6 Work with Other Types of Journal Entries
This chapter contains these topics:
In addition to basic journal entries and entries with special formats, you can enter the following journal entries:
-
Entries that will be reversed in the next accounting period
-
Entries where the G/L distribution is based on percentages rather than amounts
-
Entries involving foreign currency
6.1 Entering a Reversing Journal Entry
From General Accounting (G09), choose Journal Entries
From Journal Entry, Reports, & Inquiries (G0911), choose Journal Entry
You can enter journal entries that you want to reverse on the first day of the next G/L accounting period. Reversing journal entries are used most often for periodic accruals. The G/L date of a reversing journal entry is the first day of the next accounting period.
To enter a reversing journal entry
On Journal Entry
-
Follow the steps to enter a basic journal entry.
-
Complete the following field with R:
-
Reverse or Void
The system generates the reversing journal entry when you post the journal entry.
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Reverse or Void (R/V) | A code that controls whether transactions are automatically reversed or voided. Valid codes are:
R – Create automatic reversing entries when the original entries are posted to the general ledger. Date the reversing entries as of the first day of the following period. V – Create reversing entries (reverse the sign on the amount on the original entry) and date them as of the current date. This code is only valid if you are changing an existing transaction. To void a transaction, locate the original entry and change the Void field to V. If the journal entry has not been posted, you can delete the journal entry. Blank – Do not reverse or void transactions. |
6.1.1 What You Should Know About
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Locating reversing journal entries | When you locate an unposted journal entry, the system displays only the original journal entry. Reversing entries do not appear because the system does not create them until you post the original journal entries. After posting the journal entry, you can do the following:
|
| Changing posted journal entries to reversing entries | After you post a journal entry, you cannot change it to a reversing journal entry. To reverse a posted journal entry, do the following:
|
| Voiding reversing journal entries | After you post a reversing journal entry, the system creates the reversing entry on the first day of the following period. To void a reversing journal entry, you must void both the original entry, using a date in one G/L period, and the automatic reversing entry, which is created during the post, using a date in a different G/L period.
See Section 14.3, "Voiding a Posted Reversing Journal Entry" for more information. |
| Posting reversing journal entries to the next fiscal year | If you have 13 or 14 accounting periods, you can control whether or not reversing journal entries should be posted to either of these periods. If you normally have 13 periods, you can select to post reversing journal entries from period 12 to the first period of the next year. If you normally have 14 periods, you can select to post reversing journal entries from period 13 to the first period of the next year. |
See Also:
6.2 Entering a Percent Journal Entry
From General Accounting (G09), choose Journal Entries
From Journal Entry, Reports, & Inquiries (G0911), choose Journal Entry
You can use percentages to distribute the total amount of a journal entry among accounts. This type of journal entry is called a percent journal entry.
To enter a percent journal entry
On Journal Entry
-
Follow the steps to enter the identifiers for a basic journal entry.
-
Access the Amount to Distribute field by pressing F6.
-
Complete the following field:
-
Amount to Distribute
-
-
Follow the steps to enter the G/L distribution for a basic journal entry.
-
Complete the following field with percentage amounts and a debit or credit sign rather than currency amounts:
-
Amount
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Amt to Distribute | A number that identifies the gross amount (amount to be distributed) for a journal entry.
Form-specific information For percent journal entries, the system calculates the detailed amounts to distribute based on percentages entered in the amount fields. |
6.3 Working with Journal Entries with Foreign Currency
From General Accounting (G09), choose Journal Entries
From Journal Entry, Reports, & Inquiries (G0911), choose Journal Entry
You can enter amounts in either a foreign or the domestic currency. Foreign transactions are entered in a currency that is different from the base currency associated with the company. The system converts them to the domestic currency at the time of entry. You can also enter the domestic amount of a foreign transaction and have the system calculate the foreign amount.
Working with journal entries with foreign currency includes:
-
Entering journal entries with foreign currency
-
Locating journal entries with foreign currency
Foreign currency journal entries have two different currency codes:
-
Base Currency Code. The base currency code is the currency code of the company associated with the business unit of the first account number you enter for the journal entry.
-
Transaction Currency Code. The other currency code you might see indicates the foreign amounts originally entered for a transaction. If the transaction currency code is blank, the base currency code applies.
Figure 6-1 Journal Entry (Foreign Currency) screen
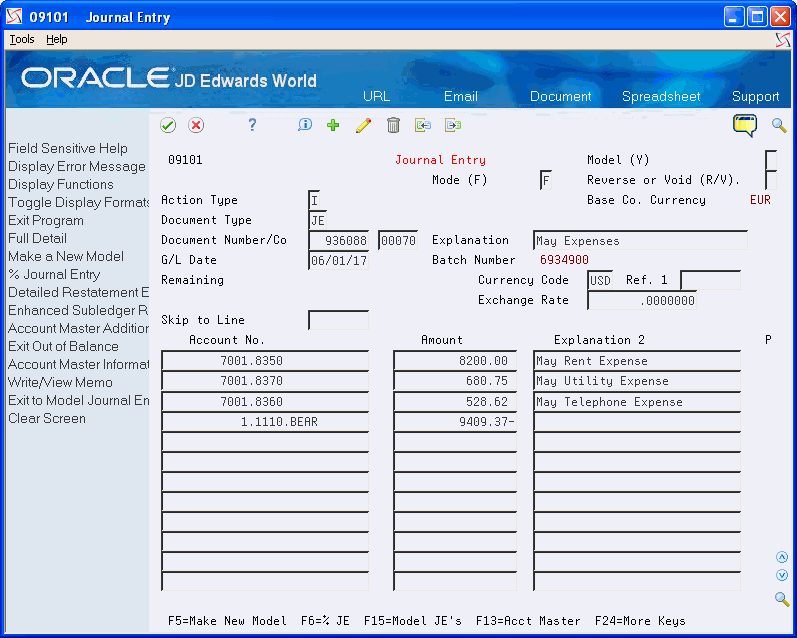
Description of "Figure 6-1 Journal Entry (Foreign Currency) screen"
6.3.1 What You Should Know About
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Ledger types | The system writes foreign transaction amounts to the CA (currency amounts) ledger and domestic amounts to the AA (actual amounts) ledger. If you use detailed currency restatement, it also creates transactions in the XA (detailed restatement amounts) ledger. The ledger type indicates which ledger or set of books is updated by the transaction. |
| Exchange rates | The system uses an exchange rate from the exchange rate table using Set Daily Transaction Rates unless you enter an exchange rate on the Journal Entry form. Do this only to override the rate that is already set up for the currency. |
| Changing journal entries using a different currency | You can set the mode (foreign or domestic) to display a journal entry in a currency other than the currency in which it originated. However, if you then enter changes, you will receive a warning message. If you ignore the message, be aware that:
|
To enter a journal entry with foreign currency
-
Follow the steps to enter a basic journal entry.
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Currency Code
-
Exchange Rate (optional)
-
-
Access the detail area to view the ledger type.
Figure 6-2 Journal Entry (Foreign Currency, Detail) screen
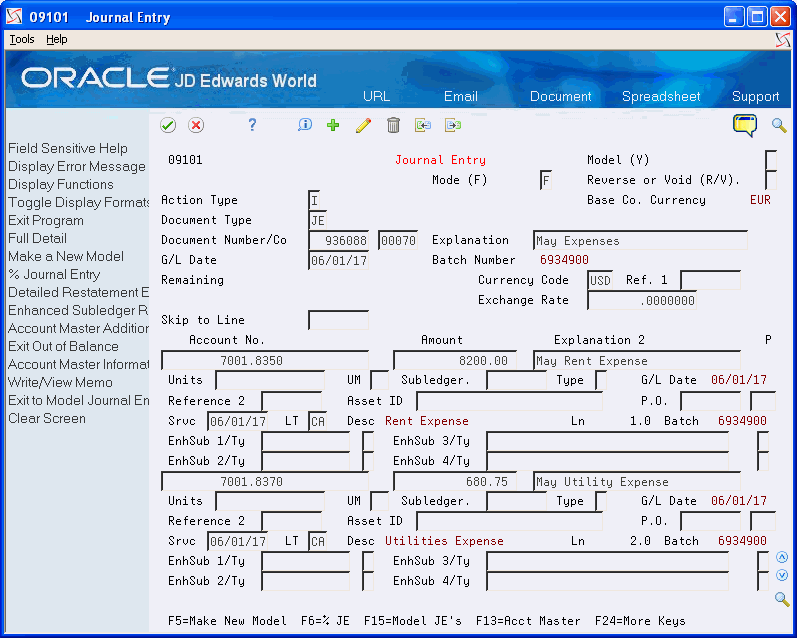
Description of "Figure 6-2 Journal Entry (Foreign Currency, Detail) screen"
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Currency Code | A code specifying the currency of the transaction. This can be any code defined on the Designate Currency Codes form.
Note: This currency field only applies to AA and CA ledger types when posting by currency is activated. Form-specific information If you leave this field blank, the system supplies the company currency code associated with the account number of the first detail line for the journal entry. |
| Exchange Rate | If you are adding a new rate for the multiplier, remove the existing divisor so the system can calculate the new rate.
Form-specific information If you leave this field blank, an exchange rate is supplied from the Exchange Rate table on the Set Daily Transaction Rates form. If you enter a transaction using an alternate currency, you can specify a spot exchange rate for the AA to XA calculation. The spot rate overrides the default exchange rate. |
To locate a journal entry with foreign currency
You can locate journal entries and review the amounts in both the base and the transaction currency.
On Journal Entry
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Document Type
-
Document Number
-
-
Review the following field:
-
Base Company Currency
-
-
Change the following field (optional):
-
Mode
-
-
Access the detail area to review the ledger type for the displayed currency.
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Base Co. Currency | A code that indicates the domestic currency of the company the account is associated with, as defined on the Designate Company Currency form. |
| Mode (F) | A code that specifies whether amounts are in the domestic currency of the company the account is associated with or in the foreign currency of the transaction. Valid codes are
D – Domestic F – Foreign Form-specific information If you enter: F – Foreign amounts appear, and the default ledger type is CA D – Domestic amounts appear, and the default ledger type is AA If you use detailed currency restatement, these codes apply: X – Transactions in the XA ledger Y – Transactions in the YA ledger Z – Transactions in the ZA ledger |