7.13 About Diagnosing Specific Problems
7.13.1 Network Communications Failure
7.13.1.1 Symptom
The system is unable to communicate over the network.
7.13.1.2 Action
Your system conforms to the Ethernet 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX standard, which states that the Ethernet 10BASE-T link integrity test function should always be enabled on both the host system and the Ethernet hub. The system cannot communicate with a network if this function is not set identically for both the system and the network hub (either enabled for both or disabled for both). This problem applies only to 10BASE-T network hubs, where the Ethernet link integrity test is optional. This is not a problem for 100BASE-TX networks, where the test is enabled by default. Refer to the documentation provided with your Ethernet hub for more information about the link integrity test function.
If you connect the system to a network and the network does not respond, use the OpenBoot PROM command watch-net-all to display conditions for all network connections:
ok watch-net-all |
For most PCI Ethernet cards, the link integrity test function can be enabled or disabled with a hardware jumper on the PCI card, which you must set manually. (See the documentation supplied with the card.) For the standard TPE and MII main logic board ports, the link test is enabled or disabled through software.
Remember also that the TPE and MII ports share the same circuitry and as a result, you can use only one port at a time.
Note -
Some hub designs permanently enable (or disable) the link integrity test through a hardware jumper. In this case, refer to the hub installation or user manual for details of how the test is implemented.
Determining the Device Name of the Ethernet Interface
To enable or disable the link integrity test for the standard Ethernet interface, or for a PCI-based Ethernet interface, you must first know the device name of the desired Ethernet interface. To list the device name:
-
Shut down the operating system and take the system to the ok prompt.
-
Determine the device name for the desired Ethernet interface, using one of the two solutions that follow.
Solution 1
Use this method while the operating system is running:
-
Become superuser.
-
Type:
# eeprom nvramrc="probe-all install-console banner apply disable-link-pulse device-name" (Repeat for any additional device names.) # eeprom "use-nvramrc?"=true
-
Reboot the system (when convenient) to make the changes effective.
Solution 2
Use this alternative method when the system is already in OpenBoot:
-
At the ok prompt, type:
ok nvedit 0: probe-all install-console banner 1: apply disable-link-pulse device-name (Repeat this step for other device names as needed.) (Press CONTROL-C to exit nvedit.) ok nvstore ok setenv use-nvramrc? true
-
Reboot the system to make the changes effective.
7.13.2 Power-On Failures
7.13.2.1 Symptom
The system attempts to power up but does not boot or initialize the monitor.
7.13.2.2 Action
-
Run POST diagnostics.
-
Observe POST results.
The front panel general fault LED should flash slowly to indicate that POST is running. Check the POST output using a locally attached terminal or a tip connection.
-
If you see no front panel LED activity, a power supply may be defective.
-
If the POST output contains an error message, then POST has failed.
The most probable cause for this type of failure is the main logic board. However, before replacing the main logic board you should:
7.13.3 Disk or CD-ROM Drive Failure
7.13.3.1 Symptom
A CD-ROM drive read error or parity error is reported by the operating system or a software application.
7.13.3.2 Action
7.13.3.3 Symptom
Disk drive or CD-ROM drive fails to boot or is not responding to commands.
7.13.3.4 Action
Test the drive response to the probe-scsi-all command as follows:
-
At the system ok prompt, type:
ok reset-all ok probe-scsi-all
-
If the SCSI device responds correctly to probe-scsi-all, a message similar to the one shown in the probe-scsi output example on "7.1 About Diagnostic Tools" is printed out.
If the device responds and a message is displayed, the system SCSI controller has successfully probed the device. This indicates that the main logic board is operating correctly.
-
If one drive does not respond to the SCSI controller probe but the others do, replace the unresponsive drive.
-
If only one internal disk drive is configured with the system and the probe-scsi-all test fails to show the device in the message, replace the drive.
-
If the problem is still evident after replacing the drive, replace the main logic board.
-
If replacing both the disk drive and the main logic board does not correct the problem, replace the associated UltraSCSI data cable and UltraSCSI backplane.
-
7.13.4 SCSI Controller Failures
To check whether the main logic board SCSI controllers are defective, test the drive response to the probe-scsi command. To test additional SCSI host adapters added to the system, use the probe-scsi-all command. You can use the OBP printenv command to display the OpenBoot PROM configuration variables stored in the system NVRAM. The display includes the current values for these variables as well as the default values. See "7.12.2.3 OBP printenv Command" for more information.
-
At the ok prompt, type:
ok probe-scsi
If a message is displayed for each installed disk, the system SCSI controllers have successfully probed the devices. This indicates that the main logic board is working correctly.
-
If a disk does not respond, make sure that each SCSI device on the SCSI bus has a unique SCSI target ID.
-
If the problem persists, replace the unresponsive drive.
-
If the problem remains after replacing the drive, replace the main logic board.
-
If the problem persists, replace the associated SCSI cable and backplane.
7.13.5 Power Supply Failure
If there is a problem with a power supply, POST lights the general fault indicator and the power supply fault indicator on the front panel. If you have more than one power supply, then you can use the LEDs located on the power supplies themselves to identify the faulty supply. The power supply LEDs indicate any problem with the AC input or DC output. See "7.12.1.3 Power Supply LEDs" for more information about the LEDs.
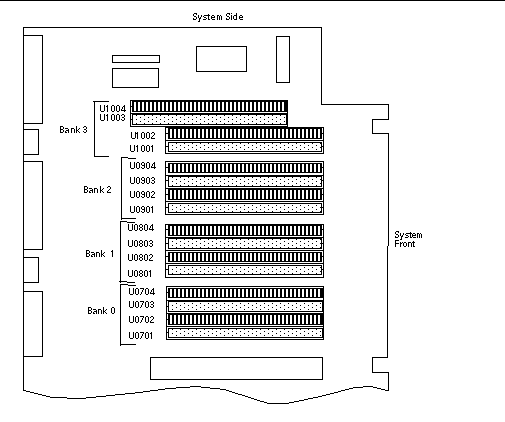
7.13.6 DIMM Failure
SunVTS and POST diagnostics can report memory errors encountered during program execution. Memory error messages typically indicate the DIMM location number ("U" number) of the failing module.
Use the following diagram to identify the location of a failing memory module from its U number.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
