Installing Web Space Server Software
Web Space Server 10.0 software installation involves downloading and unzipping the product ZIP package, configuring your operating system environment, and running an Ant setup script.
-
To Install Web Space Server Software Into an Existing Sun GlassFish Enterprise Server Configuration
-
To Install Web Space Server Software Into an Existing Oracle WebLogic Server Configuration
-
To Install Web Space Server Software Into a Clustered WebLogic Configuration
File System Layout
The root directory that is created when the Web Space Server product bundle is downloaded and unzipped is referred to throughout the entire Sun GlassFish Web Space Server 10.0 Document Collection as ws-install-dir. This ws-install-dir directory contains a subdirectory and file structure comprising, among other components, the Web Space Server product, the GlassFish Update Center, and a set of customization directories in which you can place your Web Space Server customizations and deployable components.
In addition, depending on how and which application server you have installed (Sun GlassFish Enterprise Server or Oracle WebLogic Server), the Web Space Server installation directories may also incorporate the GlassFish or WebLogic directories. For example, if installing one of the Web Space Server evaluation bundles, the GlassFish Enterprise Server directories will be included in the Web Space Server installation directories.
Regardless of where you choose to install GlassFish or WebLogic software, this document and the entire Web Space Server documentation set refer to the application server root installation directories as follows:
-
Sun GlassFish Enteprise Server: gf-install-dir
-
Oracle WebLogic Server: or-install-dir
Figure 2–1 shows the primary Web Space Server directories in more detail. Note that this illustration shows only a very limited subset of Web Space Server files and directories. Also note that this example includes the GlassFish Enterprise Server installation directories. Refer to the list following the illustration for explanations of the numbered items.
Figure 2–1 Primary Web Space Server Installation Directories
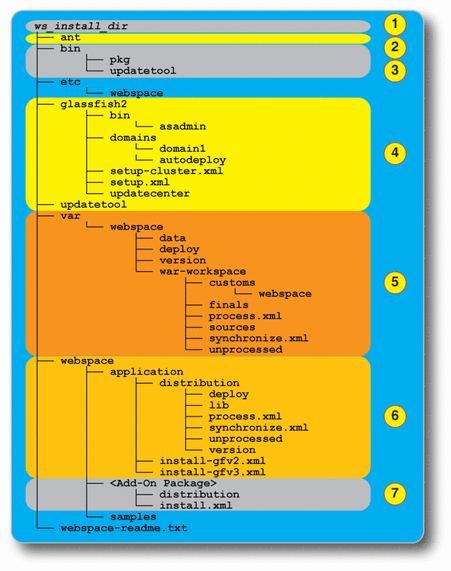

|
ws-install-dir is the root installation directory in which the Web Space Server download bundle is unzipped. If using the Web Space Server Evaluation Bundle, this directory also includes the GlassFish Enterprise Server root, referred to here as gf-install-dir. If not using the Evaluation Bundle, Web Space Server can be unzipped in gf-install-dir or some other directory of your choice. |

|
The ant directory contains a version of Ant that is compatible with Web Space Server. Web Space Server requires Ant version 1.7.1 or later, which is a newer version than that which is currently bundled with GlassFish. It is important that you use either the Ant 1.7.1 located in this ant directory or some other 1.7.1 or later version of Ant on your system rather than the version of Ant bundled with GlassFish. |

|
The bin directory contains the versions of updatetool and pkg that are compatible with Web Space Server. It is important that you use the updatetool and pkg binaries from this directory rather than the older binaries that are bundled with GlassFish Enterprise Server v2 in the gf-install-dir/updatecenter directory. |

|
The glassfish2 directory in the Web Space Server Evaluation Bundle contains GlassFish Enterprise Server v2. If you are not using a Web Space Server Evaluation Bundle, your GlassFish directory will likely be located somewhere else, and could contain GlassFish v2 or v3 software. Similarly, if you are using Oracle WebLogic Server, your WebLogic directory will be located elsewhere.. |

|
The var directory and its subdirectories are the most important in terms of customization and deployment-oriented tasks. In particular, the deploy directory contains hot-deployable WAR files that will subsequently be deployed to Web Space Server. The customs directory is where you place your customized portal-ext.properties file. This portal-ext.properties file contains your deployed application settings and any custom properties; these values override any corresponding values in the GlassFish portal.properties file. The unprocessed directory contains application files that cannot be hot deployed – for example, any application in a clustered GlassFish environment – prior to being processed. The process.xml Ant script processes the applications in the unprocessed directory and copies the resulting WAR files to the finals directory. Finally, the synchronize.xml Ant script uses the portal-ext.properties file and applications in the deployed and finals directory as input to rebuild the webspace.war file, and then deploys the new webspace.war and your applications to the GlassFish server. |

|
The webspace directory contains the Web Space Server installation and upgrade scripts. In the non-evaluation (not bundled with GlassFish) version of Web Space Server, and after installing any Web Space Server update package, run the install.xml script to install Web Space Server into an existing GlassFish environment. |

|
There is a separate <Add-On Package> directory and related subdirectories for each of the Web Space Server Add-On packages you choose to install. Refer to the Sun GlassFish Web Space Server Add-On Collection for instructions on working with any of the Web Space Server Add-On products. |
 To Install Web Space Server Software Bundled
With GlassFish
To Install Web Space Server Software Bundled
With GlassFish
This procedure describes how to install the Web Space Server ZIP package that includes Sun GlassFish Enterprise Server software. See To Install Web Space Server Software Into an Existing Sun GlassFish Enterprise Server Configuration for instructions on installing the Web Space Server ZIP package that does not include GlassFish. See Getting Sun GlassFish Web Space Server Software for information about all available Web Space Server packages.
Before You Begin
Apache Ant 1.7 or later must be installed on your system before performing the Web Space Server installation. The version of Ant bundled with Sun GlassFish does not work with Web Space Server 10.0. Make sure that Ant 1.7 or later is installed on your system, and that your PATH and ANT_HOME environment variables point to this newer version. You can verify the version of Ant that will be used by default by entering the following command in a command shell for your operating system:
ant -version |
Refer to the documentation included with your Ant package for complete installation instructions.
-
(Mac OS X systems only) Configure your Java environment.
-
If using JDK 1.6, use the Java Preferences application to specify the correct JDK version.
Also be sure to set JAVA_HOME to point to JDK 1.6.
export JAVA_HOME=/System/Library/Frameworks/JavaVM.framework/Versions/1.6.0/Home
-
If using JDK 1.5, rename the 14compatibility.jar file.
The 14compatibility.jar file includes some aspects of the Xalan XSLT processor and the Crimson XML parser that conflict with newer versions of the classes bundled with Web Space Server 10.0.
Use the following commands to rename the 14compatibility.jar file:
cd /System/Library/Frameworks/JavaVM.framework/Versions/1.5.0/ \ Classes/.compatibility sudo mv 14compatibility.jar 14compatibility.jar.orig cd /System/Library/Frameworks/JavaVM.framework/Versions/A/Resources/.compatibility sudo mv 14compatibility.jar 14compatibility.jar.orig
-
-
(Linux systems only) Increase the maximum limit on files the operating system can open.
This step is only required on some Linux systems, and resolves an issue in which some of the Web Space Server .war files fail to deploy properly in GlassFish.
-
Enter the following command to verify the open file limit in your environment:
ulimit -n
-
If the number returned is 1024 or less, modify the /etc/sysctl.conf and /etc/security/limits.conf files, as follows:
-
/etc/sysctl.conf: Add fs.file-max = 200000
-
/etc/security/limits.conf: Add the following two lines:
* soft nofile 5000 * hard nofile 5000
-
-
Reboot the system.
-
-
Download one of the Web Space Server deployment or evaluation ZIP bundles and unzip it in the directory of your choice.
For the remainder of these instructions, the directory in which the Web Space Server ZIP file is unpacked is referred to as ws-install-dir.
-
Change to the ws-install-dir/glassfish2 directory.
-
Run the Ant setup.xml script.
ant -f setup.xml
If you want to configure your Sun GlassFish server for clustering, run the setup-cluster.xml script instead.
The default GlassFish domain and database configuration proceeds. When the “BUILD SUCCESSFUL” message is displayed, the Web Space Server installation is complete.
-
Change to the ws-install-dir/glassfish2/bin directory and start the Sun GlassFish Enterprise Server default domain.
Web Space Server software is installed by default in domain1
cd ws-install-dir/glassfish2/bin ./asadmin start-domain
Some additional Web Space Server configuration occurs as the GlassFish server, database server, and the Web Space Server components are started.
-
(Mac OS X systems only) Configure the domain.xml file 64–bit JVM.
When running any 64-bit JVM such as JDK 1.6 (which runs by default in 64-bit mode on Mac OS X), you need to edit the domain.xml file in the GlassFish domain1/config directory.
-
Stop the GlassFish domain1 server.
cd ws-install-dir/glassfish2/bin ./asadmin stop-domain
-
Edit the domain.xml file for domain1, changing the PermSize and MaxPermSize property values.
This domain.xml file is located in the ws-install-dir/glassfish2/domains/domain1/config directory. Change the PermSize and MaxPermSize values as follows:
-
-XX:PermSize=192M to -XX:PermSize=256M
-
-XX:MaxPermSize=192M to -XX:MaxPermSize=256M
-
-
Restart domain1.
ws-install-dir/glassfish2/bin/asadmin start-domain
-
-
(All operating systems) Open the Web Space Server default home page.
Point your Web browser to http://localhost:8080.
Note –The page may take a long time to load the first time after server start. If you see the default GlassFish “Your site is installed” page or an empty page, wait a few minutes and then refresh the page. Subsequent page loads should proceed more rapidly. Also note that repeated attempts to access pages before the server has fully started may result in a “index.jsp resource not found exception,” which could require a server restart.
Figure 2–2 Web Space Server Example Site Main Screen
-
(Optional) Configure Web Space Server to work with a database other than the default HSQL database.
In most production environments, you will want to use a database other than the default HSQL database that is bundled with Web Space Server. See Configuring a Database for Use With Web Space Server for detailed instructions.
 To Install Web Space Server Software Into
an Existing Sun GlassFish Enterprise Server Configuration
To Install Web Space Server Software Into
an Existing Sun GlassFish Enterprise Server Configuration
This procedure describes how to install the Web Space Server ZIP package that does not include Sun GlassFish Enterprise Server software. See To Install Web Space Server Software Bundled With GlassFish for instructions on installing the Web Space Server ZIP package that does include GlassFish. See Getting Sun GlassFish Web Space Server Software for information about all available Web Space Server packages.
Before You Begin
Sun GlassFish v2.1 Enterprise Server software must be installed and running on your system before proceeding with these instructions. See Installing Sun GlassFish Enterprise Server Software for more information about installing GlassFish Enterprise Server software.
-
GlassFish version: GlassFish v2.1 is the recommended GlassFish version for production environments. Web Space Server 10.0 software works with other versions of GlassFish, but versions other than v2.1 are recommended for evaluation or testing purposes only.
-
Ant version: Apache Ant 1.7 or later must be installed on your system before performing the Web Space Server installation. The version of Ant bundled with Sun GlassFish does not work with Web Space Server 10.0. Make sure that Ant 1.7 or later is installed on your system, and that your PATH and ANT_HOME environment variables point to this newer version. You can verify the version of Ant that will be used by default by entering the following command in a command shell for your operating system:
ant -version
Refer to the documentation included with your Ant package for complete installation instructions.
-
(Mac OS X systems only) Configure your Java environment.
-
If using JDK 1.6, use the Java Preferences application to specify the correct JDK version.
Also be sure to set JAVA_HOME to point to JDK 1.6.
export JAVA_HOME=/System/Library/Frameworks/JavaVM.framework/Versions/1.6.0/Home
-
If using JDK 1.5, rename the 14compatibility.jar file.
The 14compatibility.jar file includes some aspects of the Xalan XSLT processor and the Crimson XML parser that conflict with newer versions of the classes bundled with Web Space Server 10.0.
Use the following commands to rename the 14compatibility.jar file:
cd /System/Library/Frameworks/JavaVM.framework/Versions/1.5.0/ \ Classes/.compatibility sudo mv 14compatibility.jar 14compatibility.jar.orig cd /System/Library/Frameworks/JavaVM.framework/Versions/A/Resources/.compatibility sudo mv 14compatibility.jar 14compatibility.jar.orig
-
-
(Linux systems only) Increase the maximum limit on files the operating system can open.
This step is only required on some Linux systems, and resolves an issue in which some of the Web Space Server .war files fail to deploy properly in GlassFish.
-
Enter the following command to verify the open file limit in your environment:
ulimit -n
-
If the number returned is 1024 or less, modify the /etc/sysctl.conf and /etc/security/limits.conf files, as follows:
-
/etc/sysctl.conf: Add fs.file-max = 200000
-
/etc/security/limits.conf: Add the following two lines:
* soft nofile 5000 * hard nofile 5000
-
-
Reboot the system.
-
-
Download the webspace-10.0.6-for-glassfish.zip integration bundle and unzip it in the directory of your choice.
Tip –To avoid the chance of overwriting existing GlassFish configuration settings or files, it is strongly recommended that you not unzip the Web Space Server package into an existing GlassFish directory structure.
For the remainder of these instructions, the root directory of the existing GlassFish installation is referred to as gf-install-dir, and the directory in which the Web Space Server installer has been unzipped is referred to as ws-install-dir.
-
Stop the GlassFish domain into which Web Space Server is to be installed.
For example, if Web Space Server will be installed in domainfoo:
cd gf-install-dir/bin asadmin stop-domain domainfoo
-
Add the following code to the server.policy file in the gf-install-dir/domains/domainfoo directory.
grant codeBase "file:${com.sun.aas.instanceRoot}/lib/-" { permission java.security.AllPermission; }; // permissions for Webspace grant codeBase "file:${com.sun.aas.instanceRoot}/applications/j2ee-modules/webspace/-" { permission java.security.AllPermission; }; grant codeBase "file:${com.sun.aas.instanceRoot}/applications/j2ee-modules/saw-web/-" { permission java.security.AllPermission; }; // Basic set of required permissions granted to all remaining code grant { ............... ............... permission java.lang.reflect.ReflectPermission "suppressAccessChecks"; }; grant codeBase "file:${com.sun.aas.instanceRoot}/applications/j2ee-modules/ruon-web/-" { permission java.security.AllPermission; }; grant codeBase "file:${com.sun.aas.instanceRoot}/applications/j2ee-modules/wsrp-portlet/-" { permission java.security.AllPermission; };
Note –Permissions must be granted for any Web application that needs to create database tables, similar to the Webspace example above.
-
Create a directory named ws-install-dir/var/webspace/war-workspace/customs/webspace/WEB-INF/classes, if it does not already exist, and then change to it.
mkdir -p ws-install-dir/var/webspace/war-workspace/customs/webspace/WEB-INF/classes cd ws-install-dir/var/webspace/war-workspace/customs/webspace/WEB-INF/classes
-
Create and modify a text file named portal-ext.properties, if it does not already exist.
-
Add or verify the following default properties:
auto.deploy.glassfish-tomcat.jee.deployment.enabled=true auto.deploy.glassfish-tomcat.jee.dm.id=deployer:Sun:AppServer::localhost:4848 auto.deploy.glassfish-tomcat.jee.dm.user=admin auto.deploy.glassfish-tomcat.jee.dm.passwd=adminadmin
-
Add any non-default properties your configuration may require.
For example, to use HTTPS, add the following line:
auto.deploy.glassfish-tomcat.jee.dm.id=deployer:Sun:AppServer::localhost:4848:https
-
-
Start the GlassFish domain into which Web Space Server will be installed.
For example, if Web Space Server will be installed in domainfoo:
cd gf-install-dir/bin asadmin start-domain domainfoo
-
(Optional) Configure Web Space Server to work with a database other than the default HSQL database.
In most production environments, you will want to use a database other than the default HSQL database that is bundled with Web Space Server. See Configuring a Database for Use With Web Space Server for detailed instructions. Continue with the next step, below, after configuring your database.
-
Change to the ws-install-dir/webspace/application directory.
-
Run the Ant install.xml script.
ant -f install.xml
-
Follow the prompts to complete the Web Space Server installation in the GlassFish domain you want to use.
The Web Space Server installer stops the domain you have chosen to use for the installation and installs the Web Space Server configuration and .war files.
-
Change to the gf-install-dir/bin directory and restart the Sun GlassFish Enterprise Server domain you chose to use during the Web Space Server installation.
For example:
cd gf-install-dir/bin ./asadmin start-domain domainfoo
Some additional Web Space Server configuration occurs as the GlassFish server, database server, and the Web Space Server components are started.
-
(Mac OS X systems only) Configure the domain.xml file 64–bit JVM.
When running any 64-bit JVM such as JDK 1.6 (which runs by default in 64-bit mode on Mac OS X), you need to edit the domain.xml file in the GlassFish domain_name/config directory.
-
Stop the GlassFish domain you are using for Web Space Server.
cd gf-install-dir/bin ./asadmin stop-domain domain_name
-
Edit the domain.xml file for the domain, changing the PermSize and MaxPermSize property values.
This domain.xml file is located in the gf-install-dir/domains/domain_name/config directory. Change the PermSize and MaxPermSize values as follows:
-
-XX:PermSize=192M to -XX:PermSize=256M
-
-XX:MaxPermSize=192M to -XX:MaxPermSize=256M
-
-
Restart the default domain you are using for Web Space Server.
gf-install-dir/bin/asadmin start-domain domain_name
-
-
(All operating systems) Open the Web Space Server site.
Web Space Server uses whatever HTTP/HTTPS port is defined for your domain. For example:
http://domainfoo:8080
 To Install Web Space Server Software Into
an Existing Oracle WebLogic Server Configuration
To Install Web Space Server Software Into
an Existing Oracle WebLogic Server Configuration
This procedure describes how to install the Web Space Server package specifically intended for use with WebLogic Server software. Only install this Web Space Server package on WebLogic; do not install any of the Web Space Server evaluation bundles or GlasFish bundles. See Getting Sun GlassFish Web Space Server Software for information about all available Web Space Server packages.
Before You Begin
Oracle WebLogic Server software must be installed and running on your system before proceeding with these instructions. See Installing Oracle WebLogic Server Softwarefor more information about installing Oracle WebLogic Server software.
-
WebLogic version: WebLogic 10g or 11g are the recommended WebLogic versions for production environments.
-
Ant version: Apache Ant 1.7 or later must be installed on your system before performing the Web Space Server installation. The version of Ant bundled with Sun GlassFish does not work with Web Space Server 10.0. Make sure that Ant 1.7 or later is installed on your system, and that your PATH and ANT_HOME environment variables point to this newer version. You can verify the version of Ant that will be used by default by entering the following command in a command shell for your operating system:
ant -version
Refer to the documentation included with your Ant package for complete installation instructions.
-
(Mac OS X systems only) Configure your Java environment.
-
If using JDK 1.6, use the Java Preferences application to specify the correct JDK version.
Also be sure to set JAVA_HOME to point to JDK 1.6.
export JAVA_HOME=/System/Library/Frameworks/JavaVM.framework/Versions/1.6.0/Home
-
If using JDK 1.5, rename the 14compatibility.jar file.
The 14compatibility.jar file includes some aspects of the Xalan XSLT processor and the Crimson XML parser that conflict with newer versions of the classes bundled with Web Space Server 10.0.
Use the following commands to rename the 14compatibility.jar file:
cd /System/Library/Frameworks/JavaVM.framework/Versions/1.5.0/ \ Classes/.compatibility sudo mv 14compatibility.jar 14compatibility.jar.orig cd /System/Library/Frameworks/JavaVM.framework/Versions/A/Resources/.compatibility sudo mv 14compatibility.jar 14compatibility.jar.orig
-
-
Open the WebLogic administration console in a Web browser; for example:
http://localhost:7001/console
-
Navigate to the domain in which Web Space Server will be installed, and then click on the Web Applications tab.
-
Enable the Optimistic Serialization option and save the setting.
-
Stop the WebLogic domain.
-
Download the webspace-10.0.6-for-weblogic.zip integration bundle and unzip it in the directory of your choice.
Tip –To avoid the chance of overwriting existing WebLogic configuration settings or files, it is strongly recommended that you not unzip the Web Space Server package into an existing WebLogic directory structure.
For the remainder of these instructions, the root directory of the existing WebLogic installation is referred to as or-install-dir, and the directory in which the Web Space Server installer has been unzipped is referred to as ws-install-dir.
-
Change to the ws-install-dir/webspace/application directory and run the install.xml script.
cd ws-install-dir/webspace/application ant -f ./install.xml
-
Follow the prompts to complete the Web Space Server installation in the WebLogic domain you want to use.
The Web Space Server WAR files are copied to the ws-install-dir/var/webspace/war-workspace/finals/ directory.
-
(Optional) Configure Web Space Server to work with a database other than the default HSQL database.
In most production environments, you will want to use a database other than the default HSQL database that is bundled with Web Space Server. See Configuring a Database for Use With Web Space Server for detailed instructions. Continue with the next step, below, after configuring your database.
-
Start the WebLogic domain.
-
Deploy the Web Space Server WAR files.
The Web Space Server WARs can be deployed using the GUI-based WebLogic administration console or the WebLogic command line.
-
To deploy the Web Space Server WARs using the GUI-based WebLogic administration console
-
Use a Web browser to log in to the WebLogic administration console; for example:
http://localhost:7001/console
-
Click Deployments, and manually deploy the Web Space Server WAR files, one at a time.
The Web Space Server WAR files are located in the ws-install-dir/var/webspace/war-workspace/finals/ directory.
Tip –When running WebLogic in Production mode, you must explicitly click the Start button in the WebLogic administration console for each WAR file you deploy.
-
-
To deploy the Web Space Server WARs using the WebLogic command line
-
Open a root command shell for your operating environment on the server on which WebLogic is running.
-
Add the weblogic.jar to the Java CLASSPATH.
export CLASSPATH=$CLASSPATH:or-install-dir/server/lib/weblogic.jar
-
Deploy the webspace.war file.
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl t3://localhost:7001 -user \ weblogic -password weblogic -deploy webspace.war
Note that the above command should be entered on a single line. To start the application, invoke the above command with the -start option.
-
Deploy the tunnel-web.war file.
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl t3://localhost:7001 -user \ weblogic -password weblogic -deploy tunnel-web.war
As with the webspace.war example, this command should be entered on a single line, and the application can be started by invoking the command with the -start option.
-
(Optional) Verify that the application WARs are deployed.
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl t3://localhost:7001 -user \ weblogic -password weblogic -listapps
-
-
-
(Optional) Open the Web Space Server site.
Web Space Server uses whatever HTTP/HTTPS port is defined for your domain. For example:
http://domainfoo:7001
 To Install Web Space Server Software Into
a Clustered WebLogic Configuration
To Install Web Space Server Software Into
a Clustered WebLogic Configuration
The procedure for installing Web Space Server on a WebLogic cluster are almost exactly the same as those for installing on a non-clustered WebLogic server, as described in To Install Web Space Server Software Into an Existing Oracle WebLogic Server Configuration. The only difference is that rather than deploying the Web Space Server WAR files on the primary WebLogic server, the WARs are deployed on one of the managed cluster nodes.
-
Configure your WebLogic clusters as described in the WebLogic documentation.
For example, you may want to refer to Using Clusters for Oracle WebLogic Server 11g.
-
Follow the instructions in To Install Web Space Server Software Into an Existing Oracle WebLogic Server Configuration.
-
Where the above instructions direct you to perform actions on a WebLogic server, perform them on a managed cluster node rather than the primary WebLogic server.
 To Install Web Space Server Add-Ons On a WebLogic
Server
To Install Web Space Server Add-Ons On a WebLogic
Server
This procedure explains how to install Web Space Server Add-Ons (OpenSSO, Sharepoint, SWA, among others) when Web Space Server is running on a WebLogic server. This procedure is not meant to provide exhaustive Add-On instructions, but rather only highlights the primary steps you need to take when running on a WebLogic server. For detailed instructions for you particular Web Space Server Add-On, refer to the Sun GlassFish Web Space Server 10.0 Add-On Document Collection.
Before You Begin
WebLogic and Web Space Server must be up and running before proceeding with the instructions in this section. See Installing Oracle WebLogic Server Software and To Install Web Space Server Software Into an Existing Oracle WebLogic Server Configuration for more instructions.
-
Stop and undeploy the webspace.war application file.
This step is only necessary if the Web Space Server Add-On you are installing causes the webspace.war to be rebuilt. For example, installing the OpenSSO Add-On involves rebuilding the webspace.war file.
The webspace.war file can be undeployed using the GUI-based WebLogic administration console or the WebLogic command line.
-
To undeploy the webspace.war file using the GUI-based WebLogic administration console
-
To undeploy webspace.war using the WebLogic command line
-
Open a root command shell for your operating environment on the server on which WebLogic is running.
-
Undeploy the webspace.war file.
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl t3://localhost:7001 -user \ weblogic -password weblogic -name webspace.war -undeploy -graceful
Note that the above command should be entered on a single line.
-
(Optional) Verify that the webspace.war file is undeployed.
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl t3://localhost:7001 -user \ weblogic -password weblogic -listapps
-
-
-
Follow the installation instructions for the particular Web Space Server Add-On you want to install.
-
If the Add-On you installed caused the webspace.war file to be rebuilt, manually deploy webpspace.war again.
Note –Any portlets that rely on webspace.war also need to be redeployed and started after webspace.war is redeployed.
As with undeployment, the webspace.war file can be deployed using the GUI-based WebLogic administration console or the WebLogic command line.
-
To deploy webspace.war using the GUI-based WebLogic administration console
-
Use a Web browser to log in to the WebLogic administration console; for example:
http://localhost:7001/console
-
Click Deployments, and manually deploy the webspace.war file.
The webspace.war file is located in the ws-install-dir/var/webspace/war-workspace/finals/ directory.
Tip –When running WebLogic in Production mode, you must explicitly click the Start button in the WebLogic administration console for each WAR file you deploy.
-
-
To deploy the webspace.war file using the WebLogic command line
-
Open a root command shell for your operating environment on the server on which WebLogic is running.
-
Deploy the webspace.war file.
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl t3://localhost:7001 -user \ weblogic -password weblogic -deploy webspace.war
Note that the above command should be entered on a single line. To start the application, invoke the above command with the -start option.
-
(Optional) Verify that the webspace.war file is deployed.
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl t3://localhost:7001 -user \ weblogic -password weblogic -listapps
-
-
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
