Part I Initial Configuration of Trusted Extensions
This section describes how to prepare for running Trusted Extensions. The chapters cover enabling Trusted Extensions and initial setup. For networked systems, initial setup includes configuring LDAP for Trusted Extensions.
Chapter 1, Security Planning for Trusted Extensions describes the security issues that you need to consider when configuring Trusted Extensions software on one or more Solaris systems.
Chapter 2, Configuration Roadmap for Trusted Extensions contains task maps for adding Trusted Extensions software to Solaris systems.
Chapter 3, Adding Solaris Trusted Extensions Software to the Solaris OS (Tasks) provides instructions on preparing a Solaris system for Trusted Extensions software. It also includes instructions on enabling Trusted Extensions.
Chapter 4, Configuring Trusted Extensions (Tasks) provides instructions on configuring Trusted Extensions software on a system with a monitor.
Chapter 5, Configuring LDAP for Trusted Extensions (Tasks) provides instructions on configuring LDAP for Trusted Extensions.
Chapter 6, Configuring a Headless System With Trusted Extensions (Tasks) describes how to configure and administer Trusted Extensions software on a headless system.
Chapter 1 Security Planning for Trusted Extensions
SolarisTM Trusted Extensions implements a portion of your site's security policy in software. This chapter provides an overview of the security and administrative aspects of configuring the software.
Planning for Security in Trusted Extensions
This section outlines the planning that is required before enabling and configuring Trusted Extensions software.
For a checklist of Trusted Extensions configuration tasks, see Appendix B, Configuration Checklist for Trusted Extensions. If you are interested in localizing your site, see For International Customers of Trusted Extensions. If you are interested in running an evaluated configuration, see Understanding Your Site's Security Policy.
Understanding Trusted Extensions
The enabling and configuration of Trusted Extensions involves more than loading executable files, specifying your site's data, and setting configuration variables. Considerable background knowledge is required. Trusted Extensions software provides a labeled environment that is based on the following concepts:
-
Capabilities that in most UNIX® environments are assigned to superuser are available to discrete administrative roles.
-
In addition to UNIX permissions, access to data is controlled by special security tags. These tags are called labels. Labels are assigned to users, processes, and objects, such as data files and directories.
-
The ability to override security policy can be assigned to specific users and applications.
Understanding Your Site's Security Policy
Trusted Extensions effectively enables you to integrate your site's security policy with the Solaris OS. Thus, you need to have a good understanding of the scope of your policy and the ability of Trusted Extensions software to accommodate that policy. A well-planned configuration must provide a balance between consistency with your site security policy and convenience for users who are working on the system.
Trusted Extensions is configured by default to conform with the Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation (ISO/IEC 15408) at Assurance Level EAL4 against the following protection profiles:
-
Labeled Security Protection Profile
-
Controlled Access Protection Profile
-
Role-Based Access Control Protection Profile
To meet these evaluated levels, you must configure LDAP as the naming service. Note that your configuration might no longer conform with the evaluation if you do any of the following:
-
Change the kernel switch settings in the /etc/system file.
-
Turn off auditing or device allocation.
-
Change the default entries in public files in the /usr directory.
For more information, see the Common Criteria web site.
Devising an Administration Strategy for Trusted Extensions
The root user or the System Administrator role is responsible for enabling Solaris Trusted Extensions. You can create roles to divide administrative responsibilities among several functional areas:
-
The security administrator is responsible for security-related tasks, such as setting up and assigning sensitivity labels, configuring auditing, and setting password policy.
-
The system administrator is responsible for the non-security aspects of setup, maintenance, and general administration.
-
The primary administrator is responsible for creating rights profile for the security administrator, and for fixing problems when the security and system administrators do not have sufficient privilege.
-
More limited roles can be configured. For example, an operator could be responsible for backing up files.
As part of your administration strategy, you need to decide the following:
-
Which users are handling which administration responsibilities
-
Which non-administrative users are allowed to run trusted applications, meaning which users are permitted to override security policy, when necessary
-
Which users have access to which groups of data
Devising a Label Strategy
Planning labels requires setting up a hierarchy of sensitivity levels and a categorization of information on your system. The label encodings file contains this type of information for your site. You can use one of the label_encodings files that are supplied on the Solaris Trusted Extensions installation media. You could also modify one of the supplied files, or create a new label_encodings file that is specific to your site. The file must include the Sun-specific local extensions, at least the COLOR NAMES section.
If you are supplying a label_encodings file, you must have the final version of the file ready before rebooting the system after you enable the Trusted Extensions service. The file should be on removable media.
Planning labels also involves planning the label configuration. After enabling the Trusted Extensions service, you need to decide if the system can run at a single label only, or if the system can run at multiple labels. If all of your non-administrative users can operate at the same security label, select a single-label system.
You can also configure whether labels display and which label name format is displayed. For more information, see Solaris Trusted Extensions Label Administration. You can also refer to Compartmented Mode Workstation Labeling: Encodings Format.
For International Customers of Trusted Extensions
When localizing a label_encodings file, international customers must localize the label names only. The administrative label names, ADMIN_HIGH and ADMIN_LOW, must not be localized. All labeled hosts that you contact, from any vendor, must have label names that match the label names in the label_encodings file.
Trusted Extensions supports fewer locales than does the Solaris OS. When you are working in a locale that Trusted Extensions does not support, text that is specific to Trusted Extensions, such as error messages about labels, is not translated into your locale. Solaris software continues to be translated into your locale.
Planning System Hardware and Capacity for Trusted Extensions
System hardware includes the system itself and its attached devices. Such devices include tape drives, microphones, CD-ROM drives, and disk packs. Hardware capacity includes system memory, network interfaces, and disk space.
-
Follow the recommendations for installing a Solaris release, as described in Solaris Express Installation Guide: Planning for Installation and Upgrade. Trusted Extensions features can add to those requirements:
Memory beyond the suggested minimum is required on the following systems:
-
Systems that run the Solaris Management Console, a required administrative GUI
-
Systems that run at more than one sensitivity label
-
Systems that are used by users who can assume an administrative role
-
-
More disk space is required on the following systems:
-
Systems that store files at more than one label
-
Systems whose users can assume an administrative role
-
Planning Your Trusted Network
For assistance in planning network hardware, see Chapter 2, Planning an IPv4 Addressing Scheme (Tasks), in System Administration Guide: IP Services.
As in any client-server network, you need to identify hosts by their function, that is, server or client, and configure the software appropriately. For assistance in planning, see Solaris Express Installation Guide: Custom JumpStart and Advanced Installations.
Trusted Extensions software recognizes two host types, labeled and unlabeled. Each host type has a default security template, as shown in Table 1–1.
Table 1–1 Default Host Templates in Trusted Extensions|
Host Type |
Template Name |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
|
unlabeled |
admin_low |
At initial boot, labels the global zone. After initial boot, identifies hosts that send unlabeled packets. |
|
cipso |
cipso |
Identifies hosts or networks that send CIPSO packets. CIPSO packets are labeled. |
If your network can be reached by other networks, you need to specify accessible domains and hosts. You also need to identify which Trusted Extensions hosts are going to serve as gateways. You need to identify the label accreditation range for these gateways, and the sensitivity label at which data from other hosts can be viewed.
The smtnrhtp(1M) man page provides a complete description of each host type with several examples.
Planning for Zones in Trusted Extensions
Trusted Extensions software is added to the Solaris OS in the global zone. You then configure non-global zones that are labeled. You can create one labeled zone for every unique label, though you do not need to create a zone for every label.
Part of zone configuration is configuring the network. Labeled zones must be configured to communicate with the global zone and with other zones on the network.
-
The X server that runs the desktop display is available only from the global zone. In the Solaris OS, the loopback interface, lo0, can be used to communicate with the global zone. Therefore, the desktop display is available to non-global zones over lo0.
-
By default, non-global zones use the global zone to reach the network. In the Solaris OS, each non-global zone can be configured with a unique default route that does not use the global zone.
Trusted Extensions Zones and Solaris Zones
Labeled zones differ from typical Solaris zones. Labeled zones are primarily used to segregate data. In Trusted Extensions, regular users cannot remotely log in to a labeled zone. The only interactive interface to a labeled zone is by using the zone console. Only root can gain access to the zone console.
Zone Creation in Trusted Extensions
To create a labeled zone involves copying the entire Solaris OS, and then starting the services for the Solaris OS in every zone. The process can be time-consuming. A faster process is to create one zone, then to clone the contents of that zone. The following table describes your options for zone creation in Trusted Extensions.
Planning for Multilevel Access
Typically, printing and NFS are configured as multilevel services. To access multilevel services, a properly configured system requires that every zone be able to access one or more network addresses. The following configurations provide multilevel services:
-
As in the Solaris OS, one IP address is assigned for every zone, including the global zone. A refinement of this configuration is to assign a separate network information card (NIC) to each zone. Such a configuration is used to physically separate the single-label networks that are associated with each NIC.
-
One all-zones address is assigned. One or more zones can have zone-specific addresses.
A system that meets the following two conditions cannot provide multilevel services:
-
One IP address is assigned that the global zone and the labeled zones share.
-
No zone-specific addresses are assigned.
If users in labeled zones are not supposed to have access to a local multilevel printer, and you do not need NFS exports of home directories, then you can assign one IP address to a system that you configure with Trusted Extensions. On such a system, multilevel printing is not supported, and home directories cannot be shared. A typical use of this configuration is on a laptop.
Planning for the LDAP Naming Service in Trusted Extensions
If you are not planning to install a network of labeled systems, then you can skip this section.
If you plan to run Trusted Extensions on a network of systems, use LDAP as the naming service. For Trusted Extensions. a populated Sun JavaTM System Directory Server (LDAP server) is required when you configure a network of systems. If your site has an existing LDAP server, you can populate the server with Trusted Extensions databases. To access the server, you set up an LDAP proxy on a Trusted Extensions system.
If your site does not have an existing LDAP server, you then plan to create an LDAP server on a system that is running Trusted Extensions software. The procedures are described in Chapter 5, Configuring LDAP for Trusted Extensions (Tasks).
Planning for Auditing in Trusted Extensions
By default, auditing is turned on when Trusted Extensions is installed. Therefore, by default, root login and root logout are audited. To audit the users who are configuring the system, you can create roles early in the configuration process. For the procedure, see Creating Roles and Users in Trusted Extensions.
Planning auditing in Trusted Extensions is the same as in the Solaris OS. For details, see Part VII, Solaris Auditing, in System Administration Guide: Security Services. While Trusted Extensions adds classes, events, and audit tokens, the software does not change how auditing is administered. For Trusted Extensions additions to auditing, see Chapter 24, Trusted Extensions Auditing (Overview).
Planning User Security in Trusted Extensions
Trusted Extensions software provides reasonable security defaults for users. These security defaults are listed in the Table 1–2. Where two values are listed, the first value is the default. The security administrator can modify these defaults to reflect the site's security policy. After the security administrator sets the defaults, the system administrator can create all the users, who inherit the established defaults. For descriptions of the keywords and values for these defaults, see the label_encodings(4) and policy.conf(4) man pages.
Table 1–2 Trusted Extensions Security Defaults for User Accounts|
File name |
Keyword |
Value |
|---|---|---|
|
/etc/security/policy.conf |
IDLECMD |
lock | logout |
|
|
IDLETIME |
30 |
|
|
LABELVIEW |
showsl | hidesl |
|
|
CRYPT_ALGORITHMS_ALLOW |
1,2a,md5 |
|
|
CRYPT_DEFAULT |
_unix_ |
|
|
LOCK_AFTER_RETRIES |
no | yes |
|
|
PRIV_DEFAULT |
basic |
|
|
PRIV_LIMIT |
all |
|
|
AUTHS_GRANTED |
solaris.device.cdrw |
|
|
PROFS_GRANTED |
Basic Solaris User |
|
LOCAL DEFINITIONS section of /etc/security/tsol/label_encodings |
Default User Clearance |
CNF NEED TO KNOW |
|
Default User Sensitivity Label |
PUBLIC |
The system administrator can set up a standard user template that sets appropriate system defaults for every user. For example, by default. each user's initial shell is a Bourne shell. The system administrator can set up a template that gives each user a C shell. For more information, see the Solaris Management Console online help for User Accounts.
Devising a Configuration Strategy for Trusted Extensions
Allowing the root user to configure Trusted Extensions software is not a secure strategy. The following describes the configuration strategy from the most secure strategy to the least secure strategy:
-
A two-person team configures the software. The configuration process is audited.
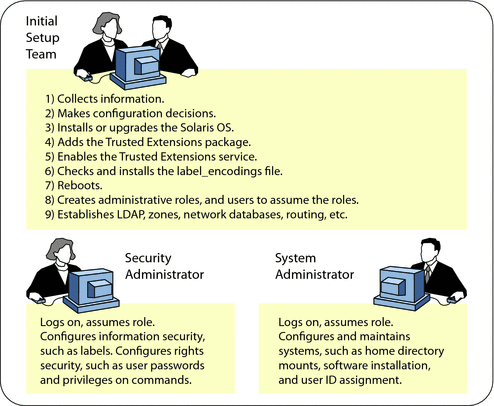
Two people are at the computer when the software is enabled. Early in the configuration process, this team creates local users and roles. The team also sets up auditing to audit events that are executed by roles. After roles are assigned to users, and the computer is rebooted, the software enforces task division by role. The audit trail provides a record of the configuration process. For an illustration of a secure configuration process, see Figure 1–1.
Note –If site security requires separation of duty, a trusted administrator completes Create Rights Profiles That Enforce Separation of Duty before creating users or roles. In this customized configuration, one role manages security, including users' security attributes. The other role manages the non-security attributes of systems and users.
-
One person enables and configures the software by assuming the appropriate role. The configuration process is audited.
Early in the configuration process, the root user creates a local user and roles. This user also sets up auditing to audit events that are executed by roles. Once roles have been assigned to the local user, and the computer is rebooted, the software enforces task division by role. The audit trail provides a record of the configuration process.
-
One person enables and configures the software by assuming the appropriate role. The configuration process is not audited.
By using this strategy, no record is kept of the configuration process.
-
The root user enables and configures the software. The configuration process is audited.
The team sets up auditing to audit every event that root performs during configuration. With this strategy, the team must determine which events to audit. The audit trail does not include the name of the user who is acting as root.
-
The root user enables and configures the software.
Task division by role is shown in the following figure. The security administrator sets up auditing, protects file systems, sets device policy, determines which programs require privilege to run, and protects users, among other tasks. The system administrator shares and mounts file systems, installs software packages, and creates users, among other tasks.
Figure 1–1 Administering a Trusted Extensions System: Task Division by Role
Collecting Information Before Enabling Trusted Extensions
As when configuring the Solaris OS, collect system, user, network, and label information before configuring Trusted Extensions. For details, see Collect System Information Before Enabling Trusted Extensions.
Backing Up the System Before Enabling Trusted Extensions
If your system has files that must be saved, perform a backup before enabling the Trusted Extensions software. The safest way to back up files is to do a level 0 dump. If you do not have a backup procedure in place, see the administrator's guide to your current operating system for instructions.
Note –
If you are migrating from a Trusted Solaris 8 release, you can restore your data only if the Trusted Extensions labels are identical to the Trusted Solaris 8 labels. Because Trusted Extensions does not create multilevel directories, each file and directory on backup media is restored to a zone whose label is identical to the file label in the backup. Backup must be completed before you reboot the system with Trusted Extensions enabled.
Results of Enabling Trusted Extensions From an Administrator's Perspective
After the Trusted Extensions software is enabled and the system is rebooted, the following security features are in place. Many features are configurable by the security administrator.
-
Auditing is enabled.
-
A Sun label_encodings file is installed and configured.
-
A trusted desktop, Solaris Trusted Extensions (GNOME), creates a windowing environment that enables Trusted Path workspaces in the global zone.
-
As in the Solaris OS, rights profiles for roles are defined. As in the Solaris OS, roles are not defined.
To use roles to administer Trusted Extensions, you must create the roles. During configuration, you create the Security Administrator role.
-
Three Trusted Extensions network databases, tnrhdb, tnrhtp, and tnzonecfg are added. The databases are administered by using the Security Templates tool and the Trusted Network Zones tool in the Solaris Management Console.
-
Trusted Extensions provides GUIs to administer the system. Some GUIs are extensions to a Solaris OS GUI.
-
A trusted editor enables administrators to modify local administrative files.
-
The Device Manager manages attached devices.
-
The Solaris Management Console provides Java-based tools to manage local and network administrative databases. The use of these tools is required for managing the trusted network, zones, and users.
-
Chapter 2 Configuration Roadmap for Trusted Extensions
This chapter outlines the tasks for enabling and configuring SolarisTM Trusted Extensions software.
Task Map: Preparing a Solaris System for Trusted Extensions
Ensure that the Solaris OS on which you plan to run Trusted Extensions supports the features of Trusted Extensions that you plan to use. Complete one of the two tasks that are described in the following task map.
|
Task |
For Instructions |
|---|---|
|
Prepare an existing or upgraded Solaris installation for Trusted Extensions. | |
|
Install the Solaris OS with Trusted Extensions features in mind. |
Task Map: Preparing For and Enabling Trusted Extensions
To prepare a Trusted Extensions system before configuring it, complete the tasks that are described in the following task map.
|
Task |
For Instructions |
|---|---|
|
Complete the preparation of your Solaris system. | |
|
Back up your system. |
For a Trusted Solaris 8 system, back up the system as described in the documentation for your release. A labeled backup can be restored to each identically labeled zone. |
|
For a Solaris system, see System Administration Guide: Basic Administration. |
|
|
Gather information and make decisions about your system and your Trusted Extensions network. |
Collecting Information and Making Decisions Before Enabling Trusted Extensions |
|
Enable Trusted Extensions. | |
|
Configure the system. |
For a system with a monitor, see Task Map: Configuring Trusted Extensions. |
|
For a headless system, see Headless System Configuration in Trusted Extensions (Task Map). |
|
|
For a Sun RayTM, see Sun Ray Server Software 4.1 Installation and Configuration Guide for the Solaris Operating System. For the Sun Ray 5 release, see the Sun Ray Server 4.2 and Sun Ray Connector 2.2 Documentation web site. Together, this server and client comprise the Sun Ray 5 package. To configure initial client-server communication, see Configuring Trusted Network Databases (Task Map). |
|
|
For a laptop, go to the OpenSolaris Community: Security web page. Click Trusted Extensions. On the Trusted Extensions page under Laptop Configurations, click Laptop instructions. |
|
|
To prevent networks from communicating with the global zone, configure the vni0 interface. For an example, see the Laptop instructions. In the Solaris OS, you do not need to configure the vni0 interface. By default, the lo0 interface is an all-zones interface. You can make your external connection, dhcp, be an all-zones interface. For instructions, see the Laptop instructions. |
Task Map: Configuring Trusted Extensions
For a secure configuration process, create roles early. The order of tasks when roles configure the system is shown in the following task map.
|
1. Configure the global zone. |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Tasks |
For Instructions |
|
|
Protect machine hardware by requiring a password to change hardware settings. |
Controlling Access to System Hardware in System Administration Guide: Security Services |
|
|
Configure labels. Labels must be configured for your site. If you plan to use the default label_encodings file, you can skip this task. | ||
|
If you are running an IPv6 network, you modify the /etc/system file to enable IP to recognize labeled packets. | ||
|
If the CIPSO Domain of Interpretation (DOI) of your network nodes is different from 1, specify the DOI in the /etc/system file. | ||
|
Boot to activate a labeled environment. Upon login, you are in the global zone. The system's label_encodings file enforces mandatory access control (MAC). | ||
|
Initialize the Solaris Management Console. This GUI is used to label zones, among other tasks. |
Initialize the Solaris Management Console Server in Trusted Extensions |
|
|
Create the Security Administrator role and other roles that you plan to use locally. You create these roles just as you would create them in the Solaris OS. You can delay this task until the end. For the consequences, see Devising a Configuration Strategy for Trusted Extensions. | ||
Skip the next set of tasks if you are using local files administer the system.
|
2. Configure a naming service. |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Tasks |
For Instructions |
|
|
If you plan to use files to administer Trusted Extensions, you can skip the following tasks. |
No configuration is required for the files naming service. |
|
|
If you have an existing Sun JavaTM System Directory Server (LDAP server), add Trusted Extensions databases to the server. Then make your first Trusted Extensions system a proxy of the LDAP server. If you do not have an LDAP server, then configure your first system as the server. | ||
|
Manually set up an LDAP toolbox for the Solaris Management Console. The toolbox can be used to modify Trusted Extensions attributes on network objects. |
Configuring the Solaris Management Console for LDAP (Task Map) |
|
|
For systems that are not the LDAP server or proxy server, make them an LDAP client. | ||
|
In the LDAP scope, create the Security Administrator role and other roles that you plan to use. You can delay this task until the end. For the consequences, see Devising a Configuration Strategy for Trusted Extensions. | ||
|
3. Create labeled zones. |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Tasks |
For Instructions |
|
|
Run the txzonemgr command. Follow the menus to configure the network interfaces, then create and customize the first labeled zone. Then, clone the rest of the zones. | ||
|
(Optional) After all zones are successfully customized, add zone-specific network addresses and default routing to the labeled zones. | ||
The following tasks might be necessary in your environment.
|
4. Complete system setup. |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Tasks |
For Instructions |
|
|
Identify additional remote hosts that require a label, one or more multilevel ports, or a different control message policy. | ||
|
Create a multilevel home directory server, then automount the installed zones. | ||
|
Configure auditing, mount file systems, and perform other tasks before enabling users to log in to the system. | ||
|
Add users from an NIS environment to your LDAP server. | ||
|
Add a host and its labeled zones to the LDAP server. | ||
Chapter 3 Adding Solaris Trusted Extensions Software to the Solaris OS (Tasks)
This chapter describes how to prepare the Solaris OS for Solaris Trusted Extensions software. This chapter also describes the information you need before enabling Trusted Extensions. Instructions on how to enable Trusted Extensions is also provided.
-
Installing or Upgrading the Solaris OS for Trusted Extensions
-
Collecting Information and Making Decisions Before Enabling Trusted Extensions
Initial Setup Team Responsibilities
Trusted Extensions software is designed to be enabled and configured by two people with distinct responsibilities. However, the Solaris installation program does not enforce this two-role task division. Instead, task division is enforced by roles. Because roles and users are not created until after installation, it is a good practice to have an initial setup team of at least two people present to enable and configure Trusted Extensions software.
Installing or Upgrading the Solaris OS for Trusted Extensions
The choice of Solaris installation options can affect the use and security of Trusted Extensions:
-
To properly support Trusted Extensions, you must install the underlying Solaris OS securely. For Solaris installation choices that affect Trusted Extensions, see Install a Solaris System to Support Trusted Extensions.
-
If you have been using the Solaris OS, check your current configuration against the requirements for Trusted Extensions. For configuration choices that affect Trusted Extensions, see Prepare an Installed Solaris System for Trusted Extensions.
 Install a Solaris System to Support Trusted Extensions
Install a Solaris System to Support Trusted Extensions
This task applies to fresh installations of the Solaris OS. If you are upgrading, see Prepare an Installed Solaris System for Trusted Extensions.
Install the Trusted Extensions Package After upgrading to the latest Dev release, and rebooting the system, open the Package Manager again to get the Trusted Extensions package. Enter trusted in the Search text area to get a list of Trusted Extensions packages. Select trusted-extensions . Then select Install/Update. There is also a new trusted-nonglobal package which enumerates the initial set of packages required in a labeled brand zone to run the Trusted Desktop. This will be retrieved from the repository when you install your first zone.
-
When installing the Solaris OS, create a user account and the root role account.
In Trusted Extensions, you use the root role to configure the system.
-
Assign a different password to each account.
-
After the default installation of OpenSolaris 2010.03 is completed, start the Package Manager.
-
Install the Trusted Extensions package.
-
For list of Trusted Extensions packages, type trusted in the Search text area.
-
Select trusted-extensions.
-
Select Install/Update.
The correct packages are installed on your system.
-
 Prepare an Installed Solaris System for Trusted Extensions
Prepare an Installed Solaris System for Trusted Extensions
This task applies to Solaris systems that have been in use, and on which you plan to run Trusted Extensions. Also, to run Trusted Extensions on an upgraded Solaris system, follow this procedure. Other tasks that might modify an installed Solaris system can be done during Trusted Extensions configuration.
Before You Begin
Trusted Extensions cannot be enabled in some Solaris environments:
-
If your system is part of a cluster, Trusted Extensions cannot be enabled on the system.
-
The enabling of Trusted Extensions in an alternate boot environment (BE) is not supported. Trusted Extensions can only be enabled in the current boot environment.
-
If non-global zones are installed on your system, remove them.
Trusted Extensions use branded zones.
-
If your system does not have a root password, create one.
Administration tools in Trusted Extensions require passwords. If the root user does not have a password, then root cannot configure the system.
Use the default crypt_unix password encryption method for the root user. For details, see Managing Password Information in System Administration Guide: Security Services.
Note –Users must not disclose their passwords to another person, as that person might then have access to the data of the user and will not be uniquely identified or accountable. Note that disclosure can be direct, through the user deliberately disclosing her/his password to another person, or indirect, for example, through writing it down, or choosing an insecure password. The Solaris OS provides protection against insecure passwords, but cannot prevent a user from disclosing her or his password, or from writing it down.
-
If you have created an xorg.conf file, you need to modify it.
Add the following line to the end of the Module section in the /etc/X11/xorg.conf file.
load "xtsol"
Note –By default, the xorg.conf file does not exist. Do nothing if this file does not exist.
-
(Optional) Dedicate a partition for audit files.
Trusted Extensions enables auditing by default. For audit files, best practice is to create a dedicated partition.
Collecting Information and Making Decisions Before Enabling Trusted Extensions
For each system on which Solaris Trusted Extensions is going to be configured, you need to know some information, and make some decisions about configuration. For example, because you are going to create labeled zones, you might want to set aside disk space where the zones can be cloned as a Solaris ZFSTM File System. Solaris ZFS provides additional isolation for the zones.
 Collect System Information Before Enabling Trusted Extensions
Collect System Information Before Enabling Trusted Extensions
-
Determine the system's main hostname and IP address.
If you are using DHCP, skip this step.
The hostname is the name of the host on the network, and is the global zone. On a Solaris system, the getent command returns the hostname, as in:
# getent hosts machine1 192.168.0.11 machine1
-
Determine the IP address assignments for labeled zones.
If you are using DHCP, skip this step.
A system with two IP addresses can function as a multilevel server. A system with one IP address must have access to a multilevel server in order to print or perform multilevel tasks. For a discussion of IP address options, see Planning for Multilevel Access.
Most systems require a second IP address for the labeled zones. For example, the following is a host with a second IP address for labeled zones:
# getent hosts machine1-zones 192.168.0.12 machine1-zones
-
Collect LDAP configuration information.
For the LDAP server that is running Trusted Extensions software, you need the following information:
-
The name of the Trusted Extensions domain that the LDAP server serves
-
The IP address of the LDAP server
-
The LDAP profile name that will be loaded
For an LDAP proxy server, you also need the password for the LDAP proxy.
-
 Make System and Security Decisions Before Enabling Trusted Extensions
Make System and Security Decisions Before Enabling Trusted Extensions
For each system on which Solaris Trusted Extensions is going to be configured, make these configuration decisions before enabling the software.
-
Decide how securely the system hardware needs to be protected.
At a secure site, this step has been done for every installed Solaris system.
-
For SPARC systems, a PROM security level and password has been provided.
-
For x86 systems, the BIOS is protected.
-
On all systems, root is protected with a password.
-
-
Prepare your label_encodings file.
If you have a site-specific label_encodings file, the file must be checked and installed before other configuration tasks can be started. If your site does not have a label_encodings file, you can use the default file that Sun supplies. Sun also supplies other label_encodings files, which you can find in the /etc/security/tsol directory. The Sun files are demonstration files. They might not be suitable for production systems.
To customize a file for your site, see Solaris Trusted Extensions Label Administration.
-
From the list of labels in your label_encodings file, make a list of the labeled zones that you need to create.
For the default label_encodings file, the labels are the following, and the zone names can be similar to the following:
Label
Zone Name
PUBLIC
public
CONFIDENTIAL : INTERNAL
internal
CONFIDENTIAL : NEED TO KNOW
needtoknow
CONFIDENTIAL : RESTRICTED
restricted
For ease of NFS mounting, the zone name of a particular label must be identical on every system. Some systems, such as multilevel print servers, do not need to have labeled zones installed. However, if you do install labeled zones on a print server, the zone names must be identical to the zone names of other systems on your network.
-
Decide when to create roles.
Your site's security policy can require you to administer Trusted Extensions by assuming a role. If so, or if you are configuring the system to satisfy criteria for an evaluated configuration, you must create roles early in the configuration process.
If you are not required to configure the system by using roles, you can choose to configure the system as superuser. This method of configuration is less secure. Audit records do not indicate which user was superuser during configuration. Superuser can perform all tasks on the system, while a role can perform a more limited set of tasks. Therefore, configuration is more controlled when being performed by roles.
-
Choose a zone creation method.
You can create zones from scratch or clone zones. These methods differ in speed of creation. For the trade-offs, see Planning for Zones in Trusted Extensions.
-
Plan your LDAP configuration.
Using local files for administration is practical for non-networked systems.
LDAP is the naming service for a networked environment. A populated LDAP server is required when you configure several machines.
-
If you have an existing Sun JavaTM System Directory Server (LDAP server), you can create an LDAP proxy server on a system that is running Trusted Extensions. The multilevel proxy server handles communications with the unlabeled LDAP server.
-
If you do not have an LDAP server, you can configure a system that runs Trusted Extensions software as a multilevel LDAP server.
-
-
Decide other security issues for each system and for the network.
For example, you might want to consider the following security issues:
-
Determine which devices can be attached to the system and allocated for use.
-
Identify which printers at what labels are accessible from the system.
-
Identify any systems that have a limited label range, such as a gateway system or a public kiosk.
-
Identify which labeled systems can communicate with particular unlabeled systems.
-
Enabling the Solaris Trusted Extensions Service
In the Solaris OS, Solaris Trusted Extensions is a service that is managed by the service management facility (SMF). The name of the service is svc:/system/labeld:default. By default, the labeld service is disabled.
 Enable Solaris Trusted Extensions
Enable Solaris Trusted Extensions
The labeld service attaches labels to communications endpoints. For example, the following are labeled:
-
All zones and the directories and files within each zone
-
All processes including window processes
-
All network communications
Before You Begin
You have completed the tasks in Installing or Upgrading the Solaris OS for Trusted Extensions and Collecting Information and Making Decisions Before Enabling Trusted Extensions.
-
Open a terminal window and enable the labeld service.
# svcadm enable -s labeld
The labeld service adds labels to the system and starts the Solaris auditing service and device allocation. Do not perform other tasks until the cursor returns to the prompt.
-
Verify that the service is enabled.
# svcs -x labeld svc:/system/labeld:default (Trusted Extensions) State: online since weekday month date hour:minute:second year See: labeld(1M) Impact: None.
-
If you plan to perform any of the following tasks, do not reboot:
-
Protect the hardware.
-
Install your own label_encodings file.
-
Run on an IPv6 network.
-
Modify the CIPSO DOI.
To perform any of these tasks, see Setting Up the Global Zone in Trusted Extensions. You will reboot after these tasks are accomplished.
-
-
Otherwise, reboot.
Chapter 4 Configuring Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
This chapter covers how to configure SolarisTM Trusted Extensions on a system with a monitor. To work properly, Trusted Extensions software requires configuration of the following: labels, zones, the network, users who can assume roles, roles, and tools.
For other configuration tasks, see Part II, Administration of Trusted Extensions.
Setting Up the Global Zone in Trusted Extensions
Before setting up the global zone, you must make decisions about your configuration. For the decisions, see Collecting Information and Making Decisions Before Enabling Trusted Extensions.
|
Task |
Description |
For Instructions |
|---|---|---|
|
Protect the hardware. |
Hardware can be protected by requiring a password to change hardware settings. |
Controlling Access to System Hardware in System Administration Guide: Security Services |
|
Configure labels. |
Labels must be configured for your site. If you plan to use the default label_encodings file, you can skip this step. | |
|
For IPv6, modify the /etc/system file. |
If you are running an IPv6 network, you modify the /etc/system file to enable IP to recognize labeled packets. | |
|
For a DOI whose value is not 1, modify the /etc/system file. |
If the CIPSO Domain of Interpretation (DOI) of your network nodes is different from 1, specify the DOI in the /etc/system file. | |
|
Reboot and log in. |
Upon login, you are in the global zone, which is an environment that recognizes and enforces mandatory access control (MAC). | |
|
Initialize the Solaris Management Console. |
Trusted Extensions adds tools to the Solaris Management Console for administering users, roles, zones, and the network. |
Initialize the Solaris Management Console Server in Trusted Extensions |
|
Configure LDAP. |
If you are using the LDAP naming service, set up the LDAP service. | |
|
If you have set up the LDAP service, make this system an LDAP client. |
 Check and Install Your Label Encodings
File
Check and Install Your Label Encodings
File
Your encodings file must be compatible with any Trusted Extensions host with which you are communicating.
Note –
Trusted Extensions installs a default label_encodings file. This default file is useful for demonstrations. However, this file might not be a good choice for your use. If you plan to use the default file, you can skip this procedure.
-
If you are familiar with encodings files, you can use the following procedure.
-
If you are not familiar with encodings files, consult Solaris Trusted Extensions Label Administration for requirements, procedures, and examples.
You must successfully install labels before continuing, or the configuration will fail.
Before You Begin
You are the security administrator. The security administrator is responsible for editing, checking, and maintaining the label_encodings file. If you plan to edit the label_encodings file, make sure that the file itself is writable. For more information, see the label_encodings(4) man page.
-
Insert the media with the label_encodings file into the appropriate device.
-
Copy the label_encodings file to the disk.
-
Check the syntax of the file and make it the active label_encodings file.
Use the command line.
-
Open a terminal window.
-
Run the chk_encodings command.
# /usr/sbin/chk_encodings /full-pathname-of-label-encodings-file
-
Read the output and do one of the following:
-
Resolve errors.
If the command reports errors, the errors must be resolved before continuing. For assistance, see Chapter 3, Creating a Label Encodings File (Tasks), in Solaris Trusted Extensions Label Administration
-
Make the file the active label_encodings file.
# cp /full-pathname-of-label-encodings-file \ /etc/security/tsol/label.encodings.site # cd /etc/security/tsol # cp label_encodings label_encodings.tx.orig # cp label.encodings.site label_encodings
-
 Caution –
Caution – Your label_encodings file must pass the Check Encodings test before you continue.
-
Example 4–1 Checking label_encodings Syntax on the Command Line
In this example, the administrator tests several label_encodings files by using the command line.
# /usr/sbin/chk_encodings /var/encodings/label_encodings1 No errors found in /var/encodings/label_encodings1 # /usr/sbin/chk_encodings /var/encodings/label_encodings2 No errors found in /var/encodings/label_encodings2 |
When management decides to use the label_encodings2 file, the administrator runs a semantic analysis of the file.
# /usr/sbin/chk_encodings -a /var/encodings/label_encodings2 No errors found in /var/encodings/label_encodings2 ---> VERSION = MYCOMPANY LABEL ENCODINGS 2.0 10/10/2006 ---> CLASSIFICATIONS <--- Classification 1: PUBLIC Initial Compartment bits: 10 Initial Markings bits: NONE ---> COMPARTMENTS AND MARKINGS USAGE ANALYSIS <--- ... ---> SENSITIVITY LABEL to COLOR MAPPING <--- ... |
The administrator prints a copy of the semantic analysis for her records, then moves the file to the /etc/security/tsol directory.
# cp /var/encodings/label_encodings2 /etc/security/tsol/label.encodings.10.10.06 # cd /etc/security/tsol # cp label_encodings label_encodings.tx.orig # cp label.encodings.10.10.06 label_encodings |
Finally, the administrator verifies that the label_encodings file is the company file.
# /usr/sbin/chk_encodings -a /etc/security/tsol/label_encodings | head -4 No errors found in /etc/security/tsol/label_encodings ---> VERSION = MYCOMPANY LABEL ENCODINGS 2.0 10/10/2006 |
 Enable IPv6 Networking in Trusted Extensions
Enable IPv6 Networking in Trusted Extensions
CIPSO options do not have an Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) number to use in the IPv6 Option Type field of a packet. The entry that you set in this procedure supplies a number to use on the local network until IANA assigns a number for this option. Trusted Extensions disables IPv6 networking if this number is not defined.
To enable an IPv6 network in Trusted Extensions, you must add an entry in the /etc/system file.
Troubleshooting
-
If error messages during boot indicate that your IPv6 configuration is incorrect, correct the entry:
-
Check that the entry is spelled correctly.
-
Check that the system has been rebooted after adding the correct entry to the /etc/system file.
-
-
If you install Trusted Extensions on a Solaris system that currently has IPv6 enabled, but you fail to add the IP entry in /etc/system, you see the following error message: t_optmgmt: System error: Cannot assign requested address time-stamp
-
If you install Trusted Extensions on a Solaris system that does not have IPv6 enabled, and you fail to add the IP entry in /etc/system, you see the following types of error messages:
-
WARNING: IPv6 not enabled via /etc/system
-
Failed to configure IPv6 interface(s): hme0
-
rpcbind: Unable to join IPv6 multicast group for rpc broadcast broadcast-number
-
 Configure the Domain of Interpretation
Configure the Domain of Interpretation
All communications to and from a system that is configured with Trusted Extensions must follow the labeling rules of a single CIPSO Domain of Interpretation (DOI). The DOI that is used in each message is identified by an integer number in the CIPSO IP Option header. By default, the DOI in Trusted Extensions is 1.
If your DOI is not 1, you must add an entry to the /etc/system file and modify the doi value in the default security templates.
-
Type your DOI entry into the /etc/system file:
set default_doi = n
This positive, non-zero number must match the DOI number in the tnrhtp database for your node and for the systems that your node communicates with.
-
Before adding the tnrhtp database to your LDAP server, modify the doi value in the default entries and all entries for local addresses.
Trusted Extensions provides two templates in the tnrhtp database, cipso and admin_low. If you have added entries for local addresses, also modify these entries.
-
Open the tnrhtp database in the trusted editor.
# /usr/dt/bin/trusted_edit /etc/security/tsol/tnrhtp
-
Copy the cipso template entry to another line.
cipso:host_type=cipso;doi=1;min_sl=ADMIN_LOW;max_sl=ADMIN_HIGH cipso:host_type=cipso;doi=1;min_sl=ADMIN_LOW;max_sl=ADMIN_HIGH
-
Comment out one of the cipso entries.
#cipso:host_type=cipso;doi=1;min_sl=ADMIN_LOW;max_sl=ADMIN_HIGH cipso:host_type=cipso;doi=1;min_sl=ADMIN_LOW;max_sl=ADMIN_HIGH
-
Modify the doi value in the uncommented cipso entry.
Make this value the same as the default_doi value in the /etc/system file.
#cipso:host_type=cipso;doi=1;min_sl=ADMIN_LOW;max_sl=ADMIN_HIGH cipso:host_type=cipso;doi=n;min_sl=ADMIN_LOW;max_sl=ADMIN_HIGH
-
Change the doi value for the admin_low entry.
#admin_low:host_type=unlabeled;min_sl=ADMIN_LOW;max_sl=ADMIN_HIGH;doi=1;def_label=ADMIN_LOW admin_low:host_type=unlabeled;min_sl=ADMIN_LOW;max_sl=ADMIN_HIGH;doi=n;def_label=ADMIN_LOW
You are finished when every doi value in every entry in the tnrhtp database is the same.
-
Troubleshooting
If the /etc/system file sets a default_doi value other than 1, and a security template for this system sets a value that does not match this default_doi value, then messages similar to the following are displayed on the system console during interface configuration:
-
NOTICE: er10 failed: 10.17.1.12 has wrong DOI 4 instead of 1
-
Failed to configure IPv4 interface(s): er10
Interface configuration failure can result in login failure:
-
Hostname: unknown
-
unknown console login: root
-
Oct 10 10:10:20 unknown login: pam_unix_cred: cannot load hostname Error 0
To correct the problem, boot the system into single-user mode and correct the security templates as described in this procedure.
See Also
For more information about the DOI, see Network Security Attributes in Trusted Extensions.
To change the doi value in the security templates that you create, see How to Construct a Remote Host Template.
To use the editor of your choice as the trusted editor, see How to Assign the Editor of Your Choice as the Trusted Editor.
 Reboot and Log In to Trusted Extensions
Reboot and Log In to Trusted Extensions
At most sites, two or more administrators, who serve as an initial setup team, are present when configuring the system.
Before You Begin
Before you first log in, become familiar with the desktop and label options in Trusted Extensions. For details, see Chapter 3, Logging In to Trusted Extensions (Tasks), in Solaris Trusted Extensions User’s Guide.
-
Reboot the system.
# /usr/sbin/reboot
If your system does not have a graphical display, go to Chapter 6, Configuring a Headless System With Trusted Extensions (Tasks).
-
Log in to the Solaris Trusted Extensions (GNOME) desktop as the user account that you created during installation.
-
In the login window, select the labeled desktop.
-
In the login dialog box, type username and the user's password.
Users must not disclose their passwords to another person, as that person might then have access to the data of the user and will not be uniquely identified or accountable. Note that disclosure can be direct, through the user deliberately disclosing his/her password to another person, or indirect, such as through writing it down, or choosing an insecure password. Trusted Extensions software provides protection against insecure passwords, but cannot prevent a user disclosing his/her password or writing it down.
-
-
Use the mouse to dismiss the Status window and the Clearance window.
GNOME will complain four times, once per workspace, that the label PUBLIC has no matching zone. Dismiss each of the four dialogs.
-
Use the mouse to dismiss four complaint dialog boxes.
GNOME complains four times, one complaint for each workspace, that the label PUBLIC has no matching zone.
-
Assume the root role.
-
Switch to fourth workspace.
-
Click the trusted stripe where your name is displayed.
The root role appears in a pulldown menu.
-
Click the root role.
Note –You must log off or lock the screen before leaving a system unattended. Otherwise, a person can access the system without having to pass identification and authentication, and that person would not be uniquely identified or accountable.
-
 Initialize the Solaris Management Console Server in Trusted Extensions
Initialize the Solaris Management Console Server in Trusted Extensions
This procedure enables you to administer users, roles, hosts, zones, and the network on this system. On the first system that you configure, only the files scope is available.
Before You Begin
You must be superuser.
To use the LDAP toolbox on the LDAP server from a Solaris Management Console that is running on a client, you must complete all of the tasks in Configuring the Solaris Management Console for LDAP (Task Map).
-
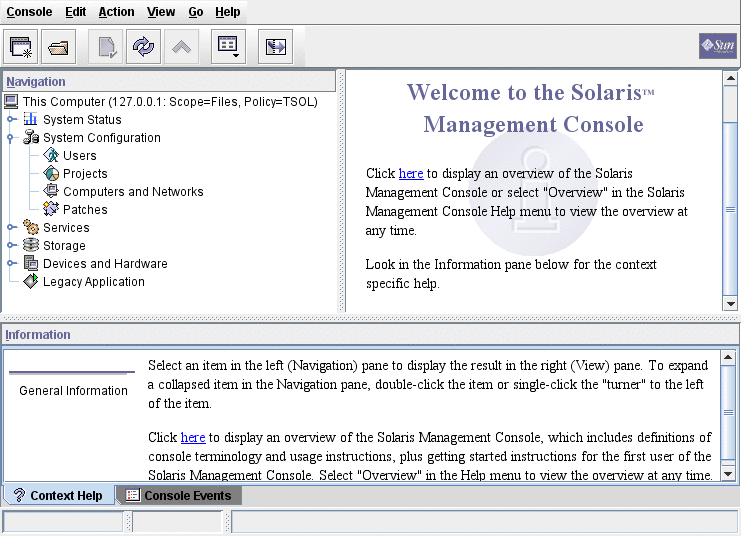
Start the Solaris Management Console.
# /usr/sbin/smc &
Note –The first time the Solaris Management Console is started, it performs several registration tasks. These tasks can take a few minutes.
Figure 4–1 Solaris Management Console Initial Window
-
Do one of the following if toolbox icons do not appear in the Solaris Management Console:
-
If the Navigation pane is not visible:
-
In the Open Toolbox dialog box that is displayed, click Load next to this system's name under Server.
If this system does not have the recommended amount of memory and swap, it might take a few minutes for the toolboxes to display. For recommendations, see Installing or Upgrading the Solaris OS for Trusted Extensions.
-
From the list of toolboxes, select a toolbox whose Policy=TSOL.
Figure 4–2 shows a This Computer (this-host: Scope=Files, Policy=TSOL) toolbox. Trusted Extensions modifies tools under the System Configuration node.
 Caution –
Caution – Do not choose a toolbox that has no policy. Toolboxes without a listed policy do not support Trusted Extensions.
Your toolbox choice depends on which scope you want to influence.
-
To edit local files, choose the Files scope.
-
To edit LDAP databases, choose the LDAP scope.
After you complete all of the tasks in Configuring the Solaris Management Console for LDAP (Task Map), the LDAP scope is available.
-
-
Click Open.
-
-
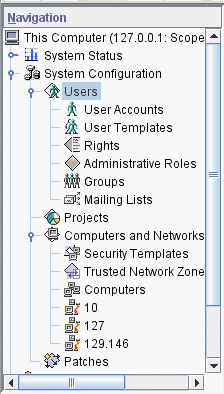
If the Navigation pane is visible, but the toolbox icons are stop signs:
-
-
If you have not yet done so, select a toolbox whose Policy=TSOL.
The following figure shows a This Computer (this-host: Scope=Files, Policy=TSOL) toolbox. Trusted Extensions modifies tools under the System Configuration node.
Figure 4–2 Trusted Extensions Tools in the Solaris Management Console
-
(Optional) Save the current toolbox.
Saving a Policy=TSOL toolbox enables a Trusted Extensions toolbox to load by default. Preferences are saved per role, per host. The host is the Solaris Management Console server.
-
Exit the Solaris Management Console.
See Also
For an overview of the Trusted Extensions additions to the Solaris Management Console, see Solaris Management Console Tools. To use the Solaris Management Console to create security templates, see Configuring Trusted Network Databases (Task Map).
 Make the Global Zone an LDAP Client
in Trusted Extensions
Make the Global Zone an LDAP Client
in Trusted Extensions
For LDAP, this procedure establishes the naming service configuration for the global zone. If you are not using LDAP, you can skip this procedure.
Use the txzonemgr script.
Note –
If you plan to set up a name server in each labeled zone, you are responsible for establishing the LDAP client connection to each labeled zone.
Before You Begin
The Sun JavaTM System Directory Server, that is, the LDAP server, must exist. The server must be populated with Trusted Extensions databases, and this system must be able to contact the server. So, the system that you are configuring must have an entry in the tnrhdb database on the LDAP server, or this system must be included in a wildcard entry before you perform this procedure.
If an LDAP server that is configured with Trusted Extensions does not exist, you must complete the procedures in Chapter 5, Configuring LDAP for Trusted Extensions (Tasks) before you perform this procedure.
-
If you are using DNS, modify the nsswitch.ldap file.
-
Save a copy of the original nsswitch.ldap file.
The standard naming service switch file for LDAP is too restrictive for Trusted Extensions.
# cd /etc # cp nsswitch.ldap nsswitch.ldap.orig
-
Change the nsswitch.ldap file entries for the following services.
The correct entries are similar to the following:
hosts: files dns ldap ipnodes: files dns ldap networks: ldap files protocols: ldap files rpc: ldap files ethers: ldap files netmasks: ldap files bootparams: ldap files publickey: ldap files services: files
Note that Trusted Extensions adds two entries:
tnrhtp: files ldap tnrhdb: files ldap
-
Copy the modified nsswitch.ldap file to nsswitch.conf.
# cp nsswitch.ldap nsswitch.conf
-
-
To create an LDAP client, use the txzonemgr script.
The Create LDAP Client menu item configures the global zone only.
-
Follow the instructions in Run the txzonemgr Script.
The title of the dialog box is Labeled Zone Manager.
-
Select Create LDAP Client.
-
Answer the following prompts and click OK after each answer:
Enter Domain Name: Type the domain name Enter Hostname of LDAP Server: Type the name of the server Enter IP Address of LDAP Server servername: Type the IP address Enter LDAP Proxy Password: Type the password to the server Confirm LDAP Proxy Password: Retype the password to the server Enter LDAP Profile Name: Type the profile name
-
Confirm or cancel the displayed values.
Proceed to create LDAP Client?
When you confirm, the txzonemgr script adds the LDAP client. Then, a window displays the command output.
-
-
Verify that the information on the server is correct.
-
Open a terminal window, and query the LDAP server.
# ldapclient list
The output looks similar to the following:
NS_LDAP_FILE_VERSION= 2.0 NS_LDAP_BINDDN= cn=proxyagent,ou=profile,dc=domain-name ... NS_LDAP_BIND_TIME= number
-
Correct any errors.
If you get an error, create the LDAP client again and supply the correct values. For example, the following error can indicate that the system does not have an entry on the LDAP server:
LDAP ERROR (91): Can't connect to the LDAP server. Failed to find defaultSearchBase for domain domain-name
To correct this error, you need to check the LDAP server.
-
Example 4–2 Using Host Names After Loading a resolv.conf File
In this example, the administrator wants a particular set of DNS servers to be available to the system. The administrator copies a resolv.conf file from a server on a trusted net. Because DNS is not yet active, the administrator uses the server's IP address to locate the server.
# cd /etc # cp /net/10.1.1.2/export/txsetup/resolv.conf resolv.conf |
After the resolv.conf file is copied and the nsswitch.conf file includes dns in the hosts entry, the administrator can use host names to locate systems.
Creating Labeled Zones
The instructions in this section configure labeled zones on a system that has been assigned at most two IP addresses. For other configurations, see the configuration options in Task Map: Preparing For and Enabling Trusted Extensions.
|
Task |
Description |
For Instructions |
|---|---|---|
|
1. Run the txzonemgr script. |
The txzonemgr script creates a GUI that presents the appropriate tasks as you configure your zones. | |
|
2. Create, install, boot, and halt the first zone. |
In the default configuration, create the PUBLIC zone. This zone forms the template for other labeled zones. | |
|
3. Manage network interfaces in the global zone. |
Configure interfaces in the global zone, or create logical interfaces and configure them in the global zone. | |
|
4. Create a clone. |
Clone the first zone. The clone is not assigned a label. | |
|
5. Verify that the first zone is working correctly. |
Test connection with a non-Trusted Extensions system. | |
|
6. Label the cloned zone. |
Add a label to a cloned zone. | |
|
7. Create a zone from a snapshot. |
Create the rest of the zones. | |
|
8. Create a labeled working environment. |
Activate the PUBLIC and INTERNAL workspaces. |
 Run the txzonemgr Script
Run the txzonemgr Script
This script steps you through the tasks to properly configure, install, initialize, and boot labeled zones. In the script, you name each zone, associate the name with a label, install the packages to create a virtual OS, and then boot the zone to start services in that zone. The script includes copy zone and clone zone tasks. You can also halt a zone, change the state of a zone, and add zone-specific network interfaces.
This script presents a dynamically-determined menu that displays only valid choices for the current circumstances. For instance, if the status of a zone is configured, the Install zone menu item is not displayed. Tasks that are completed do not display in the list.
Before You Begin
You have assumed the root role.
-
Open a terminal window in the fourth workspace.
-
Run the txzonemgr script.
# /usr/sbin/txzonemgr
The script opens the Labeled Zone Manager dialog box. This zenity dialog box prompts you for the appropriate tasks, depending on the current state of your installation.
To perform a task, you select the menu item, then press the Return key or click OK. When you are prompted for text, type the text then press the Return key or click OK.
Tip –To view the current state of zone completion, click Return to Main Menu in the Labeled Zone Manager.
 Create the First Labeled Zone
Create the First Labeled Zone
You do not have to create a zone for every label in your label_encodings file, but you can. The administrative GUIs enumerate the labels that can have zones created for them on this system.
Before You Begin
You are in the root role. The Labeled Zone Manager dialog box is displayed. To open this GUI, see Run the txzonemgr Script.
You have not created a zone yet.
-
Click OK to the following dialog box:
Do you want to create the public zone using default settings?
After the public zone is created, another terminal window appears. Its title is Zone Terminal Console: public. The public zone boots, initializes, and then prompts for the root password.
-
Press the F2 key twice to provide the password for the root role.
The zone reboots.
The Labeled Zone Manager dialog box displays the state and options for the public zone.
-
Halt the public zone by selecting Halt from the Labeled Zone Manager.
In the Zone Terminal Console window, a notice appears: Notice: Zone Halted
-
From the public zone options list, click Select another zone...
 Configure the
Network Interfaces in Trusted Extensions
Configure the
Network Interfaces in Trusted Extensions
In this task, you configure the networking in the global zone. You must create exactly one all-zones interface. An all-zones interface is shared by the labeled zones and the global zone. The shared interface is used to route traffic between the labeled zones and the global zone. To configure this interface, do one of the following:
-
Create a logical interface from a physical interface, then share the physical interface.
This configuration is the simplest to administer. Choose this configuration when your system has been assigned two IP addresses. In this procedure, the logical interface becomes the global zone's specific address, and the physical interface is shared between the global zone and the labeled zones.
-
Share a physical interface
Choose this configuration when your system has been assigned one IP address. In this configuration, the physical interface is shared between the global zone and the labeled zones.
-
Share a virtual network interface, vni0
Choose this configuration when you are configuring DHCP, or when each subnetwork is at a different label. For a sample procedure, refer to the laptop instructions in the Trusted Extensions section of OpenSolaris Community: Security web page.
In the Solaris Express Community Edition, the loopback interface in Trusted Extensions is created as an all-zones interface. Therefore, you do not need to create a vni0 shared interface.
To add zone-specific network interfaces, finish and verify zone creation before adding the interfaces. For the procedure, see Add a Network Interface to Route an Existing Labeled Zone.
Before You Begin
The public zone is halted.
The Labeled Zone Manager is displayed. To open this GUI, see Run the txzonemgr Script.
From the public zone options list, you have clicked Select another zone...
-
In the Labeled Zone Manager, select the global zone.
-
Select Configure Network Interfaces.
A list of interfaces is displayed. Look for an interface that is listed with the following characteristics:
-
Type of physical
-
IP address of your hostname
-
Template of cipso
-
State of Up
-
-
Select the interface that corresponds to your hostname.
-
From the list of commands, select Share with Shared-IP Zones.
-
Click Cancel to return to the global zone command list
-
To connect to other systems on your network that are running Trusted Extensions, select Add Multilevel Access to Remote Host...
 Clone the First Zone in Trusted Extensions
Clone the First Zone in Trusted Extensions
Before You Begin
You have completed Create the First Labeled Zone and Configure the Network Interfaces in Trusted Extensions. The public zone is still halted.
The Labeled Zone Manager dialog box is displayed. To open this GUI, see Run the txzonemgr Script.
-
From the Labeled Zone Manager, select Create a new zone...
You are prompted to Enter Zone Name.
-
Type snapshot as the zone name.
A list of options appear for the snapshot zone.
-
Select Clone...
A list of installed zones appears. The list includes the name public.
-
Double-click public.
The snapshot zone does not install automatically, so select Set Manual Booting The snapshot zone doesn't need a label since it is never booted. Verify the Boot option is not available.
-
Select Set Manual Booting.
The snapshot zone is never booted, therefore it does not need a label. Verify that the Boot option is not available.
 Verify the Status of the Public
Zone
Verify the Status of the Public
Zone
Note –
The X server runs in the global zone. Each labeled zone must be able to connect with the global zone to use the X server. Therefore, zone networking must work before a zone can be used. For background information, see Planning for Multilevel Access.
Before You Begin
The Labeled Zone Manager dialog box displays the global zone.
-
Select Select another zone and choose public.
Enter the IP address of a system on your network not running TX. Then enter Boot You see the zone booting messages in the Zone Console window. Login as root, and run ifconfig -a Verify that the primary interface and IP address are available in this zone. Verify that you can ping the host to which you previously added remote access. Now logout and close the Zone Console window.
-
Select Add Single-level Access to Remote Host...
-
In the public: Zone Console Terminal window, log in as root.
-
Run the ifconfig -a command.
# ifconfig -a
Verify that the primary interface and IP address are available in this zone.
-
Verify that you can ping the host to which you previously added single-level access.
# ping remote-single-level-host
-
Log out and close the Zone Console Terminal window.
 Create a Zone From
the Snapshot
Create a Zone From
the Snapshot
This procedure creates the internal zone. Use this procedure to create the rest of your labeled zones.
Before You Begin
You are in the root role. The Labeled Zone Manager dialog box is displayed. To open this GUI, see Run the txzonemgr Script.
You have completed Clone the First Zone in Trusted Extensions.
-
In the Labeled Zone Manager, select Select another zone.
-
Choose global.
-
Select Create a new zone:
The prompt, Enter Zone Name:, appears
-
Type internal.
A one-item list for the internal zone appears.
-
Choose Select Label....
-
From the label selection dialog box, select INTERNAL USE ONLY from the Sensitivity column and click OK.
-
In the list of options for the internal zone, select Clone....
-
Select snapshot from the list of installed zones.
snapshotis the only item in the list.
-
Select Boot.
 Activate Two Zone Workspaces
Activate Two Zone Workspaces
This procedure creates two labeled workspaces and opens a labeled window in a labeled workspace
Before You Begin
You have completed Create a Zone From the Snapshot.
-
Go to the first workspace.
The desktop background should appear.
-
Open a terminal window.
The window is labeled PUBLIC.
-
Create a workspace with a different label.
-
Open a terminal window.
The window is labeled CONFIDENTIAL : INTERNAL USE ONLY.
Adding Network Interfaces and Routing to Labeled Zones
The following tasks support environments where each zone is connected to a separate physical network.
|
Task |
Description |
For Instructions |
|---|---|---|
|
EITHER 1a: Add a network interface to each labeled zone and use the global zone to reach the external network. |
Connects each labeled zone to a separate physical network. The labeled zones use the network routing that the global zone provides. | |
|
OR 1b: Add a network interface to each labeled zone with a default route. |
Connects each zone to a separate physical network. The labeled zones do not use the global zone for routing. |
Add a Network Interface That Does Not Use the Global Zone to Route an Existing Labeled Zone |
|
2. Create a name service cache in each labeled zone. |
Configures a name service daemon for each zone. |
 Add a Network Interface to Route an
Existing Labeled Zone
Add a Network Interface to Route an
Existing Labeled Zone
This procedure adds zone-specific network interfaces to existing labeled zones. This configuration supports environments where each labeled zone is connected to a separate physical network. The labeled zones use the network routing that the global zone provides.
Note –
The global zone must configure an IP address for every subnet in which a non-global zone address is configured.
Before You Begin
You are superuser in the global zone.
For every zone, you have completed the tasks in Creating Labeled Zones.
-
In the global zone, type the IP addresses and hostnames for the additional network interfaces into the /etc/hosts file.
Use a standard naming convention, such as adding -zone-name to the name of the host.
## /etc/hosts in global zone 10.10.8.2 hostname-zone-name1 10.10.8.3 hostname-global-name1 10.10.9.2 hostname-zone-name2 10.10.9.3 hostname-global-name2
-
For the network for each interface, add entries to the /etc/netmasks file.
## /etc/netmasks in global zone 10.10.8.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.9.0 255.255.255.0
For more information, see the netmasks(4) man page.
-
In the global zone, plumb the zone-specific physical interfaces.
-
Identify the physical interfaces that are already plumbed.
# ifconfig -a
-
Configure the global zone addresses on each interface.
# ifconfig interface-nameN1 plumb # ifconfig interface-nameN1 10.10.8.3 up # ifconfig interface-nameN2 plumb # ifconfig interface-nameN2 10.10.9.3 up
-
For each global zone address, create a hostname.interface-nameN file.
# /etc/hostname.interface-nameN1 10.10.8.3 # /etc/hostname.interface-nameN2 10.10.9.3
The global zone addresses are configured immediately upon system startup. The zone-specific addresses are configured when the zone is booted.
-
-
Assign a security template to each zone-specific network interface.
If the gateway to the network is not configured with labels, assign the admin_low security template. If the gateway to the network is labeled, assign a cipso security template.
You can create security templates of host type cipso that reflect the label of every network. For the procedures to create and assign the templates, see Configuring Trusted Network Databases (Task Map).
-
Halt every labeled zone to which you plan to add a zone-specific interface.
# zoneadm -z zone-name halt
-
Start the Labeled Zone Manager.
# /usr/sbin/txzonemgr
-
For each zone where you want to add a zone-specific interface, do the following:
-
In the Labeled Zone Manager for every completed zone, select Zone Console.
-
Select Boot.
-
In the Zone Console, verify that the interfaces have been created.
# ifconfig -a
-
Verify that the zone has a route to the gateway for the subnet.
# netstat -rn
Troubleshooting
To debug zone configuration, see the following:
 Add a Network Interface That Does Not
Use the Global Zone to Route an Existing Labeled Zone
Add a Network Interface That Does Not
Use the Global Zone to Route an Existing Labeled Zone
This procedure sets zone-specific default routes for existing labeled zones. In this configuration, the labeled zones do not use the global zone for routing.
The labeled zone must be plumbed in the global zone before the zone is booted. However, to isolate the labeled zone from the global zone, the interface must be in the down state when the zone is booted. For more information, see Chapter 16, Non-Global Zone Configuration (Overview), in System Administration Guide: Virtualization Using the Solaris Operating System.
Note –
A unique default route must be configured for every non-global zone that is booted.
Before You Begin
You are superuser in the global zone.
For every zone, you have completed the tasks in Creating Labeled Zones. You are using either the vni0 interface or the lo0 interface to connect the labeled zones to the global zone.
-
For every network interface, determine its IP address, netmask, and default router.
Use the ifconfig -a command to determine the IP address and netmask. Use the zonecfg -z zonename info net command to determine if a default router has been assigned.
-
Create an empty /etc/hostname.interface file for each labeled zone.
# touch /etc/hostname.interface # touch /etc/hostname.interface:n
For more information, see the netmasks(4) man page.
-
Plumb the network interfaces of the labeled zones.
# ifconfig zone1-network-interface plumb # ifconfig zone2-network-interface plumb
-
Verify that the labeled zone's interfaces are in the down state.
# ifconfig -a zone1-network-interface zone1-IP-address down zone2-network-interface zone2-IP-address down
The zone-specific addresses are configured when the zone is booted.
-
For the network for each interface, add entries to the /etc/netmasks file.
## /etc/netmasks in global zone 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0
For more information, see the netmasks(4) man page.
-
Assign a security template to each zone-specific network interface.
Create security templates of host type cipso that reflect the label of every network. To create and assign the templates, see Configuring Trusted Network Databases (Task Map).
-
Run the txzonemgr script, and open a separate terminal window.
In the Labeled Zone Manager, you will add the network interfaces for the labeled zones. In the terminal window, you will display information about the zone and set the default router.
-
For every zone to which you are going to add a zone-specific network interface and router, complete the following steps:
-
In the terminal window, halt the zone.
# zoneadm -z zone-name halt
-
In the Labeled Zone Manager, do the following:
-
In the terminal window, configure the default router for the labeled zone's network.
# zonecfg -z zone-name zonecfg:zone-name > select net address=IP-address zonecfg:zone-name:net> set defrouter=router-address zonecfg:zone-name:net> end zonecfg:zone-name > verify zonecfg:zone-name > commit zonecfg:zone-name > exit #
For more information, see the zonecfg(1M) man page and How to Configure the Zone in System Administration Guide: Virtualization Using the Solaris Operating System.
-
Boot the labeled zone.
# zoneadm -z zone-name boot
-
In the global zone, verify that the labeled zone has a route to the gateway for the subnet.
# netstat -rn
A routing table is displayed. The destination and interface for the labeled zone is different from the entry for the global zone.
-
-
To remove the default route, select the zone's IP address, then remove the route.
# zonecfg -z zone-name zonecfg:zone-name > select net address=zone-IP-address zonecfg:zone-name:net> remove net defrouter=zone-default-route zonecfg:zone-name:net> info net net: address: zone-IP-address physical: zone-network-interface defrouter not specified
Example 4–3 Setting a Default Route for a Labeled Zone
In this example, the administrator routes the Secret zone to a separate physical subnet. Traffic to and from the Secret zone is not routed through the global zone. The administrator uses the Labeled Zone Manager and the zonecfg command, then verifies that routing works.
The administrator determines that qfe1 and qfe1:0 are not currently in use. and creates a mapping for two labeled zones. qfe1 is the designated interface for the Secret zone.
Interface IP Address Netmask Default Router qfe1 192.168.2.22 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.2 qfe1:0 192.168.3.33 255.255.255.0 192.168.3.3 |
First, the administrator creates the /etc/hostname.qfe1 file and configures the /etc/netmasks file.
# touch /etc/hostname.qfe1 |
# cat /etc/netmasks ## /etc/netmasks in global zone 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 |
Then, the administrator plumbs the network interface and verifies that the interface is down.
# ifconfig qfe1 plumb # ifconfig -a |
Then, in the Solaris Management Console, the administrator creates a security template with a single label, Secret, and assigns the IP address of the interface to the template.
The administrator halts the zone.
# zoneadm -z secret halt |
The administrator runs the txzonemgr script to open the Labeled Zone Manager.
# /usr/sbin/txzonemgr |
In the Labeled Zone Manager, the administrator selects the Secret zone, selects Add Network, and then selects a network interface. The administrator closes the Labeled Zone Manager.
On the command line, the administrator selects the zone's IP address, then sets its default route. Before exiting the command, the administrator verifies the route and commits it.
# zonecfg -z secret
zonecfg: secret > select net address=192.168.6.22
zonecfg: secret:net> set defrouter=192.168.6.2
zonecfg: secret:net> end
zonecfg: secret > verify
zonecfg: secret > commit
zonecfg: secret > info net
net:
address: 192.168.6.22
physical: qfe1
defrouter: 192.168.6.2
zonecfg: secret > exit
#
|
The administrator boots the zone.
# zoneadm -z secret boot |
In a separate terminal window in the global zone, the administrator verifies the sending and receiving of packets.
# netstat -rn Routing Table: IPv4 Destination Gateway Flags Ref Use Interface -------------------- -------------------- ----- ----- ------- --------- default 192.168.5.15 UG 1 2664 qfe0 192.168.6.2 192.168.6.22 UG 1 240 qfe1 192.168.3.3 192.168.3.33 U 1 183 qfe1:0 127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 UH 1 380 lo0 ... |
 Configure a Name Service Cache in Each
Labeled Zone
Configure a Name Service Cache in Each
Labeled Zone
This procedure enables you to separately configure a name service daemon (nscd) in each labeled zone. This configuration supports environments where each zone is connected to a subnetwork that runs at the label of the zone, and the subnetwork has its own name server for that label.
Note –
This configuration does not satisfy the criteria for an evaluated configuration. In an evaluated configuration, the nscd daemon runs only in the global zone. Doors in each labeled zone connect the zone to the global nscd daemon.
Before You Begin
You are superuser in the global zone. root must not yet be a role. You have successfully completed Add a Network Interface to Route an Existing Labeled Zone.
This configuration requires that you have advanced networking skills. If LDAP is your naming service, you are responsible for establishing the LDAP client connection to each labeled zone. The nscd daemon caches the name service information, but does not route it.
-
If you are using LDAP, verify a route to the LDAP server from the labeled zone.
In a terminal window in every labeled zone, run the following command:
zone-name # netstat -rn
-
In the global zone, start the Labeled Zone Manager.
# /usr/sbin/txzonemgr
-
Select the Configure per-zone name service, and click OK.
This option is intended to be used once, during initial system configuration.
-
Configure each zone's nscd service.
For assistance, see the nscd(1M) and nscd.conf(4) man pages.
-
Reboot the system.
-
For every zone, verify the route and the name service daemon.
-
In the Zone Console, list the nscd service.
zone-name # svcs -x name-service-cache svc:/system/name-service-cache:default (name service cache) State: online since October 10, 2010 10:10:10 AM PDT See: nscd(1M) See: /etc/svc/volatile/system-name-service-cache:default.log Impact: None.
-
Verify the route to the subnetwork.
zone-name # netstat -rn
-
-
To remove the zone-specific name service daemons, do the following in the global zone:
Creating Roles and Users in Trusted Extensions
If you are already using administrative roles, you might want to add a Security Administrator role. For sites that have not yet implemented roles, the procedure for creating them is similar to the procedure in the Solaris OS. Trusted Extensions adds the Security Administrator role and requires the use of the Solaris Management Console to administer a Trusted Extensions domain.
If site security requires two people to create user and role accounts, create custom rights profiles and assign them to roles to enforce separation of duty.
|
Task |
Description |
For Instructions |
|---|---|---|
|
Create three rights profiles that are more restrictive than default profiles. |
Creates rights profiles to manage users. These profiles are more restrictive than the default profiles that manage users. | |
|
Create a security administrator role. |
Creates a security administrator role that handles security-relevant tasks. |
Create the Security Administrator Role in Trusted Extensions |
|
Create a system administrator role that cannot set a user password. |
Creates a system administrator role and assigns to it a restricted System Administrator rights profile. | |
|
Create users to assume the administrative roles. |
Creates one or more users who can assume roles. | |
|
Verify that the roles can perform their tasks. |
Tests the roles in various scenarios. | |
|
Enable users to log in to a labeled zone. |
Starts the zones service so that regular users can log in. |
 Create Rights Profiles That Enforce
Separation of Duty
Create Rights Profiles That Enforce
Separation of Duty
Skip this procedure if separation of duty is not a site security requirement. If your site requires separation of duty, you must create these rights profiles and roles before you populate the LDAP server.
This procedure creates rights profiles that have discrete capabilities to manage users. When you assign these profiles to distinct roles, two roles are required to create and configure users. One role can create users, but cannot assign security attributes. The other role can assign security attributes, but cannot create users. When you log in to the Solaris Management Console in a role that is assigned one of these profiles, only the appropriate tabs and fields are available to the role.
Before You Begin
You must be superuser, in the root role, or in the Primary Administrator role. When you start this procedure, the Solaris Management Console must be closed.
-
Create copies of the default rights profiles that affect user configuration.
-
Copy the prof_attr file to the prof_attr.orig file.
-
Open the prof_attr file in the trusted editor.
# /usr/dt/bin/trusted_edit /etc/security/prof_attr
-
Copy the three rights profiles and rename the copies.
System Administrator:::Can perform most non-security... Custom System Administrator:::Can perform most non-security... User Security:::Manage passwords... Custom User Security:::Manage passwords... User Management:::Manage users, groups, home... Custom User Management:::Manage users, groups, home...
-
Save the changes.
-
Verify the changes.
# grep ^Custom /etc/security/prof_attr Custom System Administrator:::Can perform most non-security... Custom User Management:::Manage users, groups, home... Custom User Security:::Manage passwords...
Copying a rights profile rather than modifying it enables you to upgrade the system to a later Solaris release and retain your changes. Because these rights profiles are complex, modifying a copy of the default profile is less prone to error than building the more restrictive profile from scratch.
-
-
Start the Solaris Management Console.
# /usr/sbin/smc &
-
Select the This Computer (this-host: Scope=Files, Policy=TSOL) toolbox.
-
Click System Configuration, then click Users.
You are prompted for your password.
-
Type the appropriate password.
-
Double-click Rights.
-
Modify the Custom User Security rights profile.
You restrict this profile from creating a user.
-
Modify the Custom User Management profile.
You restrict this profile from setting a password.
-
Modify the Custom System Administrator rights profile.
The User Management profile is a supplementary profile in this profile. You prevent the system administrator from setting a password.
Next Steps
To prevent the default profiles from being used, see Step 7 in Verify That the Trusted Extensions Roles Work after you verify that the custom profiles enforce separation of duty.
 Create the Security Administrator Role
in Trusted Extensions
Create the Security Administrator Role
in Trusted Extensions
Role creation in Trusted Extensions is identical to role creation in the Solaris OS. However, in Trusted Extensions, a Security Administrator role is required. To create a local Security Administrator role, you can also use the command-line interface, as in Example 4–4.
Before You Begin
You must be superuser, in the root role, or in the Primary Administrator role.
To create the role on the network, you must have completed Configuring the Solaris Management Console for LDAP (Task Map).
-
Start the Solaris Management Console.
# /usr/sbin/smc &
-
Select the appropriate toolbox.
-
Click System Configuration, then click Users.
You are prompted for your password.
-
Type the appropriate password.
-
Double-click Administrative Roles.
-
From the Action menu, choose Add Administrative Role.
-
Create the Security Administrator role.
Use the following information as a guide:
-
Role name – secadmin
-
Full name – Security Administrator
-
Description – Site Security Officer No proprietary information here.
-
Role ID Number – ≥100
-
Role shell – Administrator's Bourne (profile shell)
-
Create a role mailing list – Leave the checkbox selected.
-
Password and confirm – Assign a password of at least 6 alphanumeric characters.
The password for the Security Administrator role, and all passwords, must be difficult to guess, thus reducing the chance of an adversary gaining unauthorized access by attempting to guess passwords.
Note –For all administrative roles, make the account Always Available, and do not set password expiration dates.
-
Available and Granted Rights – Information Security, User Security
-
If site security does not require separation of duty, select the Information Security and the default User Security rights profiles.
-
If site security requires separation of duty, select the Information Security and the Custom User Security rights profiles.
-
-
Home Directory Server – home-directory-server
-
Home Directory Path – /mount-path
-
Assign Users– This field is automatically filled in when you assign a role to a user.
-
-
After creating the role, check that the settings are correct.
Select the role, then double-click it.
Review the values in the following fields:
-
Available Groups – Add groups if required.
-
Trusted Extensions Attributes – Defaults are correct.
For a single-label system where the labels must not be visible, choose Hide for Label: Show or Hide.
-
Audit Excluded and Included – Set audit flags only if the role's audit flags are exceptions to the system settings in the audit_control file.
-
-
To create other roles, use the Security Administrator role as a guide.
For examples, see How to Create and Assign a Role by Using the GUI in System Administration Guide: Security Services. Give each role a unique ID, and assign to the role the correct rights profile. Possible roles include the following:
-
admin Role – System Administrator Granted Rights
-
primaryadmin Role – Primary Administrator Granted Rights
-
oper Role – Operator Granted Rights
-
Example 4–4 Using the roleadd Command to Create a Local Security Administrator Role
In this example, the root user adds the Security Administrator role to the local system by using the roleadd command. For details, see the roleadd(1M) man page. The root user consults Table 1–2 before creating the role. At this site, separation of duty is not required to create a user.
# roleadd -c "Local Security Administrator" -d /export/home1 \ -u 110 -P "Information Security,User Security" -K lock_after_retries=no \ -K idletime=5 -K idlecmd=lock -K labelview=showsl \ -K min_label=ADMIN_LOW -K clearance=ADMIN_HIGH secadmin |
The root user provides an initial password for the role.
# passwd -r files secadmin New Password: <Type password> Re-enter new Password: <Retype password> passwd: password successfully changed for secadmin # |
To assign the role to a local user, see Example 4–5.
 Create a Restricted System Administrator
Role
Create a Restricted System Administrator
Role
Skip this procedure if separation of duty is not a site security requirement.
In this procedure, you assign a more restrictive rights profile to the System Administrator role.
Before You Begin
You must be superuser, in the root role, or in the Primary Administrator role.
You have completed Create Rights Profiles That Enforce Separation of Duty. You are using the same toolbox that you used to create the rights profile.
-
In the Solaris Management Console, create the System Administrator role.
For assistance, see Create the Security Administrator Role in Trusted Extensions.
-
Assign the Custom System Administrator rights profile to the role.
-
Save the changes.
-
Close the Solaris Management Console.
 Create Users Who Can Assume Roles in Trusted Extensions
Create Users Who Can Assume Roles in Trusted Extensions
To create a local user, you can use the command-line interface, as in Example 4–5, instead of the following procedure. Where site security policy permits, you can choose to create a user who can assume more than one administrative role.
For secure user creation, the System Administrator role creates the user, and the Security Administrator role assigns security-relevant attributes, such as a password.
Before You Begin
You must be superuser, in the root role, in the Security Administrator role, or in the Primary Administrator role. The Security Administrator role has the least amount of privilege that is required for user creation.
The Solaris Management Console is displayed. For details, see Create the Security Administrator Role in Trusted Extensions.
-
Double-click User Accounts in the Solaris Management Console.
-
From the Action menu, choose Add User -> Use Wizard.
 Caution –
Caution – The names and IDs of roles and users come from the same pool. Do not use existing names or IDs for the users that you add.
-
Follow the online help.
You can also follow the procedures in How to Add a User With the Solaris Management Console’s Users Tool in System Administration Guide: Basic Administration.
-
After creating the user, double-click the created user to modify the settings.
Note –For users who can assume roles, make the user account Always Available, and do not set password expiration dates.
Ensure that the following fields are correctly set:
-
Description – No proprietary information here.
-
Password and confirm – Assign a password of at least 6 alphanumeric characters.
Note –When the initial setup team chooses a password, the team must select a password that is difficult to guess, thus reducing the chance of an adversary gaining unauthorized access by attempting to guess passwords.
-
Account Availability – Always Available.
-
Trusted Extensions Attributes – Defaults are correct.
For a single-label system where the labels must not be visible, choose Hide for Label: Show or Hide.
-
Account Usage – Set Idle time and Idle action.
Lock account – Set to No for any user who can assume a role.
-
-
Close the Solaris Management Console.
-
Customize the user's environment.
-
Assign convenient authorizations.
After checking your site security policy, you might want to grant your first users the Convenient Authorizations rights profile. With this profile, you can enable users to allocate devices, print PostScriptTM files, print without labels, remotely log in, and shut down the system. To create the profile, see How to Create a Rights Profile for Convenient Authorizations.
-
Customize user initialization files.
See Chapter 13, Managing Users, Rights, and Roles in Trusted Extensions (Tasks).
Also see Managing Users and Rights With the Solaris Management Console (Task Map).
-
Create multilabel copy and link files.
On a multilabel system, users and roles can be set up with files that list user initialization files to be copied or linked to other labels. For more information, see .copy_files and .link_files Files.
-
Example 4–5 Using the useradd Command to Create a Local User
In this example, the root user creates a local user who can assume the Security Administrator role. For details, see the useradd(1M) and atohexlabel(1M) man pages.
First, the root user determines the hexadecimal format of the user's minimum label and clearance label.
# atohexlabel public 0x0002-08-08 # atohexlabel -c "confidential restricted" 0x0004-08-78 |
Next, the root user consults Table 1–2, and then creates the user.
# useradd -c "Local user for Security Admin" -d /export/home1 \ -K idletime=10 -K idlecmd=logout -K lock_after_retries=no -K min_label=0x0002-08-08 -K clearance=0x0004-08-78 -K labelview=showsl jandoe |
Then, the root user provides an initial password.
# passwd -r files jandoe New Password: <Type password> Re-enter new Password: <Retype password> passwd: password successfully changed for jandoe # |
Finally, the root user adds the Security Administrator role to the user's definition. The role was created in Create the Security Administrator Role in Trusted Extensions.
# usermod -R secadmin jandoe |
 Verify That the Trusted Extensions Roles
Work
Verify That the Trusted Extensions Roles
Work
To verify each role, assume the role. Then, perform tasks that only that role can perform.
Before You Begin
If you have configured DNS or routing, you must reboot after you create the roles and before you verify that the roles work.
-
For each role, log in as a user who can assume the role.
-
Open the Trusted Path menu.
In the following trusted stripe, the user name is tester.

-
In the role workspace, start the Solaris Management Console.
$ /usr/sbin/smc &
-
Select the appropriate scope for the role that you are testing.
-
Click System Services, and navigate to Users.
You are prompted for a password.
-
Click a user.
-
The System Administrator role should be able to modify fields under the General, Home Directory, and Group tabs.
If you configured the roles to enforce separation of duty, then the System Administrator role cannot set the user's initial password.
-
The Security Administrator role should be able to modify fields under all tabs.
If you configured the roles to enforce separation of duty, then the Security Administrator role cannot create a user.
-
The Primary Administrator role should be able to modify fields under all tabs.
-
-
(Optional) If you are enforcing separation of duty, prevent the default rights profiles from being used.
Note –When the system is upgraded to a newer version of the Solaris OS, the System Administrator, User Management, and User Security default profiles are replaced.
In the trusted editor, perform one of the following steps:
-
Remove the three rights profiles from the prof_attr file.
Removal prevents an administrator from viewing or assigning these profiles. Also, remove the prof_attr.orig file.
-
Comment out the three rights profiles in the prof_attr file.
Commenting out the rights profiles prevents these profiles from being viewed in the Solaris Management Console or from being used in commands that manage users. The profiles and their contents can still be viewed in the prof_attr file.
-
Type a different description for the three rights profiles in the prof_attr file.
Edit the prof_attr file to change the description field of these rights profiles. For example, you might replace the descriptions with Do not use this profile. This change warns an administrator to not use the profile, but does not prevent the profile from being used.
-
 Enable Users to Log In to a Labeled
Zone
Enable Users to Log In to a Labeled
Zone
When the host is rebooted, the association between the devices and the underlying storage must be re-established.
Before You Begin
You have created at least one labeled zone. That zone is not being used for cloning.
-
Reboot the system.
-
Log in as the root user.
-
Restart the zones service.
# svcs zones STATE STIME FMRI offline - svc:/system/zones:default
# svcadm restart svc:/system/zones:default
-
Log out.
Regular users can now log in. Their session is in a labeled zone.
Creating Home Directories in Trusted Extensions
In Trusted Extensions, users need access to their home directories at every label at which the users work. To make every home directory available to the user requires that you create a multilevel home directory server, run the automounter on the server, and export the home directories. On the client side, you can run scripts to find the home directory for every zone for each user, or you can have the user log in to the home directory server.
 Create the Home Directory Server in Trusted Extensions
Create the Home Directory Server in Trusted Extensions
Before You Begin
You must be superuser, in the root role, or in the Primary Administrator role.
-
Install and configure the home directory server with Trusted Extensions software.
-
If you are cloning zones, make sure that you use a Solaris ZFS snapshot that has empty home directories.
-
Because users require a home directory at every label that they they can log in to, create every zone that a user can log in to. For example, if you use the default label_encodings file, you would create a zone for the PUBLIC label.
-
-
If you are using UFS and not Solaris ZFS, enable the NFS server to serve itself.
-
In the global zone, modify the automount entry in the nsswitch.conf file.
Use the trusted editor to edit the /etc/nsswitch.conf file. For the procedure, see How to Edit Administrative Files in Trusted Extensions.
automount: files
-
In the global zone, run the automount command.
-
-
For every labeled zone, follow the automount procedure in How to NFS Mount Files in a Labeled Zone. Then, return to this procedure.
-
Verify that the home directories have been created.
-
Log out of the home directory server.
-
As a regular user, log in to the home directory server.
-
In the login zone, open a terminal.
-
In the terminal window, verify that the user's home directory exists.
-
Create workspaces for every zone that the user can work in.
-
In each zone, open a terminal window to verify that the user's home directory exists.
-
-
Log out of the home directory server.
 Enable Users to Access Their Home Directories
in Trusted Extensions
Enable Users to Access Their Home Directories
in Trusted Extensions
Users can initially log in to the home directory server to create a home directory that can be shared with other systems. To create a home directory at every label, each user must log in to the home directory server at every label.
Alternatively, you, as administrator, can create a script to create a mount point for home directories on each user's home system before the user first logs in. The script creates mount points at every label at which the user is permitted to work.
Before You Begin
The home directory server for your Trusted Extensions domain is configured.
-
Choose whether to allow direct login to the server, or whether to run a script.
-
Enable users to log in directly to the home directory server.
-
Instruct each user to log in to the home directory server.
After successful login, the user must log out.
-
Instruct each user to log in again, and this time, to choose a different login label.
The user uses the label builder to choose a different login label. After successful login, the user must log out.
-
Instruct each user to repeat the login process for every label that the user is permitted to use.
-
Instruct the users to log in from their regular workstation.
Their home directory for their default label is available. When a user changes the label of a session or adds a workspace at a different label, the user's home directory for that label is mounted.
-
-
Write a script that creates a home directory mount point for every user, and run the script.
#!/bin/sh # for zoneroot in `/usr/sbin/zoneadm list -p | cut -d ":" -f4` ; do if [ $zoneroot != / ]; then prefix=$zoneroot/root/export for j in `getent passwd|tr ' ' _` ; do uid=`echo $j|cut -d ":" -f3` if [ $uid -ge 100 ]; then gid=`echo $j|cut -d ":" -f4` homedir=`echo $j|cut -d ":" -f6` mkdir -m 711 -p $prefix$homedir chown $uid:$gid $prefix$homedir fi done fi done
-
Adding Users and Hosts to an Existing Trusted Network
If you have users who are defined in NIS maps, you can add them to your network.
To add hosts and labels to hosts, see the following procedures:
-
To add a host, you use the Computers and Networks tool set in the Solaris Management Console. For details, see How to Add Hosts to the System's Known Network.
When you add a host to the LDAP server, add all IP addresses that are associated with the host. All-zones addresses, including addresses for labeled zones, must be added to the LDAP server.
-
To label a host, see How to Assign a Security Template to a Host or a Group of Hosts.
 Add an NIS User to the LDAP Server
Add an NIS User to the LDAP Server
Before You Begin
You must be superuser, in the root role, or in the Primary Administrator role.
-
From the NIS database, gather the information that you need.
-
Create a file from the user's entry in the aliases database.
% ypcat -k aliases | grep login-name > aliases.name
-
Create a file from the user's entry in the passwd database.
% ypcat -k passwd | grep "Full Name" > passwd.name
-
Create a file from the user's entry in the auto_home_ database.
% ypcat -k auto_home | grep login-name > auto_home_label
-
-
Reformat the information for LDAP and Trusted Extensions.
-
Use the sed command to reformat the aliases entry.
% sed 's/ /:/g' aliases.login-name > aliases
-
Use the nawk command to reformat the passwd entry.
% nawk -F: '{print $1":x:"$3":"$4":"$5":"$6":"$7}' passwd.name > passwd -
Use the nawk command to create a shadow entry.
% nawk -F: '{print $1":"$2":6445::::::"}' passwd.name > shadow -
Use the nawk command to create a user_attr entry.
% nawk -F: '{print $1"::::lock_after_retries=yes-or-no;profiles=user-profile, ...; labelview=int-or-ext,show-or-hide;min_label=min-label; clearance=max-label;type=normal;roles=role-name,...; auths=auth-name,..."}' passwd.name > user_attr
-
-
Copy the modified files to the /tmp directory on the LDAP server.
# cp aliases auto_home_internal passwd shadow user_attr /tmp/name
-
Add the entries in the files in Step 3 to the databases on the LDAP server.
# /usr/sbin/ldapaddent -D "cn=directory manager" -w DM-password \ -a simple -f /tmp/name/aliases aliases # /usr/sbin/ldapaddent -D "cn=directory manager" -w DM-password \ -a simple -f /tmp/name/auto_home_internal auto_home_internal # /usr/sbin/ldapaddent -D "cn=directory manager" -w DM-password \ -a simple -f /tmp/name/passwd passwd # /usr/sbin/ldapaddent -D "cn=directory manager" -w DM-password \ -a simple -f /tmp/name/shadow shadow # /usr/sbin/ldapaddent -D "cn=directory manager" -w DM-password \ -a simple -f /tmp/name/user_attr user_attr
Example 4–6 Adding a User From an NIS Database to the LDAP Server
In the following example, the administrator adds a new user to the trusted network. The user's information is stored originally in an NIS database. To protect the LDAP server password, the administrator runs the ldapaddent commands on the server.
In Trusted Extensions, the new user can allocate devices and assume the Operator role. Because the user can assume a role, the user account does not get locked out. The user's minimum label is PUBLIC. The label at which the user works is INTERNAL, so jan is added to the auto_home_internal database. The auto_home_internal database automounts jan's home directory with read-write permissions.
-
On the LDAP server, the administrator extracts user information from NIS databases.
# ypcat -k aliases | grep jan.doe > aliases.jan # ypcat passwd | grep "Jan Doe" > passwd.jan # ypcat -k auto_home | grep jan.doe > auto_home_internal
-
Then, the administrator reformats the entries for LDAP.
# sed 's/ /:/g' aliases.jan > aliases # nawk -F: '{print $1":x:"$3":"$4":"$5":"$6":"$7}' passwd.jan > passwd # nawk -F: '{print $1":"$2":6445::::::"}' passwd.jan > shadow -
Then, the administrator creates a user_attr entry for Trusted Extensions.
# nawk -F: '{print $1"::::lock_after_retries=no;profiles=Media User; labelview=internal,showsl;min_label=0x0002-08-08; clearance=0x0004-08-78;type=normal;roles=oper; auths=solaris.device.allocate"}' passwd.jan > user_attr -
Then, the administrator copies the files to the /tmp/jan directory.
# cp aliases auto_home_internal passwd shadow user_attr /tmp/jan
-
Finally, the administrator populates the server with the files in the /tmp/jan directory.
# /usr/sbin/ldapaddent -D "cn=directory manager" -w a2b3c4d5e6 \ -a simple -f /tmp/jan/aliases aliases # /usr/sbin/ldapaddent -D "cn=directory manager" -w a2b3c4d5e6 \ -a simple -f /tmp/jan/auto_home_internal auto_home_internal # /usr/sbin/ldapaddent -D "cn=directory manager" -w a2b3c4d5e6 \ -a simple -f /tmp/jan/passwd passwd # /usr/sbin/ldapaddent -D "cn=directory manager" -w a2b3c4d5e6 \ -a simple -f /tmp/jan/shadow shadow # /usr/sbin/ldapaddent -D "cn=directory manager" -w a2b3c4d5e6 \ -a simple -f /tmp/jan/user_attr user_attr
Troubleshooting Your Trusted Extensions Configuration
In Trusted Extensions, the labeled zones communicate with the X server through the global zone. Therefore, the labeled zones must have usable routes to the global zone. Also, options that were selected during a Solaris installation can prevent Trusted Extensions from using interfaces to the global zone.
netservices limited Was Run After Trusted Extensions Was Enabled
- Description:
-
Instead of running the netservices limited command before you enabled Trusted Extensions, you ran the command in the global zone afterwards. Therefore, your labeled zones are unable to connect to the X server in the global zone.
- Solution:
-
Run the following commands to open the services that Trusted Extensions requires to communicate between zones:
# svccfg -s x11-server setprop options/tcp_listen = true # svcadm enable svc:/network/rpc/rstat:default
Labeled Zone Is Unable to Access the X Server
- Description:
-
If a labeled zone cannot successfully access the X server, you might see messages such as the following:
-
Action failed. Reconnect to Solaris Zone?
-
No route available
-
Cannot reach globalzone-hostname:0
-
- Cause:
-
The labeled zones might not be able to access the X server for any of the following reasons:
-
The zone is not initialized and is waiting for the sysidcfg process to complete.
-
The labeled zone's host name is not recognized by the naming service that runs in the global zone.
-
No interface is specified as all-zones.
-
The labeled zone's network interface is down.
-
LDAP name lookups fail.
-
NFS mounts do not work.
-
- Steps toward a solution:
-
-
Log in to the zone.
You can use the zlogin command.
# zlogin -z zone-name
If you cannot log in as superuser, use the zlogin -S command to bypass authentication.
-
Verify that the zone is running.
# zoneadm list
If a zone has a status of running, the zone is running at least one process.
-
Address any problems that prevent the labeled zones from accessing the X server.
-
Initialize the zone by completing the sysidcfg process.
Run the sysidcfg program interactively. Answer the prompts in the Zone Terminal Console, or in the terminal window where you ran the zlogin command.
To run the sysidcfg process noninteractively, you can do one of the following:
-
Specify the Initialize item for the /usr/sbin/txzonemgr script.
The Initialize item enables you to supply default values to the sysidcfg questions.
-
Write your own sysidcfg script.
For more information, see the sysidcfg(4) man page.
-
-
Verify that the X server is available to the zone.
Log in to the labeled zone. Set the
DISPLAYvariable to point to the X server, and open a window.
# DISPLAY=global-zone-hostname:n.n # export DISPLAY # /usr/openwin/bin/xclock
If a labeled window does not appear, the zone networking has not been configured correctly for that labeled zone.
-
Configure the zone's host name with the naming service.
The zone's local /etc/hosts file is not used. Instead, equivalent information must be specified in the global zone or on the LDAP server. The information must include the IP address of the host name that is assigned to the zone.
-
No interface is specified as all-zones.
Unless all your zones have IP addresses on the same subnet as the global zone, you might need to configure an all-zones (shared) interface. This configuration enables a labeled zone to connect to the X server of the global zone. If you want to restrict remote connections to the X server of the global zone, you can use vni0 as the all-zones address.
If you do not want an all-zones interface configured, you must provide a route to the global zone X server for each zone. These routes must be configured in the global zone.
-
The labeled zone's network interface is down.
# ifconfig -a
Use the ifconfig command to verify that the labeled zone's network interface is both UP and RUNNING.
-
LDAP name lookups fail.
Use the ldaplist command to verify that each zone can communicate with the LDAP server or the LDAP proxy server. On the LDAP server, verify that the zone is listed in the tnrhdb database.
-
NFS mounts do not work.
As superuser, restart automount in the zone. Or, add a crontab entry to run the automount command every five minutes.
-
Do the following:
-
Additional Trusted Extensions Configuration Tasks
The following two tasks enable you to transfer exact copies of configuration files to every Trusted Extensions system at your site. The final task enables you to remove Trusted Extensions customizations from a Solaris system.
 How to Copy Files to Portable Media in Trusted Extensions
How to Copy Files to Portable Media in Trusted Extensions
When copying to portable media, label the media with the sensitivity label of the information.
Note –
During Trusted Extensions configuration, superuser or an equivalent role copies administrative files to and from portable media. Label the media with Trusted Path.
Before You Begin
To copy administrative files, you must be superuser or in a role in the global zone.
-
Allocate the appropriate device.
Use the Device Manager, and insert clean media. For details, see How to Allocate a Device in Trusted Extensions in Solaris Trusted Extensions User’s Guide.
-
In Solaris Trusted Extensions (GNOME), a File Browser displays the contents.
In this procedure, File Browser is used to refer to this GUI.
-
-
Open a second File Browser.
-
Navigate to the folder that contains the files to be copied
For example, you might have copied files to an /export/clientfiles folder.
-
For each file, do the following:
-
Deallocate the device.
For details, see How to Deallocate a Device in Trusted Extensions in Solaris Trusted Extensions User’s Guide.
-
On the File Browser for the portable media, choose Eject from the File menu.
Note –Remember to physically affix a label to the media with the sensitivity label of the copied files.
Example 4–7 Keeping Configuration Files Identical on All Systems
The system administrator wants to ensure that every machine is configured with the same settings. So, on the first machine that is configured, she creates a directory that cannot be deleted between reboots. In that directory, the administrator places the files that should be identical or very similar on all systems.
For example, she copies the Trusted Extensions toolbox that the Solaris Management Console uses for the LDAP scope, /var/sadm/smc/toolboxes/tsol_ldap/tsol_ldap.tbx. She has customized remote host templates in the tnrhtp file, has a list of DNS servers, and audit configuration files. She also modified the policy.conf file for her site. So, she copies the files to the permanent directory.
# mkdir /export/commonfiles # cp /etc/security/policy.conf \ /etc/security/audit_control \ /etc/security/audit_startup \ /etc/security/tsol/tnrhtp \ /etc/resolv.conf \ /etc/nsswitch.conf \ /export/commonfiles |
She uses the Device Allocation Manager to allocate a diskette in the global zone, and transfers the files to the diskette. On a separate diskette, labeled ADMIN_HIGH, she puts the label_encodings file for the site.
When she copies the files onto a system, she modifies the dir: entries in the /etc/security/audit_control file for that system.
 How to Copy Files From Portable Media
in Trusted Extensions
How to Copy Files From Portable Media
in Trusted Extensions
It is safe practice to rename the original Trusted Extensions file before replacing the file. When configuring a system, the root role renames and copies administrative files.
Before You Begin
To copy administrative files, you must be superuser or in a role in the global zone.
-
Allocate the appropriate device.
For details, see How to Allocate a Device in Trusted Extensions in Solaris Trusted Extensions User’s Guide.
In Solaris Trusted Extensions (GNOME), a File Browser displays the contents.
-
Insert the media that contains the administrative files.
-
If the system has a file of the same name, copy the original file to a new name.
For example, add .orig to the end of the original file:
# cp /etc/security/tsol/tnrhtp /etc/security/tsol/tnrhtp.orig
-
Open a File Browser.
-
Navigate to the desired destination directory, such as /etc/security/tsol
-
For each file that you want to copy, do the following:
-
Deallocate the device.
For details, see How to Deallocate a Device in Trusted Extensions in Solaris Trusted Extensions User’s Guide.
-
When prompted, eject and remove the media.
Example 4–8 Loading Audit Configuration Files in Trusted Extensions
In this example, roles are not yet configured on the system. The root user needs to copy configuration files to portable media. The contents of the media will then be copied to other systems. These files are to be copied to each system that is configured with Trusted Extensions software.
The root user allocates the floppy_0 device in the Device Allocation Manager and responds yes to the mount query. Then, the root user inserts the diskette with the configuration files and copies them to the disk. The diskette is labeled Trusted Path.
To read from the media, the root user allocates the device on the receiving host, then downloads the contents.
If the configuration files are on a tape, the root user allocates the mag_0 device. If the configuration files are on a CD-ROM, the root user allocates the cdrom_0 device.
 How to Remove Trusted Extensions From the
System
How to Remove Trusted Extensions From the
System
To remove Trusted Extensions from your Solaris system, you perform specific steps to remove Trusted Extensions customizations to the Solaris system.
-
As in the Solaris OS, archive any data in the labeled zones that you want to keep.
-
Remove the labeled zones from the system.
For details, see How to Remove a Non-Global Zone in System Administration Guide: Virtualization Using the Solaris Operating System.
-
Disable the Trusted Extensions service.
# svcadm disable labeld
-
Run the bsmunconv command.
For the effect of this command, see the bsmunconv(1M) man page.
-
(Optional) Reboot the system.
-
Configure the system.
Various services might need to be configured for your Solaris system. Candidates include auditing, basic networking, naming services, and file system mounts.
Chapter 5 Configuring LDAP for Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
This chapter covers how to configure the Sun JavaTM System Directory Server and the Solaris Management Console for use with Solaris Trusted Extensions. The Directory Server provides LDAP services. LDAP is the supported naming service for Trusted Extensions. The Solaris Management Console is the administrative GUI for local and LDAP databases.
You have two options when configuring the Directory Server. You can configure an LDAP server on a Trusted Extensions system, or you can use an existing server and connect to it by using a Trusted Extensions proxy server. Follow the instructions in one of the following task maps:
-
Configuring an LDAP Server on a Trusted Extensions Host (Task Map)
-
Configuring an LDAP Proxy Server on a Trusted Extensions Host (Task Map)
Configuring an LDAP Server on a Trusted Extensions Host (Task Map)
|
Task |
Description |
For Instructions |
|---|---|---|
|
Set up a Trusted Extensions LDAP server. |
If you do not have an existing Sun Java System Directory Server, make your first Trusted Extensions system the Directory Server. The other Trusted Extensions systems are clients of this server. |
Collect Information for the Directory Server for LDAP |
|
Add Trusted Extensions databases to the server. |
Populate the LDAP server with data from the Trusted Extensions system files. | |
|
Configure the Solaris Management Console to work with the Directory Server. |
Manually set up an LDAP toolbox for the Solaris Management Console. The toolbox can be used to modify Trusted Extensions attributes on network objects. |
Configuring the Solaris Management Console for LDAP (Task Map) |
|
Configure all other Trusted Extensions systems as clients of this server. |
When you configure another system with Trusted Extensions, make the system a client of this LDAP server. |
Configuring an LDAP Proxy Server on a Trusted Extensions Host (Task Map)
Use this task map if you have an existing Sun Java System Directory Server that is running on a Solaris system.
|
Task |
Description |
For Instructions |
|---|---|---|
|
Add Trusted Extensions databases to the server. |
The Trusted Extensions network databases, tnrhdb and tnrhtp, need to be added to the LDAP server. | |
|
Set up an LDAP proxy server. |
Make one Trusted Extensions system the proxy server for the other Trusted Extensions systems. The other Trusted Extensions systems use this proxy server to reach the LDAP server. | |
|
Configure the proxy server to have a multilevel port for LDAP. |
Enable the Trusted Extensions proxy server to communicate with the LDAP server at specific labels. |
Configure a Multilevel Port for the Sun Java System Directory Server |
|
Configure the Solaris Management Console to work with the LDAP proxy server. |
You manually set up an LDAP toolbox for the Solaris Management Console. The toolbox can be used to modify Trusted Extensions attributes on network objects. |
Configuring the Solaris Management Console for LDAP (Task Map) |
|
Configure all other Trusted Extensions systems as clients of the LDAP proxy server. |
When you configure another system with Trusted Extensions, make the system a client of the LDAP proxy server. |
Configuring the Sun Java System Directory Server on a Trusted Extensions System
The LDAP naming service is the supported naming service for Trusted Extensions. If your site is not yet running the LDAP naming service, configure a Sun Java System Directory Server (Directory Server) on a system that is configured with Trusted Extensions. If your site is already running a Directory Server, then you need to add the Trusted Extensions databases to the server. To access the Directory Server, you then set up an LDAP proxy on a Trusted Extensions system.
Note –
If you do not use this LDAP server as an NFS server or as a server for Sun RayTM clients, then you do not need to install any labeled zones on this server.
 Collect Information for the Directory Server for
LDAP
Collect Information for the Directory Server for
LDAP
-
Determine the values for the following items.
The items are listed in the order of their appearance in the Sun Java Enterprise System Install Wizard.
Install Wizard Prompt
Action or Information
Sun Java System Directory Server version
Administrator User ID
The default value is admin.
Administrator Password
Create a password, such as admin123.
Directory Manager DN
The default value is cn=Directory Manager.
Directory Manager Password
Create a password, such as dirmgr89.
Directory Server Root
The default value is /var/Sun/mps. This path is also used later if the proxy software is installed.
Server Identifier
The default value is the local system.
Server Port
If you plan to use the Directory Server to provide standard LDAP naming services to client systems, use the default value, 389.
If you plan to use the Directory Server to support a subsequent installation of a proxy server, enter a nonstandard port, such as 10389.
Suffix
Include your domain component, as in dc=example-domain,dc=com.
Administration Domain
Construct to correspond to the Suffix, as in, example-domain.com.
System User
The default value is root.
System Group
The default value is root.
Data Storage Location
The default value is Store configuration data on this server.
Data Storage Location
The default value is Store user data and group data on this server.
Administration Port
The default value is the Server Port. A suggested convention for changing the default is software-version TIMES 1000. For software version 5.2, this convention would result in port 5200.
 Install the Sun Java System Directory Server
Install the Sun Java System Directory Server
The Directory Server packages are available from the Sun Software Gateway web site.
-
Find the Sun Java System Directory Server packages on the Sun web site.
-
On the Sun Software Gateway page, click the Get It tab.
-
Click the checkbox for the Sun Java Identity Management Suite.
-
Click the Submit button.
-
If you are not registered, register.
-
Log in to download the software.
-
Click the Download Center at the upper left of the screen.
-
Under Identity Management, download the most recent software that is appropriate for your platform.
-
-
In the /etc/hosts file, add the FQDN to your system's hostname entry.
The FQDN is the Fully Qualified Domain Name. This name is a combination of the host name and the administration domain, as in:
192.168.5.5 myhost myhost.example-domain.com
-
Install the Directory Server packages.
Answer the questions by using the information from Collect Information for the Directory Server for LDAP.
-
Ensure that the Directory Server starts at every boot.
Templates for the SMF services for the Directory Server are in the Sun Java System Directory Server packages.
-
For a Trusted Extensions Directory Server, enable the service.
# dsadm stop /export/home/ds/instances/your-instance # dsadm enable-service -T SMF /export/home/ds/instances/your-instance # dsadm start /export/home/ds/instances/your-instance
For information about the dsadm command, see the dsadm(1M) man page.
-
For a proxy Directory Server, enable the service.
# dpadm stop /export/home/ds/instances/your-instance # dpadm enable-service -T SMF /export/home/ds/instances/your-instance # dpadm start /export/home/ds/instances/your-instance
For information about the dpadm command, see the dpadm(1M) man page.
-
-
Verify your installation.
# dsadm info /export/home/ds/instances/your-instance Instance Path: /export/home/ds/instances/your-instance Owner: root(root) Non-secure port: 389 Secure port: 636 Bit format: 32-bit State: Running Server PID: 298 DSCC url: - SMF application name: ds--export-home-ds-instances-your-instance Instance version: D-A00
Troubleshooting
For strategies to solve LDAP configuration problems, see Chapter 13, LDAP Troubleshooting (Reference), in System Administration Guide: Naming and Directory Services (DNS, NIS, and LDAP).
 Configure the Logs for the Sun Java System Directory Server
Configure the Logs for the Sun Java System Directory Server
This procedure configures three types of logs: access logs, audit logs, and error logs. The following default settings are not changed:
-
All logs are enabled and buffered.
-
Logs are placed in the appropriate /export/home/ds/instances/your-instance/logs/LOG_TYPE directory.
-
Events are logged at log level 256.
-
Logs are protected with 600 file permissions.
-
Access logs are rotated daily.
-
Error logs are rotated weekly.
The settings in this procedure meet the following requirements:
-
Audit logs are rotated daily.
-
Log files that are older than 3 months expire.
-
All log files use a maximum of 20,000 MBytes of disk space.
-
A maximum of 100 log files is kept, and each file is at most 500 MBytes.
-
The oldest logs are deleted if less than 500 MBytes free disk space is available.
-
Additional information is collected in the error logs.
-
Configure the access logs.
The LOG_TYPE for access is ACCESS. The syntax for configuring logs is the following:
dsconf set-log-prop LOG_TYPE property:value
# dsconf set-log-prop ACCESS max-age:3M # dsconf set-log-prop ACCESS max-disk-space-size:20000M # dsconf set-log-prop ACCESS max-file-count:100 # dsconf set-log-prop ACCESS max-size:500M # dsconf set-log-prop ACCESS min-free-disk-space:500M
-
Configure the audit logs.
# dsconf set-log-prop AUDIT max-age:3M # dsconf set-log-prop AUDIT max-disk-space-size:20000M # dsconf set-log-prop AUDIT max-file-count:100 # dsconf set-log-prop AUDIT max-size:500M # dsconf set-log-prop AUDIT min-free-disk-space:500M # dsconf set-log-prop AUDIT rotation-interval:1d
By default, the rotation interval for audit logs is one week.
-
Configure the error logs.
In this configuration, you specify additional data to be collected in the error log.
# dsconf set-log-prop ERROR max-age:3M # dsconf set-log-prop ERROR max-disk-space-size:20000M # dsconf set-log-prop ERROR max-file-count:30 # dsconf set-log-prop ERROR max-size:500M # dsconf set-log-prop ERROR min-free-disk-space:500M # dsconf set-log-prop ERROR verbose-enabled:on
-
(Optional) Further configure the logs.
You can also configure the following settings for each log:
# dsconf set-log-prop LOG_TYPE rotation-min-file-size:undefined # dsconf set-log-prop LOG_TYPE rotation-time:undefined
For information about the dsconf command, see the dsconf(1M) man page.
 Configure a Multilevel Port for the Sun Java System Directory Server
Configure a Multilevel Port for the Sun Java System Directory Server
To work in Trusted Extensions, the server port of the Directory Server must be configured as a multilevel port (MLP) in the global zone.
-
Start the Solaris Management Console.
# /usr/sbin/smc &
-
Select the This Computer (this-host: Scope=Files, Policy=TSOL) toolbox.
-
Click System Configuration, then click Computers and Networks.
You are prompted for your password.
-
Type the appropriate password.
-
Double-click Trusted Network Zones.
-
Double-click the global zone.
-
Add a multilevel port for the TCP protocol:
-
Add a multilevel port for the UDP protocol:
-
Click OK to save the settings.
-
Update the kernel.
# tnctl -fz /etc/security/tsol/tnzonecfg
 Populate the Sun Java System Directory Server
Populate the Sun Java System Directory Server
Several LDAP databases have been created or modified to hold Trusted Extensions data about label configuration, users, and remote systems. In this procedure, you populate the Directory Server databases with Trusted Extensions information.
Before You Begin
If site security requires separation of duty, complete the following before populating the Directory server:
-
Create a staging area for files that you plan to use to populate the naming service databases.
# mkdir -p /setup/files
-
Copy the sample /etc files into the staging area.
# cd /etc # cp aliases group networks netmasks protocols /setup/files # cp rpc services auto_master /setup/files # cd /etc/security # cp auth_attr prof_attr exec_attr /setup/files/ # # cd /etc/security/tsol # cp tnrhdb tnrhtp /setup/files
# cd /etc/inet # cp ipnodes /setup/files
-
Remove the +auto_master entry from the /setup/files/auto_master file.
-
Remove the ?:::::? entry from the /setup/files/auth_attr file.
-
Remove the :::: entry from the /setup/files/prof_attr file.
-
Create the zone automaps in the staging area.
In the following list of automaps, the first of each pair of lines shows the name of the file. The second line of each pair shows the file contents. The zone names identify labels from the default label_encodings file that is included with the Trusted Extensions software.
-
Substitute your zone names for the zone names in these lines.
-
myNFSserver identifies the NFS server for the home directories.
/setup/files/auto_home_public * myNFSserver_FQDN:/zone/public/root/export/home/& /setup/files/auto_home_internal * myNFSserver_FQDN:/zone/internal/root/export/home/& /setup/files/auto_home_needtoknow * myNFSserver_FQDN:/zone/needtoknow/root/export/home/& /setup/files/auto_home_restricted * myNFSserver_FQDN:/zone/restricted/root/export/home/&
-
-
Add every system on the network to the /setup/files/tnrhdb file.
No wildcard mechanism can be used here. The IP address of every system to be contacted, including the IP addresses of labeled zones, must be in this file.
-
Open the trusted editor and edit /setup/files/tnrhdb.
-
Add every IP address on a labeled system in the Trusted Extensions domain.
Labeled systems are of type cipso. Also, the name of the security template for labeled systems is cipso. Therefore, in the default configuration, a cipso entry is similar to the following:
192.168.25.2:cipso
Note –This list includes the IP addresses of global zones and labeled zones.
-
Add every unlabeled system with which the domain can communicate.
Unlabeled systems are of type unlabeled. The name of the security template for unlabeled systems is admin_low. Therefore, in the default configuration, an entry for an unlabeled system is similar to the following:
192.168.35.2:admin_low
-
Save the file, and exit the editor.
-
Check the syntax of the file.
# tnchkdb -h /setup/files/tnrhdb
-
Fix any errors before continuing.
-
-
Copy the /setup/files/tnrhdb file to the /etc/security/tsol/tnrhdb file.
-
Use the ldapaddent command to populate every file in the staging area.
# /usr/sbin/ldapaddent -D "cn=directory manager" \ -w dirmgr123 -a simple -f /setup/files/hosts hosts
Creating a Trusted Extensions Proxy for an Existing Sun Java System Directory Server
First, you need to add the Trusted Extensions databases to the existing Directory Server on a Solaris system. Second, to enable Trusted Extensions systems to access the Directory Server, you then need to configure a Trusted Extensions system to be the LDAP proxy server.
 Create an LDAP Proxy Server
Create an LDAP Proxy Server
If an LDAP server already exists at your site, create a proxy server on a Trusted Extensions system.
Before You Begin
You have added the databases that contain Trusted Extensions information to the LDAP server. For details, see Populate the Sun Java System Directory Server.
-
On a system that is configured with Trusted Extensions, create a proxy server.
For details, see Chapter 12, Setting Up LDAP Clients (Tasks), in System Administration Guide: Naming and Directory Services (DNS, NIS, and LDAP).
-
Verify that the Trusted Extensions databases can be viewed by the proxy server.
# ldaplist -l database
Troubleshooting
For strategies to solve LDAP configuration problems, see Chapter 13, LDAP Troubleshooting (Reference), in System Administration Guide: Naming and Directory Services (DNS, NIS, and LDAP).
Configuring the Solaris Management Console for LDAP (Task Map)
The Solaris Management Console is the GUI for administering the network of systems that are running Trusted Extensions.
|
Task |
Description |
For Instructions |
|---|---|---|
|
Initialize the Solaris Management Console. |
Initialize the Solaris Management Console. This procedure is performed once per system in the global zone. |
Initialize the Solaris Management Console Server in Trusted Extensions |
|
Register credentials. |
Authenticate the Solaris Management Console with the LDAP server. |
Register LDAP Credentials With the Solaris Management Console |
|
Enable remote administration on a system. |
By default, a Solaris Management Console client cannot communicate with a Console server on another system. You must explicitly enable remote administration. |
Enable the Solaris Management Console to Accept Network Communications |
|
Create the LDAP toolbox. |
Create the LDAP toolbox in the Solaris Management Console for Trusted Extensions. | |
|
Verify communications. |
Verify that Trusted Extensions hosts can become LDAP clients. |
Verify That the Solaris Management Console Contains Trusted Extensions Information |
 Register LDAP Credentials With the Solaris Management Console
Register LDAP Credentials With the Solaris Management Console
Before You Begin
You must be the root user on an LDAP server that is running Trusted Extensions. The server can be a proxy server.
Your Sun Java System Directory Server must be configured. You have completed one of the following configurations:
-
Configuring an LDAP Server on a Trusted Extensions Host (Task Map)
-
Configuring an LDAP Proxy Server on a Trusted Extensions Host (Task Map)
-
Register the LDAP administrative credentials.
LDAP-Server # /usr/sadm/bin/dtsetup storeCred Administrator DN:Type the value for cn on your system Password:Type the Directory Manager password Password (confirm):Retype the password
-
List the scopes on the Directory Server.
LDAP-Server # /usr/sadm/bin/dtsetup scopes Getting list of manageable scopes... Scope 1 file:Displays name of file scope Scope 2 ldap:Displays name of ldap scope
Your LDAP server setup determines the scopes that are listed. The LDAP scope is not listed until the LDAP toolbox is edited. The toolbox cannot be edited until after the server is registered.
Example 5–1 Registering LDAP Credentials
In this example, the name of the LDAP server is LDAP1 and the value for cn is the default, Directory Manager.
# /usr/sadm/bin/dtsetup storeCred Administrator DN:cn=Directory Manager Password:abcde1;! Password (confirm):abcde1;! # /usr/sadm/bin/dtsetup scopes Getting list of manageable scopes... Scope 1 file:/LDAP1/LDAP1 Scope 2 ldap:/LDAP1/cd=LDAP1,dc=example,dc=com |
 Enable the Solaris Management Console to Accept Network Communications
Enable the Solaris Management Console to Accept Network Communications
By default, Solaris systems are not configured to listen on ports that present security risks. Therefore, you must explicitly configure any system that you plan to administer remotely to accept network communications. For example, to administer network databases on the LDAP server from a client, the Solaris Management Console server on the LDAP server must accept network communications.
For an illustration of the Solaris Management Console configuration requirements for a network with an LDAP server, see Client-Server Communication With the Solaris Management Console.
Before You Begin
You must be superuser in the global zone on the Solaris Management Console server system. In this procedure, that system is called the remote system. Also, you must have command line access to the client system as superuser.
-
On the remote system, enable the system to accept remote connections.
The smc daemon is controlled by the wbem service. If the options/tcp_listen property to the wbem service is set to true, the Solaris Management Console server accepts remote connections.
# /usr/sbin/svcprop -p options wbem options/tcp_listen boolean false # svccfg -s wbem setprop options/tcp_listen=true
-
Refresh and restart the wbem service.
# svcadm refresh wbem # svcadm restart wbem
-
Verify that the wbem service is set to accept remote connections.
# svcprop -p options wbem options/tcp_listen boolean true
-
On the remote system and on any client that needs to access the Solaris Management Console, ensure that remote connections are enabled in the smcserver.config file.
Troubleshooting
If you restart or enable the wbem service, you must ensure that the remote.connections parameter in the smcserver.config file remains set to true.
 Edit the LDAP Toolbox in the Solaris Management Console
Edit the LDAP Toolbox in the Solaris Management Console
Before You Begin
You must be superuser on the LDAP server. The LDAP credentials must be registered with the Solaris Management Console, and you must know the output of the /usr/sadm/bin/dtsetup scopes command. For details, see Register LDAP Credentials With the Solaris Management Console.
-
Find the LDAP toolbox.
# cd /var/sadm/smc/toolboxes/tsol_ldap # ls *tbx tsol_ldap.tbx
-
Provide the LDAP server name.
-
Open the trusted editor.
-
Copy and paste the full pathname of the tsol_ldap.tbx toolbox as the argument to the editor.
For example, the following path is the default location of the LDAP toolbox:
/var/sadm/smc/toolboxes/tsol_ldap/tsol_ldap.tbx
-
Replace the scope information.
Replace the server tags between the <Scope> and </Scope> tags with the output of the ldap:/...... line from the /usr/sadm/bin/dtsetup scopes command.
<Scope>ldap:/<ldap-server-name>/<dc=domain,dc=suffix></Scope>
-
Replace every instance of <?server?> or <?server ?> with the LDAP server.
<Name>This Computer (ldap-server-name: Scope=ldap, Policy=TSOL)</Name> services and configuration of ldap-server-name.</Description> and configuring ldap-server-name.</Description> ...
-
Save the file, and exit the editor.
-
-
Refresh and restart the wbem service.
# svcadm refresh wbem # svcadm restart wbem
Example 5–2 Configuring the LDAP Toolbox
In this example, the name of the LDAP server is LDAP1. To configure the toolbox, the administrator replaces the instances of <?server ?> with LDAP1.
# cd /var/sadm/smc/toolboxes/tsol_ldap # /usr/dt/bin/trusted_edit /tsol_ldap.tbx <Scope>ldap:/LDAP1/cd=LDAP1,dc=example,dc=com</Scope ... <Name>This Computer (LDAP1: Scope=ldap, Policy=TSOL)</Name> services and configuration of LDAP1.</Description> and configuring LDAP1.</Description> ... |
 Verify That the Solaris Management Console Contains Trusted Extensions Information
Verify That the Solaris Management Console Contains Trusted Extensions Information
For an illustration of the Solaris Management Console configuration requirements for a network with an LDAP server and for a network without an LDAP server, see Client-Server Communication With the Solaris Management Console.
Before You Begin
You must be logged in to an LDAP client in an administrative role, or as superuser. To make a system an LDAP client, see Make the Global Zone an LDAP Client in Trusted Extensions.
To administer the local system, you must have completed Initialize the Solaris Management Console Server in Trusted Extensions.
To connect to a Console server on a remote system from the local system, you must have completed Initialize the Solaris Management Console Server in Trusted Extensions on both systems. Also, on the remote system, you must have completed Enable the Solaris Management Console to Accept Network Communications.
To administer the databases in the LDAP naming service from the LDAP client, on the LDAP server you must have completed Edit the LDAP Toolbox in the Solaris Management Console, in addition to the preceding procedures.
-
Start the Solaris Management Console.
# /usr/sbin/smc &
-
Open a Trusted Extensions toolbox.
A Trusted Extensions toolbox has the value Policy=TSOL.
-
On a trusted network that uses LDAP as a naming service, perform the following tests:
-
To check that local administrative databases can be accessed, open the following toolbox:
This Computer (this-host: Scope=Files, Policy=TSOL)
-
To check that the LDAP server's local administrative databases can be accessed, specify the following toolbox:
This Computer (ldap-server: Scope=Files, Policy=TSOL)
-
To check that the naming service databases on the LDAP server can be accessed, specify the following toolbox:
This Computer (ldap-server: Scope=LDAP, Policy=TSOL)
-
-
On a trusted network that does not use LDAP as a naming service, perform the following tests:
-
To check that local administrative databases can be accessed, open the following toolbox:
This Computer (this-host: Scope=Files, Policy=TSOL)
-
To check that a remote system's local administrative databases can be accessed, specify the following toolbox:
This Computer (remote-system: Scope=Files, Policy=TSOL)
-
-
-
Under System Configuration, navigate to Computers and Networks, then Security Templates.
-
Check that the correct templates and labels have been applied to the remote systems.
Note –When you try to access network database information from a system that is not the LDAP server, the operation fails. The Console allows you to log in to the remote host and open the toolbox. However, when you try to access or change information, the following error message indicates that you have selected Scope=LDAP on a system that is not the LDAP server:
Management server cannot perform the operation requested. ... Error extracting the value-from-tool. The keys received from the client were machine, domain, Scope. Problem with Scope.
Troubleshooting
To troubleshoot LDAP configuration, see Chapter 13, LDAP Troubleshooting (Reference), in System Administration Guide: Naming and Directory Services (DNS, NIS, and LDAP).
Chapter 6 Configuring a Headless System With Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
Configuring and administering Solaris Trusted Extensions software on headless systems such as the NetraTM series requires modifying security settings on the headless system to enable remote access. Administering a remote Trusted Extensions system requires similar setup. To run an administrative GUI, you might need to run the process on the remote system and display the GUI on the desktop system.
For an explanation of the requirements, see Chapter 14, Remote Administration in Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
Note –
The configuration methods that headless and remote systems require do not satisfy the criteria for an evaluated configuration. For more information, see Understanding Your Site's Security Policy.
Headless System Configuration in Trusted Extensions (Task Map)
On headless systems, a console is connected by means of a serial line to a terminal emulator window. The line is typically secured by the tip command. Depending on what type of second system is available, you can use one of the following methods to configure a headless system. The methods are listed from more secure to less secure in the following table. These instructions also apply to remote systems.
|
Task |
Description |
For Instructions |
|---|---|---|
|
Enable remote login by the root user. |
If you are not using LDAP, you must initially log in to the headless system as root. If you are using LDAP, you can skip this procedure. | |
|
Enable remote login. |
Enable remote login for a user who can assume the root role or another administrative role. | |
|
Enable the administration of Trusted Extensions systems from an unlabeled system. | ||
|
Enable a user to access the global zone on a headless system. |
How to Enable Specific Users to Log In Remotely to the Global Zone in Trusted Extensions |
|
|
(Optional) Enable the display of administrative GUIs. |
Enable administrative GUIs that run on the headless system to display on the desktop system. | |
|
(Optional) Enable virtual network computing (vnc) |
From any client, uses the Xvnc server on the remote Trusted Extensions to display a multilevel session back to the client. |
How to Use Xvnc to Remotely Access a Trusted Extensions System |
|
Choose a configuration and administration method to set up the headless system. |
Assume a role or become superuser to administer the remote system. |
Use the rlogin or ssh Command to Log In and Administer a Headless System in Trusted Extensions |
|
Use the Solaris Management Console on the headless system. |
Use a Remote Solaris Management Console to Administer in the Files Scope |
|
|
If you have no windowing system, you can use serial login as superuser. This procedure is insecure. |
No configuration is required. |
Note –
Consult your security policy to determine which methods of remote administration are permissible at your site.
 Enable Remote Login by root User
in Trusted Extensions
Enable Remote Login by root User
in Trusted Extensions
As in the Solaris OS, root can log in remotely from a labeled system when the CONSOLE entry is disabled.
If you plan to administer a remote system by editing local files, use this procedure.
-
In the trusted editor, comment out the CONSOLE= line in the /etc/default/login file.
# /usr/dt/bin/trusted_edit /etc/default/login
The edited line appears similar to the following:
#CONSOLE=/dev/console
-
Permit root user login over an ssh connection.
Modify the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file. By default, ssh is enabled on a Solaris system.
# /usr/dt/bin/trusted_edit /etc/ssh/sshd_config
The edited line appears similar to the following:
PermitRootLogin yes
Next Steps
To log in as the root user from an unlabeled system, you must also complete Enable Remote Login From an Unlabeled System.
To enable remote login by a role, continue with Enable Remote Login by a Role in Trusted Extensions.
 Enable Remote Login by a Role in Trusted Extensions
Enable Remote Login by a Role in Trusted Extensions
Follow this procedure only if you must administer a headless system by using the rlogin or ssh command.
Configuration errors can be debugged remotely.
Before You Begin
If you are using local files to administer the remote system, you have completed Enable Remote Login by root User in Trusted Extensions. Then, as the root user, perform this task on both systems.
-
On both systems, identify the other system as a labeled system.
The desktop system and the headless system must identify each other as using the identical security template. For the procedure, see How to Assign a Security Template to a Host or a Group of Hosts.
To assign a temporary label, see Example 6–1.
-
On both systems, create identical users and roles.
The names and IDs must be identical, and the role must be assigned to the user on both systems. To create users and roles, see Creating Roles and Users in Trusted Extensions.
-
To contact a remote Solaris Management Console, do the following on both systems:
-
Add the other system's host name and IP address to the /etc/hosts file.
# /usr/dt/bin/trusted_edit /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost 192.168.66.66 local-system-name loghost 192.168.66.12 remote-system-name
-
To allow remote role assumption, modify the pam.conf file to relax PAM policy.
-
Copy the /etc/pam.conf file to /etc/pam.conf.orig.
# cp /etc/pam.conf /etc/pam.conf.orig
-
In the trusted editor, open the pam.conf file.
# /usr/dt/bin/trusted_edit /etc/pam.conf
-
Copy the default entries under Account management.
-
In each copied entry, change other to smcconsole.
-
To the copied pam_roles.so.1 entry, add allow_remote.
Use the Tab key between fields. This section now appears similar to the following:
# Solaris Management Console definition for Account management # smcconsole account requisite pam_roles.so.1 allow_remote smcconsole account required pam_unix_account.so.1 smcconsole account required pam_tsol_account.so.1 # Default definition for Account management # Used when service name is not explicitly mentioned for account management # other account requisite pam_roles.so.1 other account required pam_unix_account.so.1 other account required pam_tsol_account.so.1
-
Save the file and exit the editor.
-
(Optional) Copy the file to /etc/pam.conf.site.
# cp /etc/pam.conf /etc/pam.conf.site
If you upgrade the system to a later release, you must then evaluate if you should copy the changes from /etc/pam.conf.site into the pam.conf file.
-
-
Example 6–1 Creating a Temporary Definition of a Trusted Extensions Host Type
In this example, the administrator wants to start configuring a remote Trusted Extensions system before the host type definitions are set up. To do so, the administrator uses the tnctl command on the remote system to temporarily define the host type of the desktop system:
remote-TX# tnctl -h desktop-TX:cipso |
Later, the administrator wants to reach the remote Trusted Extensions system from a desktop system that is not configured with Trusted Extensions. In this case, the administrator uses the tnctl command on the remote system to temporarily define the host type of the desktop system as an unlabeled system that runs at the ADMIN_LOW label:
remote-TX# tnctl -h desktop-TX:admin_low |
 Enable Remote Login From an Unlabeled System
Enable Remote Login From an Unlabeled System
Before You Begin
This procedure is not secure.
You have relaxed PAM policy to allow remote role assumption, as described in Enable Remote Login by a Role in Trusted Extensions.
-
On the trusted system, apply the appropriate security template to the unlabeled system.
 Caution –
Caution – With the default settings, another unlabeled system could log in and administer the remote system. Therefore, you must change the 0.0.0.0 network default from ADMIN_LOW to a different label. For the procedure, see How to Limit the Hosts That Can Be Contacted on the Trusted Network.
-
In the trusted editor, open the /etc/pam.conf file.
# /usr/dt/bin/trusted_edit /etc/pam.conf
-
Find the smcconsole entries.
-
Add allow_unlabeled to the tsol_account module.
Use the Tab key between fields.
smcconsole account required pam_tsol_account.so.1 allow_unlabeled
After your edits, this section appears similar to the following:
# Solaris Management Console definition for Account management # smcconsole account requisite pam_roles.so.1 allow_remote smcconsole account required pam_unix_account.so.1 smcconsole account required pam_tsol_account.so.1 allow_unlabeled
 Use a Remote Solaris Management Console to Administer in the Files Scope
Use a Remote Solaris Management Console to Administer in the Files Scope
If you are not using LDAP, and you want to use the Solaris Management Console on a remote system, you enable remote connection to the Console. This procedure is not sufficient to enable access for the LDAP scope.
To enable access for the LDAP scope, you must complete all the procedures in Configuring the Solaris Management Console for LDAP (Task Map).
Before You Begin
Both systems are labeled systems.
You have completed the following procedures:
-
Complete Enable the Solaris Management Console to Accept Network Communications.
-
On the desktop system, become a user that is defined identically on both systems.
-
On the desktop system, assume the role that is defined identically on both systems.
-
On the desktop system, start the Solaris Management Console.
# /usr/sbin/smc &
-
In the Server dialog box, type the name of the headless system.
Then, choose the Scope=Files toolbox.
This Computer (remote-system: Scope=Files, Policy=TSOL)
 Enable the Remote Display of Administrative GUIs
Enable the Remote Display of Administrative GUIs
The procedure for remote display on a desktop is identical to the procedure on a Solaris system that is not configured with Trusted Extensions. This procedure is placed here for convenience.
-
On the desktop system, enable processes from the headless system to display.
-
On the headless system, set the DISPLAY variable to the desktop system.
headless $ DISPLAY=desktop:n.n headless $ export DISPLAY=n:n
 Use the rlogin or ssh Command
to Log In and Administer a Headless System in Trusted Extensions
Use the rlogin or ssh Command
to Log In and Administer a Headless System in Trusted Extensions
This procedure enables you to use the command line and the txzonemgr GUI to administer a headless system as superuser or as a role.
Note –
Remote login by using the rlogin command is less secure than remote login by using the ssh command.
To use the Solaris Management Console to administer a remote system does not require you to use a remote login command. For the procedure, see How to Remotely Administer Systems by Using the Solaris Management Console From a Trusted Extensions System.
Before You Begin
You have completed Enable Remote Login by a Role in Trusted Extensions.
You are a user who is enabled to log in to the headless system with that same user name and user ID, and you can assume the same role on the headless system that you can assume on the desktop system.
-
On the desktop system, enable processes from the headless system to display.
desktop $ xhost + headless-host desktop $ echo $DISPLAY :n.n
-
Ensure that you are the user who is identically defined on both systems.
-
From a terminal window, remotely log in to the headless system.
-
Assume the role that is defined identically on both systems.
Use the same terminal window. For example, assume the root role.
headless $ su - root Password: Type the root password
You are now in the global zone. You can now use this terminal to administer the headless system from the command line.
-
Enable processes on the headless system to display on the desktop system.
Note –You can also display remote GUIs by logging in with the ssh -X command. For more information, see the ssh(1) man page. For an example, see Example 6–2.
headless $ DISPLAY desktop:n.n headless $ export DISPLAY=n:n
You can now administer the headless system by using Trusted Extensions GUIs. For example, start the txzonemgr GUI:
headless $ /usr/sbin/txzonemgr
The Labeled Zone Manager runs on the remote system and displays on the desktop system.
Example 6–2 Configuring Labeled Zones on a Headless System
In this example, the administrator uses the txzonemgr GUI to configure labeled zones on a labeled headless system from a labeled desktop system. As in the Solaris OS, the administrator enables X server access to the desktop system by using the -X option to the ssh command. The user install1 is defined identically on both systems, and can assume the role remoterole.
TXdesk1 $ xhost + TXnohead4 TXdesk1 $ whoami install1 |
TXdesk1 $ ssh -X -l install1 TXnohead4 Password: Ins1PwD1 TXnohead4 $ |
To reach the global zone, the administrator assumes the role remoterole. This role is defined identically on both systems.
TXnohead4 # su - remoterole Password: abcd1EFG |
Then, the administrator starts the txzonemgr GUI.
TXnohead4 $ /usr/sbin/txzonemgr & |
The Labeled Zone Manager runs on the headless system and displays on the desktop system.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
