4 Extending the Functionality of the SAP SuccessFactors Connector
You can extend the functionality of the connector to address your specific business requirements.
The following topics are discussed in this section:
Note:
From Oracle Identity Manager Release 11.1.2 onward, lookup queries are not supported. See Managing Lookups in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for information about managing lookups by using the Form Designer in the Oracle Identity Manager System Administration console.
4.1 Adding New User Attributes for Reconciliation
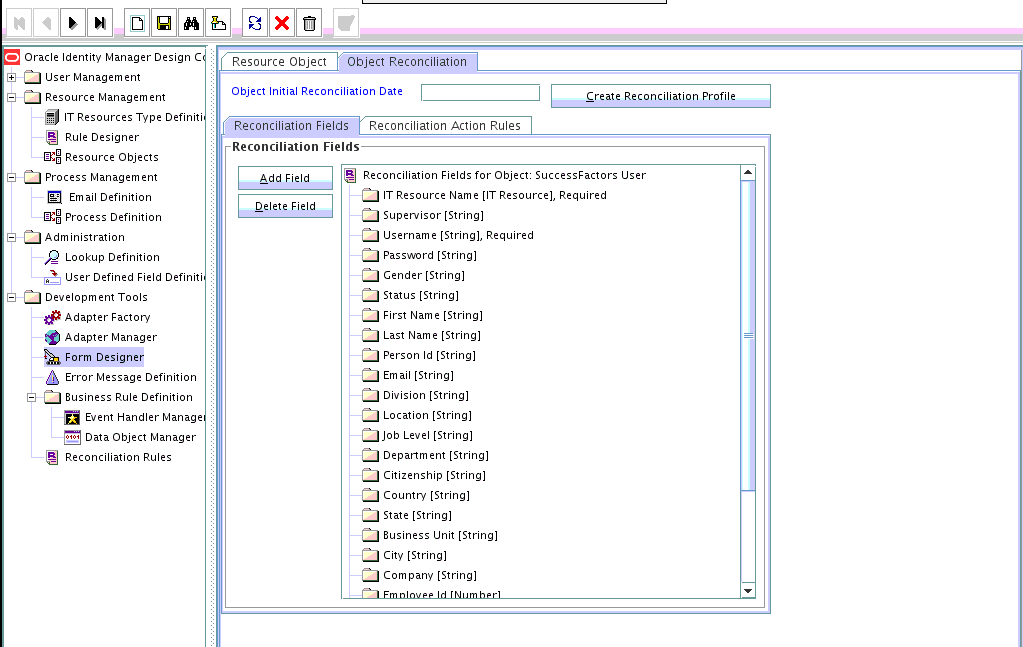
The connector provides a default set of attribute mappings for reconciliation between Oracle Identity Manager and the target system. If required, you can add new user attributes for reconciliation.
The default attribute mappings for reconciliation are listed in Table 1-24 and Table 1-28.
Note:
Only single-valued attributes can be mapped for reconciliation.
The following topics discuss the procedure to add new attributes for users:
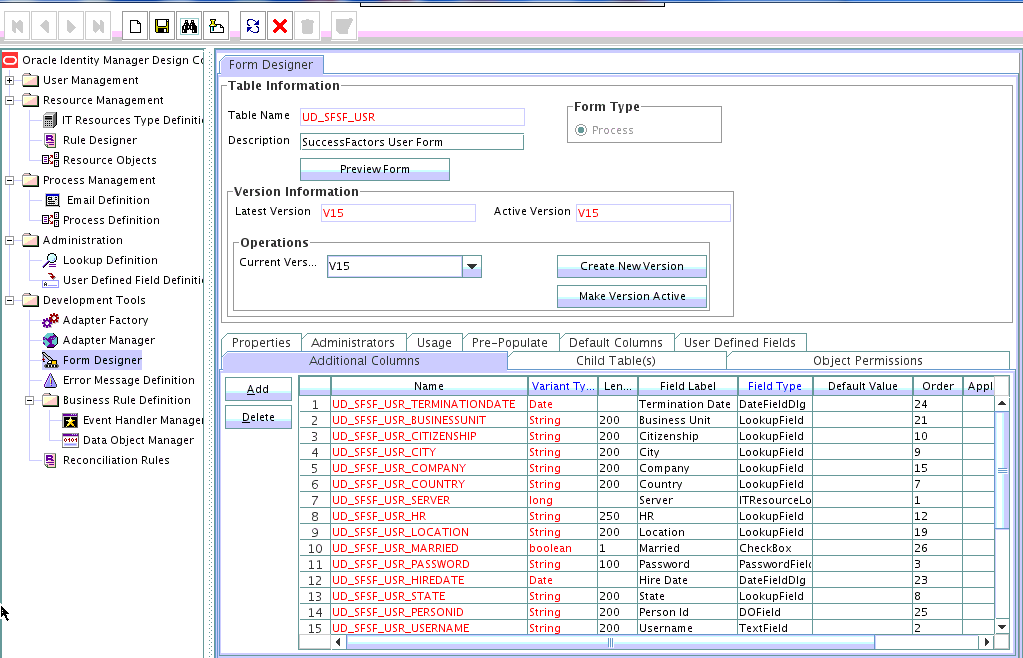
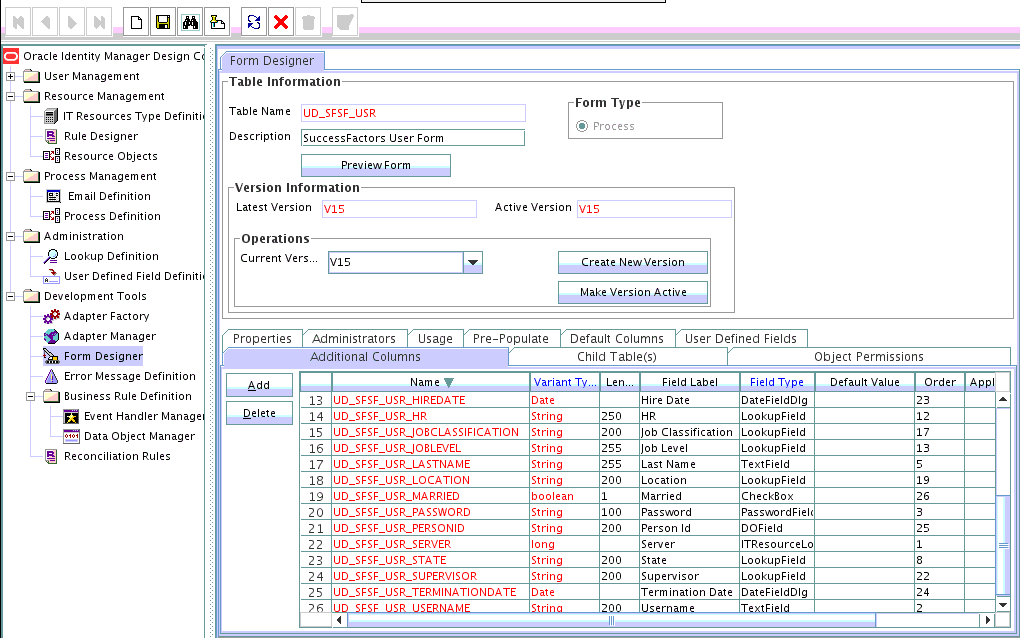
4.1.2 Adding Attributes to the Resource Object
You can add the new attribute to the resource object in the Resource Objects section of Oracle Identity Manager Design Console.
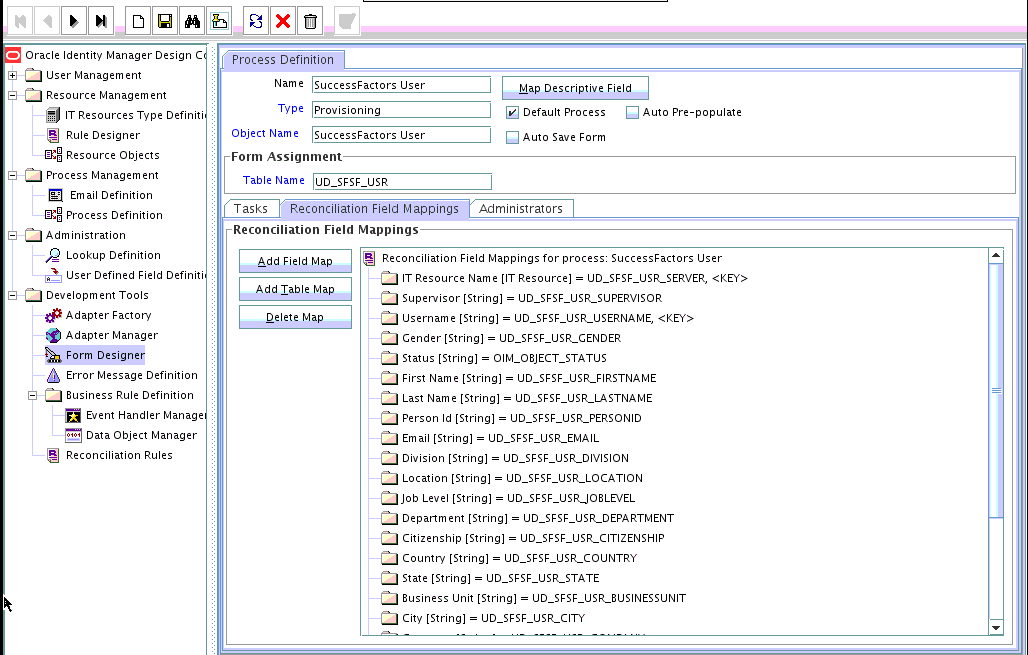
4.1.3 Creating Reconciliation Field Mapping
You create a reconciliation field mapping for the new attribute in the Process Definition section of Oracle Identity Manager Design Console.
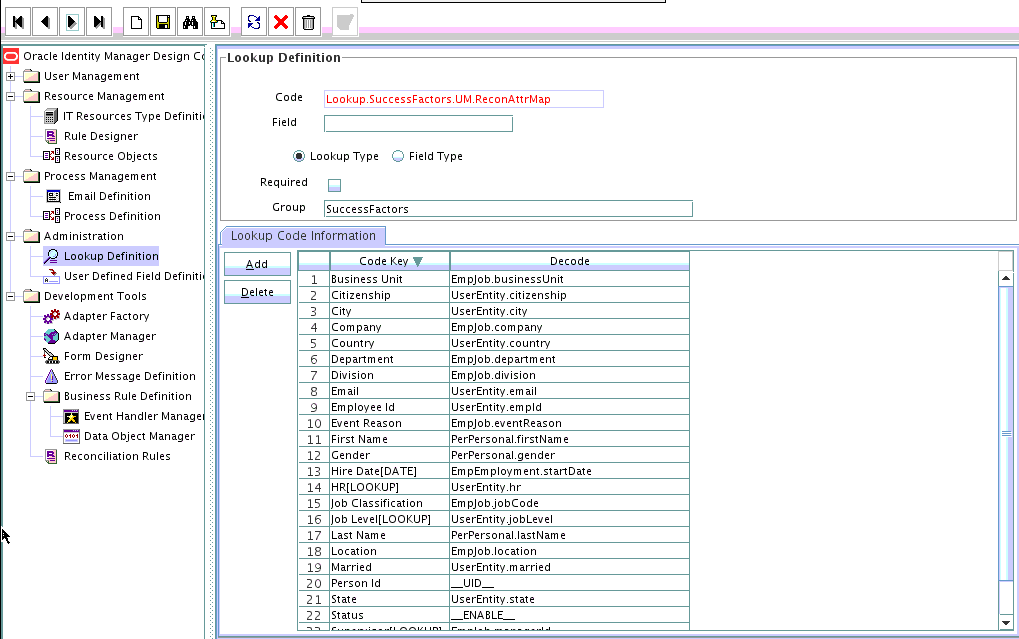
4.1.4 Creating Entries in Lookup Definitions
You create an entry for the newly added attribute in the lookup definition that holds attribute mappings for reconciliation.
4.1.5 Performing Changes in a New UI Form
You must replicate all changes made to the Form Designer of the Design Console in a new UI form.
- Log in to Oracle Identity System Administration.
- Create and activate a sandbox.
- Create a new UI form to view the newly added field along with the rest of the fields.
- Associate the newly created UI form with the application instance of your target system. To do so, open the existing application instance for your resource, from the Form field, select the form, and then save the application instance.
- Publish the sandbox.
4.2 Adding New User Attributes for Provisioning
The connector provides a default set of attribute mappings for provisioning between Oracle Identity Manager and the target system. If required, you can add new user attributes for provisioning.
The default attribute mappings for provisioning are listed in Table 1-26.
The following topics discuss the procedure to add new user attributes for provisioning:
4.2.1 Adding New Attributes for Provisioning
You add a new attribute on the process form in the Form Designer section of Oracle Identity Manager Design Console.
To add a new attribute on the process form:
Note:
If you have already added an attribute for reconciliation, then you need not repeat steps performed as part of that procedure.
4.2.2 Creating Entries in Lookup Definitions for Provisioning
You create an entry for the newly added attribute in the lookup definition that holds attribute mappings for provisioning.
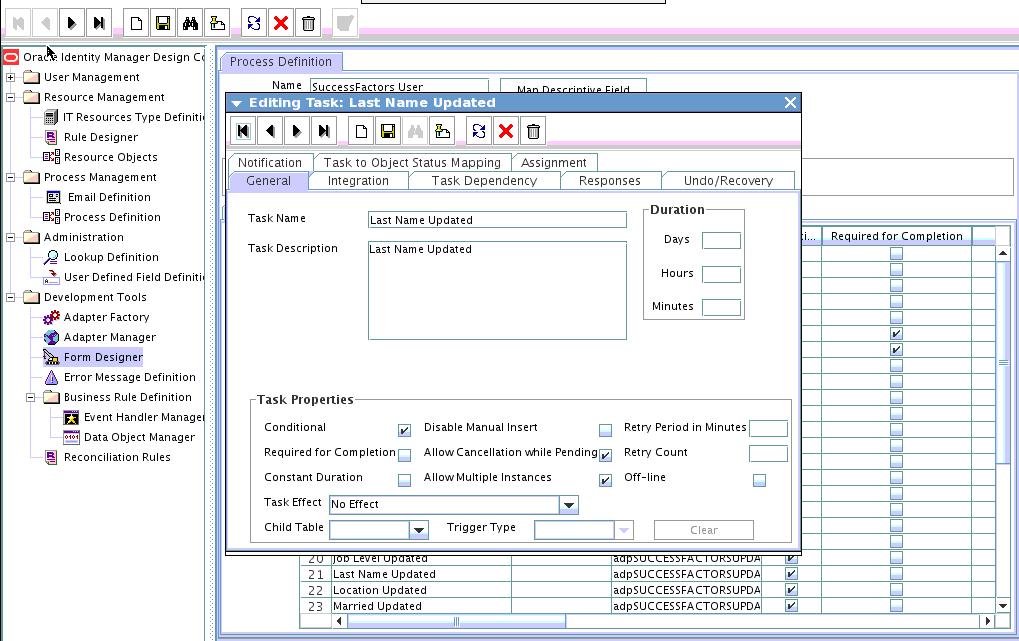
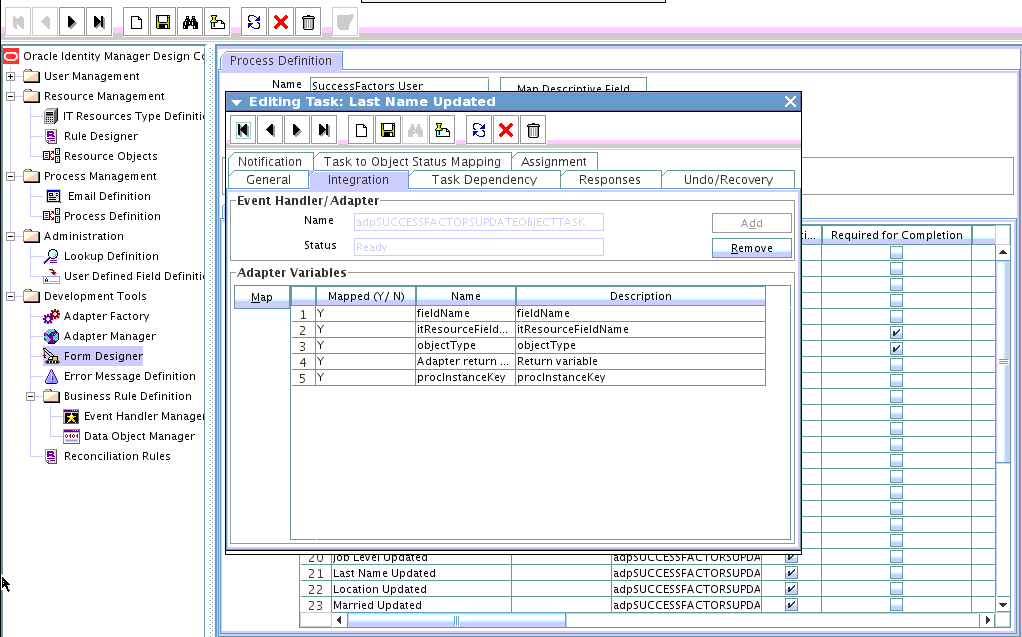
4.2.3 Creating a Task to Enable Update Operations
You create a task to enable updates on the new user attribute during provisioning operations. If you do not perform this procedure, you cannot modify the value of the attribute after you set a value for it during the Create User provisioning operation.
4.2.4 Replicating Form Designer Changes to a New UI Form
You must replicate all changes made to the Form Designer of the Design Console in a new UI form.
- Log in to Oracle Identity System Administration.
- Create and activate a sandbox.
- Create a new UI form to view the newly added field along with the rest of the fields.
- Associate the newly created UI form with the application instance of your target system. To do so, open the existing application instance for your resource, from the Form field, select the form, and then save the application instance.
- Publish the sandbox.
4.3 Configuring Validation of Data During Reconciliation and Provisioning
You can configure validation of reconciled and provisioned single-valued data according to your requirements.
To configure validation of data:
4.4 Configuring Transformation of Data During User Reconciliation
You can configure transformation of reconciled single-valued account data according to your requirements.
To configure transformation of single-valued account data fetched during reconciliation:
4.5 Configuring the Connector for Multiple Installations of the Target System
You must create copies of the connector to configure it for multiple installations of the target system.
The following example illustrates this requirement:
The London and New York offices of Example Multinational Inc. have their own installations of the target system. The company has recently installed Oracle Identity Manager, and they want to configure Oracle Identity Manager to link all the installations of the target system.
To meet the requirement posed by such a scenario, you must create copies of the connector. See Cloning Connectors in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for more information.
4.6 Defining the Connector
Defining a connector is equivalent to registering the connector with Oracle Identity Manager. You can define a customized or reconfigured connector using Oracle Identity System Administration. After you define a connector, a record representing the connector is created in the Oracle Identity Manager database.
A connector is automatically defined when you install it using the Install Connectors feature or when you upgrade it using the Upgrade Connectors feature. You must manually define a connector if:
-
You import the connector by using the Deployment Manager.
-
You customize or reconfigure the connector.
-
You upgrade Oracle Identity Manager.
The following events take place when you define a connector:
-
A record representing the connector is created in the Oracle Identity Manager database. If this record already exists, then it is updated.
-
The status of the newly defined connector is set to Active. In addition, the status of a previously installed release of the same connector automatically is set to Inactive.
See Defining Connectors in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for detailed information about the procedure to define connectors.
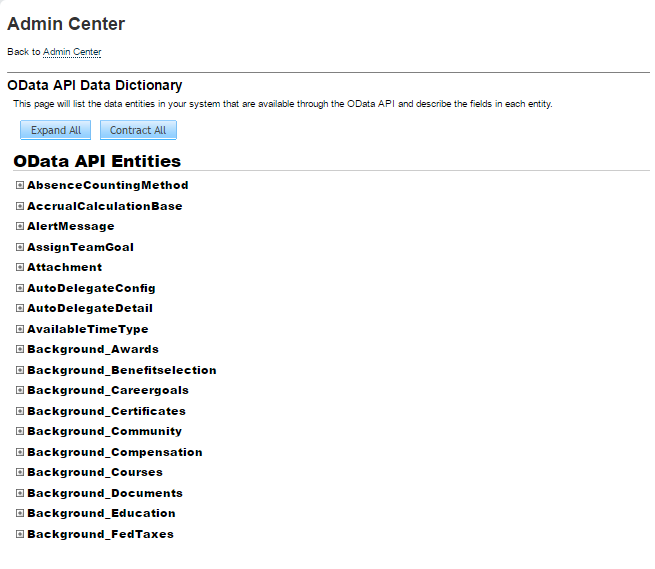
4.7 Understanding OData API Dictionary
The OData API Dictionary component stores a bundle of object entities. Each SuccessFactors instance contains ready-to-use object entities. The object entities in the OData API Dictionary can also be customized as per requirement.
4.7.1 About OData API Dictionary
Every SuccessFactors instance has several object entities. The OData API Dictionary bundles these object entities and presents them in a tabular format. The SuccessFactors object entities contain information such as allowed operations, attributes (also referred to as property name) and labels.
4.7.2 Viewing OData API Dictionary in the SAP SuccessFactors Connector
SAP SuccessFactors provides an option to view existing object entities listed under the OData API Dictionary link.
4.7.3 Adding Custom Attributes and Object Entities in Oracle Identity Manager
SAP SuccessFactors provides a ready-to-use OData API Dictionary. Apart from the ready-to-use object entities present in the OData API Dictionary, if you require a new attribute and a new object entity, then you need to customize the OData API Dictionary. Using the OData API Dictionary component, all customized object entities are mapped to their corresponding attributes in the target system.
-
Firstly in your SuccessFactors instance, you need to search for the custom attribute that is present in the OData API Dictionary. Make a note of the custom attribute and the entity object below which this custom attribute is listed. For more information about customizing the OData API Dictionary, contact SAP SuccessFactors support .
- After obtaining the required information about custom attribute and object entity, you need to add this new attribute to Oracle Identity Manager. This new attribute (with the help of Code key and Decode values) provides a mapping between the custom attribute and the target system.
4.7.4 Providing Values in Static Lookups
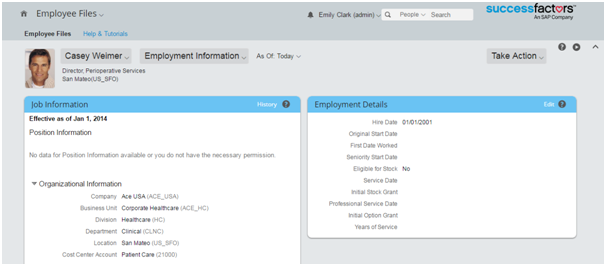
SuccessFactors provides an option to add values to the static lookup definition. Adding values is a requirement to associate code key and decode values in the target system. To add values in the static lookups for SuccessFactors, first you need to check if any code value is present for the attribute under consideration. If a code value is present, then the same needs to be added to the corresponding lookup definition in Oracle Identity Manager.
San Mateo (US_SFO). The US_SFO is the value which needs to be provided as the Code Key and the value San Mateo (US_SFO) or just the name of the location San Mateo as the Decode value for the static Lookup Location. These two values need to be present under Lookup.Location in Oracle Identity Manager Process Form page.
Figure 4-9 Providing Values in a Static Lookup
Description of "Figure 4-9 Providing Values in a Static Lookup"