Creating an Environment
Environments include the external systems, Logical Hosts, integration servers and message servers used by a Project and contain the configuration information for these components. Environments are created using the Enterprise Designer’s Environment Editor. The following example uses the prjSwift_BP_Sample Project.
-
From the Enterprise Designer’s Enterprise Explorer, click the Environment Explorer tab.
-
Right-click the Repository and select New Environment. A new Environment is added to the Environment Explorer tree.
-
Rename the new Environment to envSwift_BP_Sample.
-
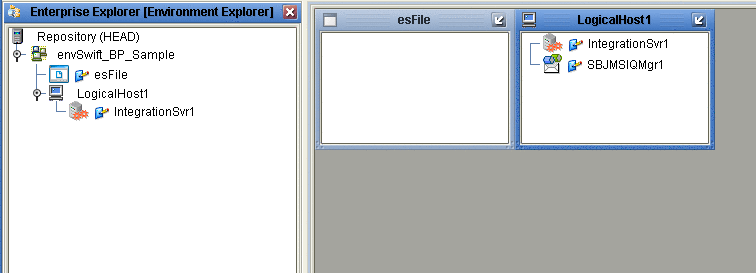
Right-click envSwift_BP_Sample and select New File External System. Name the External System esFile. Click OK. esFile is added to the Environment Editor.
-
Right-click envSwift_BP_Sample and select New Logical Host. The LogicalHost1 box is added to the Environment and LogicalHost1 is added to the Environment Editor tree.
-
Right-click LogicalHost1 and select New > Sun SeeBeyond Integration Server. A new Integration Server (IntegrationSvr1) is added to the Environment Explorer tree under LogicalHost1 (see Creating an Environment).
-
For the prjSwift_JCD_Sample only, the Environment must also include a JMS IQManager. To add an IQ Manager, right-click LogicalHost1 and select New > SeeBeyond JMS IQManager. A new JMS IQ Manager (SBJmsIQMgr1) is added to the Environment Explorer tree under LogicalHost1.
-
Save your current changes to the Repository.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
