| A P P E N D I X A |
|
How the IDE Supports Deployment of J2EE Modules and Applications |
This appendix briefly describes the server plugin. The server plugin is the IDE's mechanism for deploying and executing J2EE module and application. The server plugin provides the following IDE features:
This appendix focuses on the deploy and execute menu commands. It describes processing required to deploy an application and explains how the plugins perform this processing.
If you understand how the deployment facility works you can use it effectively. Procedures for using the deployment facility are included in a number of the scenarios in this book.
Deployment is the process of delivering the executable form of a module or an application to a J2EE application server. The executable form that is delivered to the server as an archive that contains compiled versions of the source files that make up the module or application. The compiled files are accompanied by a deployment descriptor that describes the contents and organization of the archive. The archived files are installed in directories that are managed by the application server.
When you execute a module or application, the application server executes the installed copy of the application in a process that is controlled by the application server. This process provides the necessary runtime environment.
To deploy successfully, the application source files must be compiled in a manner that is compatible with the specific application server product. The deployment descriptor must include all the information that is required by the specific application server product.
These needs are met by identifying a target application server for the product and compiling the source files and generating the deployment descriptor specifically for the target application server.)
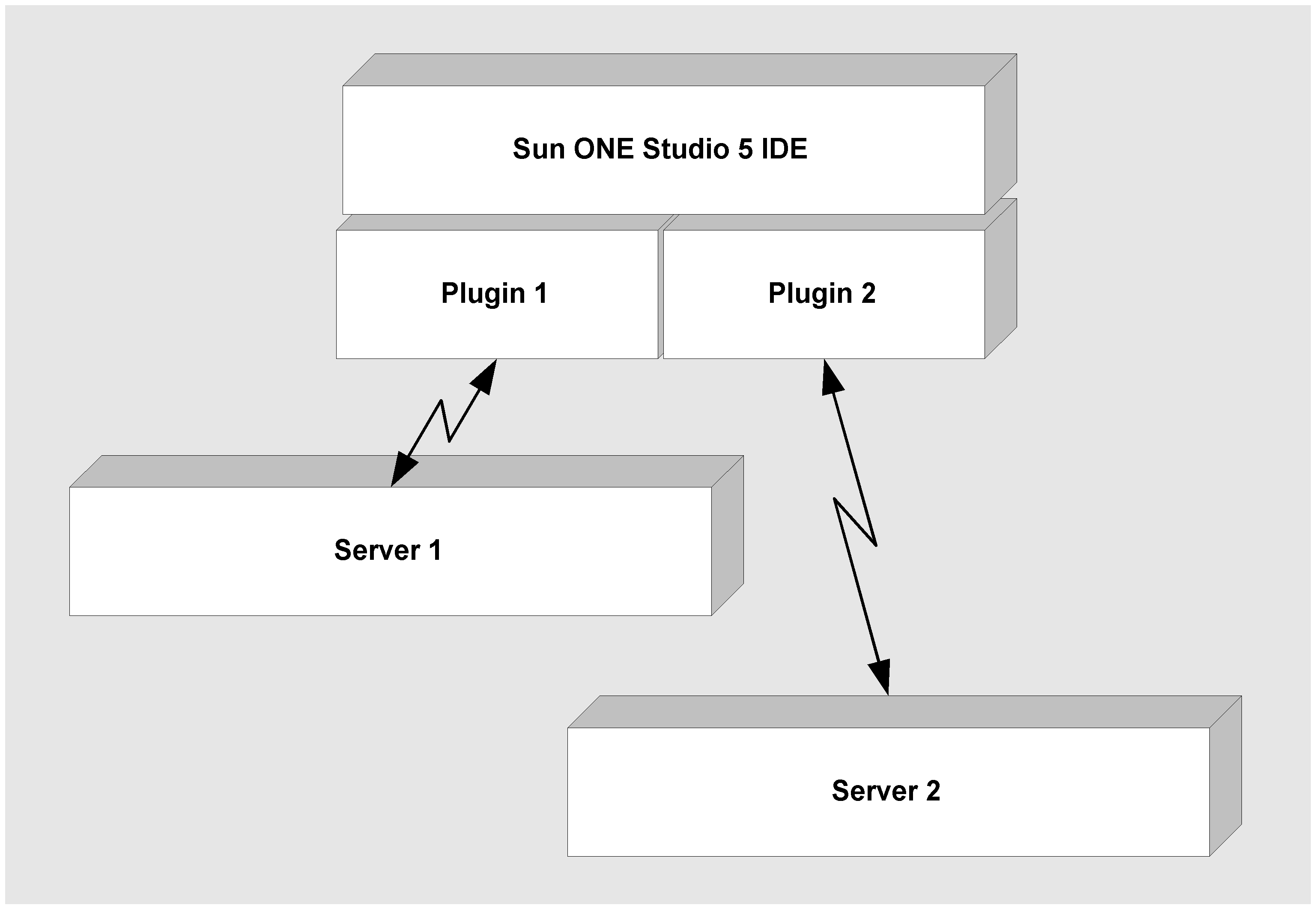
To enable the IDE to deploy to a variety of web and application servers, the concept of a server plug-in has been developed. A plugin is an IDE module that manages the interaction between the IDE and a specific server product. When you deploy an application, you choose the server to which it will be deployed. The IDE uses the appropriate plugin to process your Deploy command. This enables it to generate the appropriate commands for the server's deployment tool and include the appropriate server-specific deployment descriptor files in the files it passes to the server. This is illustrated in FIGURE A-1.
 [ D ]
[ D ]
For the application developer who is deploying an application, the plugins provide:
This section summarizes the processing performed by the plugin when you deploy and execute an application.
1. Assemble your application. Use property sheets to supply J2EE standard deployment descriptor elements and the non-standard elements required by the server.
2. After you assemble the application, specify a target server instance.
3. Choose the IDE's Deploy command to begin the deployment process.
4. The IDE identifies all of the files needed to create a WAR or EAR file for the application. This includes the J2EE components identified in the deployment descriptor, and any Java classes or static resources used by those files. The IDE identifies all file dependencies in the components.
5. The IDE identifies the server product to which the application is being deployed.
6. The plugin validates the files for the WAR or EAR file.
7. The IDE generates the WAR or EAR file for the application. This includes a J2EE deployment descriptor, separate files with server-specific deployment tags, and any stub or skeleton classes required for remote method invocations.
8. The plugin passes the WAR or EAR file to the server.
9. The server takes over, reads the deployment descriptors and the server-specific deployment files, and deploys the WAR or EAR file according to its own standards.
When this process is complete, the IDE will automatically start a web browser and open the application's welcome page. If you chose to deploy and execute separately, you can start a web browser and one of the application's web pages.
Web modules and J2EE applications are the only items that can actually be deployed to servers and executed. However, you may want to test smaller units of business logic that you are developing. The Sun ONE Studio 5 IDE makes it possible to deploy and execute smaller units of business logic by automatically generating modules and applications for the components you want to test. It can also generate test clients for some types of components. For more information on these features, see Building Web Components and Building Enterprise JavaBeans Components.
Copyright © 2003, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.