| Sun Fire V60x and Sun Fire V65x Server User Guide
|
|
Troubleshooting the Server
|
This chapter explains how to detect and isolate faulty components within the Sun Sun Fire V60x and Sun Fire V65x servers. The chapter contains these sections:
6.1 Diagnosing System Errors
Use the following tools to help you isolate server problems:
6.1.1 LEDs
You can use the diagnostic LED indications to isolate faults. See Front and Rear Panel LEDs, Server Main Board Fault LEDs, System ID LEDs, and POST LED Indicators.
6.1.2 Beep Codes
A built-in server speaker indicates failures with audible beeps. See POST Error Beep Codes.
6.1.3 POST Screen Messages
For many failures, the BIOS sends error codes and message to the screen. See POST Screen Messages
6.1.4 System Utilities
The following utilities are available to help troubleshoot system errors:
- Platform Confidence Test (PCT). The PCT is used to test major subsystems and analog sensors of the system board.
- System Setup Utility (SSU). The SSU is used to read the System Event Log (SEL).
6.1.4.1 Platform Confidence Test (PCT)
The PCT consists of up to 31 tests that test the following subsystems:
- Processor
- Memory
- Input/output
- Management
The PCT supplies three testing levels:
- Quick Test. This runs a subset of available tests and identifies processor, memory, cache and hard drives.
- Comprehensive Tests. This runs Quick Tests and identifies keyboard, mouse, ports and controllers.
- Comprehensive Tests with Looping. This runs Comprehensive Tests, continually loops through tests until stopped, and enables identification of intermittently failing FRUs.
For information on how to run the PCT, see Run Platform Confidence Test (PCT).
6.1.4.2 System Setup Utility (SSU)
The SSU is intended to help with troubleshooting system errors, and can be used to read the System Event log (SEL).
For information on how to run the SSU, see Using the Service Partition Menu.
6.2 Front and Rear Panel LEDs
This section describes the front- and rear-panel status LEDs on the Sun Fire V60x and Sun Fire V65x servers.
6.2.1 Front-Panel System Status LED
The front-panel system status LED is located as shown in FIGURE 6-1.
FIGURE 6-1 Location of Front-Panel System Status LED
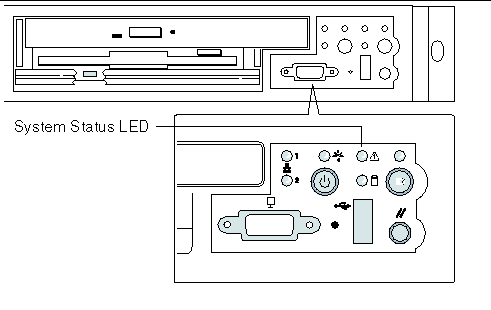
The front-panel system status LED has the states indicated in TABLE 6-1.
TABLE 6-1 System Status LED States
|
System Status LED State
|
System Condition
|
|
CONTINUOUS GREEN
|
Indicates the system is operating normally.
|
|
BLINKING GREEN
|
Indicates the system is operating in a degraded condition.
|
|
BLINKING AMBER
|
Indicates the system is in a non-critical condition.
|
|
CONTINUOUS AMBER
|
Indicates the system is in a critical or non-recoverable condition.
|
|
NO LIGHT
|
Indicates POST/system stop.
|
Critical Condition
A critical condition or non-recoverable threshold crossing is indicated with a continuous amber status LED and is associated with the following events:
- Temperature, voltage, or fan critical threshold crossing.
- Power subsystem failure. The Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) asserts this failure condition whenever it detects a power control fault (for example, if the BMC detects that the system power remains on even though the BMC has asserted the signal to turn off power to the system).
- The system is unable to power up due to incorrectly installed processor(s), or processor incompatibility.
- A satellite controller such as the HSC, or another IMPI-capable device, such as an add-in server management PCI card, sends a critical or non-recoverable state, by means of the Set Fault Indication command to the BMC.
- Critical Event Logging errors, including System Memory Uncorrectable ECC error and Fatal/Uncorrectable Bus errors, such as PCI SERR and PERR.
Non-Critical Condition
A non-critical condition is indicated with a blinking amber status LED and signifies that at least one of the following conditions is present:
- Temperature, voltage, or fan non-critical threshold crossing.
- Chassis intrusion.
- Satellite controller sends a non-critical state, through the Set Fault Indication command, to the BMC.
- A Set Fault Indication command from the system BIOS. The BIOS may use the Set Fault Indication command to indicate additional, non-critical status such as system memory or CPU configuration changes.
Degraded Condition
A degraded condition is indicated with a blinking green status LED and signifies that at least one of the following conditions is present:
- Non-redundant power supply operation. This only applies when the BMC is configured for a redundant power subsystem. The power unit configuration is configured via OEM SDR records.
- A processor is disabled by FRB or BIOS.
- BIOS has disabled or mapped out some of the system memory.
Refer to the Sun Fire V60x and Sun Fire V65x Servers Troubleshooting Guide for information on how to isolate the server component responsible for any of the critical, non-critical, or degraded conditions listed above.
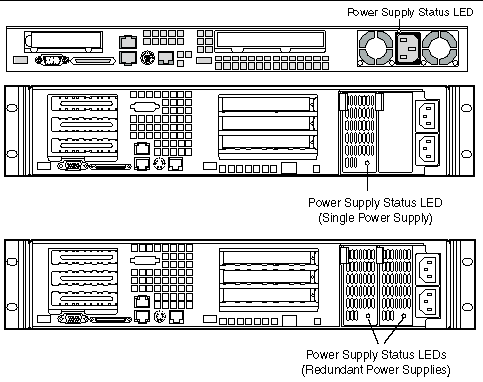
6.2.2 Rear Panel Power Supply Status LED
The rear-panel power supply status LEDs are located as shown in FIGURE 6-2.
FIGURE 6-2 Location of Sun Fire V60x and Sun Fire V65x Servers Rear-Panel Power Supply Status LEDs
 [ D ]
[ D ]
The rear-panel power supply status LED has the states indicated in TABLE 6-2.
TABLE 6-2 Power Supply Status LED States
|
Power Supply LED State
|
Power Supply Condition
|
|
OFF
|
No AC power present to power supply
|
|
BLINKING GREEN
|
AC power present, but only the standby outputs are on
|
|
GREEN
|
Power supply DC outputs on and OK
|
|
BLINKING AMBER
|
PSAlert# signal asserted, power supply on
|
|
AMBER
|
Power supply shutdown due to over current, over temperature, over voltage, or under voltage
|
|
AMBER or OFF
|
Power supply failed and AC fuse open or other critical failure
|
|
Note - If redundant power supplies are used in the Sun Fire V65x server, the power supply LEDs have the following meaning:
Both LEDs off = no power to power supplies or both power supplies bad
Both LEDs blinking green = power supplies receiving AC power, but server is off
Both LEDs solid green = server is fully powered on and power supplies are good
One LED solid green and one LED amber = AC power missing from one of the power supplies
|
6.2.3 Other LEDs
There are several additional LEDs on the front and rear panels that indicate status and activity. See Chapter 3 for more details on these LEDs.
6.3 Server Main Board Fault LEDs
There are several fault and status LEDs built into the server board (see FIGURE 6-3). Some of these LEDs are visible only when the chassis cover is removed. The LEDs are explained in this section.
FIGURE 6-3 Fault and Status LEDs on the Server Board
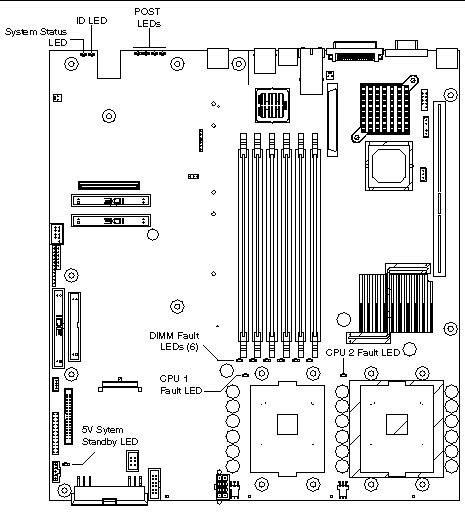
The fault LEDs are summarized below. See the Sun Fire V60x and Sun Fire V65x Servers Troubleshooting Guide for a complete description.
- POST LEDs: To help diagnose POST failures, a set of four bi-color diagnostic LEDs is located on the back edge of the main board. Each of the four LEDs can have one of four states:
Off, Green, Red, or Amber. During the POST process, each light sequence represents a specific Port-80 POST code. If a system should hang during POST, the diagnostic LEDs present the last test executed before the hang. When you read the LEDs, they should be observed from the back of the system. The most significant bit (MSB) is the first LED on the left, and the least significant bit (LSB) is the last LED on the right.
See POST LED Indicators for details regarding the POST LED display.
- CPU Fault LEDs: A fault indicator LED is located next to each of the processor sockets. If the server Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) detects a processor fault, the corresponding LED illuminates.
- Memory Fault LEDs: A fault indicator LED is located next to each of the DIMM sockets. If the BMC detects a fault in a given DIMM, the corresponding LED illuminates.
One LED for each DIMM is illuminated if that DIMM has an uncorrectable or multi-bit memory error. The LEDs maintain the same state across power switches, power down, or loss of AC power.
- Fan Fault LEDs: Depending on the server model, the fan header may include a fan fault LED. If the BMC detects a fan fault, the LED illuminates. If the fan fault LED is lit, the entire fan module must be replaced.
- System Status LED: Indicates functional status of the server board. Glows green when all systems are operating normally. Glows amber when one or more systems are in a fault status. This LED mirrors the function of the system status LED on the front panel.
See TABLE 6-1 for a description of the LED states.
- +5V Standby LED: This green LED is on when the server is plugged into AC power, whether or not the server is actually powered on. AC power is applied to the system as soon as the AC cord is plugged into the power supply.
- System ID LED: This blue LED can be illuminated to identify the server when it is part of a large stack of servers. See System ID LEDs for details.
6.4 System ID LEDs
A pair of blue LEDs, one at the rear of the server, and one on the front panel, can be used to easily identify the server when it is part of a large stack of servers. A single blue LED located at the back edge of the server board is visible through the rear panel. The two LEDs mirror each other and can be illuminated by the Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) either by pressing a button on the chassis front panel or through server-management software. When the button is pressed on the front panel, both LEDs illuminate and stay illuminated until the button is pushed again. If the LED is illuminated through a remote System Identify command, the LED turns off after a timeout period. See FIGURE 6-3 for the location of the rear Main Board LED. The front panel ID LED and the ID activation button are shown in FIGURE 6-4.
FIGURE 6-4 Location of Front-Panel ID Pushbutton and LED
6.5 Power-On Self Test (POST)
During the power-on self test (POST), the server may indicate a system fault by:
- Displaying error codes and messages at the display screen
- Beeping the speaker in a coded sequence
- Illuminating the POST LEDs, visible from the rear panel, in a coded fashion
6.5.1 POST Screen Messages
During POST, if an error is detected, the BIOS displays an error code and message on the screen. The tables in this section describe the standard and extended POST error codes and their associated messages. The BIOS prompts the user to press a key in case of serious errors. Some of the error messages are preceded by the string "Error" to highlight the fact that the system may be malfunctioning. All POST errors and warnings are logged in the System Event Log (SEL). See Managing the System Event Log for more details on the SEL.
|
Note - All POST errors are logged to the SEL, which is capable of holding approximately 3200 entries. After the SEL is full, no further errors are logged. The SEL can be cleared using the SSU or the BIOS setup. The SEL is automatically cleared after running the PCT. See Managing the System Event Log for more details.
|
TABLE 6-3 and TABLE 6-4 contain the POST error messages and error codes.
TABLE 6-3 Standard POST Error Messages and Codes
|
Error Code
|
Error Message
|
Pause On Boot
|
|
100
|
Timer Channel 2 error
|
Yes
|
|
101
|
Master Interrupt Controller
|
Yes
|
|
102
|
Slave Interrupt Controller
|
Yes
|
|
103
|
CMOS battery failure
|
Yes
|
|
104
|
CMOS options not set
|
Yes
|
|
105
|
CMOS checksum failure
|
Yes
|
|
106
|
CMOS display error
|
Yes
|
|
107
|
Insert key pressed
|
Yes
|
|
108
|
Keyboard locked message
|
Yes
|
|
109
|
Keyboard stuck key
|
Yes
|
|
10A
|
Keyboard interface error
|
Yes
|
|
10B
|
System memory size error
|
Yes
|
|
10E
|
External cache failure
|
Yes
|
|
110
|
Floppy controller error
|
Yes
|
|
111
|
Floppy A: error
|
Yes
|
|
112
|
Floppy B: error
|
Yes
|
|
113
|
Hard disk 0 error
|
Yes
|
|
114
|
Hard disk 1 error
|
Yes
|
|
115
|
Hard disk 2 error
|
Yes
|
|
116
|
Hard disk 3 error
|
Yes
|
|
117
|
CD-ROM disk 0 error
|
Yes
|
|
118
|
CD-ROM disk 1 error
|
Yes
|
|
119
|
CD-ROM disk 2 error
|
Yes
|
|
11A
|
CD-ROM disk 3 error
|
Yes
|
|
11B
|
Date/time not set
|
Yes
|
|
11E
|
Cache memory bad
|
Yes
|
|
120
|
CMOS clear
|
Yes
|
|
121
|
Password clear
|
Yes
|
|
140
|
PCI error
|
Yes
|
|
141
|
PCI memory allocation error
|
Yes
|
|
142
|
PCI IO allocation error
|
Yes
|
|
143
|
PCI IRQ allocation error
|
Yes
|
|
144
|
Shadow of PCI ROM failed
|
Yes
|
|
145
|
PCI ROM not found
|
Yes
|
|
146
|
Insufficient memory to shadow PCI ROM
|
Yes
|
TABLE 6-4 Extended POST Error Messages and Codes
|
Error Code
|
Error Message
|
Pause On Boot
|
|
8100
|
Processor 1 failed BIST
|
No
|
|
8101
|
Processor 2 failed BIST
|
No
|
|
8110
|
Processor 1 internal error (IERR)
|
No
|
|
8111
|
Processor 2 internal error (IERR)
|
No
|
|
8120
|
Processor 1 thermal trip error
|
No
|
|
8121
|
Processor 2 thermal trip error
|
No
|
|
8130
|
Processor 1 disabled
|
No
|
|
8131
|
Processor 2 disabled
|
No
|
|
8140
|
Processor 1 failed FRB-3 timer
|
No
|
|
8141
|
Processor 2 failed FRB-3 timer
|
No
|
|
8150
|
Processor 1 failed initialization on last boot.
|
No
|
|
8151
|
Processor 2 failed initialization on last boot.
|
No
|
|
8160
|
Processor 01: unable to apply BIOS update
|
Yes
|
|
8161
|
Processor 02: unable to apply BIOS update
|
Yes
|
|
8170
|
Processor P1 :L2 cache failed
|
Yes
|
|
8171
|
Processor P2 :L2 cache failed
|
Yes
|
|
8180
|
BIOS does not support current stepping for Processor P1
|
Yes
|
|
8181
|
BIOS does not support current stepping for Processor P2
|
Yes
|
|
8190
|
Watchdog timer failed on last boot
|
No
|
|
8191
|
4:1 core to bus ratio: processor cache disabled
|
Yes
|
|
8192
|
L2 Cache size mismatch
|
Yes
|
|
8193
|
CPUID, processor stepping are different
|
Yes
|
|
8194
|
CPUID, processor family are different
|
Yes
|
|
8195
|
Front side bus speed mismatch: System halted
|
Yes, Halt
|
|
8196
|
Processor models are different
|
Yes
|
|
8197
|
CPU speed mismatch
|
Yes
|
|
8198
|
Failed to load processor microcode
|
Yes
|
|
8300
|
Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) failed to function
|
Yes
|
|
8301
|
Front panel controller failed to function
|
Yes
|
|
8305
|
Hotswap controller failed to function
|
Yes
|
|
8420
|
Intelligent System Monitoring chassis opened
|
Yes
|
|
84F1
|
Intelligent System Monitoring forced shutdown
|
Yes
|
|
84F2
|
Server Management Interface failed
|
Yes
|
|
84F3
|
BMC in update mode
|
Yes
|
|
84F4
|
Sensor Data Record (SDR) empty
|
Yes
|
|
84FF
|
System event log full
|
No
|
|
8500
|
Bad or missing memory in slot 3A
|
Yes
|
|
8501
|
Bad or missing memory in slot 2A
|
Yes
|
|
8502
|
Bad or missing memory in slot 1A
|
Yes
|
|
8504
|
Bad or missing memory in slot 3B
|
Yes
|
|
8505
|
Bad or missing memory in slot 2B
|
Yes
|
|
8506
|
Bad or missing memory in slot 1B
|
Yes
|
|
8601
|
All memory marked as fail: forcing minimum back online
|
Yes
|
6.5.2 POST Error Beep Codes
The tables in this section list the POST error beep codes. Prior to system video initialization, the BIOS and BMC use these beep codes to notify users of error conditions.
TABLE 6-5 BMC-Generated POST Beep Codes
|
Beep Code
|
Description
|
|
1
|
One short beep before boot (normal, not an error)
|
|
1-2
|
Search for option ROMs. One long beep and two short beeps on checksum failure.
|
|
1-2-2-3
|
BIOS ROM checksum
|
|
1-3-1-1
|
Test DRAM refresh
|
|
1-3-1-3
|
Test 8742 keyboard controller
|
|
1-3-3-1
|
Auto size DRAM. System BIOS stops execution here if the BIOS does not detect any usable memory DIMMs.
|
|
1-3-4-1
|
Base RAM failure. BIOS stops execution here if entire memory is bad.
|
|
2-1-2-3
|
Check ROM copyright notice.
|
|
2-2-3-1
|
Test for unexpected interrupts.
|
|
1-5-1-1
|
FRB failure (processor failure)
|
|
1-5-2-2
|
No processors installed or processor socket 1 is empty
|
|
1-5-2-3
|
Processor configuration error (for example, mismatched VIDs)
|
|
1-5-2-4
|
Front-side bus select configuration error (for example, mismatched BSELs)
|
|
1-5-4-2
|
Power fault: DC power unexpectedly lost (for example, power good from the power supply was deasserted)
|
|
1-5-4-3
|
Chipset control failure
|
|
1-5-4-4
|
Power control failure (for example, power good from the power supply did not respond to power request)
|
TABLE 6-6 BIOS-Generated Boot Block POST Beep Codes
|
Beep Code
|
Error Message
|
Description
|
|
1
|
Refresh timer failure
|
The memory refresh circuitry on the motherboard is faulty.
|
|
2
|
Parity error
|
Parity can not be reset
|
|
3
|
Base memory failure
|
Base memory test failure. See TABLE 6-7 for additional error details.
|
|
4
|
System timer
|
System timer is not operational
|
|
5
|
Processor failure
|
Processor failure detected
|
|
6
|
Keyboard controller Gate A20 failure
|
The keyboard controller may be bad. The BIOS cannot switch to protected mode.
|
|
7
|
Processor exception interrupt error
|
The CPU generated an exception interrupt.
|
|
8
|
Display memory read/write error
|
The system video adapter is either missing or its memory is faulty. This is not a fatal error.
|
|
9
|
ROM checksum error
|
System BIOS ROM checksum error
|
|
10
|
Shutdown register error
|
Shutdown CMOS register read/write error detected
|
|
11
|
Invalid BIOS
|
General BIOS ROM error
|
TABLE 6-7 Memory 3-Beep and LED POST Error Codes
|
Beep Code
|
Debug Port 80h Error Indicator
|
Diagnostic LED Decoder
(G = green, R = red, A = amber)
|
Meaning
|
|
|
|
MSB
|
|
|
LSB
|
|
|
3
|
00h
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
No memory was found in the system
|
|
3
|
01h
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
G
|
Memory mixed type detected
|
|
3
|
02h
|
Off
|
Off
|
G
|
Off
|
EDO is not supported
|
|
3
|
03h
|
Off
|
Off
|
G
|
G
|
First row memory test failure
|
|
3
|
04h
|
Off
|
G
|
Off
|
Off
|
Mismatched DIMMs in a row
|
|
3
|
05h
|
Off
|
G
|
Off
|
G
|
Base memory test failure
|
|
3
|
06h
|
Off
|
G
|
G
|
Off
|
Failure on decompressing post module
|
|
3
|
07h
|
Off
|
G
|
G
|
G
|
Generic memory error
|
|
08h
|
G
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
|
09h
|
G
|
Off
|
Off
|
G
|
|
0Ah
|
G
|
Off
|
G
|
Off
|
|
0Bh
|
G
|
Off
|
G
|
G
|
|
0Ch
|
G
|
G
|
Off
|
Off
|
|
0Dh
|
G
|
G
|
Off
|
G
|
|
3
|
0Eh
|
G
|
G
|
G
|
Off
|
SMBUS protocol error
|
|
3
|
0Fh
|
G
|
G
|
G
|
G
|
Generic memory error
|
6.5.3 BIOS Recovery Beep Codes
In rare cases, when the system BIOS has been corrupted, a BIOS recovery process must be followed to restore system operability. During recovery mode, the video controller is not initialized. One high-pitched beep announces the start of the recovery process. The entire process takes two to four minutes. A successful update ends with two high-pitched beeps. In the event of a failure, two short beeps are generated and a flash code sequence of 0E9h, 0EAh, 0EBh, 0ECh, and 0EFh appears at the Port 80 diagnostic LEDs (see TABLE 6-8).
TABLE 6-8 BIOS Recovery Beep Codes
|
Beep Code
|
Error Message
|
Port 80h LED Indicators
|
Description
|
|
1
|
Recovery started
|
|
Start recovery process.
|
|
2
|
Recovery boot error
|
Flashing series of post codes:
E9h
EAh
EBh
ECh
EFh
|
Unable to boot to floppy, ATAPI, or ATAPI CDROM. Recovery process will retry.
|
|
Series of long low-pitched single beeps
|
Recovery failed
|
EEh
|
Unable to process valid BIOS recovery images. BIOS already passed control to OS and flash utility.
|
|
Two long high pitched beeps
|
Recovery complete
|
EFh
|
BIOS recovery succeeded, ready for powerdown, reboot.
|
6.5.4 POST LED Indicators
To help diagnose POST failures, a set of four bi-color diagnostic LEDs is located on the back edge of the server Main Board. Each of the four LEDs can have one of four states: Off, Green, Red, or Amber.
The LED diagnostics feature consists of a hardware decoder and four dual color LEDs. During boot block POST and post boot block POST, the LEDs display all normal Port80 codes representing the progress of the BIOS POST. Each POST code is represented by a combination of colors from the four LEDs. The LEDs are in pairs of green and red. The POST codes are broken into two nibbles, an upper and a lower nibble. Each bit in the upper nibble is represented by a red LED and each bit in the lower nibble is represented by a green LED. If both bits are set in the upper and lower nibble, both red and green LEDs are illuminated, resulting in an amber color. Likewise, if both bits are clear, the red and green LEDs are off.
During the POST process, each light sequence represents a specific Port-80 POST code. If a system should hang during POST, the diagnostic LEDs present the last test executed before the hang. When you read the LEDs, observe them from the back of the system. The most significant bit (MSB) is the leftmost LED, and the least significant bit (LSB) is the rightmost LED.
|
Note - When comparing a diagnostic LED color string from the server Main Board to those listed in the diagnostic LED decoder in the following tables, the LEDs on the Main Board should be referenced when viewed by looking into the system from the back. Reading the LEDs from left to right, the most-significant bit is located on the left.
|
TABLE 6-9 Boot Block POST Progress LED Codes (Port 80h Codes)
|
POST Code
|
Diagnostic LED Decoder
(G = green, R = red, A = amber)
|
Description
|
|
|
MSB
|
|
|
LSB
|
|
|
10h
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
R
|
The NMI is disabled. Start power-on delay. Initialization code checksum verified.
|
|
11h
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
A
|
Initialize the DMA controller, perform the keyboard controller BAT test, start memory refresh, and enter 4 GB flat mode.
|
|
12h
|
Off
|
Off
|
G
|
R
|
Get start of initialization code and check BIOS header.
|
|
13h
|
Off
|
Off
|
G
|
A
|
Memory sizing.
|
|
14h
|
Off
|
G
|
Off
|
R
|
Test base 512K of memory. Return to real mode. Execute any OEM patches and set up the stack.
|
|
15h
|
Off
|
G
|
Off
|
A
|
Pass control to the uncompressed code in shadow RAM. The initialization code is copied to segment 0 and control will be transferred to segment 0.
|
|
16h
|
Off
|
G
|
G
|
R
|
Control is in segment 0. Verify the system BIOS checksum. If the system BIOS checksum is bad, go to checkpoint code E0h; otherwise, going to checkpoint code D7h.
|
|
17h
|
Off
|
G
|
G
|
A
|
Pass control to the interface module.
|
|
18h
|
G
|
Off
|
Off
|
R
|
Decompression of the main system BIOS failed.
|
|
19h
|
G
|
Off
|
Off
|
A
|
Build the BIOS stack. Disable USB controller. Disable cache.
|
|
1Ah
|
G
|
Off
|
G
|
R
|
Uncompress the POST code module. Pass control to the POST code module.
|
|
1Bh
|
A
|
R
|
Off
|
R
|
Decompress the main system BIOS runtime code.
|
|
1Ch
|
A
|
R
|
Off
|
A
|
Pass control to the main system BIOS in shadow RAM.
|
|
E0h
|
R
|
R
|
R
|
Off
|
Start of recovery BIOS. Initialize interrupt vectors, system timer, DMA controller, and interrupt controller.
|
|
E8h
|
A
|
R
|
R
|
Off
|
Initialize extra module if present.
|
|
E9h
|
A
|
R
|
R
|
G
|
Initialize floppy controller.
|
|
EAh
|
A
|
R
|
A
|
Off
|
Try to boot floppy diskette.
|
|
EBh
|
A
|
R
|
A
|
G
|
If floppy boot fails, initialize ATAPI hardware.
|
|
ECh
|
A
|
A
|
R
|
Off
|
Try booting from ATAPI CD-ROM drive.
|
|
EEh
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
Off
|
Jump to boot sector.
|
|
EFh
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
G
|
Disable ATAPI hardware.
|
TABLE 6-10 POST Progress LED Codes (Port 80h Codes)
|
POST Code
|
Diagnostic LED Decoder
(G = green, R = red, A = amber)
|
Description
|
|
|
MSB
|
|
|
LSB
|
|
|
20h
|
Off
|
Off
|
R
|
Off
|
Uncompress various BIOS modules.
|
|
22h
|
Off
|
Off
|
A
|
Off
|
Verify password checksum.
|
|
24h
|
Off
|
G
|
R
|
Off
|
Verify CMOS checksum.
|
|
26h
|
Off
|
G
|
A
|
Off
|
Read microcode updates from BIOS ROM.
|
|
28h
|
G
|
Off
|
R
|
Off
|
Initializing the processors. Set up processor registers. Select least featured processor as the BSP.
|
|
2Ah
|
G
|
Off
|
A
|
Off
|
Go to Big Real mode.
|
|
2Ch
|
G
|
G
|
R
|
Off
|
Decompress INT13 module.
|
|
2Eh
|
G
|
G
|
A
|
Off
|
Keyboard controller test: the keyboard controller input buffer is free. Next, the BAT command will be issued to the keyboard controller.
|
|
30h
|
Off
|
Off
|
R
|
R
|
Swap keyboard and mouse ports, if needed.
|
|
32h
|
Off
|
Off
|
A
|
R
|
Write command byte 8042: the initialization after the keyboard controller BAT command test is done. The keyboard command byte will be written next.
|
|
34h
|
Off
|
G
|
R
|
R
|
Keyboard Init: the keyboard controller command byte is written. Next, the pin 23 and 24 blocking and unblocking commands will be issued.
|
|
36h
|
Off
|
G
|
A
|
R
|
Disable and initialize the 8259 programmable interrupt controller.
|
|
38h
|
G
|
Off
|
R
|
R
|
Detect configuration mode, such as CMOS clear.
|
|
3Ah
|
G
|
Off
|
A
|
R
|
Chipset initialization before CMOS initialization.
|
|
3Ch
|
G
|
G
|
R
|
R
|
Init system timer: the 8254 timer test is over. Starting the legacy memory refresh test next.
|
|
3Eh
|
G
|
G
|
A
|
R
|
Check refresh toggle: the memory refresh line is toggling. Checking the 15 second on/off time next.
|
|
40h
|
Off
|
R
|
Off
|
Off
|
Calculate CPU speed.
|
|
42h
|
Off
|
R
|
G
|
Off
|
Init interrupt vectors: interrupt vector initialization is done.
|
|
44h
|
Off
|
A
|
Off
|
Off
|
Enable USB controller in chipset.
|
|
46h
|
Off
|
A
|
G
|
Off
|
Initialize SMM handler. Initialize USB emulation.
|
|
48h
|
G
|
R
|
Off
|
Off
|
Validate NVRAM areas. Restore from backup if corrupted.
|
|
4Ah
|
G
|
R
|
G
|
Off
|
Load defaults in CMOS RAM if bad checksum or CMOS clear jumper is detected.
|
|
4Ch
|
G
|
A
|
Off
|
Off
|
Validate date and time in RTC.
|
|
4Eh
|
G
|
A
|
G
|
Off
|
Determine number of microcode patches present.
|
|
50h
|
Off
|
R
|
Off
|
R
|
Load microcode to all CPUs.
|
|
52h
|
Off
|
R
|
G
|
R
|
Scan SMBIOS GPNV areas.
|
|
54h
|
Off
|
A
|
Off
|
R
|
Early extended memory tests.
|
|
56h
|
Off
|
A
|
G
|
R
|
Disable DMA.
|
|
58h
|
G
|
R
|
Off
|
R
|
Disable video controller.
|
|
5Ah
|
G
|
R
|
G
|
R
|
8254 timer test on channel 2.
|
|
5Ch
|
G
|
A
|
Off
|
R
|
Enable 8042. Enable timer and keyboard IRQs. Set video mode initialization before setting the video mode is complete. Configuring the monochrome mode and color mode settings next.
|
|
5Eh
|
G
|
A
|
G
|
R
|
Initialize PCI devices and motherboard devices. Pass control to video BIOS. Start serial console redirection.
|
|
60h
|
Off
|
R
|
R
|
Off
|
Initialize memory test parameters.
|
|
62h
|
Off
|
R
|
A
|
Off
|
Initialize AMI display manager module. Initialize support code for headless system if no video controller is detected.
|
|
64h
|
Off
|
A
|
R
|
Off
|
Start USB controllers in chipset.
|
|
66h
|
Off
|
A
|
A
|
Off
|
Set up video parameters in BIOS data area.
|
|
68h
|
G
|
R
|
R
|
Off
|
Activate ADM: the display mode is set. Displaying the power-on message next.
|
|
6Ah
|
G
|
R
|
A
|
Off
|
Initialize language module. Display splash logo.
|
|
6Ch
|
G
|
A
|
R
|
Off
|
Display sign on message, BIOS ID, and processor information.
|
|
6Eh
|
G
|
A
|
A
|
Off
|
Detect USB devices.
|
|
70h
|
Off
|
R
|
R
|
R
|
Reset IDE Controllers.
|
|
72h
|
Off
|
R
|
A
|
R
|
Displaying bus initialization error messages.
|
|
74h
|
Off
|
A
|
R
|
R
|
Display setup message: the new cursor position has been read and saved. Displaying the hit setup message next.
|
|
76h
|
Off
|
A
|
A
|
R
|
Ensure timer keyboard interrupts are on.
|
|
78h
|
G
|
R
|
R
|
R
|
Extended background memory test start.
|
|
7Ah
|
G
|
R
|
A
|
R
|
Disable parity and NMI reporting.
|
|
7Ch
|
G
|
A
|
R
|
R
|
Test 8237 DMA controller: the DMA page register test passed. Performing the DMA controller 1 base register test next.
|
|
7Eh
|
G
|
A
|
A
|
R
|
Initialize 8237 DMA controller: the DMA controller 2 base register test passed. Programming DMA controllers 1 and 2 next.
|
|
80h
|
R
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Enable mouse and keyboard: the keyboard test has started. Clearing the output buffer and checking for stuck keys. Issuing the keyboard reset command next
|
|
82h
|
R
|
Off
|
G
|
Off
|
Keyboard interface test: A keyboard reset error or stuck key was found. Issuing the keyboard controller interface test command next.
|
|
84h
|
R
|
G
|
Off
|
Off
|
Check stuck key enable keyboard: the keyboard controller interface test is complete. Writing the command byte and initializing the circular buffer next.
|
|
86h
|
R
|
G
|
G
|
Off
|
Disable parity NMI: the command byte was written and global data initialization has completed. Checking for a locked key next.
|
|
88h
|
A
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Display USB devices.
|
|
8Ah
|
A
|
Off
|
G
|
Off
|
Verify RAM size: Checking for a memory size mismatch with CMOS RAM data next.
|
|
8Ch
|
A
|
G
|
Off
|
Off
|
Lock out PS/2 keyboard/mouse if unattended start is enabled.
|
|
8Eh
|
A
|
G
|
G
|
Off
|
Initialize boot devices: the adapter ROM had control and has now returned control to the BIOS POST. Performing any required processing after the option ROM returned control.
|
|
90h
|
R
|
Off
|
Off
|
R
|
Display IDE mass storage devices.
|
|
92h
|
R
|
Off
|
G
|
R
|
Display USB mass storage devices.
|
|
94h
|
R
|
G
|
Off
|
R
|
Report the first set of POST errors to Error Manager.
|
|
96h
|
R
|
G
|
G
|
R
|
Boot password check: the password was checked. Performing any required programming before Setup next.
|
|
98h
|
A
|
Off
|
Off
|
R
|
Float processor initialize: performing any required initialization before the coprocessor test next.
|
|
9Ah
|
A
|
Off
|
G
|
R
|
Enable Interrupts 0, 1, 2: checking the extended keyboard, keyboard ID, and NUM Lock key next. Issuing the keyboard ID command next.
|
|
9Ch
|
A
|
G
|
Off
|
R
|
Initialize FDD devices. Report second set of POST errors to error messager.
|
|
9Eh
|
A
|
G
|
G
|
R
|
Extended background memory test end.
|
|
A0h
|
R
|
Off
|
R
|
Off
|
Prepare and run setup: Error manager displays and logs POST errors. Waits for user input for certain errors. Execute setup.
|
|
A2h
|
R
|
Off
|
A
|
Off
|
Set base expansion memory size.
|
|
A4h
|
R
|
G
|
R
|
Off
|
Program chipset setup options, build ACPI Tables, and build INT15h E820h table. Note that the Solaris OS does not support ACPI.
|
|
A6h
|
R
|
G
|
A
|
Off
|
Set display mode.
|
|
A8h
|
A
|
Off
|
R
|
Off
|
Build SMBIOS table and MP tables.
|
|
AAh
|
A
|
Off
|
A
|
Off
|
Clear video screen.
|
|
ACh
|
A
|
G
|
R
|
Off
|
Prepare USB controllers for operating system.
|
|
AEh
|
A
|
G
|
A
|
Off
|
One beep to indicate end of POST. No beep if silent boot is enabled.
|
|
000h
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
POST completed. Passing control to INT 19h boot loader next.
|
6.6 Contacting Technical Support
For technical support, call the phone numbers listed below, according to your location.
United States 1-800-USA-4SUN (1-800-872-4786)
UK Tel: +44 870-600-3222
France Tel: +33 1 34 03 5080
Germany Tel: +49 1805 20 2241
Italy Tel: +39 02 92595228, Toll Free 800 605228
Spain Tel: +011 3491 767 6000
See the following link for US, Europe, South America, Africa, and APAC local country telephone numbers:
http://www.sun.com/service/contacting/solution.html
For general support and documentation on the servers, see the following link:
http://www.sun.com/supporttraining/

 [ D ]
[ D ]

