| C H A P T E R 19 |
|
Device-Specific User Interface Framework |
The Subscriber Portal component of Content Delivery Server is a browser-based application that can be accessed on a PC or on the subscriber’s device. Because the browsers used by different devices have different capabilities, Content Delivery Server provides a framework for generating Subscriber Portal pages that are tailored to the capabilities of the different devices. This framework applies only to the version of the Subscriber Portal that runs on a subscriber’s device, not to the version that runs on a PC.
The version of the Subscriber Portal that runs on mobile devices was created using Apache Struts (see http://jakarta.apache.org/struts/ for information on this framework). Subscriber Portal pages are provided for devices that use browsers based on WML and XHTML. The pages provided are suitable for many devices. However, if you are supporting a device that does not correctly show the pages of the Subscriber Portal or you want to take advantage of a device’s special capabilities, you can create a version of the Subscriber Portal pages specifically for that device.
This chapter includes the following topics:
The Subscriber Portal consists of pages created using JavaServer PagesTM technology (JSPTM pages). These JSP pages are generated from XML files that describe the pages to be produced and XSL style sheets that describe how the page elements are to be rendered. A version of the Subscriber Portal, that is, one set of JSP pages, is generated for each style sheet. Each set of pages is stored in a subdirectory with the same name as the name of the style sheet. These subdirectories are in the following locations:
server-domain is the value specified for the app.server.domain property in the configuration file.
When the Catalog Manager administrator adds a device to the list of supported devices, one of the capabilities specified for the device is the browser type. The browser type specified for the device determines which version of the pages is used.
The Struts framework is used to build the device-based Subscriber Portal. In the following cases, Content Delivery Server extends the Struts tag libraries to ensure that characters are XML or WML encoded:
The files that contain the page definitions for the device-based Subscriber Portal are identified in the following table. These files are in the $CDS_HOME/deployment/deployment-name/markup_generation/page-defs directory. The use of these files is described in Section 19.1.3, Processes and Page Usage.
The pages for the device-based Subscriber Portal are defined once using XML. The XML files are then processed with each existing style sheet to generate the JSP pages for each version of the Subscriber Portal that is needed. The following table describes the elements that can be used in each page.
|
Inserts a single line break in an item element of a list element, between link elements in a navbar element, or within a text element. |
|
|
Provides a button for a form and is used to submit data. This element appears under a form element. A button can contain the following elements:
|
|
|
Adds a horizontal line to a page between elements under either the view element or the form element. |
|
|
Provides a field on a form in which a user can enter information. A field can contain the following elements:
|
|
|
Describes a form for the page and appears under the view element. A view can have only one form. A form can contain the following elements:
Using the provided style sheets, button elements are displayed at the bottom of the form. All other elements are displayed in the order in which they appear. |
|
|
Provides an image for a page and appears under a view element or a form element. An image can contain the following elements:
|
|
|
Contains code that uses syntax for the JSP technology (JSP syntax). This element can appear under any element and does not contain any elements. Include the code in a CDATA section so that the XML page definitions remain valid. The code can include the following JSP syntax:
For example, the following code segment shows the use of scripting elements and variables to set the value of the title element: <title> <jsp><!CDATA[<%=title%>]]></jsp> </title> To include the code at the top of the page, set the attribute header for this element to true. If the attribute is set to false or does not appear, the code in jsp elements is generated in the order in which the elements appear. |
|
|
Provides a link on the page and appears under either the navbar element or an item element of a list element. A link contains the following elements:
For example, the following code segment shows a link to a page outside of the Subscriber Portal. <link> <name>Yahoo</name> <url><jsp>"http://wap.yahoo.com"</jsp></url> </link> To indicate that the link is used to download purchased content, set the attribute download for this element to true. This attribute is used by the style sheets to determine the tag to use for some devices and content types. |
|
|
Provides a list of items for a page and appears under the view element or the form element. The list element contains one or more item elements. An item element contains a link element, a break element, or a jsp element that contains code that writes text, for example, <bean:encodedmessage> or <bean:encodedwrite>. |
|
|
Provides a set of links that are displayed as a group, such as ok and cancel or yes and no. These links are automatically separated by a navspacer. The navbar element appears under the view element or the form element and contains one or more link elements and navspacer elements. To specify the orientation of the navigation bar, set the attribute orientation. Valid values are horizontal and vertical. The default is vertical. Note - Some browsers might not have the capability to group the links. |
|
|
Divides links in a navigation bar and appears between link elements under the navbar element. Note - Links in a navbar are automatically divided with navspacers. Use a navspacer element to further divide the links. |
|
|
Describes the list of items included in a field of type select and appears under the field element. Use option when the list of items is known. Use optionlist when the list is dynamically generated. An option contains the following elements: According to the style sheet, the value of the optionlist element must be valid HTML statements that contain all of the option elements for a select statement. Use a jsp element for the code that generates the valid HTML option tags, for example: <optionlist> <jsp><![CDATA[<%=getOptions()%>]]></jsp> </optionlist> The method getOptions is expected to return a String that contains option elements similar to the following example: <option value=”1”>One</option> <option value=”2”>Two</option> <option value=”3”>Three</option> |
|
|
Provides the text for the page and appears under the view element or the form element. The text element generally contains a <jsp> tag that contains a <bean:encodedmessage>, <bean:encodedwrite>, or <html:encodederrors> tag and can also contain one or more break or link elements. This element can have the following attributes: |
|
|
Provides the title used for the page and appears under the view element. The title element generally contains a <jsp> tag that contains a <bean:encodedmessage> or <bean:encodedwrite> tag. |
|
|
Describes the page and is the top-most element. This element contains the following elements: For a WML-based browser, the view represents a card. For an HTML-based browser, the view represents the body. |
The following code example shows a page that contains a form. This sample is the file $CDS_HOME/dist/cds/markup_generation/page_defs/_login.xml.
The following code example shows a page that contains links to other pages. This sample is the file $CDS_HOME/dist/cds/markup_generation/page_defs/_main_menu.xml.
Style sheets provide templates that describe how to render each element used to define a JSP page. These elements are described in TABLE 19-2. Style sheets interpret the XML page definitions and create the JSP pages for a given device or class of devices.
Set up style sheets to render markup according to the capabilities of the device used. For example, when an XML definition specifies a link, the style sheet for one type of browser might render the link in color, where the style sheet for a different type of browser might render the link with an underline.
Content Delivery Server provides the following style sheets with the product. These style sheets are in the $CDS_HOME/deployment/deployment-name/markup_generation/stylesheets directory.
These style sheets are suitable for many devices. However, if the pages of the Subscriber Portal do not display well on a device, a new style sheet can be created to define a different rendering of the elements. Only those elements that do not display well need to be included in the new style sheet. For example, if a device uses the XHTML-Alternate.xsl style sheet and only links and fields render poorly, create a style sheet that imports XHTML-ALternate.xsl and includes definitions for only links and fields.
The following sections describe the general process flow of the primary functions of the Subscriber Portal. These descriptions identify the pages shown to subscribers on their device and the files used to generate the pages. The files are described in TABLE 19-1.
The following figure shows the process of logging in to the Subscriber Portal and the options available after the subscriber is logged in. The description that follows the figure identifies the XML file used for each page.
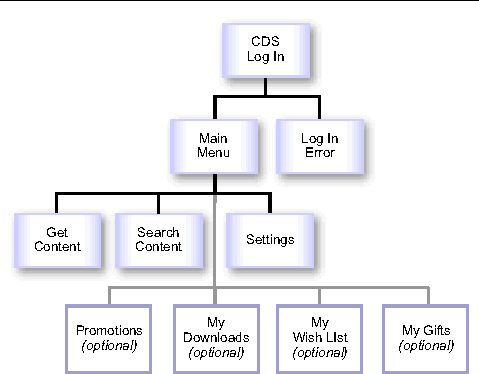
1. The CDS Log In page, generated from _login.xml, is the first page shown to the subscriber.
2. If login is successful, the main page of the Subscriber Portal, generated from _main_menu.xml, is shown. If the login fails, an error is shown on the CDS Log In page. If the subscriber’s account is disabled, or the login fails three times in a row, a page in which the login is disabled, generated from _login_disabled.xml, is shown.
3. From the Main Menu page, the following actions are available:
The following figure shows the process of viewing available content.
FIGURE 19-2 View Content Process
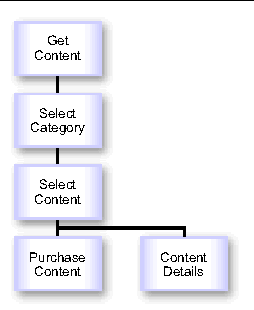
1. When the subscriber clicks Get Content on the Main Menu, the Select Category page, generated from _catalog_menu.xml, is shown. This page shows the list of categories that are available to the subscriber.
2. When the subscriber clicks a category name in the list of categories, the Select Content page, generated from _catalog_menu.xml, is shown. This page shows the list of content and content bundles that are available to the subscriber.
3. When the subscriber clicks an item of content in the content list, either the Purchase Content page or the Content Details page, both generated from _detail.xml, is shown.
See Section 19.1.3.9, Purchase or Download Process for a description of these options.
The following figure shows the process of searching content.
FIGURE 19-3 Search for Content Process
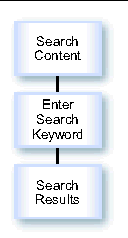
1. When the subscriber clicks Search Content on the Main Menu, the Search Content page, generated from _search.xml, is shown. This page prompts the subscriber for the search criteria.
2. After the search completes, the Search Results page, generated from _catalog_menu.xml, is shown. This page shows the list of content that matches the search criteria.
The following figure shows the process of setting preferences.
FIGURE 19-4 Set Preferences Process
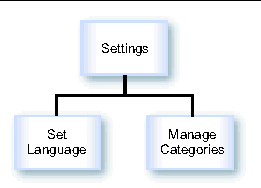
When the subscriber clicks Settings on the Main Menu, the Settings page, generated from _user_admin_menu.xml, is shown. This page provides the following options:
The Promotions option is available on the Main Menu page only if campaigns are set up in the Vending Manager and the option to receive notifications about promotions is on in the subscriber’s profile. When the subscriber clicks Promotions, the Promotions page, generated from _catalog_menu.xml, is shown. This page shows the list of promotions that are available.
When the subscriber selects a promotion, the details for that promotion, generated from _campaign.xml, are shown. When the subscriber clicks an item of content included in the promotion, the Purchase Content page, generated from _detail.xml, is shown. From this page, the subscriber can download the item or purchase the item for a friend. See Section 19.1.3.9, Purchase or Download Process for information on the purchase process.
The My Downloads list is available on the Main Menu page only if the subscriber previously purchased content. When the subscriber clicks My Downloads, the My Downloads page, generated from _catalog_menu.xml, is shown. This page shows the list of content that the subscriber has purchased.
When the subscriber selects an item of content, the Content Details page, generated from _detail.xml, is shown. From this page, the subscriber can download the item, purchase the item for a friend, or tell a friend about the item. See Section 19.1.3.9, Purchase or Download Process for information on the purchase process.
My Wish List is available on the Main Menu page only if the subscriber added content to the wish list when browsing content using the PC-based Subscriber Portal. When the subscriber clicks My Wish List, the My Wish List page, generated from _catalog_menu.xml, is shown. This page shows the list of content that the subscriber has downloaded.
When the subscriber selects an item of content, the Purchase Content page, generated from _detail.xml, is shown. See Section 19.1.3.9, Purchase or Download Process for information on the purchase process.
The My Gifts list is available on the Main Menu page only if the subscriber received a gift or purchased a gift for another subscriber. When the subscriber clicks My Gifts, the My Gifts page, generated from _my_gifts_menu.xml, is shown.
If the subscriber received a gift, the My Gifts page has a link for Gifts Received. When the subscriber clicks the Gifts Received link, the Gifts Received page, generated from _catalog_menu.xml, is shown. This page shows the list of content that the subscriber received as gifts. When the subscriber selects an item of content, the details for the gift, generated from _gift_details.xml, are shown. To accept a gift, the subscriber clicks the Download Gift link and the Download page, generated from _download.xml, is shown.
If the subscriber purchased a gift for another subscriber, the My Gifts page includes a link for Gifts Sent. When the subscriber clicks the Gifts Sent link, the Gifts Sent page, generated from _catalog_menu.xml, is shown. This page shows the list of content that the subscriber purchased as gifts. When the subscriber selects an item of content, the details for the gift, generated from _gift_details.xml, are shown. Gifts of content charged on a subscription basis have an option to cancel the gift. If the subscriber cancels a gift subscription, a page confirming the request, generated from _gift_cancel_confirm.xml, is shown. If the request completes successfully, a notification page, generated from _gift_cancel_success.xml, is shown.
The following figure shows the process of either purchasing content or downloading content already purchased. The purchase process is initiated from the Purchase Content page. The download process is initiated from the Content Details page. Both pages are generated from the _detail.xml file.
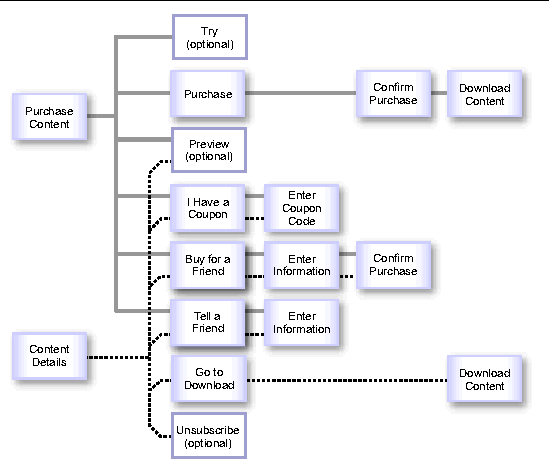
The Purchase Content page is shown if the subscriber has not yet purchased the selected content or if the license requires that the content be purchased again. The Content Details page is shown if the subscriber has purchased the selected content. The following options are provided as noted:
The try option is available only on the Purchase Content page and only if the administrator set up a trial for the item.
The purchase option is available only on the Purchase Content page.
If multiple previews are available, the list of previews, generated from _preview_list.xml, is shown. When a preview is selected, the Preview page is shown as described above.
The preview option is available on both pages if the content can be previewed.
The coupon option is available on both pages.
The message that the recipient of the gift receives includes a link to the gift. When the recipient clicks the link and accesses the Subscriber Portal, a notification about the gift, generated from _share_content_receive.xml, is shown.
The gift option is available on both pages.
The message sent to the friend includes a link to the content. When the recipient clicks the link and accesses the Subscriber Portal, a notification about the content, generated from _share_content_receive.xml, is shown.
The share option is available on both pages.
The download option is available only on the Content Details page.
The unsubscribe option is available only on the Content Details page and only if the subscriber has a subscription to the content.
Generate the device-specific pages on a test system to avoid disrupting the production system. When you are sure that the generated pages are correct, move the files created to your production system.
To generate a version of the Subscriber Portal that is tailored to a specific device or set of devices, follow these steps:
1. Create an XSL style sheet in the $CDS_HOME/deployment/deployment-name/markup_generation/stylesheets directory.
Give the new style sheet a name that identifies the device or device category for which the generated pages will be used. Import a parent style sheet based on the browser category that the device uses. For example, if the browser category is XHTML, include the statement <xsl:import href="XHTML-Basic.xsl"/> in the style sheet. Follow the structure of the parent style sheet. Templates are needed only for those elements that do not render correctly, or to take advantage of advanced capabilities that are offered on a device.
2. Run the command cdsi genmarkup -ss stylesheet where stylesheet is the name of the style sheet that you created in Step 1 and does not include the .xsl extension.
This command processes all of the XML files in the $CDS_HOME/deployment/deployment-name/markup_generation/page-defs directory against the new style sheet and generates a set of JSP pages. The results are placed in the $CDS_HOME/deployment/deployment-name/markup_generation/jsps/stylesheet directory.
3. Move the directory that contains the generated JSP pages to the Subscriber Portal application directory on each application server where you deployed a Subscriber Portal.
4. Add the name of the style sheet to the $CDS_HOME/deployment/deployment-name/conf/browser.config file.
This file maintains the list of supported browser types from which the Catalog Manager administrator chooses when adding a device. For example, if you created a style sheet named XHTML-newBrowser.xsl to support a new browser type, add the following statement to the file:
device.markup.browser.option=XHTML-newBrowser
If you want to make changes to the version of the Subscriber Portal that is run on mobile devices, you can change the page definitions and regenerate the JSP pages. The changes that you make are only seen when the Subscriber Portal is accessed from a mobile device. Changes made to the XML page definitions do not affect the version of the Subscriber Portal that runs on a PC.
Make the changes on a test system to avoid disrupting the production system. When you are sure that the generated pages are correct, move the files created to your production system.
To change a page, follow these steps:
1. Edit an existing XML file in the $CDS_HOME/deployment/deployment-name/markup_generation/page-defs directory or create a new file and add it to the directory.
See Section 19.1.1, Page Definitions for a description of the elements that can be included in a file.
2. Run the command cdsi genmarkup -ss all.
This command processes all of the XML files in the $CDS_HOME/deployment/deployment-name/markup_generation/page-defs directory against all of the style sheets in the $CDS_HOME/deployment/deployment-name/markup_generation/stylesheets directory and generates a new set of JSP pages for each style sheet. Each set of pages is placed in the $CDS_HOME/deployment/deployment-name/markup_generation/jsps/stylesheet directory, where stylesheet is the name of the style sheet used to generate the pages.
3. Move the directories that contain the generated JSP pages to the Subscriber Portal application directory on each application server where you deployed a Subscriber Portal.
If you have a good understanding of Java technology, XML, and Struts, you can add a page to the Subscriber Portal to customize the page flow.
As an example of customizing the page flow, this section describes the process for adding a Terms and Conditions page before the main menu is shown. To add the page, follow these steps:
1. In the $CDS_HOME/deployment/deployment-name/markup_generation/page-defs directory, create the XML file that defines the page that you want to add.
See Section 19.1.1, Page Definitions for information on the page elements that you can use. The Terms and Conditions page for this example could be defined as shown in the following code example.
2. Add the strings used in the page definition to each language version of the SubscriberPortalLocaleResource.properties file in the $CDS_HOME/deployment/deployment-name/localization directory.
The name of the properties that you add corresponds to the values that you specified for the key parameters, for example:
device.newPage.title=Terms and Conditions device.newPage.instructions=Here are the latest updates to the site’s Terms and Conditions device.newPage.continue=Continue |
3. Generate all of the pages for the Subscriber Portal.
a. Run the command cdsi genmarkup -ss all.
This command processes all of the XML files in the $CDS_HOME/deployment/deployment-name/markup_generation/page-defs directory against all of the style sheets in the $CDS_HOME/deployment/deployment-name/markup_generation/stylesheets directory and generates a new set of JSP pages for each style sheet. Each set of pages is placed in the $CDS_HOME/deployment/deployment-name/markup_generation/jsps/stylesheet directory, where stylesheet is the name of the style sheet used to generate the pages.
b. Move the directories that contain the generated JSP pages to the Subscriber Portal application directory on each application server where you deployed a Subscriber Portal.
4. Create a handler that contains the business logic for the new page.
The handler must extend com.sun.content.server.subscriberportal.device.BaseDeviceHandler and implement the doExecute method. CODE EXAMPLE 19-4 shows a call to this method. See the output of the Javadoc tool provided with Content Delivery Server for information on this class.
Place the compiled class in a JAR file in one of the following locations:
The following code example shows a sample handler that determines if the Terms and Conditions page should be shown.
5. Edit the struts-config.xml file to indicate how to handle the page in the page flow.
This file is in one of the following locations:
a. Remove the following section of code:
b. Add the following code in place of the section that you removed:
Copyright © 2008, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.