To Create a Data Store
-
In the Admin Console, choose Data Store from the Create menu.
The Create Data Store window is displayed. It is similar to the Modify Data Store window shown in Figure 4-2.
-
In the General Section, in the Data Store Suffix field, specify the distinguished name of the naming context stored in this data store.
To specify more than one naming context, click the More Suffixes button.
-
Specify the path name to the directory where this database is to be stored.
-
Specify whether the data store is read-only or not.
By default, it is not.
-
Specify whether the last modification attributes should be recorded.
When this option is enabled, the creator's DN, a creation timestamp, the modifier's DN, and a modification timestamp are added in the entry. This enables you to search the directory for entries created or modified since a particular date or time. This can be useful if you are synchronizing changes across data stores, or you are using partial replication.
-
Specify the cache size limit, in entries and in bytes.
See "Caching" for details.
-
Specify congestion thresholds.
See "Congestion Thresholds" for details.
-
Optionally, you can specify which attributes to index in the database.
See "To Create Indexes" for details.
-
In the Naming Contexts section, specify the master and slave subtrees held in this data store.
These are naming contexts that are subtrees or objects under the naming context used to name the data store. If you do not specify any naming contexts, the distinguished name of the data store itself is added to the list of master naming contexts automatically, but it is not displayed until you save the naming contexts information. See "Naming Contexts" for details.
-
Choose Naming Context from the Create menu.
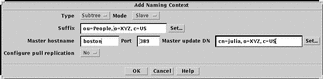
The Add Naming Context window is displayed. Figure 4-3 shows the appearance of the window when Slave mode is selected.
Figure 4-3 Add Naming Context window (Slave Mode)
-
Specify:
-
The subtree type (subtree or object)
-
The DN of the subtree or object in the Suffix field
-
The mode (master or slave)
-
-
If the naming context is a replica (slave), specify:
-
The name of the server from which it is replicated in the Master hostname field
-
The Master Update DN that dspushd will use when the master initiates the bind to replicate changes.
-
Whether you want the slave to pull updates from the master. If so, see "To Create Replicas" for details on how to specify the bind parameters.
-
-
Click OK to save the naming context information.
The new naming context is displayed in the Naming Contexts section.
-
-
Optionally, you can replicate any of the stored naming contexts to a different server.
If you do, you must create the naming context on the target server following the procedure described in Step 9, because the replication procedure does not create it automatically. See "Setting Up Replication" for details.
-
Click OK in the Create Data Store window to save the data store definition.
-
Add a directory entry for the root of the data store.
See "Creating the Root Entry" for details of how to add an entry to the directory. You cannot add any entries to this data store until this root entry exists.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
