Setting Up Oracle Cost Management
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Overview of Setting Up
- Setup Checklist
- Setup Steps
- Default Interorganization Options
- Default Inter-Organization Transfer Accounts
- Setting Up Periods
- Defining Cost Types
- Defining Activities and Activity Costs
- Defining Subelements
- Defining Material Subelements
- Defining Overhead
- Defining Material Overhead Defaults
- Mass Editing Item Accounts
- Mass Editing Cost Information
- Setting Cost Controls
- Copying Costs
- Default Basis Types
- Associating Expenditure Types with Cost Elements
- Defining Category Accounts
- Account Update Restrictions
- Associating WIP Accounting Classes with Categories
- Project Cost Groups
- Profile Options and Security Functions
- Landed Cost Management (LCM)
- Cost Management Security Functions
Overview of Setting Up
This section contains an overview of each task you need to complete to set up Oracle Cost Management.
Related Product Setup Steps
The following steps may need to be performed to implement Oracle Cost Management. These steps are discussed in detail in the Setting Up sections of other Oracle product user’s guides.
Set Up Underlying Oracle E-Business Suite Technology
You need to complete several other setup steps, including:
-
Performing system–wide setup tasks such as configuring concurrent managers and printers
-
Managing data security, which includes setting up responsibilities to allow access to a specific set of business data and complete a specific set of transactions, and assigning individual users to one or more of these responsibilities.
-
Setting up Oracle Workflow
-
Setting up an Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator responsibility. See: Setting Up Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator, Oracle Applications System Administrator's Guide
See also:
Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide
Oracle Workflow Guide
Oracle General Ledger Setup Steps
Use the Setting Up General Ledger section in the General Ledger User’s Guide for help in completing the following setup steps.
| Step | Reference |
|---|---|
| Define Your ledger for Perpetual Costing See: Defining Ledgers, Oracle General Ledger User's Guide. Note: If you are not implementing Oracle General Ledger, you can use the Ledger window in Oracle Inventory or Oracle Cost Management to define your ledger. | Common Applications |
| See: Entering Daily Rates, Oracle General Ledger User's Guide | Common Applications |
Oracle Inventory Setup Steps
Use the Setting Up Oracle Inventory section in the Oracle Inventory User’s Guide for help in completing the following setup steps.
| Step | Reference |
|---|---|
| Define Organizations See: Inventory Structure, Inventory User's Guide. | Common Applications |
| Define Organization Parameters for Perpetual Costing. See: Defining Organization Parameters, Oracle Inventory User's Guide . Note: Organization parameters define the costing method for your organization, the general ledger transfer option (Required), the organization level default and system accounts, and the inter–organization transfer information. |
Common Applications |
| Define Units of Measure. See: Defining Units of Measure, Oracle Inventory User's Guide. Note: If you are not implementing Oracle Inventory, you can use the Units of Measure window in Oracle Inventory to define your units of measure. |
Common Applications |
| Define Subinventories. See: Defining Subinventories, Oracle Inventory User's Guide. | Common Applications |
| Define Categories See: Defining Categories, Oracle Inventory User's Guide. | Common Applications |
| Define Category Sets. See: Defining Category Sets, Oracle Inventory User's Guide. | Common Applications |
| Open Accounting Periods. See: Maintaining Accounting Periods, Oracle Inventory User's Guide. | Common Applications |
| Define Default Category Sets. See: Defining Default Category Sets, Oracle Inventory User's Guide. | Common Applications |
| Define Items, Item Attributes, and Controls. See: Defining Item Attribute Controls, Oracle Inventory User's Guide. | Common Applications |
| Define Account Aliases. See: Defining Account Aliases, Oracle Inventory User's Guide. | Common Applications |
| Launch Transaction Managers. See: Launching Transaction Managers, Oracle Inventory User's Guide (Oracle Inventory User’s Guide). | Common Applications |
Oracle Purchasing Setup Steps
Use the Setting Up Oracle Purchasing section in the Oracle Purchasing User’s Guide for help in completing the following steps.
Note: These steps are required only if you plan to use Purchasing as part of costing.
| Step | Reference |
|---|---|
| Define Receiving Options and Controls. See: Setup Overview, Oracle Applications User's Guide. | Common Applications |
| Define Purchasing Options. See: Defining Purchase Options, Oracle Purchasing User's Guide. | Common Applications |
Oracle Bills of Material Setup Steps
Use the Setting Up Oracle Bills of Material section in the Oracle Bills of Materials User’s Guide for help in completing the following steps.
Note: These steps are required only if you plan to use Bills of Material as part of costing.
| Step | Reference |
|---|---|
| Define Bills of Material Parameters. See: Defining Bills of Material Parameters, Oracle Bills of Material User's Guide. | Common Applications |
| Define Resources. See: Defining a Resource, Oracle Bills of Material User's Guide. | Common Applications |
| Define Departments. See: Defining a Department, Oracle Bills of Material User's Guide. | Common Applications |
| Assign Resources to a Department | Common Applications |
| Define Overheads and Assign them to Departments. See: Defining a Resource, Oracle Bills of Material User's Guide. | Common Applications |
Oracle Work in Process Setup Steps
Use the Setting Up Oracle Work in Process section for help in completing the following steps.
Note: These steps are required only if you plan to use Work in Process as part of costing.
| Step | Reference |
|---|---|
| Define WIP Accounting Classes and Valuation Accounts | Common Applications |
| Define WIP Parameters | Common Applications |
Setup Flowchart
Some of the steps outlined in this flowchart and setup checklist are required and some are optional. Required step with defaults refers to setup functionality that comes with pre-seeded, default values in the database; however, you should review those defaults and decide whether to change them to suit your business needs. If you want or need to change them, you should perform that setup step. You need to perform optional steps only if you plan to use the related feature or complete certain business functions.
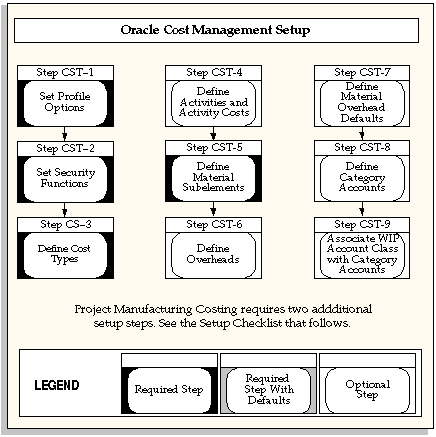
Note: Oracle Cost Management does not support costing for process inventory organizations. If you open costing setup windows in a process inventory organization context, then an error message displays a message indicating that the function is not available for a process organization, and the window process will not open.
Setup Checklist
The following table lists setup step. After you log on to Oracle E-Business Suite, complete these steps to implement Oracle Cost Management:
| Step No. | Required | Step |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Required | Set Cost Management Profile Options |
| Step 2 | Required | Set Cost Management Security Functions |
| Step 3 | Required | Define Cost Types |
| Step 4 | Optional | Defining Activities and Activity Costs |
| Step 5 | Only Available and Required for Project Manufacturing Costing | Define Cost Groups |
| Step 6 | Optional | Define Material Subelements |
| Step 7 | Optional | Define Overheads |
| Step 8 | Optional | Define Material Overhead Defaults |
| Step 9 | Only Available and Required for Project Manufacturing Costing | Associate Expenditure Types with Cost Element |
| Step 10 | Optional | Define Category Accounts |
| Step 11 | Optional | Associate WIP Account Classes with Category Accounts |
Setup Steps
Step 1: Set Personal Profile Options
Cost Management personal profile options control defaults within windows as well as data processing options.
Step 2: Set Security Functions
Cost Management security functions determine what information can be viewed, created, updated, and deleted in certain windows in Cost Management.
See: Cost Management Security Functions.
Step 3: Define Cost Types
You must define cost types. Each cost type contains a unique set of costs and has its own set of cost controls.
-
Default: Frozen for Standard Costing, Average and Average Rates for Average Costing
-
Context: N/A
See: Defining Cost Types.
Step 4: Defining Activities and Activity Costs
You can define activities, activity rate information, and activity and activity cost type associations. You can assign an activity to any cost. If you use the activity basis type, you can directly assign the activity cost to the item. When you use the other basis types, the cost is based on the subelement, basis type, and entered rate or amount. The activity defaults from the subelement; and, if needed, you can override the default.
Default: N/A
Context: N/A
See: Defining Item Costs and Defining Activities and Activity Costs.
Step 5: Define Cost Groups
You can define cost groups and use them to group project related costs.
Note: This step is conditionally required if you plan to transfer project costs to Oracle Projects.
Default: The organization's default cost group.
Context: Additional cost groups are required to group project related costs.
See: Defining Project Cost Groups and Project Manufacturing Implementation Manual.
Step 6: Define Material Subelements
Material subelements classify material costs, such as plastic or metal. A material subelement has a default activity and a default basis type assigned to it.
Default: N/A
Context: N/A
See: Defining Material Subelements.
Step 7: Define Overheads
You can use material overhead and overhead cost subelements to add indirect costs to item costs on either a percentage basis or as a fixed amount.
Default: N/A
Context: N/A
See: Defining Overhead.
Step 8: Define Material Overhead Defaults
You can define and update default material overhead subelements and rates at the organization or category level. When you define items in Oracle Inventory, these defaults are automatically used. This speed data entry when defining items.
Default: N/A
Context: N/A
See: Defining Material Overhead Defaults.
Step 9: Associate Expenditure Types with Cost Elements
You must associate expenditure types with cost elements so that project transfers and the project related costs associated with miscellaneous transactions can be properly processed once they are transferred to Oracle Projects.
Note: This step is conditionally required if you to plan to transfer project costs to Oracle Projects.
Default: N/A
Context: N/A
See: Associating Expenditure Types with Cost Elements.
Step 10: Define Category Accounts (Optional)
You can define category accounts. Category accounts are part of the product line accounting setup.
Default: N/A
Context: N/A
See: Product Line Accounting Setup and Defining Category Accounts.
Step 11: Associate WIP Accounting Classes with Categories (Optional)
You can associate WIP accounting classes with category accounts. Default WIP accounting classes are part of product line accounting setup.
Default: N/A
Context: N/A
See: Product Line Accounting Setup and Associating WIP Accounting Classes with Categories.
Important: Oracle recommends that you set the Interface Manager to run in five minute intervals.
Default Interorganization Options
This option determines how you charge your internal cost to transfer material between organizations. For example, transfer costs might include the cost of preparing the paperwork, the cost of boxing the item for shipment, or a formal transfer profit charged between the sending and receiving organizations. This is different from the transportation cost that you pay to a freight carrier to physically move the material. This is different from the transportation cost paid to a freight carrier.
These options affect your entries in Inter-Organization Transfer:
| No transfer charges | Do not add transfer charges to a material transfer. |
| Predefined percent of transaction value | Add a predefined percent of the transaction value to the material transfer. Define a default percentage in Define Organization Parameters. |
| Requested added value | Request a discrete value to add to the material transfer. Enter the value in the Transfer Between Organizations at the time of the transfer. |
| Requested percent of transaction value | Request a percentage of the transfer value to add to the material transfer. Enter the value in Transfer Between Organizations at the time of the transfer. |
Default Inter-Organization Transfer Accounts
Oracle Inventory uses the following inter-organization accounts as defaults when you define a relationship between the current organization and another organization:
| Inter-Inventory Transfer Credit | Collects the cost of the transfer charge. These charges reduce expenses for the sending organization. |
| Inter-Organization Payable | Used by the receiving organization as a clearing account, and represents inter-company payables. Reconcile inter-organization payable and receivable accounts during period close. |
| Intransit Inventory | Represents the value of transferred inventory that has not arrived at the receiving organization. Depending on the Free On Board (FOB) point defined for this transfer, the Intransit inventory is owned by either the shipping organization, FOB receipt, or the receiving organization, FOB shipment. Inventory uses this account when the transfer organizations use intransit inventory. If you use average costing, this account defaults from the organization level material account and you cannot change it.. |
| Inter-Organization Receivable | Used by the shipping organization as a clearing account, and represents inter-company receivables. You should reconcile inter-organization payable and receivable accounts during period close. |
| Inter-Organization PPV | Under standard costing, the receiving organization uses this account to recognize the difference between the shipping organization standard cost and the receiving organization standard cost. |
Note: These defaults are defined for each organization and the appropriate accounts from each organization are used when an inter-organization relationship is defined.
Setting Up Periods
Cost Management uses the accounting periods you define for your general ledger. You define accounting periods through period types and a calendar.
To set up periods
-
Define an accounting period type.
Period types can be months, quarters, or years. Specify the number per year of the period type and whether the type corresponds to a system calendar (January to December) or a fiscal calendar. See: Period Types, Oracle General Ledger User's Guide.
-
Define the accounting periods in your calendar and associate one calendar with each General Ledger you set up.
Inventory allows you to have multiple calendars, such as a fiscal calendar for one ledger and a different calendar for another ledger.
For each calendar, name the periods within the calendar (such as month names: Jan., Feb., and so on), the accounting period type, the year and quarter of the period, the period number, and the start and end date of the period..
-
Open the accounting periods you defined in your calendar for transaction collection purposes.
All Inventory and Work in Process transactions require an open period. The transaction date you specify (typically the current date) must fall within an open period. See: Maintaining Accounting Periods, Oracle Inventory User's Guide.
Important: You can only open the period type accounted by your ledger. For most organizations, this is the monthly period type. You also cannot open an adjustments-type period-such as a thirteenth period for year-end adjustments.
Inventory also allows you to have multiple open periods for late transactions or correction of data before period close.
Defining Cost Types
A cost type is a set of costs uniquely identified by name. Two cost types are predefined for you, Frozen (for standard costs) and Average. You can define and update an unlimited number of additional simulation or unimplemented cost types. Each cost type has its own set of cost controls.
Cost Types for Average Costing
In a manufacturing average costing organization, two costs types are required for inventory valuation and transaction costing: the Average cost type and a user-defined Average Rates cost type. These two cost types are defined as follows:
| Average | This cost type holds the current average unit cost of items on hand, and is used to value transactions such as issues and transfers out (see transaction table below for details). You can update costs in this cost type only by using the average cost update routine. A history is kept of all such update transactions. This cost type is seeded and does not have to be defined. |
| Average Rates cost type | This user-defined cost type holds resource to overhead associations and current overhead rates, and any other user-defined subelement rates to be used in cost rollups and to cost applicable transactions. |
Important: You must define an Average Rates cost type to hold subelement rates/amounts. There should be no information associated with this cost type; any information found is ignored. After defining this cost type, you must select it when defining the Average Rates Cost Type parameter in the Organization Parameters window in Oracle Inventory. Rates/amount in this cost type are used, as applicable, until you redefine them. See: Setting Up Average Costing and Defining Costing Information, Oracle Inventory User's Guide.
| Predefined Cost Type Name | Costing Method | Purpose | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frozen | Standard | Frozen standard costs | Used to value transactions and inventory balances for organizations that use standard costing. This cost type is not available for organizations using average costing. |
| Average | Average | Average costs | Used to value transactions and inventory balances for organizations that use average costing. This cost type is not available for organizations using standard costing. |
| None; user-defined | Average | Average rates | Used to hold resource to overhead associations, current overhead rates, and any other user-defined subelement rates used in cost rollups and to cost applicable transactions. This cost type is not available for organizations using standard costing. You must define a cost type for average rates. |
| None; user-defined | Either standard or average | All other cost types | Use all other cost types for any purpose: cost history, product cost simulation, or to develop future frozen costs. These costs are not implemented (not frozen) costs. You can transfer costs from all other cost types to update the Frozen cost type. |
Prerequisites
- To define, update, or delete cost information, the Cost Types: Maintain security function must be included as part of the responsibility. See: Cost Management Security Functions.
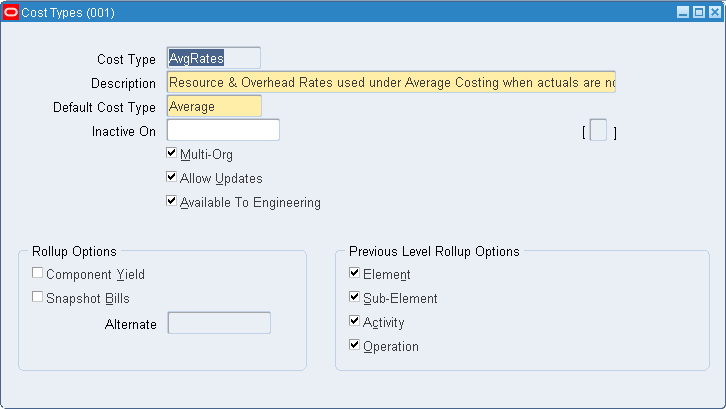
To define a cost type
-
Navigate to the Cost Types window.
-
Enter a cost type name.
-
Select the default cost type.
For items where costs have not been defined for the cost type, the default cost type is used as the next source of costs that the cost rollup and the inventory value reports use for items not associated with the cost type being rolled up or reported upon. You can have a cost type default to itself. The default reflects the current organization's costing method: Frozen for standard costing and Average for average costing.
-
Select a date on which to inactivate the cost type. You cannot inactivate the Frozen or Average cost types. You can still inquire (but not change) inactive cost types. Inquiring has no effect on bill assemblies or work in process.
-
Indicate whether the cost type is a multi-organization cost type to share with other organizations.
Note: If disabled, this cost type name is available only to the inventory organization that creates it. If enabled, only the cost type name is shared, not the costs.
-
Indicate whether to allow updates in this cost type.
If Multi-Org is selected, then the Allow Updates functionality is disabled.
If Allow Updates is set to enabled (the default), then you can change this cost type by using processes such as mass edits, copy cost information, cost rollup, and cost update. To freeze the cost information in this cost type, disable the Allow Updates functionality. Even if updates are not allowed, you can still use this cost type to report, inquire, and update Frozen costs.
-
Indicate whether this cost type is available to Oracle Engineering.
-
Select rollup options:
-
Indicate whether to include the effect of component yield when rolling up costs for this cost type.
Important: Changing the Include Component Yield flag when there are open WIP jobs in the inventory organization may result in inaccurate cost variances. For example, if the standard cost rollup includes component yield and the Include Component Yield flag is clear, then backflush transactions will no longer factor in component yield and artificial variances will result.
-
Indicate whether to save a snapshot of the bill of material structure for items that you roll up. This creates an alternate bill. (This is available only if you have Oracle Bills of Material installed.) Oracle recommends that you use an alternate designator intended for the specific purpose of maintaining a snapshot of the bill being rolled up.
If Snapshot of Bills is enabled, you must select an alternate name. You can then run the Indented Bill of Material Cost report for the alternate, even if the primary bill has changed.
-
-
Select previous level rollup options. These options determine how much information is generated by the rollup. (These options do not effect the total unit cost.) If all options are not selected (if the options are clear), then the rollup generates one record for all prior level costs and stores the total in the material cost element. The options are as follows:
Element: Indicates that detail cost information by cost element is retained at previous levels. If not selected (cleared), then all prior level costs are stored in the material cost element.
Subelement: Indicates whether to track subelement costs at previous levels. If not selected, then all prior level information does not reference a subelement.
Note: For cost types to be frozen, retain detail for at least the cost element and subelement.
Activity: Indicates whether to track activity costs at previous levels. If not selected, then all prior level information does not reference an activity.
Operation: Indicates whether to track operation costs at previous levels. If not selected, then all prior level information does not reference an operation.
Related Topics
Updating Pending Costs to Frozen Standard Costs
Defining Activities and Activity Costs
Define activities, activity rate information, and activity and cost type associations. Use activities to assign indirect costs to items based upon the effort expended to obtain or produce the item, rather than as a percentage of a direct cost or an amount per item.
Activities are processes or procedures that consume costs and time. In addition to cost elements and subelements, costs may be associated with an activity. Activities may be directly related to building items, such as runtime or setup time; or they may be indirect, such as purchase order generation, payroll, and engineering activities. The goal of activity based cost accounting is to accurately identify your product costs, especially overhead costs.
Prerequisites
- To define, update, or delete cost information, the Activities: Maintain security function must be included as part of the responsibility. See: Cost Management Security Functions.
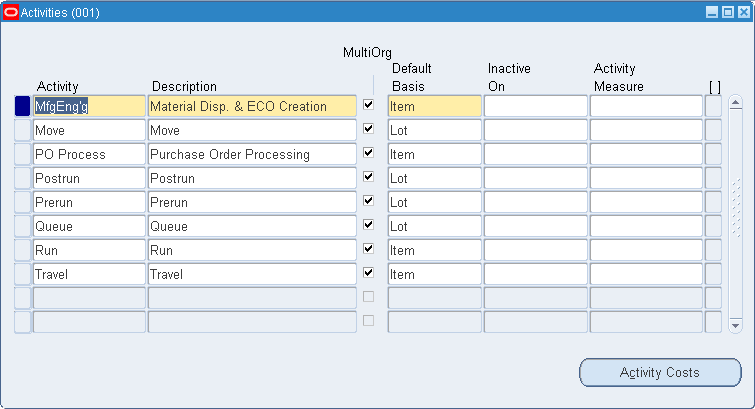
To define activities and activity costs
-
Navigate to the Activities window.
-
Enter an activity.
-
Check Multi-Org to indicate whether the activity name is a multi-organization activity to share with other organizations.
Note: If disabled, the name is only available to the organization that creates it. If enabled, only the activity name is shared, not the activity.
-
Select the activity default basis.
Basis is the method used to determine how to charge a transaction or apply product costs. The value you select here is defaulted when you define item costs. The activity default basis will override the subelement default basis as long as the basis is valid for the cost element. See: Defining Item Costs.
Activity: Used to apply activity costs to items. The activity basis type can only be used with the material overhead subelement. The item cost is calculated by multiplying the activity cost by the ratio of the number of times the activity occurs, divided into the cumulative quantity of the item associated with those occurrences.
Item: Used to earn and apply costs for all subelements. For material and material overhead subelements, you charge a fixed amount per item. For resource, outside processing, and overhead subelements, you charge a fixed amount per item moved in an operation.
Lot: Used to earn and apply costs for all subelements. The item cost is calculated the same as an Item basis cost, except the unit cost is divided by the cost type lot size to derive the cost per item.
-
Optionally, select a date to inactivate the activity.
An inactive activity cannot be assigned as a default activity when defining material subelements, resources, or overhead. An inactive activity also cannot be associated with any resource when defining a routing, with a material overhead subelement when defining material overhead defaults, or with any subelement when defining item costs, even if the activity is the default activity for the subelement.
An inactive activity, however, can still be used when defining item costs. (This applies for a new item if the inactive activity was previously specified for a material subelement as material overhead defaults were defined.) Also, previously defined subelements referencing an inactive activity can still be used.
-
Enter the Activity Measure (allocation basis or cost driver) for your activity. For example, if the activity is allocating purchasing costs, the activity measure might be the number of purchase orders generated during a given period.
-
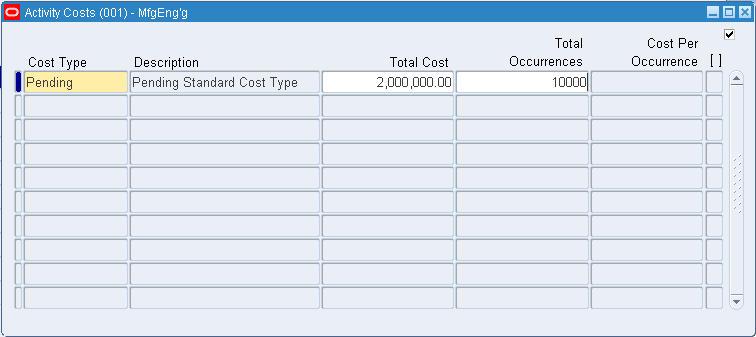
Choose the Activity Costs button and select a cost type to associate with your activity. Each activity can be associated with any number of cost types and each cost type and activity combination can have a different cost.
-
Enter the total cost budgeted for the activity cost pool. This is the total activity cost you expect to incur during a specified time.
-
Enter the total number of times you expect to perform this activity during the budget period.
The system calculates the cost per occurrence by dividing the total cost by the total occurrences. This cost is used when you use a basis type activity for the material overhead subelement.
Defining Subelements
You can define the following subelements in Cost Management:
You can define resource subelements in Oracle Bills of Material. See: Defining a Resource, Oracle Bills of Material User's Guide.
Defining Material Subelements
Material subelements classify material costs, such as plastic or metal. A material subelement has a default activity and a default basis type assigned to it.
Prerequisites
- To define, update, or delete cost information, the Material Subelements: Maintain security function must be included as part of the responsibility. See: Cost Management Security Functions.
To define material subelements
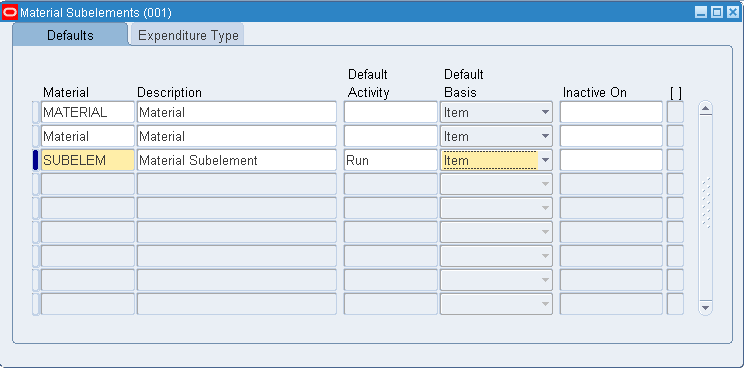
-
Navigate to the Material Subelements window.
-
In the Defaults tabbed region, enter a material subelement name.
-
Select the default activity. This activity is defaulted each time the subelement is used to define an item cost.
Activities are processes or procedures that consume costs and time. In addition to the cost element and subelement, all costs are associated with an activity. Activities may be directly related to building items, such as runtime or setup time; or they may be indirect, such as purchase order generation, payroll, and engineering change order activities. See: Defining Activities and Activity Costs.
-
Select the default basis for the material subelement. This basis type is defaulted when you define item costs. Basis is the method used to determine how to charge a transaction or apply product costs. The options are as follows:
Item: Used for all subelements. For material and material overhead subelements, you charge a fixed amount per item. This is the default.
Lot: Used for all cost elements. The item cost is calculated by dividing the order cost by the lot size.
-
Optionally, select a date on which to inactivate the material subelement.
Note: You cannot disable the default material subelement for the organization.
A disabled material subelement cannot be used to define a material cost when defining item costs, or to define a default material subelement when defining organization parameters.
You can continue to use item costs previously defined for the inactive material subelement.
To associate an expenditure type with a subelement
-
If the Project Cost Collection Enabled parameter in the Organization Parameters window is set, you must associate an expenditure type with each subelement. See: Organization Parameters Window, Oracle Inventory User's Guide
You can only select expenditure types that belong to the Inventory expenditure class. Expenditure types are defined in Oracle Projects.
-
Save your work.
You can use material overhead and overhead cost subelements to add indirect costs to item costs on either a percentage basis or as a fixed amount in both standard and average costing organizations.
Each overhead subelement has a default basis, a default activity, and an absorption account. The overhead absorption account offsets the corresponding overhead cost pool in the general ledger.
You can base the overhead charge on the number of resource units or percentage of resource value earned in the routing operation. Or, you can set up move-based overheads where the rate or amount is charged for each item moved in an operation. To do this, use the Item or Lot basis types.
You can base the material overhead charge on a percentage of the total value, which is earned when you receive purchase orders or perform WIP completion transactions. Or, you can use the Item or Lot basis types.
You can apply each of these subelements using different basis types for increased flexibility. Material overhead is earned when an item is received into inventory or completed from work in process. Overhead, based upon resources, is earned as the assembly moves through operations in work in process.
Defining Overhead
You can use material overhead and overhead cost subelements to add indirect costs to item costs on either a percentage basis or as a fixed amount in both standard and average costing organizations.
Each overhead subelement has a default basis, a default activity, and an absorption account. The overhead absorption account offsets the corresponding overhead cost pool in the general ledger.
You can base the overhead charge on the number of resource units or percentage of resource value earned in the routing operation. You can also set up move-based overheads where the rate or amount is charged for each item moved in an operation. To do this, use the Item or Lot basis types.
You can base the material overhead charge on a percentage of the total value, which is earned when you receive purchase orders or perform WIP completion transactions. You can also use the Item or Lot basis types.
You can apply each of these subelements, using different basis types, for increased flexibility. Material overhead is earned when an item is received into inventory or completed from work in process. Overhead, based upon resources, is earned as the assembly moves through operations in work in process.
Material Overhead is earned by an item during purchase order receipt, inter-organization receipt, and WIP completion transactions. You can choose to decide if material overhead is to be earned during purchase order receipt, inter-organization transactions, and assembly returns and completions for non-standard costing organizations. You have the flexibility to decide if the transaction is going to earn material overhead, depending on the item type.
Note: If you use Oracle Bills of Materials, you must first define the bill of material parameters to use the overhead cost element in the Overhead window. If the bills of material parameters are not set up, you only have access to material overhead cost element. See: Defining Bills of Material Parameters, Oracle Bills of Material User's Guide.
Prerequisites
- To define, update, or delete cost information, the Overheads: Maintain security function must be included as part of the responsibility. See: Cost Management Security Functions.
Defining overhead
-
Navigate to the Overheads window.
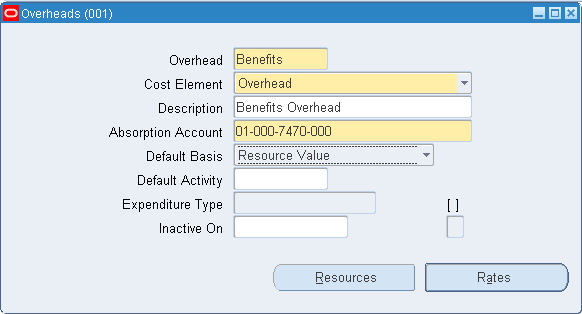
-
Enter an overhead name.
-
Material Overhead: Define material overhead.
Overhead: Define resource and move-based overhead. This is only available if Bills of Material is installed.
-
Select an overhead absorption account.
This is the offset account for any cost earned to the inventory or work in process value.
-
Select a default basis type to be used as a default for the overhead being defined.
This basis type is used to determine how the overhead cost is earned and how it is applied to product costs. See: Default Basis Types.
-
Select a default activity to use for this overhead.
Activities are processes or procedures that consume costs and time. Your activities may be directly related to building your items, such as runtime or setup time; or they may be indirect, such as purchase order generation, payroll, and engineering activities. The goal of activity based cost accounting is to accurately identify your product costs, especially overhead costs. See: Defining Activities and Activity Costs
Note: Negative item costs are not supported in Oracle Cost Management.
-
If the Project Cost Collection Enabled parameter in the Organization Parameters window is set, you must associate an expenditure type with each subelement. See: Organization Parameters Window, Oracle Inventory User's Guide.
You can only select expenditure types that belong to the Burden Transactions expenditure class.
-
Optionally, select a date on which to inactivate a material overhead or overhead.
An inactive overhead subelement cannot be used to define an overhead cost (when defining item costs) or associated with a resource (when defining a resource).
You can continue to use item costs previously defined for and resources previously associated with the inactive overhead subelement. The cost rollup will continue to roll up previously defined inactive overhead subelements.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To earn overheads and material overheads based on resource units or value, you must associate resources to overhead and material overhead for a specific cost type. Choose the Resources button to open the Resource Overhead Associations window.
-
To associate department and overhead combinations with a cost type, choose the Rates button to open the Overhead Rates window. This option is available for overheads only.
-
-
Save your work.
To associate resources to overhead for a cost type
-
Navigate to the Resource Overhead Associations window.
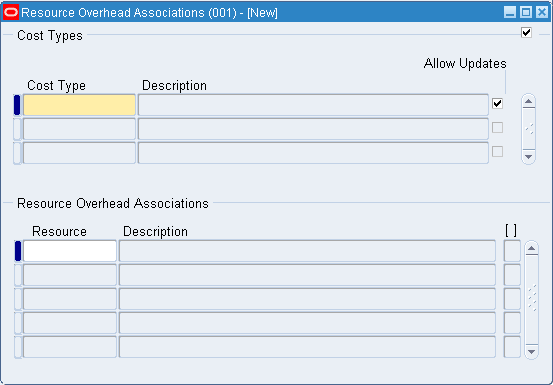
-
Select a cost type to associate resources to overhead with.
This is only necessary for material overhead and overhead subelements with a basis type of Resource Value or Resource Units.
Important: You only apply these overheads when they are associated with a resource.
-
Save your work.
To associate department and overhead combinations with a cost type
-
Navigate to the Overhead Rates window.
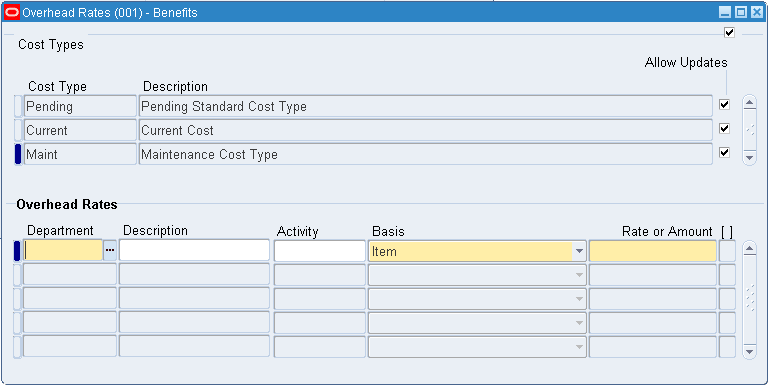
-
Select a department and enter an overhead rate or amount.
The department will be associated with the overhead being defined in the selected cost type. The specified overhead rate or amount will be used for that department. Rates and amounts are required for both resource and move (item or lot basis type) overheads.
-
Optionally, select an activity. The default is the activity selected as the default in the Overheads window. See: Defining Overhead.
-
Select the basis. The default is the basis selected as the default in the Overheads window. See: Default Basis Types.
-
Enter the percentage rate or the fixed amount, as appropriate for the basis. If the basis is resource value, enter a rate in this field. If the basis is resource units, item, or lot, enter an amount in this field.
-
Save your work.
To define material overhead absorption rules
You can decide if material overhead is to be earned during purchase order receipt and inter-organization transactions. You have the flexibility to decide if the transaction is going to earn material overhead, depending on the item type. The rules you define override the default material overhead absorption for purchase order receipt, assembly completion and return, and inter-organization transfers for Standard, Average, FIFO, and LIFO, costing organizations. The rules you define will not override material overhead absorption for work in process completion transactions in standard costing organizations.
-
Navigate to the Material Overhead Absorption Rules.
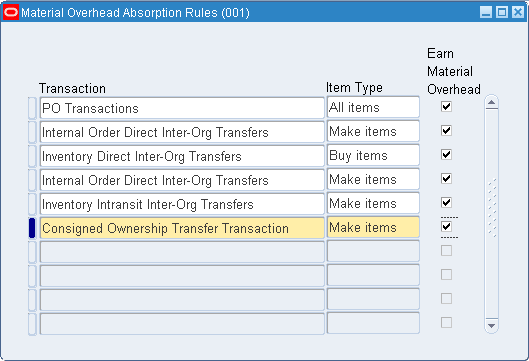
-
Select a valid Transaction from the list of values to specify a transaction that you wish to define a rule against.
-
Select an Item Type from the list of values. Valid values are Make items, Buy items, and All items.
-
Indicate whether the transaction earns material overhead.
Inter- organization Transfer Accounting Distribution Examples for Standard Costing Organizations
Item M1 is being transferred from Organization O1 to Organization O2. The costs for the item are set up for both organizations as follows:
Organization Item Cost Element Cost O1 (Sending) M1 Material 12 O1 (Sending) M1 Material Overhead 2 O2 (Receiving) M1 Material 10 O2 (Receiving) M1 Material Overhead (Transfer) 2 O2 (Receiving) M1 Material Overhead (Transportation) 3 The following tables display distributions if the material overhead absorption rules have been set to earn material overhead for the receiving organization.
FOB Receipt
The accounting entries for the sending organization O1 are as follows:
Account Debit Credit Inter-organization Receivables 19 - Intransit Inventory - 14 Transfer Cost - 2 Transportation Cost - 3 The accounting entries for the receiving organization O2 are as follows:
Account Debit Credit Inventory Valuation (Material) 10 - Inventory Valuation (Material Overhead) 5 (2 + 3) - Purchase Price Variance 6 - Material Overhead Absorption - 2 Inter-organization Payables - 19 (12 + 2 + 2 + 3) FOB Shipment
The accounting entries for the sending organization O1 are as follows:
Account Debit Credit Inter-organization Receivables 16 - Intransit Inventory - 14 Transfer Cost - 2 The accounting entries for the receiving organization O2 are as follows:
Account Debit Credit Inventory Valuation (Material) 10 - Inventory Valuation (Material Overhead) 5 (2 + 3) - Purchase Price Variance 6 (3 + 3) - Material Overhead Absorption - 2 Inter-organization Payables - 16 (12 + 2 + 2) Freight - 3 The following tables display distributions if the material overhead absorption rules have been set to NOT earn material overhead for the receiving organization.
FOB Receipt
The accounting entries for the receiving organization O2 are as follows:
Account Debit Credit Inventory Valuation (Material) 10 - Inventory Valuation (Material Overhead) 5 (2 + 3) - Purchase Price Variance 4 - Inter-organization Payables - 19 (12 + 2 + 2 + 3) FOB Shipment
The accounting entries for the receiving organization O2 are as follows:
Account Debit Credit Inventory Valuation (Material) 10 - Inventory Valuation (Material Overhead) 5 (2 + 3) - Purchase Price Variance 4 (1 + 3) - Inter-organization Payables - 16 (12 + 2 + 2) Freight - 3 Purchase Order Receipt Accounting Distribution Examples for a Standard Cost Organization.
A purchase order is received at a purchase order price of 10. The costs associated with item M1 are as follows:
Cost Element Cost Material 12 Material Overhead 2 The following table displays distributions if the material overhead absorption rules have been set to earn material overhead.
Purchase Order Receipt Transaction
Account Debit Credit Inventory Valuation (Material) 12 - Inventory Valuation (Material Overhead) 2 - Purchase Price Variance - 2 Receiving Inspection - 10 Material Overhead Absorption - 2 The following table displays distributions if the material overhead absorption rules have been set to NOT earn material overhead.
Account Debit Credit Inventory Valuation (Material) 12 - Inventory Valuation (Material Overhead) 2 - Purchase Price Variance - 4 Receiving Inspection - 10 Inter–organization Transfer Accounting Distribution Examples for Average Costing Organizations
Item M1 is being transferred from Organization O1 to Organization O2. The material overhead rate for item M1 in the receiving organization, O2, is 3 per item. The Transfer Cost is 2, while the Transportation Cost is 3. The costs for the item are set up for both organizations as follows:
Organization Item Cost Element Cost O1 (Sending) M1 Material 12 O1 (Sending) M1 Material Overhead 2 O2 (Receiving) M1 Material 10 O2 (Receiving) M1 Material Overhead 2 The following tables display distributions if the material overhead absorption rules have been set to earn material overhead for the receiving organization.
FOB Receipt
The accounting entries for the sending organization O1 are as follows:
Account Debit Credit Inter-organization Receivables 19 - Intransit Inventory - 14 Transfer Cost - 2 Transportation Cost - 3 The accounting entries for the receiving organization O2 are as follows:
Account Debit Credit Inventory Valuation (Material) 12 - Inventory Valuation (Material Overhead) 10 (7 + 3) - Material Overhead Absorption - 3 Inter-organization Payables - 19 (12 + 2 + 2 + 3) The re-averaged cost of M1 in receiving organization O2 is as follows:
Cost Element Cost Material 11 [(12 + 10)/2] Material Overhead 6 [(2 + 10)/2] FOB Shipment
The accounting entries for the sending organization O1 are as follows:
Account Debit Credit Inter-organization Receivables 16 - Intransit Inventory - 14 Transfer Cost - 2 The accounting entries for the receiving organization O2 are as follows:
Account Debit Credit Inventory Valuation (Material) 12 - Inventory Valuation (Material Overhead) 10 (2 + 3 + 3 + 2) - Material Overhead Absorption - 3 Inter-organization Payables - 16 (12 + 2 + 2) Freight - 3 The re-averaged cost of M1 in receiving organization O2 is as follows:
Cost Element Cost Material 11 [(12 + 10)/2] Material Overhead 6 [(2 + 10)/2] The following tables display distributions if the material overhead absorption rules have been set to NOT earn material overhead for the receiving organization.
FOB Receipt
The accounting entries for the receiving organization O2 are as follows:
Account Debit Credit Inventory Valuation (Material) 12 - Inventory Valuation (Material Overhead) 7 (2 + 2 + 3) - Inter-organization Payables - 19 (12 + 2 + 2 + 3) The re-averaged cost of M1 in receiving organization O2 is as follows:
Cost Element Cost Material 11 [(12 + 10)/2] Material Overhead 4.5 [(2 + 7/2] FOB Shipment
The accounting entries for the receiving organization O2 are as follows:
Account Debit Credit Inventory Valuation (Material) 12 - Inventory Valuation (Material Overhead) 7 (2 + 2 + 3) - Inter-organization Payables - 16 (12 + 2 + 2) Freight - 3 The re-averaged cost of M1 in receiving organization O2 is as follows:
Cost Element Cost Material 11 [(12 + 10)/2] Material Overhead 4.5 [(2 + 7/2] Purchase Order Receipt Accounting Distribution Examples for an Average Costing Organization
A purchase order is received at a purchase order price of 10. The material overhead rate for item M1 in organization, O2, is 2 per item. The costs associated with item M1 are as follows:
Cost Element Cost Material 12 Material Overhead 2 The following table displays distributions if the material overhead absorption rules have been set to earn material overhead.
Purchase Order Receipt Transaction
Account Debit Credit Inventory Valuation (Material) 10 - Inventory Valuation (Material Overhead) 2 - Receiving Inspection - 10 Material Overhead Absorption - 2 The re-averaged cost of M1 in receiving organization O2 is as follows:
Cost Element Cost Material 11 [(12 + 10)/2] Material Overhead 2 [(2 + 2/2] The following table displays distributions if the material overhead absorption rules have been set to NOT earn material overhead.
Account Debit Credit Inventory Valuation (Material) 10 - Receiving Inspection - 10 The re-averaged cost of M1 in receiving organization O2 is as follows:
Cost Element Cost Material 11 [(12 + 10)/2] Material Overhead 1 [(2 + 0/2] Assembly Completion and Return Accounting Distribution Example for an Average Costing Organization
A bill of material for item A consists of items B and C. The costs associated are as follows:
Item Cost Element Present Average Cost A Material 8 B Material 5 B Material Overhead 2 C Material 5 C Material Overhead 5 The material overhead rates for Item A are:
Item Cost Element Present Average Cost A Material Overhead - 1 2 A Material Overhead - 2 3 The following table displays distributions, at assembly completion, if the material overhead absorption rules have been set to earn material overhead.
WIP Assembly Completion Transactions
Account Debit Credit Inventory Valuation (Material) 10 - Inventory Valuation (Material Overhead) 7 - Inventory Valuation (Material Overhead) 5 - WIP Valuation (Material) - 10 WIP Valuation (Material Overhead) - 7 Material Overhead Absorption - 5 The re-averaged cost of item A is as follows:
Cost Element Cost Material 9 [(8 + 10)/2] Material Overhead 6 [(5 + 7)/2] The following tables depict the material overhead absorbed at a different rate than the standard rate in the current organization:
Item Cost Element Present Average Cost A Material Overhead - 1 1 A Material Overhead - 2 2 Account Debit Credit Inventory Valuation (Material) 10 - Inventory Valuation (Material Overhead) 7 - Inventory Valuation (Material Overhead) 3 - WIP Valuation (Material) - 10 WIP Valuation (Material Overhead) - 7 Material Overhead Absorption - 3 The re-averaged cost of item A is as follows:
Cost Element Cost Material 9 [(8 + 10)/2] Material Overhead 5 [(7 + 3)/2] The following table displays distributions, at assembly completion, if the material overhead absorption rules have been set to NOT earn material overhead.
Account Debit Credit Inventory Valuation (Material) 10 - Inventory Valuation (Material Overhead) 7 - WIP Valuation (Material) - 10 WIP Valuation (Material Overhead) - 7 The re-averaged cost of item A is as follows:
Cost Element Cost Material 9 [(8 + 10)/2] Material Overhead 3.5 [(7 + 0)/2]
Related Topics
Defining Material Overhead Defaults
You can define and update default material overhead subelements and rates. These defaults speed data entry when defining items.
When you define items, these material overheads are defaulted into the Frozen cost type under standard costing, and into the cost type you defined to hold average rates under average costing. See: Defining Cost Types.
For buy items, enter material costs. For make items, roll up costs. You can specify an organization and category default for the same material overhead subelement. When you have multiple defaults for the same subelement, the category default takes precedent over the organization default. If you have two category level defaults, the default that matches the item's planning code takes precedence.
Prerequisites
- You must be in the master cost organization to define material overhead defaults.
To define material overhead defaults
-
Navigate to the Material Overhead Defaults window.
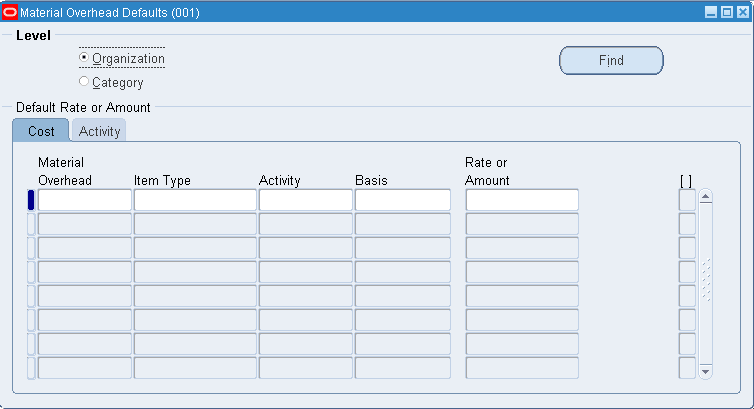
-
Select a default level for the material overhead subelement and rate. The options are by organization or by inventory item category.
-
If you select category as the default level, select an item category. See: Overview of Item Categories, Oracle Inventory User's Guide.
-
In the Cost tabbed region, select a material overhead subelement to assign to the current organization or category.
You can enter a material overhead subelement more than once. For the same material overhead subelement, material overhead rates you assign to a specific category override any material overhead rates you assign to an organization.
-
Select the item type: make items, buy items, or all items.
The system applies the default material overhead based upon an item's planning code. This determines the material overhead subelements and rates for items for items you purchase, manufacture, or for all items.
Within a category or organization, if the value you enter for Item Type matches the item's Make or Buy item attribute, the system uses the material overhead information associated with it instead of the information you enter for the All items value.
-
Select an activity. You can associate the subelement with any activity.
The default is derived from the default activity you assigned when you defined material overhead. See: Defining Overhead.
-
Select a basis. The default is the value you entered for the default basis when you defined overhead.
Activity: Directly associate the activity cost with the item.
Item: Assign a fixed cost per item.
Lot: Assign a lot charge to items and operations.
Resource units: Charge overhead by multiplying the overhead amount by the number of resource units earned in the routing operation.
Resource value: Charge overhead by multiplying the overhead rate by the resource value earned in the routing operation.
Total value: Charge overhead by multiplying the total cost of the item, less material overhead earned at this level, by the material overhead rate.
-
Enter the rate or amount for the material overhead as appropriate for the basis.
Material overhead subelements with basis types of Total value and Resource value are usually defined as rates; those with basis types of Item, Lot, Activity and Resource units are usually defined as amounts.
Note: Negative item costs are not supported in Oracle Cost Management.
-
If you select Activity for the basis, open the Activity tabbed region and:
-
Enter the number of activity occurrences for the current costing period, i.e., the total number of times this activity is performed during the current costing period.
-
Enter the total number of items you expect to be associated with the activity during the current costing period, i.e., the total number of units that flow through the activity during the same period.
-
Related Topics
Defining Items, Oracle Inventory User's Guide and
Defining Item Attribute Controls, Oracle Inventory User's Guide.
Mass Editing Item Accounts
Mass edit account assignments for selected items. These accounts include: Cost of Goods Sold, Encumbrance, Expense, and Sales. You can edit your account assignments for all items, a category of items, or a specific item.
Important: If you share standard costs, you do not share the item accounts. If you need to change your accounts, you must change them in all organizations.
To mass edit item accounts
-
Navigate to the Mass Edit Item Accounts window.
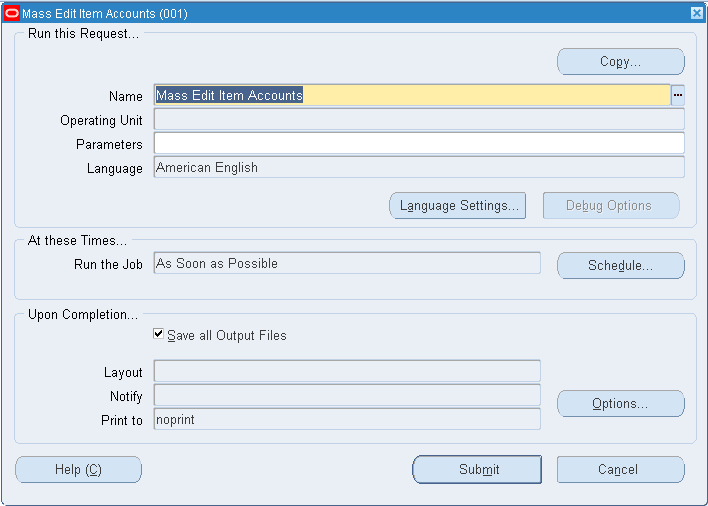
-
In the Parameters window, select which account type to change. The options are Cost of Goods Sold, Encumbrance, Expense, or Sales accounts.
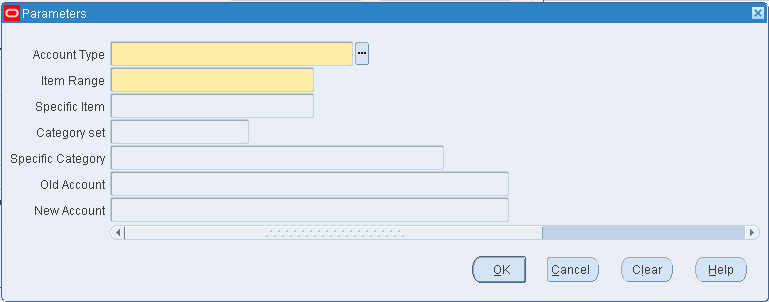
-
Select an item range option. You can edit item accounts for All items, all items in a specific Category, or a Specific item.
-
If you selected Category in the Item Range field, select either a category set or a category. See: Overview of Item Categories, Oracle Inventory User's Guide.
If you selected Specific item in the Item Range field, select an item.
-
Optionally, select the old account for the item. Only these accounts are edited.
For example, if you choose Cost of Goods Sold as your account type, All Items as your item range, and enter 123-456-000000 as the old account, only accounts with this criteria are changed. If you do not specify an old account, all old Cost of Goods Sold accounts for all items are replaced with the account you specify in the New field.
-
Choose OK to save your work.
All items that meet the account type and old account number criteria entered are updated to the new account number.
Related Topics
Standard Request Submission, Oracle Applications User's Guide.
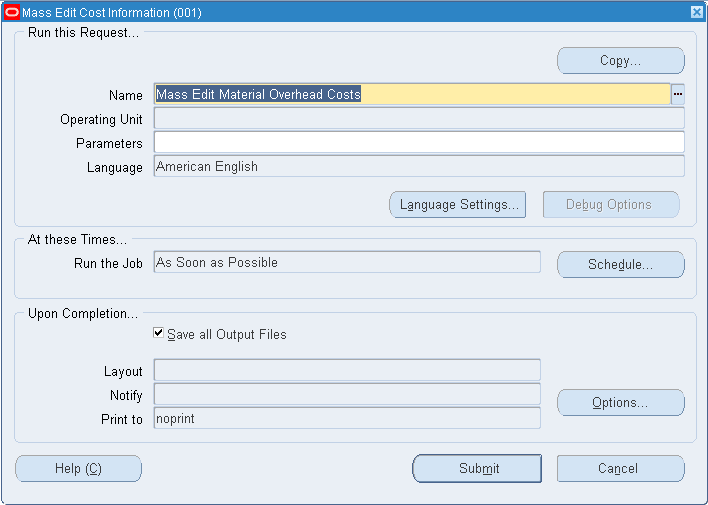
Mass Editing Cost Information
You can apply mass edits to cost information, including:
-
Apply new activity rates to item costs
-
Edit item shrinkage rates to a specified rate or a rate equal to your planning shrinkage rates
-
Create new costs and change costs to a specified amount by a percentage or an absolute amount
-
Create new costs by averaging the purchase order price for open purchase orders or historical purchase order receipts, or actual accounts payable invoice prices for items
Important: You may want to limit mass edits to subelements with similar basis types. All subelements to be edited should be either rate-based or amount-based. The values entered for Fixed Rate and Change Amount fields have drastically different effects on subelement cost, depending on the basis. For example, if you enter 10 for Fixed Rate, the mass edit updates the subelement cost for amount-based subelements to 10 units of your ledger currency. If the subelement has a rate-based type, the mass edit updates the subelement rate to 1000 percent, not 10 percent.
To mass edit cost information
-
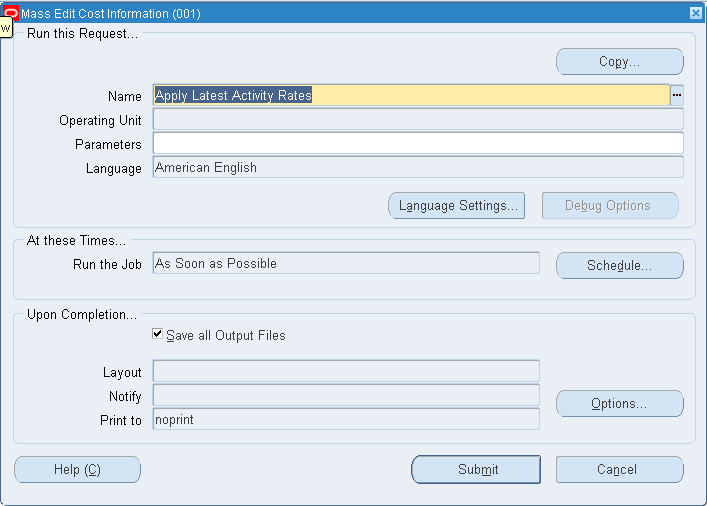
Navigate to the Mass Edit Cost Information window: See: Standard Request Submission, Oracle Applications User's Guide.
-
Select a Request Name.
Apply Latest Activity Rates: Change item costs after modifying activity rates.
Change Cost Shrinkage Rates: Modify the costing shrinkage rates for items. This can be a specific rate or the item's planning shrinkage rate.
Mass Edit Actual Material Costs: Generate costs for items based upon purchasing activity. You can update item costs to be an average of or equal to actual accounts payable invoices, open purchase orders, or historical purchase order receipts for the specified date range.
Mass Edit Material Costs: Update material subelements by a fixed amount or a percentage as appropriate for the basis type.
Mass Edit Material Overhead Costs: Update material overhead subelements by a fixed amount or a percentage, as appropriate for the basis type.
See the instructions below for further information.
To apply latest activity rates to item costs
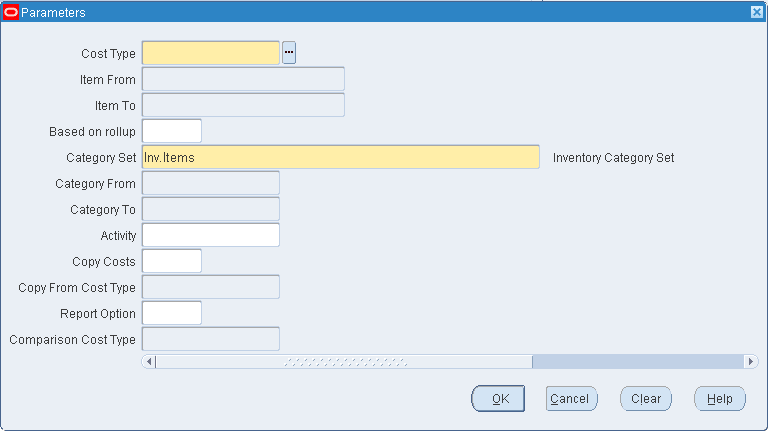
-
Select a cost type.
-
Select a range of Items From and To.
-
Indicate whether to edit only items that have a Based on Rollup attribute set to Yes, only those items that have a Based on Rollup set to No, or leave Based on Rollup blank to indicate all items.
-
Select a Category Set. The default is the category for your costing functional responsibility.
-
Optionally, select a range of Categories From and To.
-
Optionally, select an activity. The new rates are applied to only this activity.
-
Optionally, indicate whether to copy costs from a specific cost type before performing the mass edit. If you set Copy Costs to Yes, specify the cost type to copy costs from.
-
Indicate whether to print a cost type comparison report. If enabled, specify another cost type to compare with the current cost type.
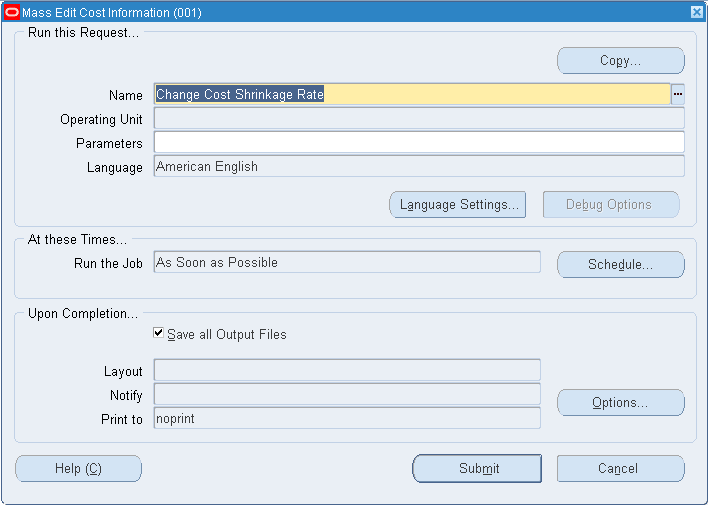
To change the cost shrinkage rate
-
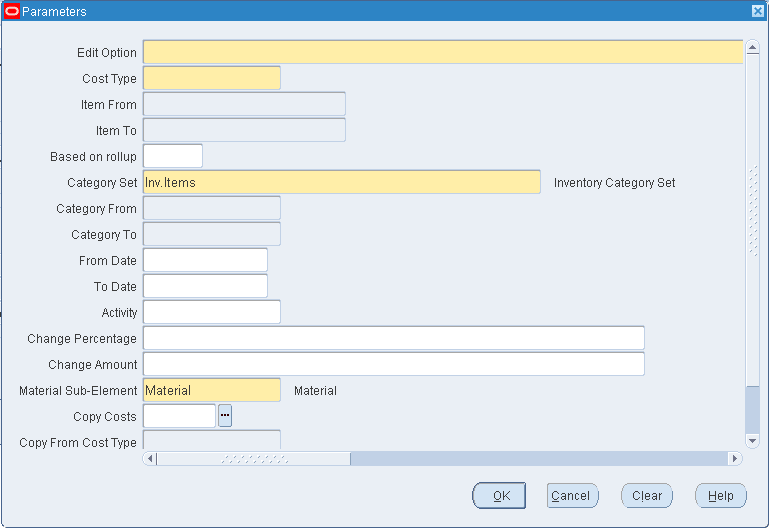
Select an edit option: whether to update the item shrinkage rate to equal the item's planning shrinkage rate or a specified rate.
-
Select a cost type.
-
Select a range of Items From and To.
-
Select a Category Set.
-
Optionally, select a range of Categories From and To.
-
If you selected to update the shrinkage to specified shrinkage, enter the Fixed Rate (as a decimal). This must be less than 1.
-
Optionally, indicate whether to copy costs from a specific cost type before performing the mass edit. If you set Copy Costs to Yes, specify the cost type to copy costs from.
-
Indicate whether to print a cost type comparison report. If enabled, specify the cost type to compare with the current cost type.
To mass edit actual material costs
-
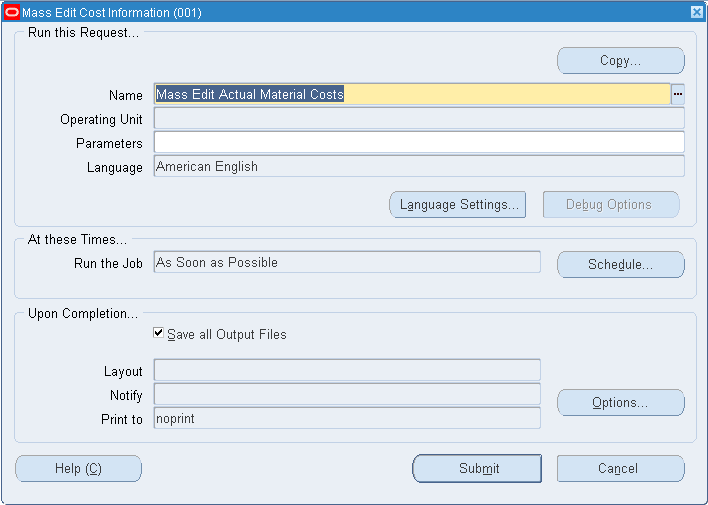
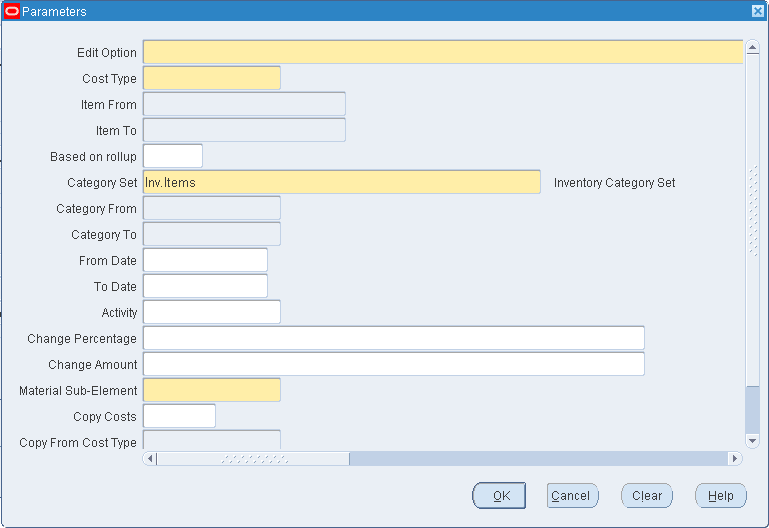
Update material costs to open PO average: This edit uses a hierarchy of dates when determining if the record falls within the specified date range. The hierarchy is as follows: the promised date from the purchase order shipment is used; if this date is not entered, the need-by date from the purchase order shipment is used; and, if this date is not entered, the approval date of the purchase order is used. The approval date always exists, as it is generated by the system upon approval of the purchase order. The mass edit uses only approved purchase orders.
Note: Non-recoverable tax is included in the Open PO Price for the mass edit concurrent program Update Material Costs to Open PO Average.
Update material costs to PO receipt average: This edit uses the transaction date of the purchase order receipt into inventory when determining if the record falls within the specified date range.
Update material costs to invoice cost: This edit uses the accounting date accounts payable used for the invoice posting when determining if the record falls within the specified date range.
-
Select a cost type.
-
Select a range of Items From and To.
-
Indicate whether to edit only items that have a Based on Rollup attribute set to Yes, only those items that have a Based on Rollup set to No, or all items.
-
Select a Category Set.
-
Optionally, select a range of Categories From and To.
-
Optionally, select a date range.
-
Optionally, select an activity.
Only subelements associate with this activity are edited.
-
Optionally, enter an Change Percentage value (expressed as a decimal) by which to increase or decrease the average cost calculated by the mass edit.
For example, if the mass edit calculates an average cost of 100 and you enter a value of 0.10, the resulting cost of the subelement is 110. You can use the Change Percentage field with the Change Amount field.
-
Optionally, enter an Change Amount to increase or decrease the average cost calculated by the mass edit, or change the average cost after it is modified by the amount entered in the Change Percentage field, if appropriate. For example, if the mass edit calculates an average cost of 100 and you enter a value of 0.10 in the Change Percentage field and a value of 10 in this field, the resulting cost of the subelement is 120:
(calculated average cost x (1 + change percentage) + change amount) -
Select a material subelement to limit the mass edit to items associated with a specific material subelement.
This subelement is also used by the mass edit when it creates new item costs. The default is the organization's default material subelement, if one exists.
-
Optionally, indicate whether to copy costs from a specific cost type before performing the mass edit. If you set Copy Costs to Yes, specify the cost type to copy costs from.
-
Indicate whether to print a cost type comparison report. If enabled, specify the cost type to compare with the current cost type.
To mass edit material costs
-
Select a cost type.
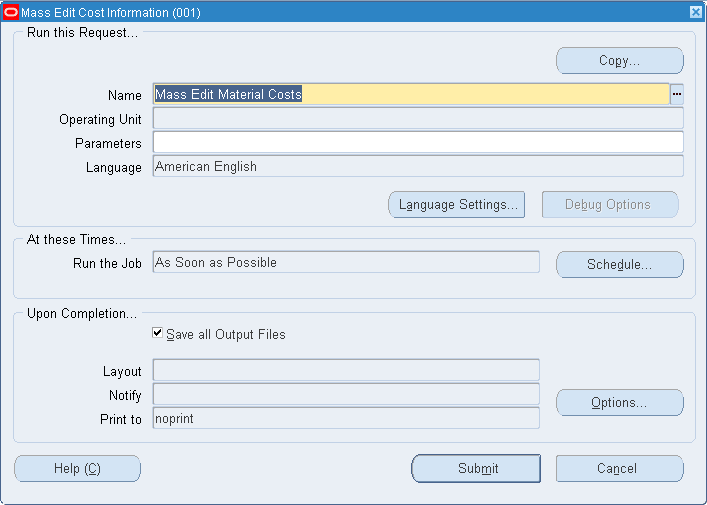
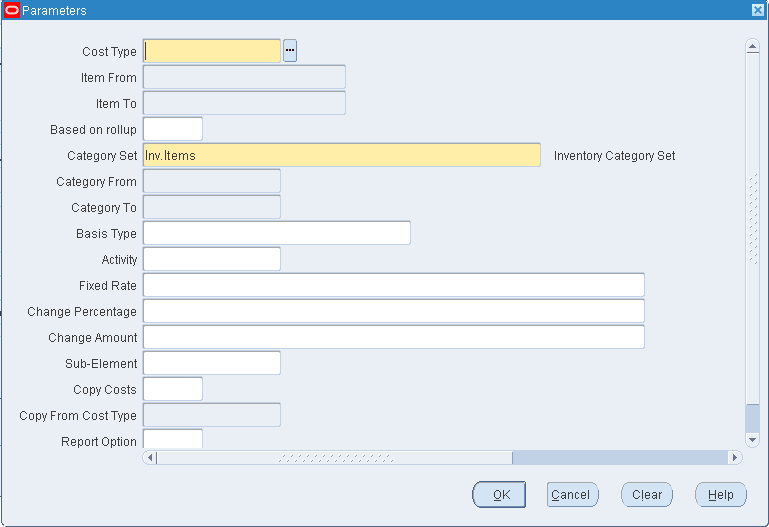
-
Select a range of Items From and To.
-
Indicate whether to edit only items that have a Based on Rollup attribute set to Yes, only those items that have a Based on Rollup set to No, or leave blank to indicate all items.
-
Select a Category Set. The default is the category for your costing functional responsibility.
-
Optionally, select a range of Categories From and To.
-
Optionally, select a basis type by which to limit the mass edit.
-
Optionally, select a specific activity to mass edit only subelements associated with a specific activity.
-
Optionally, select a value to change the current subelement amount to a new fixed amount.
You can use this value with the Change Percentage and/or the Change Amount fields.
Leave this field blank to have the current subelement amount modified by the values entered in the Change Percentage and/or the Change Amount fields.
-
Optionally, enter an Change Percentage (positive or negative) by which to increase or decrease the subelement amount.
The Fixed value, if not blank, is multiplied by the Change Percentage value. If the Fixed field is blank, the current subelement amount is multiplied by the Change Percentage.
For example, if the value for Fixed is 200 and the value for Change Percentage is -5, the resulting cost of the subelement is 190:
fixed or current amount x (1 + (change percentage / 100)) -
Optionally, enter an Change Amount by which to increase or decrease the subelement amount by a fixed amount.
For example, the subelement amount before this update is 25, and you enter 10 in the Change Amount field, the new amount for the subelement is 35.
A Change Amount can also be used with an Change Percentage to increase or decrease the subelement cost after it is modified by the amount entered in the Change Percentage field. If, the Change Amount is 10 and the Change Percentage is 5, the resulting cost of the subelement is 195:
fixed or current amount x (1 + (change percentage / 100)) + change amount -
Select a material subelement by which to limit the mass edit of items associated with a specific material subelement.
-
Optionally, indicate whether to copy costs from a specific cost type before performing the mass edit. If you set Copy Costs to Yes, specify the cost type to copy costs from.
-
Indicate whether to print a cost type comparison report. If enabled, specify the cost type to compare with the current cost type.
To mass edit material overhead costs
-
Select a cost type.
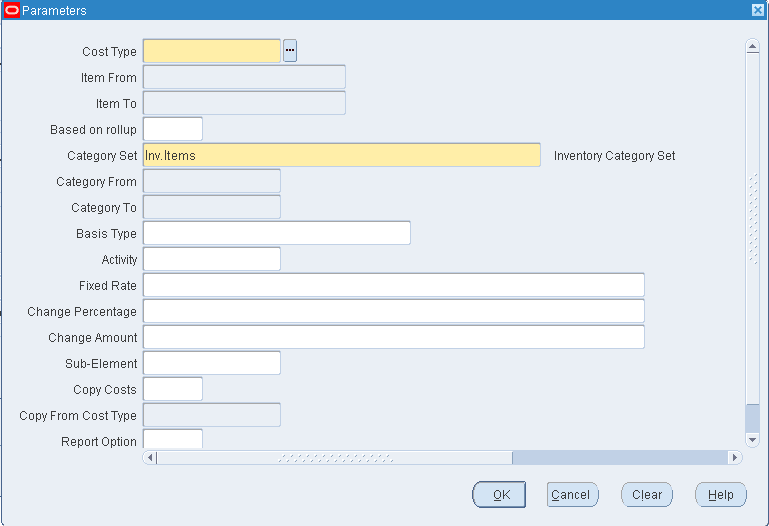
-
Select a range of Items From and To.
-
Indicate whether to edit only items that have a Based on Rollup attribute set to Yes, only those items that have a Based on Rollup set to No, or leave blank to indicate all items.
-
Select a Category Set. The default is the category for your costing functional responsibility.
-
Optionally, select a range of Categories From and To.
-
Optionally, select a basis type by which to limit the mass edit.
-
Optionally, select a specific activity to mass edit only items associated with a specific activity.
-
Optionally, select a value to change the current subelement rate or amount to a new fixed rate or amount.
The system considers this a currency amount if the subelement being updated has a basis type of Item, Lot, or Resource Units. For example, if the ledger currency is U.S. Dollars, 10 = $10. If the subelement basis type is Resource Value or Total Value, the value entered is used as a percentage (for example, 10 = 1000%). You can use this value with the Change Percentage and/or the Change Amount fields.
Leave this field blank to have the current subelement rate or amount modified by the values entered in the Change Percentage and/or the Change Amount fields.
-
Optionally, enter an Change Percentage (positive or negative) by which to increase or decrease the subelement rate or amount.
The Fixed Rate value, if not blank, is multiplied by the Change Percentage value. If the Fixed Rate field is blank, the current subelement rate or amount is multiplied by the Change Percentage. For example, if Fixed Rate is 0.20 and Change Percentage is -10, the resulting rate of the subelement is 0.18:
fixed or current rate or amount x (1 + (increase percentage / 100)) -
Optionally, enter an Change Amount by which to increase or decrease the subelement rate or amount by a fixed amount.
The system uses this value as a currency amount if the subelement being updated has a basis type of Item, Lot, or Resource Units. For example, if the ledger currency is U.S. Dollars, the subelement amount before this update is 25, and you enter 10 in this field, the new amount for the subelement is 35. If the subelement basis type is Resource Value or Total Value, the value you enter is used as a percentage. For example, if the subelement rate before this update is 250% and you enter 0.25, the new rate for the subelement is 275%.
An Change Amount can also be used with an Change Percentage to increase or decrease the subelement cost after it is modified by the amount entered in the Change Percentage field. If, the Change Amount is 10 and the Change Percentage is 5, the resulting cost of the subelement is 195:
fixed or current amount x (1 + (change percentage / 100)) + change amount -
Select a material overhead subelement by which to limit the mass edit of items associated with a specific material overhead subelement.
-
Optionally, indicate whether to copy costs from a specific cost type before performing the mass edit. If you set Copy Costs to Yes, specify the cost type to copy costs from.
-
Indicate whether to print a cost type comparison report. If enabled, specify the cost type to compare with the current cost type.
Related Topics
Standard Request Submission, Oracle Applications User's Guide.
Setting Cost Controls
The Set Cost Controls concurrent program is a mass edit program that lets you set the following fields for item costs in a batch process:
-
Based On Rollup flag
-
Defaulted flag
-
Lot Size
You have the option of manually setting each field value, copying the values from another cost type, or copying from default values from an item definition.
To set Cost Controls
-
From the Cost Mass Edits menu, navigate to the Set Cost Controls concurrent program. The Parameters window appears.
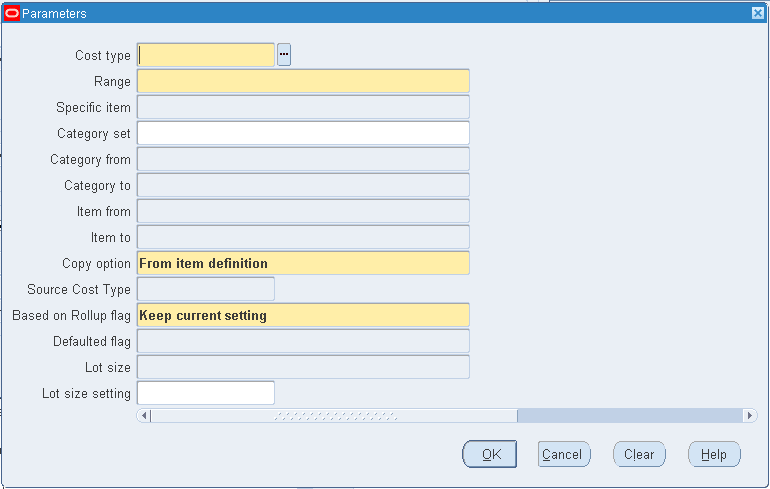
-
Select a Cost Type.
-
Select the Range.
-
Enter the Specific item if you selected Specific item in the Range field.
-
Select a Category Set.
-
Optionally, select a range of Categories From and To.
-
Select a range of Items From and To.
Note: Specific Item, Item From, Item To, Category Set, Category from and Category to are always enabled. You can populate any or all of these fields, but all values will be ignored except for the field(s) matching the Range selection. For example, if you select Range of items for the Range value, then only the values in Item From and Item To will be used to create the item list.
-
Select a Copy option. You can set the Copy Option to 'From item definition' or 'From cost type'.
If you select 'From item definition', then the values for Based on Rollup or Lot size that specify Copy are populated from the item definition of the corresponding organization and item. If you select 'From item definition', then the Defaulted flag cannot specify Copy because this flag is not available in the item definition.
If you select 'From item cost type', then the values for any of the three fields specifying Copy are populated from the item cost that corresponds to the Source Cost Type entered in the next field.
-
If you selected the 'From Cost Type Copy' option, then select a Source Cost Type.
-
Select a value for the Based On Rollup flag. Available values include:
-
Set to Yes
-
Set to No
-
Copy
-
Keep current setting
-
-
Select a value for the Defaulted Flag. Available values include:
-
Set to Yes
-
Set to No
-
Copy (Only available if the Copy option is selected is 'From item cost type')
-
Keep current setting
-
-
Select a value for Lot Size. Available values include:
-
Set to number
-
Copy
-
Keep current setting
-
-
If you selected 'Set to Number' in the Lot Size field, then enter a number in the Lot Size Setting field.
-
If all parameters are entered, then click OK.
-
Click Submit in the Request window to run the request.
Note: Normally, the Based on Rollup flag should only be set to 'No' if the shrinkage rate is zero because purchased items should not have a shrinkage factor, only assembled items. This program allows the flag to be set to 'No' even when a nonzero shrinkage rate exists. If you specify a source for the Based on Rollup field that sets the value to 'No' (either explicitly or by copying), then the program checks the shrinkage rate in the target items. For any record that contains a nonzero shrinkage rate, the program first sets this shrinkage rate to zero, and then updates the Based on Rollup flag to 'No'. It also updates the Usage Rate for the item cost accordingly. It indicates this by setting the concurrent request status to WARNING and a log file displays the details.
The defaulted flag can only be updated to 'Yes' if user-defined (manually-entered) costs do not exist. If you specify a source for the defaulted field that sets it to 'Yes' (either explicitly or by copying), then the program checks for existing user-defined costs. If there are user-defined costs, then the program does not update the defaulted flag. It indicates this by setting the concurrent request status to WARNING and log displays the details.
Copying Costs
You can copy from one cost type to another and specify an item or a category range. You can copy from the Frozen cost type, but you cannot copy to the Frozen cost type. Under average costing, you can copy from the Average cost type, but you cannot copy to the Average cost type. Under FIFO/LIFO costing, you can copy from the FIFO/LIFO cost type, but you cannot copy to the FIFO/LIFO cost type.
In a standard cost, inventory organization, you can perform a standard cost update from the newly copied costs. In average, FIFO, or LIFO cost, inventory organizations, copied costs are generally used for simulations or comparisons only.
You can copy item costs within an organization or across organizations.
Within an organization, you can also copy resource and overhead costs, or resource and overhead associations. There are three copying options:
-
merge and update existing costs
-
copy over new information only
-
remove and replace all cost information
Across organizations, you have the flexibility to create new sub-elements, if required, or summarize the item costs over all sub-elements into a pre-defined, summary sub-element in the destination organization.
You can use interorganizational cost copy to copy item cost information across two different organizations, specifying which items you want to include in the item cost copy.
Interorganizational cost copy supports supply chain cost rollup. Supply chain cost rollup enables you to estimate item costs created within BOM.
Copy Cost Examples: Copy from Cost Type 1 to Cost Type 2
Initial values in Cost Type 1 and Cost Type 2
| Item | From: Cost Type 1 | To: Cost Type 2 |
|---|---|---|
| A | 20 | Does not exist (Null) |
| B | 10 | 50 |
| C | Does not exist (Null) | 30 |
The results for the Merge and Update Existing Costs option are: A = 20, B = 10, and C = 30. Item C did not exist in Cost Type 1, so C's value in Cost Type 2 does not change.
The results for the New Information Only option are: A = 20, B = 50, and C = 30. Item A did not exist in Cost Type 2, so its value is copied from Cost Type 1. Item B has a cost in Cost Type 2, so it's value does not change. Item C did not exist in Cost Type 1, so C's value in Cost Type 2 does not change.
The results for the Remove and Replace All Cost Information option are: A = 20, B = 10, and item C does not exist. These are the same values found in Cost Type 1; all values in Cost Type 1 replace those in Cost Type 2.
Note: You can also use the Supply Chain Cost Rollup to copy costs for based-on rollup items (assemblies). When the assembly does not exist in the Supply Chain Cost type that you roll up, the rollup copies the assembly information from the default cost type.
Note: For costs that are copied across organizations, the based on rollup flag for all copied costs is set as User-Defined.
To copy costs between cost types
-
Navigate to the Copy Cost Information window.
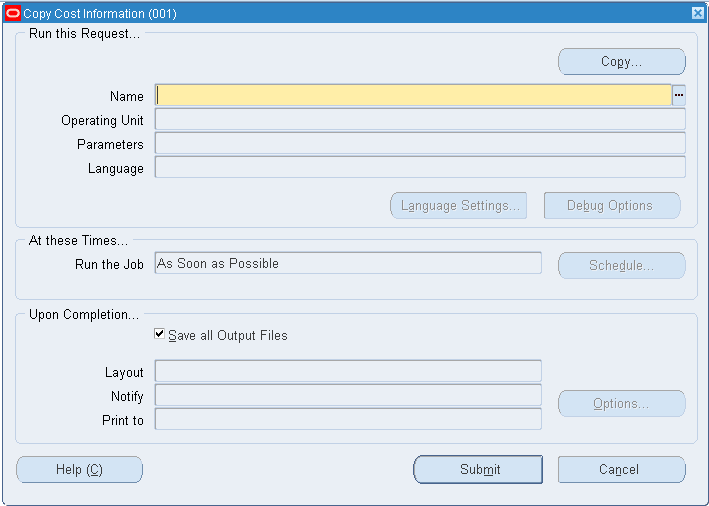
-
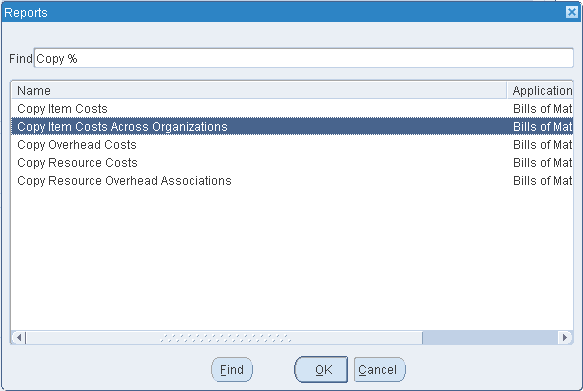
Select the Name of the request. This identifies what to copy:
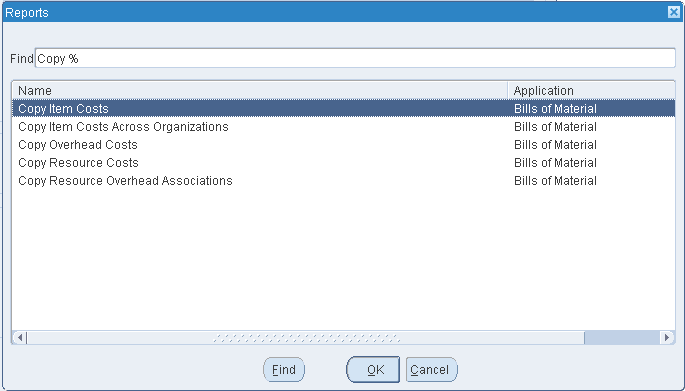
Copy Item Costs: copy item costs between cost types.
Copy Item Costs Across Organizations: copy item costs between organizations to maintain the same standard cost in multiple organizations but not to share costs.
Copy Overhead Costs: copy overhead costs between cost types.
Copy Resource Costs: copy resource costs between cost types.
Copy Resource Overhead Associations: copy resource and overhead associations between cost types.
-
Merge and update existing costs: Costs that do not exist in the To cost type are copied, costs that already exist in the To cost type are updated, costs that exist only in the To cost type are left unchanged. The system compares total costs to determine which costs to update. The system does not compare by sub-element.
New cost information only: Costs that do not exist in the To cost type are copied; all other costs are left unchanged.
Remove and replace all cost information: All costs in the To cost type are deleted and replaced with costs in the From cost type.
-
Select a cost type to copy From.
-
Select a cost type to copy To.
-
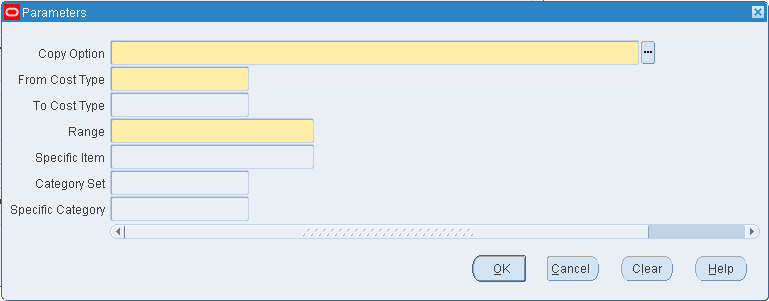
Do one of the following:
-
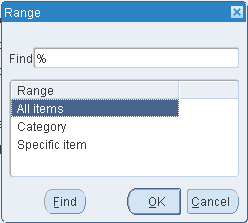
If you are copying item costs between cost types or across organizations, select All Items, those belonging to a Category, or a Specific Item. If you select Category, specify a Category Set or a Specific Category. If you select Specific Item, specify the item.
-
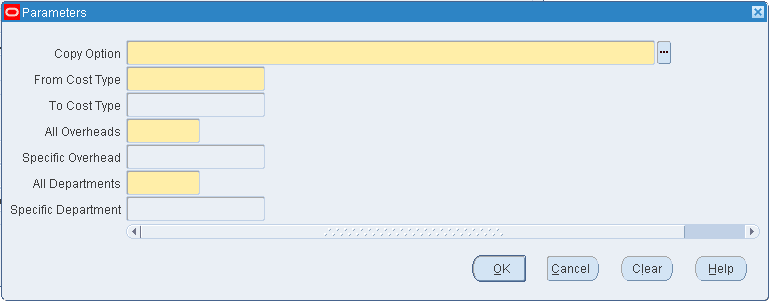
If you are copying overhead costs, indicate whether to copy All Overheads or a Specific Overhead that you enter. Indicate whether to copy All Departments or a Specific Department that you enter.
-
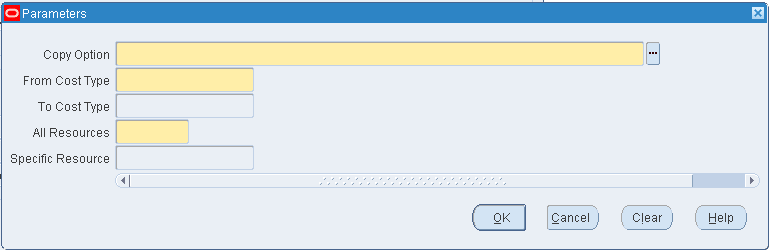
If you are copying resource costs, indicate whether to copy All Resources or a Specific Resource that you enter.
-
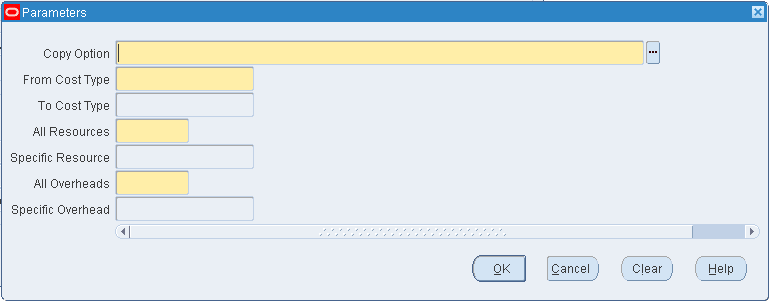
If you are copying resource overhead associations, indicate whether to copy All Resources or a Specific Resource that you select. Indicate whether to copy All Overheads or a Specific Overhead that you select.
-
If you are copying across organizations, select the Name of the request as Copy Item Costs Across Organizations.
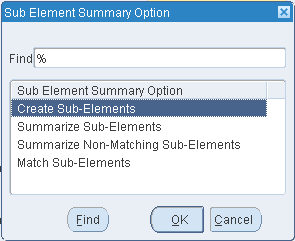
If you are copying across organizations, select a sub-element option from the Sub-Element Summary Option parameter based on the following:
-
Creating new sub-elements
-
Summarizing sub-elements and using a default sub-element
-
Keeping matching sub-elements as is and summarizing unmatched sub-elements
-
Performing a regular cost copy only when all sub-elements match
Note: The Sub-Element Summary Option determines the method of cost copy if matching sub-elements do not exist in the from and to organizations. With this option, costs are summarized within the context of a cost element. The cost copy across organizations process does not enable the total cost to be summarized into a single cost element in the destination organization.
-
If you select the Sub-Element Summary Option as Create Sub-Elements or Match Sub-Elements, the Summary Sub- Elements for material, material overhead, resource, outside processing and overhead are not enabled.
-
If you select the Sub-Element Summary Option as Create Sub-Elements, the system will automatically create missing sub-elements in the destination organization with default accounts from the organization parameters. After saving your newly created sub-elements with default accounts, you can change the accounts that are associated to your sub-elements.
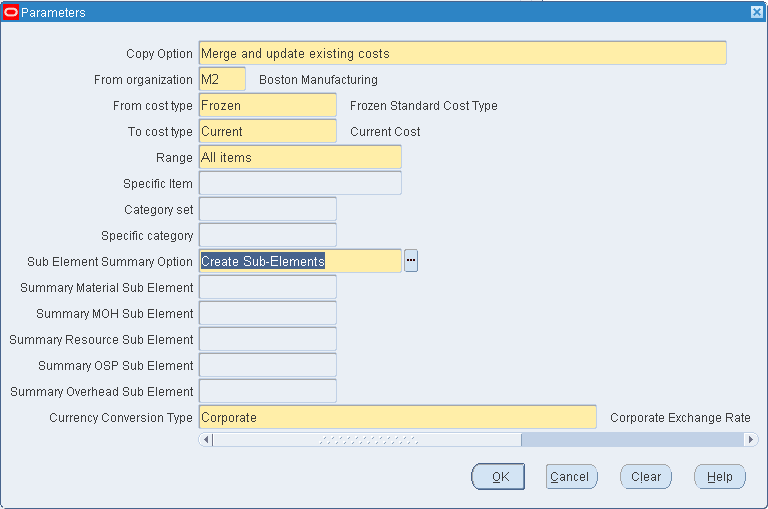
-
If you select the Sub-Element Summary Option as Summarize Sub-Elements or Summarize Non-Matching Sub-Elements, you need to specify the Summary Sub-Elements for material, material overhead, resource, outside processing and overhead. When you Summarize Sub-Elements, the total cost in each cost element will be copied to one sub-element. When you Summarize Non-Matching Sub-Elements, the system summarizes the costs of the non-matching sub-elements into a single sub-element. For each option, the default sub-element is defined with a basis type of Item.
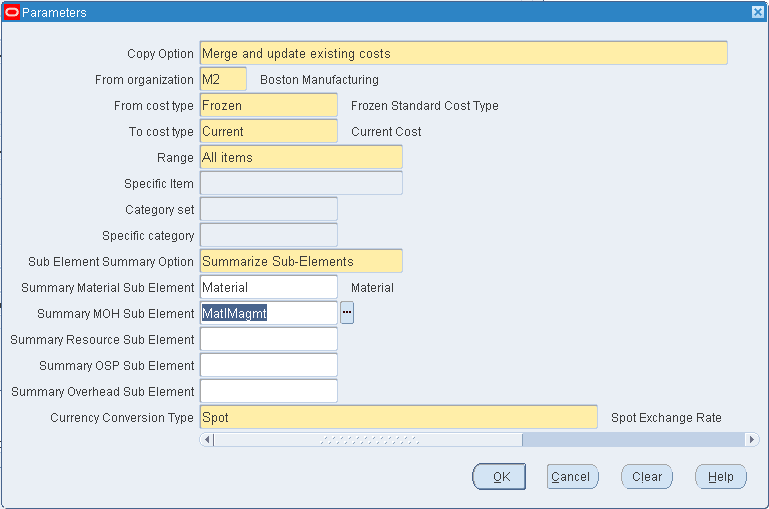
-
Specify the Currency Conversion Type in order to handle currency conversions.
-
Default Basis Types
This basis type is used to determine how the overhead cost is earned and how it is applied to product costs.
| Activity | Used to apply activity costs to items. The activity basis type can only be used with the material overhead subelement. The item cost is calculated by multiplying the activity cost by the ratio of the number of times the activity occurs divided into the cumulative quantity of the item associated with those occurrences. |
| Item (default) | Used to earn and apply costs for all subelements. For material and material overhead subelements, you charge a fixed amount per item. For resource, outside processing, and overhead subelements, you charge a fixed amount per item moved in an operation. |
| Lot | Used to earn and apply costs for all subelements. The item cost is calculated the same as an Item basis cost except that the unit cost is divided by the cost type standard lot size to derive the cost per item. |
| Resource units | Used for material overhead and overhead subelements. For the overhead subelement, you earn and apply a fixed amount of overhead for each resource unit you earn on the operation. For the material overhead subelement, this basis type may be used to apply overhead to an item's product cost. However, these costs are not earned in work in process. |
| Resource value | Used for material overhead and overhead subelements. For the overhead subelement, you earn and apply a percentage of the resource value you earn on the operation as overhead. For the material overhead subelement, this basis type may be used to apply overhead to an item's product cost. However, these costs are not earned in work in process. |
| Total value | Used to earn and apply costs with the material overhead subelement. This cost is applied to product cost and earned as a percentage of the item's total cost less any this level material overhead. For purchased items, the cost is earned when the item is received. For assemblies, the cost is earned when the assembly is completed from a job or schedule. |
Associating Expenditure Types with Cost Elements
Expenditure types are used to classify project-related transaction costs that are collected using the Cost Collector then transferred to Oracle Projects.
You must associate in and out expenditure types with each of the five cost elements so that costs for the following inventory transfer transactions can be collected and transferred to Oracle Projects.
-
Subinventory transfers between locators with different projects or tasks. See: Transferring Between Organizations, Oracle Inventory User's Guide.
-
Miscellaneous issue from a project locator. See: Performing Miscellaneous Transactions, Oracle Inventory User's Guide.
-
Miscellaneous Receipt into a project locator.
-
Project related miscellaneous transactions which issue inventory to, or receive it from, Projects.
In expenditure types are used to cost the value of transfers into a project. Out expenditure types are used to cost the value of transfers out of a project.
To define expenditure types for cost elements
-
Navigate to the Expenditure Types for Cost Elements window.
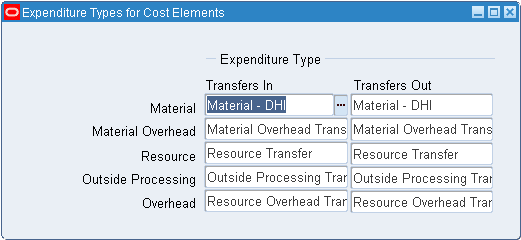
-
Select a Transfer In / Transfer Out Expenditure type for each of the following cost elements:
Material: A general ledger account to accumulate material costs. This is usually an asset account.
Material Overhead: A general ledger account to accumulate material overhead or burden costs. This is usually an asset account.
Resource: A general ledger account to accumulate resource costs. This is usually an asset account.
Outside Processing: A general ledger account to accumulate outside processing costs. This is usually an asset account.
Overhead: A general ledger account to accumulate resource overhead or department overhead costs. This is usually an asset account.
Important: You can choose only Expenditure Types that are not defined as Rate Required in Oracle Projects.
Defining Category Accounts
You can use the Category Accounts Summary window to define, query, and update category valuation and expense accounts. If your current organization is a standard costing organization, you can define category accounts at the category and optionally subinventory level. If your current organization is an average costing organization you must define category accounts at the cost group/category level.
You can only define category accounts for categories that belong to the default category set for the product line functional area. See: Defining Category Sets, Oracle Inventory User's Guide and Defining Default Category Sets, Oracle Inventory User's Guide.
Account Update Restrictions
You cannot update category accounts if any of the restrictions explained in the following table exist:
| Condition Preventing Account Update | Standard Costing Organization | Average Costing Organization |
|---|---|---|
| On hand Quantity > 0 | Quantities exist in the subinventory. Note: If subinventory is null, all subinventories in the organization are considered. | Quantities exist in any locator associated with the cost group |
| Pending Transactions | Pending transactions associated with the subinventory and category exist | Pending transactions associated with the project and cost group exist |
| Uncosted Transactions | Uncosted transactions associated with the subinventory and category exist | Unclosed transactions associated with the cost group exist |
To define or change category accounts in a standard costing organization
-
Navigate to the Category Accounts window. The Find Category Accounts window appears.
-
Choose New to define a new category account. Choose Find to search for an existing record.
You can select a category, or subinventory, or both when searching for records. The Category Accounts Summary window appears.
-
Optionally, select a Subinventory.
If a subinventory is not selected, then you can define accounts that are specific to the category. Once you define a category account with a null subinventory, the accounts that are associated with that category are defaulted each time you define a new category/subinventory combination for that category.
-
Select a Category.
When you select a category, accounts are defaulted from the organization level.
-
Select account numbers for the following:
Note: All subinventories that contain items belonging to the selected category set use these accounts for inventory valuation. You therefore cannot change an account if there is on–hand inventory in any of these subinventories.
Material: A default general ledger account to accumulate material costs for this category/subinventory combination. This is usually an asset account.
Outside Processing: A default general ledger account to accumulate outside processing costs for this category/subinventory combination. This is usually an asset account.
Material Overhead: A default general ledger account to accumulate material overhead or burden costs for this category/subinventory combination. This is usually an asset account.
Overhead: A default general ledger account to accumulate resource or department overhead costs for this for this category/subinventory combination. This is usually an asset account.
Resource: A default general ledger account to accumulate resource costs for this category/subinventory combination. This is usually an asset account.
Encumbrance: A default general ledger account to hold the value of encumbrances against subinventory items belonging to this category set.
Bridging: This account is optional.
You can also optionally enter an Analytical Invoice Price Variance, Analytical Purchase Mirror, Non–Invoiced Sales Order, Non–Invoiced Revenue, Analytical Revenue Mirror, Analytical Margins of Goods Sold, and Average Cost Variance account.
-
Save your work.
Associating WIP Accounting Classes with Categories
In a standard costing organization, you can associate standard discrete and repetitive assembly WIP accounting classes with categories that belong to the default category set for the Product Line Functional area. In an average costing organization, you can create similar associations by associating accounting classes with categories and cost groups.
The defaults defined in this window can be defaulted when you create discrete jobs, associate repetitive assemblies with production lines, and when you perform work order–less completions. See: WIP Accounting Class Defaults, Oracle Work in Process User's Guide.
The category/accounting class associations can be changed as required.
To define default WIP accounting classes for categories in a standard costing organization
-
Navigate to the Default WIP Accounting Classes for Categories window. The Find Default WIP Accounting Classes for Categories window appears.
-
Choose the New button. The Default WIP Accounting Classes for Categories window appears.
-
Select a Category.
You must select a category. You can only select categories that belong to the default category set for the Product Line Functional area.
You cannot enter a duplicate cost group/category combination.
-
Select a Standard Discrete and/or Repetitive Assembly Accounting Class.
You can only select active Standard Discrete and Repetitive Assembly accounting classes. You can optionally associate both a Standard Discrete and Repetitive Assembly accounting class with the same category. See: WIP Accounting Classes, Oracle Work in Process User's Guide.
To define default WIP accounting classes for categories in a average costing organization
-
Navigate to the Default WIP Accounting Classes for Categories window. The Find Default WIP Accounting Classes for Categories window appears.
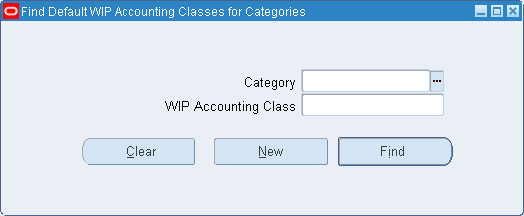
-
Choose the New button. The Default WIP Accounting Classes for Categories window appears.
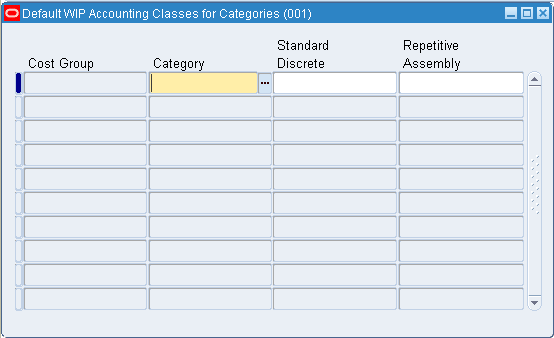
-
Select a Cost Group.
If the Project Cost Collection Enabled parameter in the Organization Parameters window is set, then the cost group specified in the Project Manufacturing parameters window is defaulted but can be overridden. See: Organization Parameters Window, Oracle Inventory User's Guide, and Assigning Project Parameters, Oracle Project Manufacturing User's Guide. If the Project Cost Collection Enabled parameter is not set, then you cannot select a cost group and the organization’s default cost group is used.
-
Select a Category.
You must select a category. You can only select categories that belong to the default category set for the Product Line Functional area.
You cannot enter a duplicate cost group/category combination.
-
Select a Standard Discrete Accounting Class.
You can only select an active Standard Discrete accounting class.
See: WIP Accounting Classes, Oracle Work in Process User's Guide.
-
Save your work.
Project Cost Groups
You can define and subsequently use project cost groups if the Project Cost Collection Enabled parameter in the Organization Parameters window in Oracle Inventory is set. Project cost groups are used to group project related costs.
Organization’s Cost Group
The organization’s default cost group is seeded when you install Cost Management. This is a multiple organization (multi–org) cost group and is used as the default in organizations that have a Costing Method of Average and the CST: Average Costing Option profile option set to Inventory and Work in Process. These organizations do not, however, have to have their Project Cost Collection Enabled parameter set.
The valuation accounts defined in the Organization Parameters window are used for this cost group and cannot be changed or made inactive. However, in an organization that is Project Cost Collection Enabled the name and description of this cost group can be changed.
If you assign a project the organization’s default cost group, then the project is costed at common inventory costs.
User–Defined Cost Groups
A project must be associated with a project cost group. If you do not specifically assign a project to a user–defined cost group, costs for that project are derived using the organization’s default cost group. Project cost groups can have more than one project assigned to them. Project cost groups can be specific to an organization or available in multiple organizations. If a cost group is assigned to projects that are defined in multiple inventory organizations, it must be defined as a multi–org cost group.
Average costs are calculated and held at the cost group level within each inventory organization; since subinventory valuation accounts cannot be defined at a level lower than the level at which average costs are held, value in every locator belonging to a project in a particular cost group is held in that group’s valuation accounts.
Through the use of cost groups, an item may have a different cost in different projects as well as a unique cost in common inventory, all within the same organization. Item costs can apply to a single project if each project belongs to a distinct cost group, or apply to a group of projects if all projects in the group are associated to the same project cost group. Items in common inventory belong to the organization’s default cost group and are costed separately from items in projects.
Defining Project Cost Groups
You can define and subsequently use project cost groups if the Project Cost Collection Enabled parameter in the Organization Parameters window in Oracle Inventory is set. See: Organization Parameters Window, Oracle Inventory User's Guide.
For each project cost group, you must define five elemental subinventory valuation accounts, an average cost variance account, and an encumbrance account. You can use different accounts or the same account for all five elemental accounts.
You do not have to use separate accounts to maintain elemental visibility for project related costs. Cost visibility is maintained at the subelemental level through the use of expenditure types. You can associate WIP accounting classes with a project cost group. This association defines which WIP accounting classes are valid for use with the project or projects belonging to this cost group. By restricting the use of a WIP class to only one cost group, you can avoid commingling Work in Process costs for multiple projects into one set of valuation accounts.
To define project cost groups
-
Navigate to the Cost Groups window.
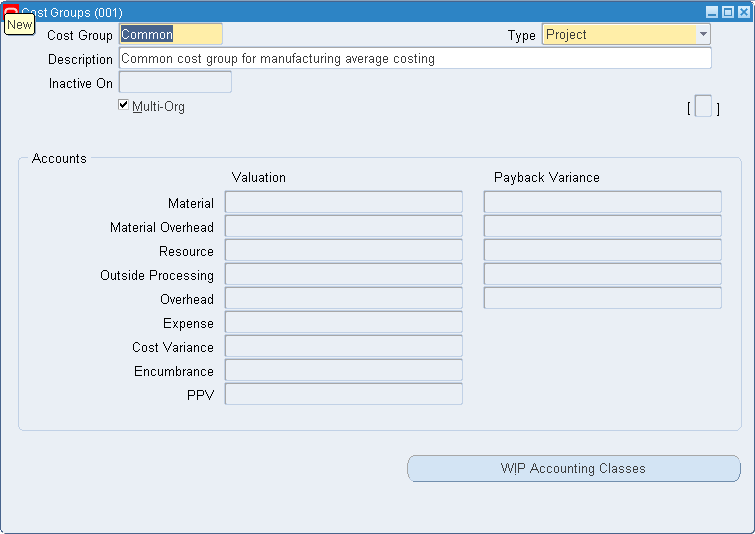
-
Enter an alphanumeric name to identify the Cost Group.
-
Enter a cost group Description.
-
Enter an Inactive On date.
As of this date, you can no longer assign this project cost group to a project, however, you can query and process records that use it. If you do not enter a Inactive On date, the cost group is valid indefinitely.
-
Check Multi–Org to indicate that the cost group name can be shared with other organizations.
Note: If not set to Multi–Org, the cost group is only available to the organization that it is created in. If enabled, only the cost group name is shared across organizations.
If the project cost group is to include projects that are defined in multiple inventory organizations, it must be defined as a multi–org cost group.
-
Enter account numbers:
When you define a cost group for an organization, the accounts defined in the Organization Parameters window appear by default, but you can change them. See: Organization Parameters, Oracle Inventory User's Guide and Defining Costing Information, Oracle Inventory User's Guide See: Organization Parameters, Oracle Inventory User's Guide and Defining Costing Information, Oracle Inventory User's Guide.
You can make changes to the cost group accounts within a given organization if:
-
Material On-hand Quantities contain zero quantity.
-
Cost Quantity Layers (for non-standard costing organizations) contain zero quantity.
-
There are no pending material transactions.
-
There are no uncosted material transactions.
-
Note: Locators that reference projects that belong to a project cost group use these accounts for inventory valuation. You therefore cannot change an account if there is on–hand inventory in any of the following locators:
Material: A general ledger account to accumulate material costs for this cost group. This is usually an asset account.
Material Overhead: A general ledger account to accumulate material overhead or burden costs for this cost group. This is usually an asset account.
Resource: A general ledger account to accumulate resource costs for this cost group. This is usually an asset account.
Outside Processing: A general ledger account to accumulate outside processing costs for this cost group. This is usually an asset account.
Overhead: A general ledger account to accumulate resource overhead or department overhead costs for this cost group. This is usually an asset account.
Average Cost Variance: A general ledger account to accumulate the balances that may occur when transactions are processed for an item whose on–hand inventory is negative. This account represents the inventory valuation error caused by issuing inventory before receiving it.
Encumbrance: A general ledger account to hold the value of encumbrances against subinventory items.
Borrow Payback Variance Account: A general ledger account that is used to track the difference between the current average cost and the original borrowing cost. This account is mandatory.
To associate WIP accounting classes with the cost group
-
Choose the WIP Accounting Classes button. The WIP Accounting Classes for Cost Groups window appears.
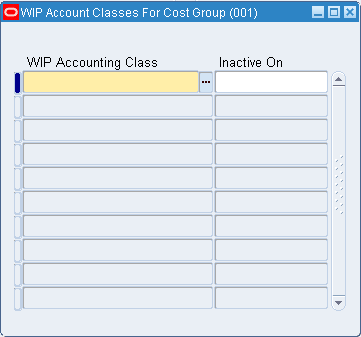
-
Select a WIP Accounting Class.
You can only select any Standard Discrete Accounting Class. See: WIP Accounting Classes, Oracle Work in Process User’s Guide and Defining WIP Accounting Classes, Oracle Work in Process User’s Guide.
-
Save your work.
Profile Options and Security Functions
During implementation the system administrator sets up security functions and profile options.
Profile Options
During implementation, you set a value for each user profile option to specify how Oracle Cost Management controls access to and processes data.
Generally, the system administrator sets and updates profile values. See: Setting User Profile Options, Oracle Applications System Administrator's Guide.
Implementing Profile Options Summary
The table below indicates whether you (the User) can view or update the profile option and at which System Administrator levels the profile options can be updated: at the user, responsibility, application, or site levels.
A Required profile option requires you to provide a value. An Optional profile option already provides a default value, so you only need to change it if you do not want to accept the default.
| User | Sys Admin | Sys Admin | Sys Admin | Sys Admin | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Profile Option | User | User | Resp | App | Site | Required | Default Value |
| CST: Accrual Age In Days | - | - | Yes | - | Yes | No | Last Activity Date |
| CST: Allow Early Inventory Period | - | - | - | - | Yes | No | No |
| CST: Category Accounts Definition Level | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | Yes | No | Subinventory |
| CST: Cost Rollup - Include Phantom's This Level Material/MOH Costs | - | 0 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| CST: Cost Rollup – Wait For Table Locks | - | - | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | None |
| CST: Cost Update Debug Level | 0 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | None |
| CST:Exchange Rate Type | - | - | - | - | Yes | Yes | None |
| CST: Item Category for Inflation Adjustment Columbia Only | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| CST: Item Category Set for Inflation Adjustment Columbia Only | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| CST: Maintain Cost Privilege | - | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| CST: Mark Zero Cost Records As Error During Cost Collection | - | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| CST: Period Summary | - | - | - | - | Yes | No | Automatic |
| CST: Price Index for Inflation Adjustment Columbia Only | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| CST: Transfer Pricing Option | - | - | - | - | Yes | No | No |
| CST: View Cost Privilege | - | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | None |
| Yes | You can update the profile option |
| - | You can view the profile option value but you cannot change it. |
| 0 | You cannot view or change the profile option value. |
CST: Accrual Age In Days
Indicates whether to use the last receipt date or last activity date for age in days calculation.
Last Activity Date: A PO distribution's age in days is determined by the last invoice date or last receipt date, whichever occurs at last.
Last Receipt Date: A PO distribution's age in days is always determined by the last receipt date.
CST: Allow Early Inventory Period Close
This profile option determines whether an inventory accounting period can be to closed earlier than the period end date specified.
Yes: The period is allowed to be closed earlier than the period end date.
No: The period is not allowed to be closed earlier than the period end date.
CST: Category Accounts Definition Level
Indicates the definition level for category accounts.
Subinventy: The category accounts are defined at subinventory level.
Cost Group: The category accounts are defined at cost group level.
CST: Cost Rollup - Include Phantom's This Level Material/MOH Costs
This profile option determines if a phantom subassembly's this level material and material overhead cost should be rolled up into final assembly's cost.
Yes: The phantom subassembly's this level material and material overhead cost will be rolled up into final assembly's cost.
No: The phantom subassembly's this level material and material overhead cost will not be rolled up into final assembly's cost.
CST: Cost Rollup – Wait For Table Lock
Indicates whether the cost rollup waits until the desired information in Cost Management tables is available:
Yes: The program will continually attempt to lock the tables.
No: The program tries 10 attempts to lock tables before ending rollup request.
CST: Cost Update Debug Level
Indicates none or the level and type of debug messages to print in the cost update log file.
Regular: Every subroutine.
Extended: Every SQL statement.
Full: Same as Extended and keeps any temporary data in the database.
CST: Exchange Rate Type
Indicates how to convert foreign currency. The options are period average rate or period end rate.
This profile is also used to control the exchange rate type used for the Margin Analysis Report, the Material Distribution Report, and the WIP Distribution Report. When entering a foreign exchange rate for one of these reports, you must specify the exchange rate type. For reporting profit and loss results, different countries use different financial standards. For example, U.S. companies convert using the period average rate, and Australian companies use the period end rate.
CST: Item Category for Inflation Adjustment
Ignore this unless you are using the Colombia responsibility.
See: Oracle Financials for Colombia User’s Guide.
CST: Item Category Sets for Inflation Adjustment
Ignore this unless you are using the Colombia responsibility.
See: Oracle Financials for Colombia User’s Guide.
CST: Maintain Cost Privilege
This profile option is used in the security function when you define, update, or delete cost information. The profile option must be set to Yes to submit the Purge Standard Cost Update History concurrent program.
Yes: Profile option is enabled.
No: Profile option is disabled.
CST: Mark Zero Cost Records As Error During Cost Collection
Transactions with zero actual cost that are not reported to Oracle Projects are flagged with an error status by the Cost Collection Manager based on the value set for the profile option CST: Mark Zero Cost Records As Error During Cost Collection. Zero cost transactions are flagged with an error when this profile value is set to 'Yes'.
CST:Period Summary
This profile option is used to indicate if period summarization is performed when the closing an accounting period using the Inventory Accounting Periods window. The values are:
Automatic: Period summarization process is performed automatically when the period is closed. The status of the period becomes Closed after the summarization process is completed. This is the default value.
Manual: When a period is closed, the period summarization process is not automatically launched. The status of the period is Closed not Summarized. You must run the Period Close Reconciliation report if you want to calulate summarization data -and at that point the status becomes Closed.
See: Period Summarization Process and Period Close Reconciliation Report.
CST: Price Index for Inflation Adjustment
Ignore this unless you are using the Colombia responsibility.
See: Oracle Financials for Colombia User’s Guide.
CST: Transfer Pricing Option
This profile option is used to enable transfer price functionality for intercompany accounting. See: Transfer Price Costing Your choices are:
No: Transfer price costing is disabled. This is the default value.
Yes, Price Not As Incoming Cost: The incoming cost to the receiving organization is the shipping organization’s inventory cost.
Yes, Price As Incoming Cost: The incoming cost to the receiving organization is based on the transfer price.
Note: For intercompany transfers between process and discrete inventory organizations, the incoming cost of an item is equal to its defined transfer price. This cost rule applies regardless of the value specified in the profile option CST: Transfer Pricing Option. The cost processor always assumes a profile option value of ‘Yes, Transfer Price as Incoming Cost’. Profile option values of No or Yes, Price Not as Incoming Cost are ignored in these transfers.
CST: View Cost Privilege
This profile option determines whether certain costing reports indicate display cost information.
Related Topics
Setting User Profile Options, Oracle Applications User's Guide
Profile Options in Oracle Application Object Library, Oracle Applications User's Guide
Landed Cost Management (LCM)
Landed Cost Management (LCM) is enabled at the Organization level.
To enable Landed Cost Management at the Organization level
-
Navigate to the Organizations window:
Inventory > Setup > Organization > Parameters
-
Select the Landed Cost Management Enabled check box.
-
Navigate to the Organizations window, Other Accounts tab:
Inventory > Setup > Organization > Parameters > Other Accounts (T)
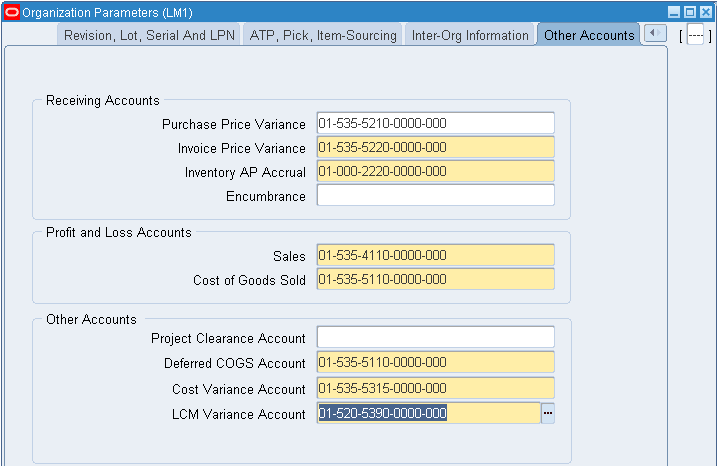
-
Enter the Landed Cost variance account.
Note: Oracle Logistics is responsible for making changes. Oracle Costing uses this window to enable LCM and use the landed cost variance account for the accounting entries.
-
Save your work.
To set up Purchase Order Receiving Options
-
Navigate to the Receiving Options window:
Inventory > Setup > Receiving > Receiving
-
Set up the Landed Cost Absorption account.
Note: Logistics is responsible for making changes. Oracle Costing uses this window to enable LCM.
-
Save your work.
Cost Management Security Functions
Security function options specify how Oracle Cost Management controls access to and processes data. The system administrator sets up and maintains security functions.
Privilege to View Cost (CST_VIEW_COST_INFORMATION)
Determines whether the privilege to view costing information can be prohibited from the following windows:
-
Resources (in Bills of Material)
-
Departments (in Bills of Material)
-
Indented Bills of Material (in Bills of Material and Engineering)
Note: By leaving the Privilege to View Cost security function as part of a user’s responsibility, but excluding the Privilege to Maintain Cost function, you can allow the user to print reports but not change any stored costs.
Privilege to Maintain Cost (CST_MAINTAIN_COST_INFORMATION)
Determines whether the privilege to create, update, or delete costing information can be prohibited from the following windows:
The following windows are governed by this function:
-
Bills of Material (in Bills of Material and Engineering)
-
Routing (in Bills of Material and Engineering)
Note: To use either of the Cost Rollup options where costs are committed to the database, the Privilege to Maintain Cost security function must be included as part of the responsibility.
Cost Group: Maintain (CST_CSTFDCGA_MAINTAIN)
Determines whether the privilege to create, update, or delete cost group information can be prohibited from the Define Cost Group window.
Activities: Maintain (CST_CSTFDATY_MAINTAIN)
Determines whether costing information can be created, updated, or deleted from the Activities window.
Cost Types: Maintain (CST_CSTFDCTP_MAINTAIN)
Determines whether costing information can be created, updated, or deleted from the Cost Types window.
Item Costs: Maintain (CST_CSTFITCT_MAINTAIN)
Determines whether costing information can be created, updated, or deleted from the Item Costs window.
Material Subelements: Maintain (CST_CSTFDMSE_MAINTAIN)
Determines whether costing information can be created, updated, or deleted from the Material Subelements window.
Overheads: Maintain (CST_CSTFDOVH_MAINTAIN)
Determines whether costing information can be created, updated, or deleted from the Overheads window.