Inventory or Purchasing, you should use their Units of Measure windows.
When using Oracle Assets, you need to set up units only if you use the units of production depreciation method.
-
Enter a unique name for the unit of measure.
-
Enter a unique abbreviation for the unit of measure with a maximum length of three characters.
For example, EA for each or HRS for hours.
-
Enter a unit of measure class.
-
Indicate if this is the base unit of measure for the unit of measure class.
-
Save your work.
-
You can delete existing units of measure that are not base units of measure if no standard or item specific conversions are defined.
To make a unit of measure inactive
-
Enter the date on which the unit of measure becomes inactive. As of this date, you can no longer assign standard or item-specific conversions to the unit of measure.
Related Topics
Examples of Units of Measure
The following table presents units of measure.
| Unit of Measure Class | Unit of Measure | Unit of Measure Code | Base Unit of Measure? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity | each | EA | Yes |
| Quantity | dozen | DZ | No |
| Weight | gram | GR | Yes |
| Weight | kilogram | KG | No |
Defining Unit of Measure Conversions
Unit of measure conversions are numerical factors that enable you to perform transactions in units other than the primary unit of the item being transacted. You can define:
-
a conversion for a specific item within a unit of measure class (Intra-class)
-
a conversion for a specific item between unit of measure classes (Inter-class)
Unit of measure conversions are not organization-specific.
You must define a conversion between a non-base unit of measure and the base unit of measure before you can assign the non-base unit of measure to an item.
Specifying Which Conversion to Use
When you define an item you decide which type of unit of measure conversion to use:
-
Item specific: Only uses unit of measure conversions unique to this item. If none exist, you can only transact this item in its primary unit of measure.
-
Standard: Uses standard unit of measure conversions for this item if an item-specific conversion is not available.
-
Both: Uses both item-specific and standard unit of measure conversions. If both exist for the same unit of measure and item combination, the item-specific conversion is used.
Unit of Measure Conversions During Transactions
Whenever you enter an item's quantity, the default is the primary unit of measure for the item. The list of values for the unit of measure field displays all units of measure for which you have defined standard and/or item-specific conversions from the primary unit of measure.
Transactions are performed in the unit of measure you specify. The conversion happens automatically and item quantities are updated in the primary unit of measure of the item.
Important: Inventory transactions and on hand balance supports decimal precision to 5 digits after the decimal point. Oracle Work in Process supports decimal precision to 6 digits. Other Oracle Applications support different decimal precision. As a result of the decimal precision mismatch, transactions another Oracle Application passes may be rounded when processed by Inventory. If the transaction quantity is rounded to zero, Inventory does not process the transaction. It is therefore suggested that the base unit of measure for an item is set up such that transaction quantities in the base unit of measure not require greater than 5 digits of decimal precision.
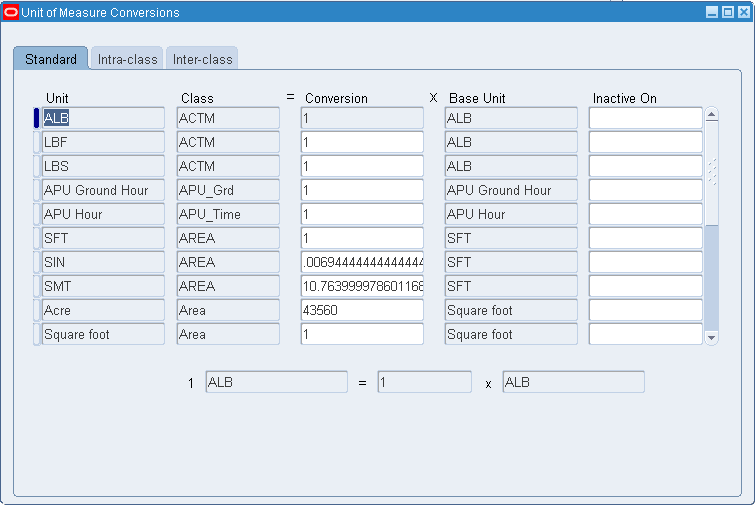
To define a Standard conversion for any item
-
Navigate to the Unit of Measure Conversions window.
-
Select the Standard tabbed region.
-
Enter a unit of measure.
-
Enter the conversion factor by which the unit of measure is equivalent to the base unit of measure established for this class.
For example, if one DZ (this unit of measure) is equivalent to 12 EA (base unit), the conversion factor is 12. Or, if EA is equal to one-twelfth of a DZ, the conversion factor is 0.08333.
-
Save your work.
To define a conversion for a specific item within a unit of measure class (Intra-class)
-
Navigate to the Unit of Measure Conversions window.
-
Select the Intra-class tabbed region.
-
Enter an item.
-
Enter a unit of measure.
-
Enter the conversion factor by which the unit of measure is equivalent to the base unit of measure established for this class.
For example, if one LB (this unit of measure) is equivalent to 16 OZ (base unit), the conversion factor is 16.
-
Save your work.
To define a conversion for a specific item between unit of measure classes (Inter-class)
-
Navigate to the Unit of Measure Conversions window.
-
Select the Inter-class tabbed region.
-
Select an item.
-
Select the destination base unit of measure of the class to which you are converting a unit of measure.
-
Enter the conversion factor by which the source base unit is equivalent to the destination base unit.
For example, if one ML (source base unit) is equivalent to one GR (destination base unit), the conversion factor is one.
-
Save your work.
To make a unit of measure conversion inactive
-
Enter the date on which the conversion becomes inactive.
As of this date, you can no longer use the unit of measure conversion.
Related Topics
Examples of Unit of Measure Conversions
Lot Specific Unit of Measure Conversions
Examples of Unit of Measure Conversions
The following table presents standard conversions.
Standard Conversions
| Unit of Measure Class | Unit of Measure | Unit of Measure Code | Base Unit of Measure? | Standard Conversion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity | each | EA | Yes | - |
| Quantity | dozen | DZ | No | 1 DZ = 12 EA |
| Weight | gram | GR | Yes | - |
| Weight | pound | LB | No | 1LB = 454 GR |
| Time | second | SE | Yes | - |
| Time | minute | MI | No | 1 MI = 60 SE |
The following table presents item-specific, intra-class conversions.
Item-specific Intra-class Conversions
| Item | Unit of Measure Class | Unit of Measure | Unit of Measure Code | Conversion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| soda pop | Quantity | case | CS | 1 CS = 24 EA |
| canned tomatoes | Quantity | case | CS | 1 CS = 10 EA |
The following table presents item-specific, inter-class conversions.
Item-specific Inter-class Conversions
| Item | Destination Base Unit | Class | Conversion | Source Base Unit | Class | Mathematical Relationship |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gasoline | gram | Weight | 1.35 | milliliter | Volume | 1.35 ML = 1 GR |
| water | gram | Weight | 1 | milliliter | Volume | 1 ML = 1 GR |
Lot-Specific Unit of Measure Conversions
Lot specific conversions enable you to perform a specific inter-class conversion for a given lot. This enables you to establish more granular control over the transactional quantities of a lot. For example, the standard inter-class conversion for a lot controlled item is one gallon equals 15 pounds; however, when you receive a particular lot of the item, 1 gallon equals 16 pounds. You can create a lot specific unit of measure for this instance.
You can create lot-specific unit of measure conversions for on-hand lots or lots with a zero balance. If you create a lot-specific conversion for a lot with on-hand quantities, you can automatically update the quantities in the system to more accurately reflect the on-hand quantity.
You can also view the history of changes made to the lot unit of measure conversion, and the corresponding quantity changes.
To create a lot specific unit of measure conversion:
-
Navigate to the Lot Inter-Class Unit of Measure Conversions window.
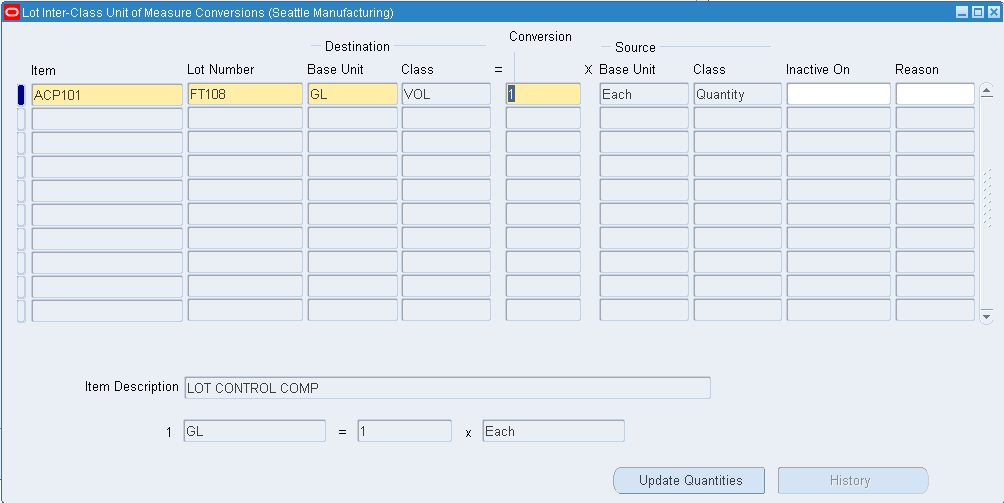
-
Enter the item number in the Item field.
-
Enter the lot number in the Lot Number field.
-
Select the destination base unit of measure of the class to which you are converting the unit of measure.
-
Enter the conversion factor by which the source base unit is equivalent to the destination base unit.
For example, if 16 pounds (source base unit) is equivalent to 1 Gallon (destination base unit), the conversion factor is 16.
-
Optionally, enter an inactive date for the conversion. This is the date when the unit of measure conversion for the lot reverts back to the standard inter-class conversion.
-
Optionally, enter a transaction reason for the conversion. See Defining Transaction Reasons for more information.
-
Save your work.
To update lot on-hand quantities:
-
Select a lot-specific unit of measure conversion.
-
Click Update Quantities on the Lot Inter-Class Unit of Measure Conversions window.
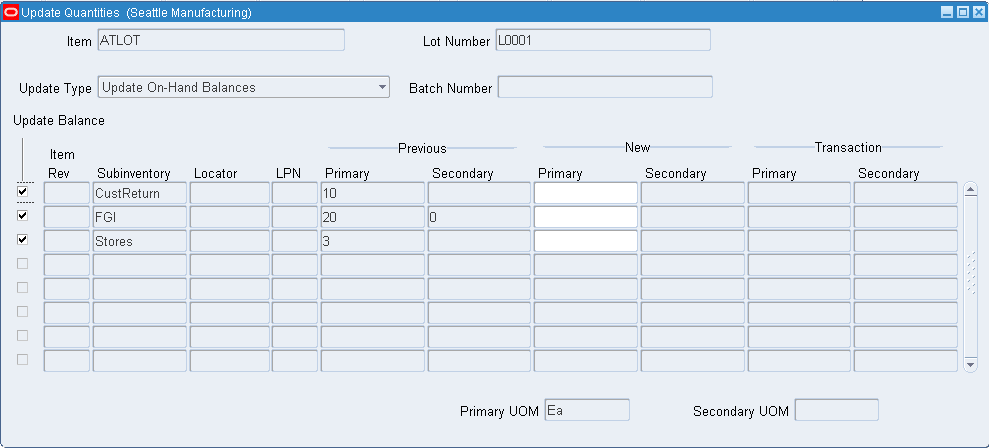
-
Select the Update Type. The available choices are:
-
Update On-Hand Balances: This enables you to enter a new primary or secondary on-hand balance. The system automatically recalculates the other on-hand balance as well as the transaction quantities based on the conversion factor.
-
Recalculate Batch Primary Quantity: The system automatically recalculates the new primary on-hand quantity and process-batch quantity based on the conversion factor. The secondary quantity remains the same. The system automatically updates additional on-hand quantities that the batch transaction did not create. If the lot was yielded only by the batch, then the system does not update the transaction quantities.
-
Recalculate Batch Secondary Quantity: The system automatically recalculates the new secondary on-hand quantity and process-batch quantity based on the conversion factor. The primary quantity remains the same. The system automatically updates additional on-hand quantities that the batch transaction did not create. If the lot was yielded only by the batch, then the system does not update the transaction quantities.
-
Recalculate On-Hand Primary Quantity: The system automatically recalculates the primary quantity based on the conversion factor. The secondary quantity remains the same, and the system updates the transaction quantities.
-
Recalculate On-Hand Secondary Quantity: The system automatically recalculates the secondary quantity based on the conversion factor. The primary quantity remains the same, and the system updates the transaction quantities.
-
-
Verify the Update Balance check box is selected. If you do not want to update the balance for the row, deselect the Update Balance check box.
-
Review the location and transaction information. These fields are display only: Organization, Rev, LPN Subinventory, Locator Primary Transaction, and Secondary Transaction. You can update the new primary or secondary quantity if you select Update On-hand Balances as the update type.
-
Save your work.
To view lot conversion history:
-
Select a lot-specific unit of measure conversion.
-
Click History in the Lot Inter-Class Unit of Measure Conversions window.
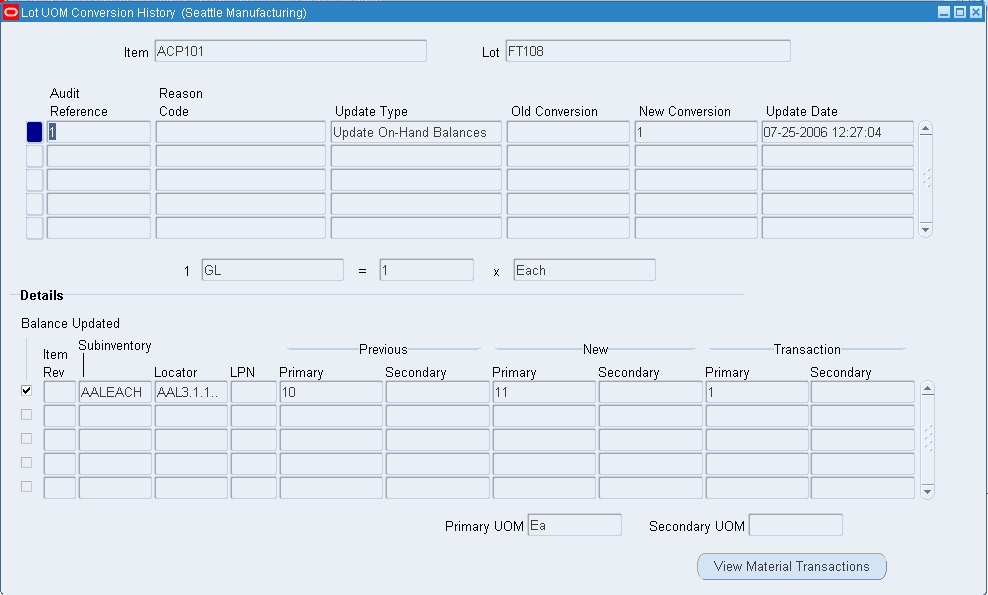
-
View the lot transaction history information. This is a display window, and you cannot make any changes within it. It contains the following information:
-
Audit Reference: The internal system reference number.
-
Reason: The transaction reason for the lot update.
-
Update Type: The type of update performed on the lot.
-
Old Conversion: The standard inter-class conversion rate for the item.
-
New conversion: The lot-specific conversion rate for the lot.
-
Update Date: The day that you updated the lot quantities.
-
Balance Updated: If selected, the system-updated lot on hand balance.
-
Org: Organization where the lot resides.
-
Rev: Item revision for the lot.
-
LPN: LPN where the lot resides if applicable.
-
Subinventory: Subinventory where the lot resides.
-
Locator: Locator where the lot resides if applicable.
-
Previous Primary and Secondary Quantities: The on-hand primary and secondary quantities before the lot update transaction.
-
New Primary and Secondary Quantities: The on-hand primary and secondary quantities after the lot update transaction.
-
Transaction Primary and Secondary Quantities: The primary and secondary transaction quantities.
-
-
Click View Material transactions to view the transaction information. For more information, Viewing Material Transactions.
-
Close the window when finished.
Related Topics
Defining Unit of Measure Conversions