| Solstice Enterprise Manager 4.1 Managing Your Network |
|
Graphing Collected Data
Solstice Enterprise Manager (Solstice EM) provides the Grapher tool for graphing trends in attribute or alarm data. The graphs are useful for viewing trend data and identifying areas for improvement over time.
This chapter comprises the following topics:
- Section 10.2 Getting Started With Grapher
- Section 10.3 Loading Data Into Grapher
- Section 10.4 Displaying Graphs
- Section 10.5 Selecting Streams to Display as Graphs
- Section 10.6 Displaying Graphical Dimensions
- Section 10.7 Plotting Values in Different Ways
- Section 10.8 Changing Viewing Angles in 3-D Graphs
- Section 10.9 Setting Graph Colors
- Section 10.10 Changing the Display of the Plotted Data
- Section 10.11 Saving a Graph to a File
- Section 10.12 Printing a Graph
- Section 10.13 Replotting a Graph
- Section 10.14 Merging Graphs
10.1 Overview
Using the Grapher tool, you can plot attribute or alarm data as two-dimensional line graphs or three-dimensional bar graphs. The following figure shows an example of a trend plotted as a 3-D graph.
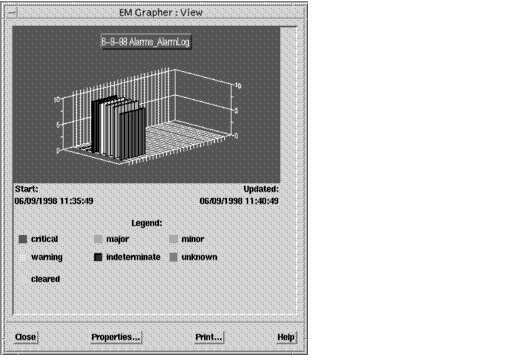
FIGURE 10-1 Trends in Alarm Data Plotted in the Grapher View Dialog10.2 Getting Started With Grapher
To display a graph of data in the Grapher, you must have already collected attribute data in Data Collections and displayed it in the SNM Results Browser.

To Use Grapher
1. Start Grapher in one of the following ways:
- In the SNM Results Browser, right-click in the upper region, then click Graph in the Streams menu.
- In the Alarm Manager window, click Tools->Grapher. In the Alarms - Graph dialog:
- In the Name field, type a name for the graph.
- In the Input field, select whether you want to graph alarm summary data or data about selected devices.
- In the Plot field, select whether you want to graph data by alarm type as a function of count or severity as a function of count.
- In the Type field, select whether you want the graph to be a static display of current data or a dynamic display that changes according to a specified time interval as data is updated.
- If you choose to create a dynamic graph, the Update interval field becomes active and you can specify a time interval, in minutes, for updating the graph.
- Click OK. The Grapher window displays, listing all graphs that you created. Double-click the name of the graph you want to view or select the name and click Object->View. The Grapher: View dialog displays the graph according to your specifications.
- From an operating system prompt, execute: em_grapher
2. Perform any task discussed in this chapter.3. Click File->Close in the Grapher window when you are finished.10.3 Loading Data Into Grapher
When you start the Grapher tool from the SNM Results Browser, the attributes you want to graph display as a stream. By starting the Grapher from the command line, you need to import the file that you want to graph.

To Load a File
- Click File->Import and, in the Import Graph dialog, select the file to be graphed.
10.4 Displaying Graphs
Once you have loaded the streams of information that you want to view as graphs, you can graph the information by double-clicking the stream.

To Display a Graph
1. Click the attribute stream that you want to plot.2. Click Object->View.
- The View dialog displays containing the graph.
10.5 Selecting Streams to Display as Graphs
You can select one or more graphs to display, you can deselect any selections, and you can delete streams listed in the Grapher window.

To Select All Streams
- Click Edit->Select All in the Grapher window.

To Deselect All Streams
- When all streams are selected, click Edit->Deselect All to deselect them.

To Delete a Selected Stream
- Click Edit->Delete in the Grapher window.
10.6 Displaying Graphical Dimensions
In the Grapher, you can select to display your graphs as two-dimensional line graphs or three-dimensional bar graphs. The default setting is three dimensions.
You can also set the features of the graph including the colors of the graph, and the mode in which to view the graph, whether you use absolute, cumulative, or delta values for plotting.

To Display a Graph in 2-Dimensions
1. After displaying a graph, click Properties in the View dialog.2. Move the Properties dialog adjacent to the View dialog.
- In this way, you can compare selections that you make in the Properties dialog with their effect on the graph in the View dialog.
3. Click the 2-D button in the Display in field in the Properties dialog.4. Click Apply to view the change in the appearance of the graph.5. Click OK to accept the change.

To Display a 2-Dimensional Graph in
3-Dimensions1. After displaying a graph, click Properties in the View dialog.2. Move the Properties dialog adjacent to the View dialog.
- In this way, you can compare selections that you make in the Properties dialog with their effect on the graph in the View dialog.
3. Click the 3-D button in the Display in field of the Properties dialog.4. Click Apply to view the change in the appearance of the graph.5. Click OK to accept the change.10.7 Plotting Values in Different Ways
In the Grapher tool, you can plot information in three ways:
- Absolute
- Cumulative
- Delta
Absolute plots all current values. Cumulative plots, in increments, data that has been obtained over time. Delta plots the difference between the current value and the previous value.

To Plot Values in Different Ways
1. After displaying a graph, click Properties in the View dialog.2. Move the Properties dialog adjacent to the View dialog.
- In this way, you can compare selections that you make in the Properties dialog with their effect on the graph in the View dialog.
3. Select the option in the Plot Value field to select Absolute, Cumulative, or Delta. Notice the differences in how the data is plotted in the graph.4. Click Apply to view the change.5. Click OK to accept the change.10.8 Changing Viewing Angles in 3-D Graphs
To view the information displayed in 3-D graphs from different angles, you can rotate the graph:
- Vertically along the X-axis
- Diagonally along the Y-axis
- Horizontally along the Z-axis
10.8.1 Changing the X-Axis, Vertical Rotation
Rotating the graph along the X-axis causes the graph to turn vertically toward you. You can look down at the graph from the top between 80 and 90 degrees, or up into the graph from the bottom between 270 and 280 degrees, or you can set the X-axis to 0 degrees for a two-dimensional representation of the bar graph. The default setting of the X-axis is 15 degrees.

To Change the Vertical Rotation
1. After displaying a graph, click Properties in the View dialog.2. Move the Properties dialog adjacent to the View dialog.
- In this way, you can compare selections that you make in the Properties dialog with their effect on the graph in the View dialog.
3. Drag the scroll bar left or right in the X-Axis field of the Properties dialog to change settings.4. Click Apply to view the change in the appearance of the graph.5. Click OK to accept the change.10.8.2 Changing the Y-Axis, Diagonal Rotation
Rotating the graph on the Y-axis causes the graph to turn diagonally away from you. The default setting of the Y-axis is 0 degrees.

To Change the Diagonal Rotation
1. After displaying a graph, click Properties in the View dialog.2. Move the Properties dialog adjacent to the View dialog.
- In this way, you can compare selections that you make in the Properties dialog with their effect on the graph in the View dialog.
3. Drag the scroll bar left or right in the Y-Axis field of the Properties dialog to change settings.4. Click Apply to view the change in the appearance of the graph.5. Click OK to accept the change.10.8.3 Changing the Z-Axis, Horizontal Rotation
- Rotating the graph on the Z-axis causes it to turn horizontally. Side views of the graph, which show all lines plotted on a 3-D graph, can be seen at 90 degrees and 270 degrees. At 180 degrees, you view the graph from the back. The default setting of the Z-axis is 45 degrees.

To Change the Horizontal Rotation
1. After displaying a graph, click Properties in the View dialog.2. Move the Properties dialog adjacent to the View dialog.
- In this way, you can compare selections that you make in the Properties dialog with their effect on the graph in the View dialog.
3. Drag the scroll bar left or right in the Z-Axis field of the Properties dialog to change settings.4. Click Apply to view the change in the appearance of the graph.5. Click OK to accept the change.10.9 Setting Graph Colors
The Data Area and the Background are charcoal gray by default. The Mesh is light gray by default. The Foreground is white by default. The Grapher tool assigns default colors for each attribute plotted as a line or a bar on the graph.
You can change the color of the graphical display in the Grapher tool, which consists of four colored regions:
- Background, which consists of the area behind the graph and attribute heading
- Foreground, which consists of the axis lines, demarcation lines, measurements, and name heading that serves as the title of the graph
- Data Area, which refers to the area within the perimeter of the graph
- Mesh, which refers to the vertical increment lines that form a mesh with the horizontal increment lines

To Change the Background Color
1. After displaying a graph, click Properties in the View dialog.2. Move the Properties dialog adjacent to the View dialog.
- In this way, you can compare selections that you make in the Properties dialog with their effect on the graph in the View dialog.
3. Click Background Color in the Properties dialog.4. Click a square in the Background Color dialog to select a background color.5. Click Apply to view the change in the appearance of the graph.6. Click OK to accept the change.

To Change the Foreground Color
1. After displaying a graph, click Properties in the View dialog.2. Move the Properties dialog adjacent to the View dialog.
- In this way, you can compare selections that you make in the Properties dialog with their effect on the graph in the View dialog.
3. Click Foreground Color in the Properties dialog.4. Click a square in the Foreground Color dialog to select a foreground color.5. Click Apply to view the change in the appearance of the graph.6. Click OK to accept the change.

To Change the Color of the Data Area
1. After displaying a graph, click Properties in the View dialog.2. Move the Properties dialog adjacent to the View dialog.
- In this way, you can compare selections that you make in the Properties dialog with their effect on the graph in the View dialog.
3. Click Data Area Color in the Properties dialog.
- The Data Area Color dialog displays.
4. Click a square in the Data Area Color dialog to select a color for the data area.5. Click Apply to view the change in the appearance of the graph.6. Click OK to accept the change.

To Change the Mesh Color
1. After displaying a graph, click Properties in the View dialog.2. Move the Properties dialog adjacent to the View dialog.
- In this way, you can compare selections that you make in the Properties dialog with their effect on the graph in the View dialog.
3. Click Mesh Color in the Properties dialog.4. Click a square in the Mesh Color dialog to select a color for the mesh increment lines.5. Click Apply to view the change in the appearance of the graph.6. Click OK to accept the change.10.10 Changing the Display of the Plotted Data
You can change how the plotted data displays in the graph by specifying which attribute information to display and designating the color of plotted lines and bars.

To Plot a Specific Attribute
1. After displaying a graph, click Properties in the View dialog.2. Move the Properties dialog adjacent to the View dialog.
- In this way, you can compare selections that you make in the Properties dialog with their effect on the graph in the View dialog.
3. Click an attribute to plot in the Dataset field.
Note – In the Dataset field, you select attributes one at a time.
4. Click Yes in the Visible field to display the attribute.5. Click Apply to view the change in the appearance of the graph.6. Click OK to accept the change.

To Remove Plotted Information
1. After displaying a graph, click Properties in the View dialog.2. Move the Properties dialog adjacent to the View dialog.
- In this way, you can compare selections that you make in the Properties dialog with their effect on the graph in the View dialog.
3. In the Dataset field, click a plotted attribute to remove from the graph.
Note – In the Dataset field, you select attributes one at a time.
4. Click No in the Visible field to remove the displayed attribute from the graph.5. Click Apply to view the change in the appearance of the graph.6. Click OK to accept the change.

To Select a Color for the Plotted Data
1. After displaying a graph, click Properties in the View dialog.2. Move the Properties dialog adjacent to the View dialog.
- In this way, you can compare selections that you make in the Properties dialog with their effect on the graph in the View dialog.
3. Click an attribute in the Dataset field.4. Ensure that Yes is selected in the Visible field to display the attribute in the graph.5. Click Color.
- The Data Set Color dialog displays.
6. Click a square in the Data Set Color dialog to select a color for the attribute that you want to display on the graph.7. Click Apply to view the change in the appearance of the graph.8. Click OK to accept the change.10.11 Saving a Graph to a File
When you have finished working on a graph, you can save it to a file.
- Click File->Export and, in the Export Graph dialog, select the file to which you want to save the graph.
10.12 Printing a Graph
You can print any graph you create to a PostScript® file or to a printer.

To Print a Graph to a PostScript File
1. Click Print in the View dialog.2. In the Print dialog:
- Click the button of the Print to file field.
- Type the path and name of the file to which you want to save.
- Click OK.
- or
- Click the ellipsis (...) button.
- Select a path and file from the File Selection dialog.
- Click OK.
3. Click OK in the Print dialog.
- The information is sent to the PostScript file you specified.

To Send a Graph to the Printer
1. Click Print in the View dialog.2. Click the button of the Printer field.3. Select a configured printer by clicking the down arrow of the Printer field.4. Click OK.
- The graph is sent to the printer you specified.
10.13 Replotting a Graph
You can replot a graph at any time by clicking Object->View.
10.14 Merging Graphs
You can superimpose graphs on one another by selecting more than one stream in the Grapher window and clicking Object->View to graph them.
|
Sun Microsystems, Inc. Copyright information. All rights reserved. |
Doc Set | Contents | Previous | Next | Index |