| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Java CAPS REST Binding Component User's Guide Java CAPS Documentation |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Java CAPS REST Binding Component User's Guide Java CAPS Documentation |
Using the REST Binding Component
About the REST Binding Component
REST Binding Component Features
Working With the REST BC WSDL Document
Creating the REST BC WSDL Document
To Create a WSDL Document for REST Inbound
To Create a WSDL Document for REST Outbound
New WSDL Wizard Properties for REST
Configuring REST BC WSDL Attributes
To Configure REST BC WSDL Attributes
Service Level REST WSDL Element
Binding Level REST WSDL Elements
Configuring the REST Binding Component Runtime Properties
To Configure REST BC Runtime Properties
REST Binding Component Runtime Property Descriptions
Creating Application Configurations for Connectivity Parameters (URLs)
To Create Application Configurations
To Add the Application Configuration to the Endpoint
To Change Application Configuration Values
To Create an Application Variable
To Use an Application Variable for Password Protection
Using REST BC Normalized Message Properties in a Business Process
Using Predefined Normalized Message Properties
To Use Predefined Normalized Message Properties in Mapper View
To Use Predefined Normalized Message Properties in Source View
Normalized Message Properties for REST
You can define normalized message properties in a BPEL process in order to dynamically assign values to the runtime properties for the REST BC. The normalized message properties for each JBI component are accessed from the BPEL Designer Mapper view. When you expand a variable's Properties folder it exposes the variable's predefined NM properties, as well as the standard BPEL-specific WSDL properties used in correlation sets, assigns, and expressions . If the specific NM property you need is not currently listed, additional NM properties can be added.
Normalized message properties provide the following capabilities:
Getting and setting transport context properties, such as REST headers.
Getting and setting request parameters.
Dynamically configuring REST properties.
Predefined normalized message properties are automatically available from the BPEL Designer's Mapper view. You can use additional properties by adding them directly to the source code. You can either define these properties using the BPEL Designer Mapper, or by entering the code directly into the source view.
You can perform additional tasks when working with normalized message properties, such as creating additional properties, deleting properties, creating property shortcuts, and so on. For more information, see Using Normalized Message Properties in Oracle Java CAPS BPEL Designer and Service Engine User’s Guide.
You can access most of the normalized message properties from the BPEL Mapper. Certain properties, such as path and query parameters, need to be defined in the Source view.
A list of available normalized message properties appears.
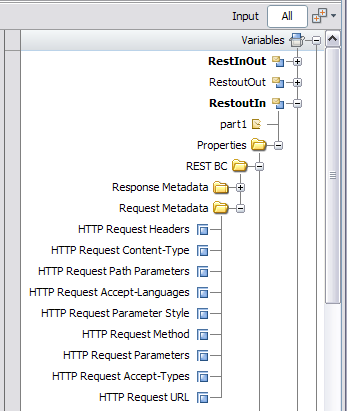
For a complete list of normalized message properties for the REST BC, see Normalized Message Properties for REST.
You can define any of the normalized message properties using the Source view. You can only access path or query parameters from the Source view.
The BPEL source code for the process is now visible.
xmlns:sxnmp="http://www.sun.com/wsbpel/2.0/process/executable/SUNExtension /NMProperty"
For path and query parameters, separate normalized message properties are created for each. For example,
<assign name="AssignActivity">
<copy>
<from variable="GetCustomerNameIn"
sxnmp:nmProperty="org.glassfish.openesb.rest.path-params.custName"/>
<to>$CustomerQuery_OperationIn.part/ns0:param1</to>
</copy>
</assign>Example 1 Using REST BC Normalized Message Properties for Query Parameters
There are two methods to use normalized message properties to encode information as query parameters in an outbound REST call. Both methods are illustrated below in examples that show how to define query parameters for a simple address.
The following example illustrates defining all the parts and assigning their values as a single string.
<copy>
<from>'{"street":"800 Royal Oaks Blvd.", "city":"Monrovia", "state":"CA",
"zip":"91016"}'</from>
<to variable="YahoomapIn" sxnmp:nmProperty="org.glassfish.openesb.rest.params"/>
</copy>
The following example illustrates defining each part as a query parameter and assigning the values individually.
<copy>
<from>'800 Royal Oaks Blvd.'</from>
<to variable="YahoomapIn"
sxnmp:nmProperty="org.glassfish.openesb.rest.params.street"/>
</copy>
<copy>
<from>'Monrovia'</from>
<to variable="YahoomapIn"
sxnmp:nmProperty="org.glassfish.openesb.rest.params.city"/>
</copy>
<copy>
<from>'CA'</from>
<to variable="YahoomapIn"
sxnmp:nmProperty="org.glassfish.openesb.rest.params.state"/>
</copy>
<copy>
<from>'91016'</from>
<to variable="YahoomapIn"
sxnmp:nmProperty="org.glassfish.openesb.rest.params.zip"/>
</copy>
Normalized message properties are either specific to the binding component being used or generally available to all participating JBI components. The following topics describe both types of normalized message properties.
The following table lists and described the general properties that are available to all JBI components. All property values are of the type java.lang.String.
Table 10 General Normalized Message Properties
|
The following properties are specific to the REST Binding Component. Available properties are different for request messages than for response messages. All property values are of the type java.lang.String.
Table 11 REST Binding Component NM Properties (Request)
|
Table 12 REST Binding Component NM Properties (Response)
|