| Previous Contents Index DocHome Next |
| iPlanet Application Server Administrator's Guide |
Chapter 12 Balancing User-Request Loads
This chapter describes load balancing, which optimizes the ability of each iPlanet Application Server to process users' requests by keeping those requests balanced among several iPlanet Application Server machines.This chapter contains the following topics:
How Load Balancing Works
Requirements for Load Balancing
What Is Sticky Load Balancing?
Selecting a Load Balancing Method
Per Component Response Time Load Balancing
How Load Balancing Works
The goal of load balancing is to evenly distribute the workload between multiple iPlanet Application Server machines. When you use the iASAT to configure load balancing, you want distribute user requests as optimally as possible.For example, if you find that many users access an application during peak usage hours, you can duplicate the application's components, such as AppLogics and servlets, on several iPlanet Application Server machines and enable load balancing. As one iPlanet Application Server machine reaches its optimal handling capacity, subsequent requests are sent to another iPlanet Application Server machine with duplicate application components. With requests evenly distributed between your servers, you can decrease response time.
You can specify the load balancing method for an iPlanet Application Server machine. The load balancing method you choose is either Web Connector Plug-in driven or iPlanet Application Server driven.
Web Connector Plug-in driven: The Web Connector Plug-in chooses which iPlanet Application Server instance in which to send the request.
iPlanet Application Server driven: Load balancing decisions are left to iPlanet Application Server. Server and request statistics are collected and communicated from one iPlanet Application Server machine to another in a cluster via multicasting. For more information about multicasting, see Configuring Multiple Servers.
Requirements for Load Balancing
Before your application is load balanced, the following requirements must be met:
The application's components must be duplicated on at least two iPlanet Application Server machines or on every iPlanet Application Server machine that is to participate in load balancing.
For information about enabling load balancing, see .The distribution levels for the application components must be distributed for either specific iPlanet Application Server machines or globally to all iPlanet Application Server machines in the enterprise.
What Is Sticky Load Balancing?
If requests within the same session are processed by more than one iPlanet Application Server machine or process, session information that is not configured to be distributed is lost. Therefore, certain application components are marked for session or "sticky" load balancing and processed on the same server, thereby eliminating the loss of session information.When an application component is marked for sticky load balancing, it is processed by the same iPlanet Application Server machine or processed where it is initially invoked. For example, an application component called ShopCart is duplicated on two application servers for load balancing, Server A and Server B. If ShopCart is invoked by Client 1 on Server B, all subsequent sticky requests for that ShopCart from Client 1 are processed on Server B only. In other words, ShopCart "sticks" to Server B for the duration of Client 1's session. However, at the same time, Client 2 may access ShopCart on Server A without affecting Client 1's use of ShopCart on Server B. This maintains the integrity of state and session information for an application component that does not distribute session information.
This section describes the following topics:
When to Use Sticky Load Balancing
When to Use Sticky Load Balancing
Sticky load balancing is necessary for application components that have interdependencies, but are running in a distributed environment. Such application components typically have the following characteristics:
originally written to run on one machine
For example, a heavily used, pre-existing application is ported to run on iPlanet Application Server. Because the application is heavily used, it is distributed across several iPlanet Application Server machines to increase availability. When a user makes a request that invokes a sticky application component, the load-balancing service determines which iPlanet Application Server machine should handle that request. Once that server is chosen, all subsequent requests that use sticky application components are handled by that server. If that server becomes burdened with many users' requests, the load balancer forwards new requests to another iPlanet Application Server machine and that server processes all new session requests. This maintains an effective degree of load balancing.depend on session information to run properly
wrapped, not rewritten, to run in an iPlanet Application Server environment
Enabling Sticky Load Balancing
Enable sticky load balancing if there are multiple iPlanet Application Server machines and certain application components cannot distribute session and state information.To enable sticky load balancing, perform the following steps:
On the iASAT toolbar, click Application to open the Application window.
In the left pane of the Application window, select the server where you want to enable sticky load balancing.
Open the application group that contains the application component or components for which you want to enable sticky load balancing.
In the right pane of the Application window, select the application component for which you want to enable sticky load balancing.
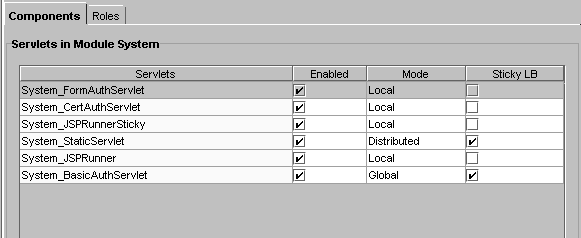
In the Sticky LB column, click the checkbox for the selected application component.
Repeat steps 4 and 5 for each application component where you want to enable sticky load balancing.
- Sticky load balancing is turned on for the selected component.
Click Toggle Sticky LB to select or deselect all Sticky LB checkboxes.
Sticky Load Balancing and Foreign Sticky Cookies
Normally, a web connector can only dispatch requests to iPlanet Application Server instances that are positioned specifically in iPlanet Registry. For example, requests for application components which are configured LOCAL will be dispatched to the instance configured in the following iPlanet Registry key:Software/iPlanet/Application Server/6.0/CCSO/HTTPAPI/GXIP
Requests for application components which are configured DISTRIBUTED can be dispatched to any iPlanet Application Server instance that is delineated for the target component, in the following iPlanet Registry key:
Software/iPlanet/Application Server/6.0/GDS/subtreemaps
In other words, potential instances must be deciphered from the web connector's registry. However, there is a less obvious alternative for the web connector when requests arrive with sticky cookies set. When a web connector processes a request with a sticky cookie, it dispatches the request based on the sticky targeting value. It is possible, when configured correctly and intentionally, for a web connector to properly dispatch requests for sticky targets of which it would unfamiliar. For instance, when a separate load balancing tier is in front of a set of application servers, it is possible for a web connector to receive a sticky request for a target application server which it has never had a connection to previously. It is also possible for the web connector to ignore the sticky targeting for instances of which the web connector is not aware. The set of instances in which a web connector will allow sticky targeting is decided depending on the instances that are part of the same multicast group.
Selecting a Load Balancing Method
When configuring your server for load balancing, you must choose a load balancing method. Each method provides a different way to decide "who" makes the load balancing decisions. In other words, are load balancing decisions left to the server itself or does the web connector plug-in make the decisions?This section describes the following topics:
Load Balancing with the Web Connector Plug-in
Load Balancing with the Web Connector Plug-in
If load balancing is left to the web connector plug-in you can choose to load balance:
Per Component Response Time (Default)
Per Server Response Time
- The Web Connector Plug-in measures application component response time to determine where to forward an application request. This is the default load balancing choice.
Round Robin
- The Web Connector Plug-in measures server response time to determine where to forward an application request. This choice offers lower overhead than Per Component Response Time.
- Requests distributed across servers based on a weighting scheme you specify
- The plug-in distributes requests across iPlanet Application Server machines according to the weights you specify. This load balancing option does not incur overhead since it is based solely on the weights that you specify and data collection regarding component or server response time is not required.
Load Balancing with iPlanet Application Server
If load balancing decisions are left to iPlanet Application Server, the application server uses a combination of hardware resource profiles (including CPU load and disk I/O) and Request Execution profiles (including result caching and servlet execution rate) to load balance individual requests. Server and request statistics are communicated from one iPlanet Application Server machine to another in a cluster via multicasting. Multicasting gives more control to the administrator, and is suitable for sophisticated scenarios.
Per Component Response Time Load Balancing
Per-component response time is based on a measure of an iPlanet Application Server machine's average response time for a specific application component.The per-component method enables richer, more detailed load balancing decisions by the Web Connector Plug-in. Keep in mind that this scenario involves a little more overhead than the per-server method. The per-component method is best suited to situations where one application component has a response time that differs widely from server to server due to varying performance characteristics.
To enable per component response time load balancing, perform the following steps:
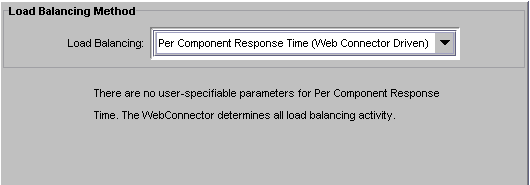
On the iASAT toolbar, click Load Balancing to open the Load Balancing window.
In the left pane, select the server for which you want to specify the load balancing method.
In the Load Balancing drop-down box, choose Per Component Response Time (Web Connector Plug-in Driven) to specify the web connector plug-in will make load balancing decisions based on component response time statistics. This is the default.
Per Server Response Time Load Balancing
Per-server response time is based on a measure of an iPlanet Application Server machine's average response time across all the application components that machine processes.The per-server method is best in situations where an application component has a similar response time from server to server.
To enable per server response time load balancing, perform the following steps:
On the iASAT toolbar, click Load Balancing to open the Load Balancing window.
In the left pane, select the server for which you want to specify the load balancing method.
In the Load Balancing drop-down box, choose Per Server Response Time (Web Connector Plug-in Driven) to specify the Web Connector Plug-in will make load balancing decisions based on server response time statistics.
Round Robin Load Balancing
When you choose round robin load balancing method, you need to specify how each iPlanet Application Server machine participating in round robin load balancing is weighted. By default, this value is one (1) unless otherwise changed. When all servers have equal weights, round robin load balancing will send equal numbers of requests to each server. You should use a weighted system when you have servers of unequal capacity. For example, if you have four machines of differing performance characteristics participating round robin, you would probably want to route more requests to the fastest machines. You do this by assigning each iPlanet Application Server machine a weight. If you assign four iPlanet Application Server machines weights of:
for every 8 requests, 4 requests will be routed to machine 1, 2 requests routed to machine 2 and so on. For a fine-grain control over the number of requests, you may want to think in terms of "how many requests out of 1000 should go to this server. For example, specifying weights of 135, 270, and 595 would offer fine-grain precision over the number of requests being sent to a server.
- Machine 1 = 4
- Machine 2 = 2
- Machine 3 = 1
- Machine 4 = 1
To setup round robin load balancing, perform the following steps.
Start iPlanet Registry Editor.
Set the following key to 1.
- (See "About iPlanet Registry Editor)
- The editor opens and displays the keys and values that apply to iPlanet Application Server.
Highlight the following key:
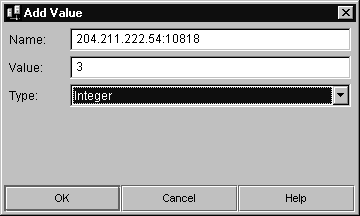
Choose Edit, then Add Value.
- SOFTWARE\iPlanet\Application Server\6.0\CCSO\Loadb\ServerWeights
Enter the name (IP Address and port number), Value (weight) for each iPlanet Application Server machines participating in round robin load balancing and set the Type to Integer.
- The Add Value dialog box opens
Save and close the editor.
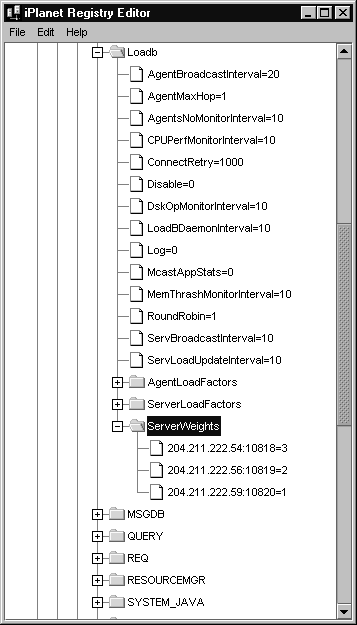
- For example, for three IPLANET APPLICATION SERVER machines with IP addresses (of KXS) of:
- a. 204.211.222.54:10818
- b. 204.211.222.56:10819
- c. 204.211.222.59:10820
- assign the following values:
- SOFTWARE\iPlanet\Application Server\6.0\CCSO\LoadB\ServerWeights
- 204.211.222.54:10818=3
- 204.211.222.56:10819=2
- 204.211.222.59:10820=1
- Under this weighting scheme, for every 6 requests the Web Connector Plug-in will route three requests to port 10818, two requests to port 10819, and one request to port 10820.
User-Defined Criteria Load Balancing
If you decide that iPlanet Application Server and not the web connector plug-in will make the load-balancing decisions for your enterprise, the load-balancing service then decides which iPlanet Application Server machine should process a request based on the weight factors you specify for the Server Load and Application Component Performance criteria. You set these factors using the iASAT's Load Balancing window. When determining weight factors, you must decide how important each criteria is for keeping your applications running optimally.The weight factors in iASAT are initially set to default values based on the most typical applications that run on an iPlanet Application Server machine. You can adjust these factors for either Server Load criteria or Application Component criteria to optimize your specific application.
This section describes the following topics:
Adjusting Weight Factors for Server Load Criteria
Adjusting Weight Factors for Application Component Performance Criteria
Adjusting Weight Factors for Server Load Criteria
The Server Load value quantifies the load on an iPlanet Application Server machine while the server is processing users' requests. This value is calculated for each iPlanet Application Server machine by the load-balancing service within the respective server. You can adjust the weight factors for Server Load criteria to optimize how application requests are distributed across multiple iPlanet Application Server machines based on system resources.The Server Load value is used as one of the criterion for calculating the Application Component Performance value. The Server Load criteria are described in the following table:
Each Server Load criterion is multiplied with a weight factor you set. That value is averaged with the other values to determine the final Server Load value. This value is then used as one of the Application Component Performance criteria.
To adjust the weight factors for Server Load criteria, perform the following steps:
On the iASAT toolbar, click Load Balancing to open the Load Balancing window.
In the left pane, select the server for which you want to adjust the weight factors.
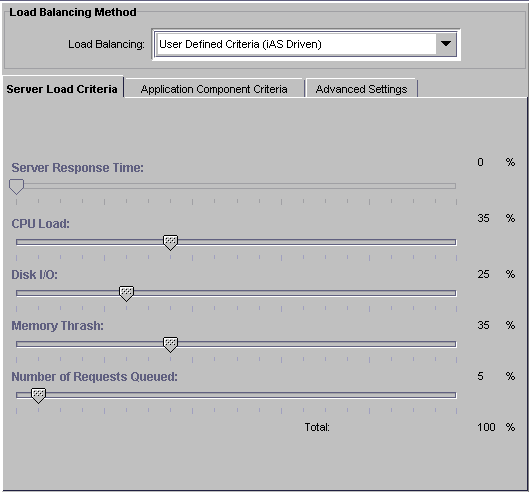
In the Load Balancing drop-down box, choose User Defined Criteria (iPlanet Application Server Driven) to specify the server will make load balancing decisions.
In the right pane of the Load Balancing window, use the sliding scale markers to adjust the weight factor for each criterion. For a description of the criterion see,Adjusting Weight Factors for Server Load Criteria.
- You can then adjust the weight factors as your enterprise requires. With the Server LoadCriteria tab active, the following window appears:
When finished, click Apply Changes to save the settings.
- The grand total of all weight factors must equal 100.
Adjusting Weight Factors for Application Component Performance Criteria
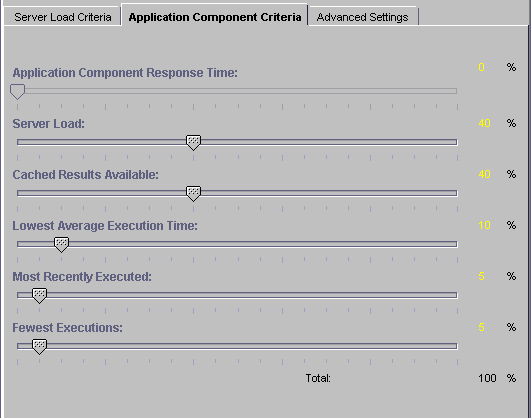
The Application Component Performance value represents the performance of the application components running on an iPlanet Application Server machine. This value is calculated for each application component participating in load balancing. Load balancing then occurs on an application component basis and increases distribution.The Application Component Performance value includes five application criteria. The load-balancing service compares iPlanet Application Server machines based on the weight factor you assign for each application criterion. The server with the highest total value is chosen to process requests for that application component. The Application Component Performance criteria are described in the following table:
Each application criterion is multiplied by a weight factor you set. Each value is then averaged to determine the final Application Component Performance value. The final value is used by the load-balancing service to determine which iPlanet Application Server machine is best able to handle new users' requests.
To adjust the weight factors for Application Component Performance criteria, perform the following steps:
On the iASAT toolbar, click Load Balancing to open the Load Balancing window.
In the left pane, select the server for which you want to adjust the weight factors.
In the Load Balancing drop-down box, choose User Defined Criteria (iPlanet Application Server Driven) to specify the server will make load balancing decisions.
Click the Application Component Criteria tab.
- You can then adjust the weight factors as your enterprise requires.
In the right pane of the Load Balancing window, use the sliding scale markers to adjust the weight factor for each criterion.
When finished, click Apply Changes to save the settings.
- The grand total of all weight factors must equal 100.
Adjusting Update and Broadcast Intervals
You can set the time at which an iPlanet Application Server machine updates the Server Load and Application Component Performance criteria. If these values change frequently and drastically, it is useful to update the values often. Unfortunately, you increase the amount of work the iPlanet Application Server machine is doing by updating values frequently. You can save server resources by increasing the time between updates if the criteria values do not change often.This theory applies to setting the broadcast intervals, as well; if values are changing often and drastically, the broadcast intervals should be short, updating servers often. This increases network traffic load, so it is important to find an optimal balance.
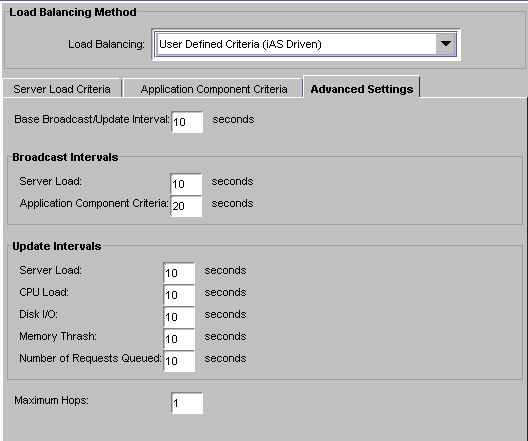
Broadcast and update intervals are relative to the Base Broadcast/Update Interval. This is the interval at which the load-balancing service "wakes up" and performs any updates, checks to see if any updates were received, and broadcasts any new values.
Broadcast and update intervals that are even multiples of the base interval are invoked when the load-balancing service "wakes up." In other words, if the base value is 300 seconds, and the Server Load and Application Component Criteria broadcast intervals are at 900 seconds each, these values are broadcast every third time the load-balancing service "wakes up." The other two times the load-balancing service awakens, it reevaluates the distribution order based on whether it received any updates from other iPlanet Application Server machines.
You can set update and broadcast intervals for several entities, as described in the following table:
To adjust the update and broadcast intervals, perform the following steps:
Click the Load Balancing on the iASAT toolbar to open Load Balancing window.
In the left pane of the Load Balancing window, select the server for which you want to adjust the advanced settings.
In the Load Balancing drop-down box, choose User Defined Criteria (iPlanet Application Server Driven) to specify the server will make load balancing decisions.
Click the Advanced Settings tab.
In the right pane of the Load Balancing window, under each interval parameter, set the time as a multiple of the base time for that parameter.
In the Max Hops text area, specify the maximum number of times an application component is passed between servers.
Changing the Multicast Host Address for Load Balancing
Change the multicast server host address and port number to balance application loads across networks, such as across cities. Within a network, the default address does not need to be changed unless you are experiencing a conflict.To change the multicast host address, perform the following steps:
Start iPlanet Registry Editor
Open the following key:
- (See "About iPlanet Registry Editor)
Double-click the MCastHost String value.
- SOFTWARE\iPlanet\Application Server\6.0\GMS\KES
For the value data, specify the IP address for the new host and click OK.
- The String editor dialog box appears.
Double-click the MCastPort DWORD value.
For the value data, specify the port number for the new host and click OK.
- The DWORD editor dialog box appears.
- The new multicast address is in effect.
Previous Contents Index DocHome Next
Copyright © 2001 Sun Microsystems, Inc. Some preexisting portions Copyright © 2001 Netscape Communications Corp. All rights reserved.
Last Updated November 09, 2001