Working With IP Addresses in the DHCP Service (Task Map)
You can use DHCP Manager or the pntadm command to add IP addresses, modify their properties, and remove them from the DHCP service. Before you work with IP addresses, you should refer to Table 10–2 to become familiar with IP address properties. The table provides information for users of DHCP Manager and pntadm.
Note –
This section does not include procedures for using the pntadm command. However Table 10–2 includes examples of using pntadm to specify IP address properties while adding and modifying IP addresses. Also refer to the pntadm man page for more information about pntadm.
The following task map lists tasks you must perform to add, modify, remove IP addresses and the procedures used to carry them out.
|
Task |
Description |
Instructions |
|---|---|---|
|
Add single or multiple IP addresses to DHCP service. |
Add IP addresses on networks that are already managed by the DHCP service by using DHCP Manager. |
How to Add a Single IP Address (DHCP Manager) How to Duplicate an Existing IP Address (DHCP Manager) |
|
Change properties of an IP address. |
Change any of the IP address properties described in Table 10–2. | |
|
Remove IP addresses from DHCP service. |
Prevent the use of specified IP addresses by DHCP. |
How to Mark Addresses Unusable (DHCP Manager) How to Mark Addresses Unusable (pntadm) |
|
Assign consistent address to a DHCP client. |
Set up a client to receive the same IP address each time it requests its configuration. |
How to Assign a Consistent IP Address to a DHCP Client (DHCP Manager) How to Assign a Consistent IP Address to a DHCP Client (pntadm) |
The following table lists and describes the properties of IP addresses.
Table 10–2 IP Address Properties|
Property |
Description |
How to Specify in pntadm Command |
|---|---|---|
|
Network address |
Address of the network that contains the IP address you are working with. The network address is displayed in the Networks list on the Addresses tab in DHCP Manager.
|
The network address must be the last argument on the pntadm command line used to create, modify, or delete an IP address. For example, to add an IP address to network 10.21.0.0 pntadm -A ip-address options 10.21.0.0 |
|
IP address |
Address you are working with, whether you are creating, modifying, or deleting it. The IP address is displayed in the first column of the DHCP Manager's Addresses tab. |
The IP address must accompany the -A, -M, and -D options to the pntadm command. For example, to modify IP address 10.21.5.12 pntadm -M 10.21.5.12 options 10.21.0.0 |
|
Client name |
Host name mapped to the IP address in the hosts table. This name may be automatically generated by DHCP Manager when addresses are created. If you create a single address, you can supply the name. |
Specify the client name with the -h option. For example, to specify client name carrot12 for 10.21.5.12: pntadm -M 10.21.5.12 -h carrot12 10.21.0.0 |
|
Owning server |
DHCP server that manages the IP address and is responsible for responding to the DHCP client's request for IP address allocation. |
Specify the owning server name with the -s option. For example to specify server blue2 to own 10.21.5.12: pntadm -M 10.21.5.12 -s blue2 10.21.0.0 |
|
Configuration macro |
Macro the DHCP server uses to obtain network configuration options from the dhcptab. Several macros are created automatically when you configure a server and add networks. See About Macros for more information about macros. When DHCP Manager creates addresses, it creates a server macro and assigns that macro as the configuration macro for each address. |
Specify the macro name with the -m option. For example, to assign the server macro blue2 to address 10.21.5.12 pntadm -M 10.21.5.12 -m blue2 10.21.0.0 |
|
Client ID |
Text string that is unique within the DHCP service. If the client ID is listed as 00, the address is not allocated to any client. If you specify a client ID when modifying the properties of an IP address, you manually bind the address to that client for its exclusive use. The client ID is determined by the vendor of the DHCP client. If your client is not a Solaris DHCP client, consult your DHCP client documentation for more information. |
Specify the client ID with the -i option. For example, to assign client ID 08002094121E to address 10.21.5.12 pntadm -M 10.21.5.12 -i 0108002094121E 10.21.0.0 |
|
|
For Solaris DHCP clients, the client ID is derived from the client's hexadecimal hardware address, preceded by the ARP code for the type of network, such as 01 for Ethernet. The ARP codes are assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) in the ARP Parameters section of the Assigned Numbers standard at http://www.iana.com/numbers.html For example, a Solaris client with the hexadecimal Ethernet address 8:0:20:94:12:1e would use the client ID 0108002094121E. The client ID is listed in DHCP Manager and pntadm when a client is currently using an address. Tip: As superuser on the Solaris client system, type the following command to obtain the Ethernet address for the interface: ifconfig -a |
|
|
Reserved |
The setting that specifies the address is reserved exclusively for the client indicated by the client ID, and the DHCP server cannot reclaim the address. If you choose this option, you manually assign the address to the client. |
Specify that the address is reserved, or manual, with the -f option. For example, to specify that IP address 10.21.5.12 is reserved for a client: pntadm -M 10.21.5.12 -f MANUAL 10.21.0.0 |
|
Lease type/policy |
The setting that determines how DHCP manages the use of the IP address by clients. A lease may be dynamic or permanent. See Dynamic and Permanent Lease Type for a complete explanation. |
Specify that the address would be permanently assigned with the -f option. Addresses are dynamically leased by default. For example, to specify that IP address 10.21.5.12 has a permanent lease: pntadm -M 10.21.5.12 -f PERMANENT 10.21.0.0 |
|
Lease expiration time |
Date and time when the lease expires, applicable only when a dynamic lease is specified. The date is specified in mm/dd/yyyy format. |
Specify an absolute lease expiration time with -e. For example, to specify an expiration time of January 1, 2002: pntadm -M 10.21.5.12 -e 01/01/2002 10.21.0.0 |
|
BOOTP setting |
The setting that marks the address as reserved for BOOTP clients. See Supporting BOOTP Clients with DHCP Service (Task Map) for more information about supporting BOOTP clients. |
Reserve an address for BOOTP clients with -f. For example, to reserve IP address 10.21.5.12 for BOOTP clients: pntadm -M 10.21.5.12 -f BOOTP 10.21.0.0 |
|
Unusable setting |
The setting that marks the address so it cannot be assigned to any client. |
Mark an address unusable with -f. For example, to mark IP address 10.21.5.12 unusable: pntadm -M 10.21.5.12 -f UNUSABLE 10.21.0.0 |
Adding Addresses to the DHCP Service
Before you add addresses, you must add the network that owns them to the DHCP service. See Adding DHCP Networks for information about adding networks.
You can add addresses with DHCP Manager or pntadm.
On networks that are already managed by the DHCP service, you can add addresses in several ways with DHCP Manager:
-
Add a single IP address – Place one new IP address under DHCP management.
-
Duplicate an existing IP address – Copy the properties of an existing IP address managed by DHCP, and supply a new IP address and client name.
-
Add a range of multiple IP addresses – Use the Address Wizard to place a series of IP addresses under DHCP management.
The following figure shows the Create Address dialog box. The Duplicate Address dialog box is identical to the Create Address dialog box, except that the text fields display the values for an existing address.
Figure 10–8 Create Address Dialog Box
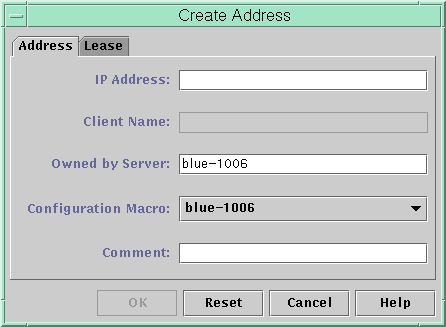
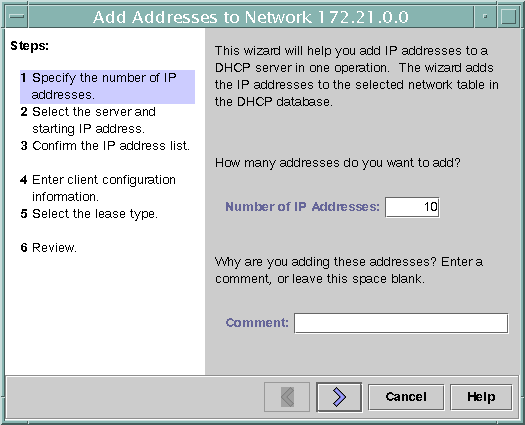
The following figure shows the first dialog of the Address Wizard, used to add a range of IP addresses.
Figure 10–9 Address Wizard
How to Add a Single IP Address (DHCP Manager)
-
Select the Addresses tab.
-
Select the network where the new IP address is to be added.
-
Choose Create from the Edit menu.
The Create Address dialog box opens.
-
Select or type values for the address settings on the Address and Lease tabs.
See Table 10–2 for information about the settings.
-
Click OK.
How to Duplicate an Existing IP Address (DHCP Manager)
-
Select the Addresses tab.
-
Select the network where the new IP address is located.
-
Select the address whose properties you want to duplicate.
-
Choose Duplicate from the Edit menu.
-
Change the IP address and client name for the address.
Most other options should remain the same, but you can change them if necessary.
-
Click OK.
How to Add Multiple Addresses (DHCP Manager)
-
Select the Addresses tab.
-
Select the network where the new IP addresses are to be added.
-
Choose Address Wizard from the Edit menu.
The Address Wizard prompts you to provide values for the IP address properties. See Table 10–2 for more information about the properties. Making Decisions for IP Address Management (Task Map) includes more extensive information.
-
Click the right arrow button as you finish entering information in each screen, and click Finish on the last screen.
The Addresses tab is updated with the new addresses.
How to Add Addresses (pntadm)
-
Become superuser or a user assigned to the DHCP Management profile.
-
Type a command of the following format:
# pntadm -A ip-address options network-address
Refer to the pntadm man page for a list of options you can use with pntadm -A. In addition, Table 10–2 shows some sample pntadm commands that specify options.
Note –You can write a script to add multiple addresses with pntadm. See Example 12–1 for an example.
Modifying IP Addresses in the DHCP Service
After you add IP addresses to the DHCP service, you can modify any of the properties described in Table 10–2 by using DHCP Manager or the pntadm -M command. See the pntadm man page for more information about pntadm -M.
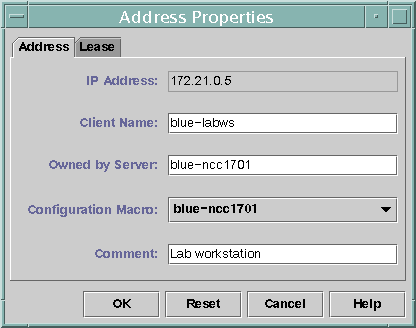
The following figure shows the Address Properties dialog box that you use to modify IP address properties.
Figure 10–10 Address Properties Dialog Box
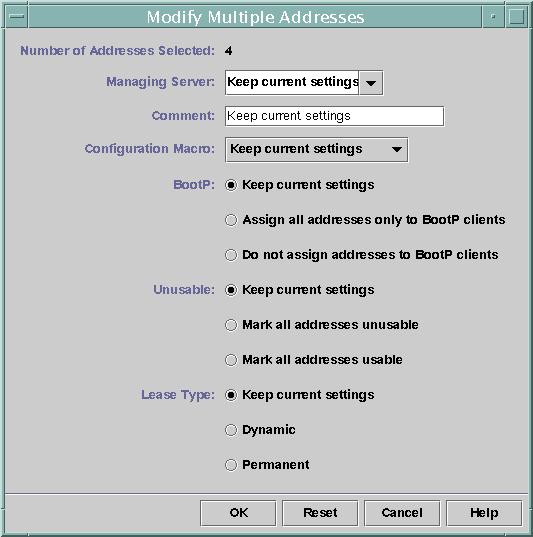
The following figure shows the Modify Multiple Addresses dialog box that you use to modify multiple IP addresses.
Figure 10–11 Modify Multiple Addresses Dialog Box
How to Modify IP Address Properties (DHCP Manager)
-
Select the Addresses tab.
-
Select the IP address's network.
-
Select one or more IP addresses you want to modify.
If you want to modify more than one address, press the Control key while you click with the mouse to select multiple addresses. You can also press the Shift key while you click to select a block of addresses.
-
Choose Properties from the Edit menu.
The Modify Addresses dialog box or the Modify Multiple Address dialog box opens.
-
Change the appropriate properties.
Click the Help button or refer to Table 10–2 for information about the properties.
-
Click OK.
How to Modify IP Address Properties (pntadm)
-
Become superuser or a user assigned to the DHCP Management profile.
-
Enter a command of the following format:
# pntadm -M ip-address options network-address
Many options can be used with the pntadm command, which are documented in the pntadm man page.
Table 10–2 shows some sample pntadm commands that specify options.
Removing Addresses From DHCP Service
At times you might want the DHCP service to stop managing a particular address or group of addresses. The method you use to remove an address from DHCP depends on whether you want the change to be temporary or permanent.
-
To temporarily prevent the use of addresses, you can mark them unusable in the Address Properties dialog box as described in Marking IP Addresses Unusable by the DHCP Service.
-
To permanently prevent the use of addresses by DHCP clients, delete the addresses from the DHCP network tables, as described in Deleting IP Addresses from DHCP Service.
Marking IP Addresses Unusable by the DHCP Service
You can use the pntadm -M command with the -f UNUSABLE option to mark addresses unusable.
In DHCP Manager, you use the Address Properties dialog box, shown in Figure 10–10, to mark individual addresses, and the Modify Multiple Addresses dialog box, show in Figure 10–11, to mark multiple addresses, as described in the following procedure.
How to Mark Addresses Unusable (DHCP Manager)
-
Select the Addresses tab.
-
Select the IP address's network.
-
Select one or more IP addresses you want to mark unusable.
If you want to mark more than one address unusable, press the Control key while you click with the mouse to select multiple addresses. You can also press the Shift key while you click to select a block of addresses.
-
Choose Properties from the Edit menu.
The Modify Addresses dialog box or the Modify Multiple Address dialog box opens.
-
If you are modifying one address, select the Lease tab.
-
Select Address is Unusable.
If you are editing multiple addresses, select Mark All Addresses Unusable.
-
Click OK.
How to Mark Addresses Unusable (pntadm)
-
Become superuser or a user assigned to the DHCP Management profile.
-
Enter a command of the following format:
# pntadm -M ip-address -f UNUSABLE network-address
For example, to mark address 10.64.3.3 as unusable, type:
pntadm -M 10.64.3.3 -f UNUSABLE 10.64.3.0
Deleting IP Addresses from DHCP Service
You should delete IP addresses from the DHCP service database if you no longer want the address to be managed by DHCP. You can use the pntadm -D command or DHCP Manager's Delete Address dialog box.
The following figure shows the Delete Address dialog box.
Figure 10–12 Delete Address Dialog Box
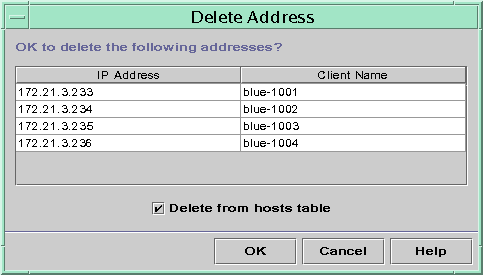
How to Delete IP Addresses from DHCP Service (DHCP Manager)
-
Select the Addresses tab.
-
Select the IP address's network.
-
Select one or more IP addresses you want to delete.
If you want to delete more than one address, press the Control key while you click with the mouse to select multiple addresses. You can also press the Shift key while you click to select a block of addresses.
-
Choose Delete from the Edit menu.
The Delete Address dialog box lists the address you selected so you can confirm the deletion.
-
If you want to delete the host names from the hosts table, select Delete From Hosts Table.
If the host names were generated by DHCP Manager, you might want to delete the names from the hosts table.
-
Click OK.
How to Delete IP Addresses from DHCP Service (pntadm)
-
Become superuser or a user assigned to the DHCP Management profile.
-
Type a command of the following format:
# pntadm -D ip-address
If you include the -y option, the host name is deleted from the name service in which it is maintained.
Setting Up DHCP Clients for a Consistent IP Address
The Solaris DHCP service attempts to provide the same IP address to a client that has previously obtained an address through DHCP. However, it is not always possible when a dynamic lease is used.
Routers, NIS/NIS+, DNS servers, and other hosts critical to the network should not use DHCP because they should not rely on the network to obtain their IP addresses. Clients such as print or file servers should have consistent IP addresses as well, but can be set up to receive their network configurations through DHCP.
You can set up a client to receive the same IP address each time it requests its configuration if you reserve, or manually assign, the client's ID to the address you want it to use. You can set up the reserved address to use a dynamic lease to make it easy to track the use of the address, or a permanent lease if you do not need to track address use. However, you might not want to use permanent leases because once a client obtains a permanent lease, it does not contact the server again and cannot obtain updated configuration information unless it releases the IP address and restarts the DHCP lease negotiation. A diskless client is an example of a client that should use a reserved address with a dynamic lease.
You can use the pntadm -M command or DHCP Manager's Address Properties dialog box.
The following figure shows the Lease tab of the Address Properties dialog box used to modify the lease.
Figure 10–13 Address Properties Lease Tab
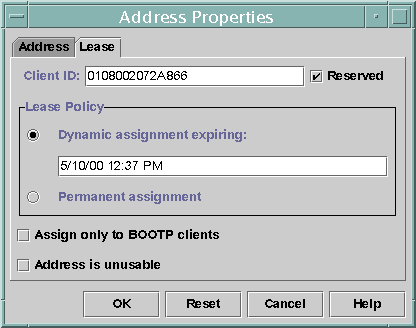
How to Assign a Consistent IP Address to a DHCP Client (DHCP Manager)
-
Determine the client ID for the client you want to have a permanent IP address.
See the entry for client ID in Table 10–2 for information about how to determine the client ID.
-
Select the Addresses tab in DHCP Manager.
-
Select the appropriate network.
-
Double-click the IP address you want to the client to use.
The Address Properties window opens.
-
Select the Lease tab.
-
In the Client ID field, type the client ID you determined from the client's hardware address.
See the Client ID entry in Table 10–2 for more information.
-
Select the Reserved option to prevent the IP address from being reclaimed by the server.
-
In the Lease Policy area of the window, select Dynamic or Permanent assignment.
Select Dynamic if you want the client to negotiate to renew leases, and thus be able to track when the address is used. Because you selected Reserved, the address cannot be reclaimed even when it uses a dynamic lease. You do not need to enter an expiration date for this lease. The DHCP server calculates the expiration date based on the lease time.
If you select Permanent, you cannot track the use of the IP address unless you enable transaction logging.
How to Assign a Consistent IP Address to a DHCP Client (pntadm)
-
Become superuser or a user assigned to the DHCP Management profile.
-
Type a command of the following format:
# pntadm -M ip-address -i client-id -f MANUAL+BOOTP network-address
Refer to the Client ID entry in Table 10–2 for more information about how to determine client identifiers.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
