3 Work with Variable Numerator Allocations
This chapter contains these topics:
Variable numerator allocations allow you to redistribute amounts from one or more business units to one or more business units with a common category code. For example, you can distribute an expense based on the number of people in a department.
3.1 Setting Up Variable Numerator Allocations
From General Accounting (G09), choose Allocations
From Allocations (G0923), choose Specify Var/Num Computations
The system calculates variable numerator allocations by computing percentages that are applied to the balance of an account or range of accounts. It then distributes the resulting balances to another account or range of accounts. You can specify accounts by business unit category code instead of by business unit/account range.
The percentages represent fractions of the total of the balances in the accounts that you specify. The balance total is the denominator and the individual account balances are the numerators of the fractions.
The system calculates variable numerator allocations as follows:
-
Gathers balances from a range of accounts (the Based Upon accounts)
-
Computes the percentage of the total for each account balance
-
Applies the appropriate percentage to the balance of an account or range of accounts (the Allocate accounts)
-
Creates journal entries to distribute the resulting amounts to a third range of accounts (the Apply To accounts)
-
Calculates an offset (if needed) to balance the resulting journal entries and distribute it to the contra/clearing account you specify
-
Stores the computation specification in the Variable Allocation table (F0912B).
Setting up variable numerator allocations consists of:
-
Defining a variable numerator allocation
-
Adding an allocation amount
-
Identifying the calculation
-
Identifying the G/L distribution
3.1.1 Example: The Variable Numerator Allocation
In this example, you allocate a year-to-date salary expense amount (12,000) to several business units (BU). You want to base the allocation amount for each business unit on the number of people in the business unit, compared to the total number of people in the department.
Figure 3-1 Variable Numerator Allocation Example
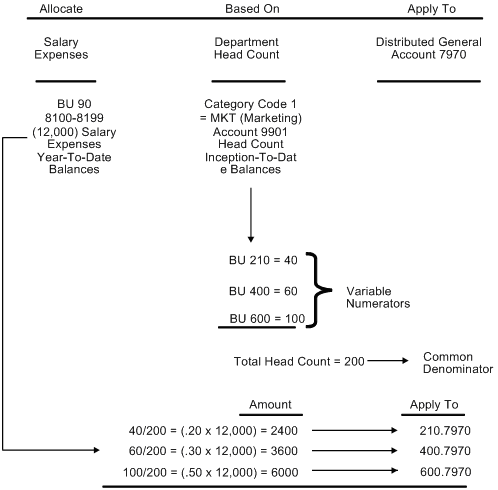
Description of "Figure 3-1 Variable Numerator Allocation Example"
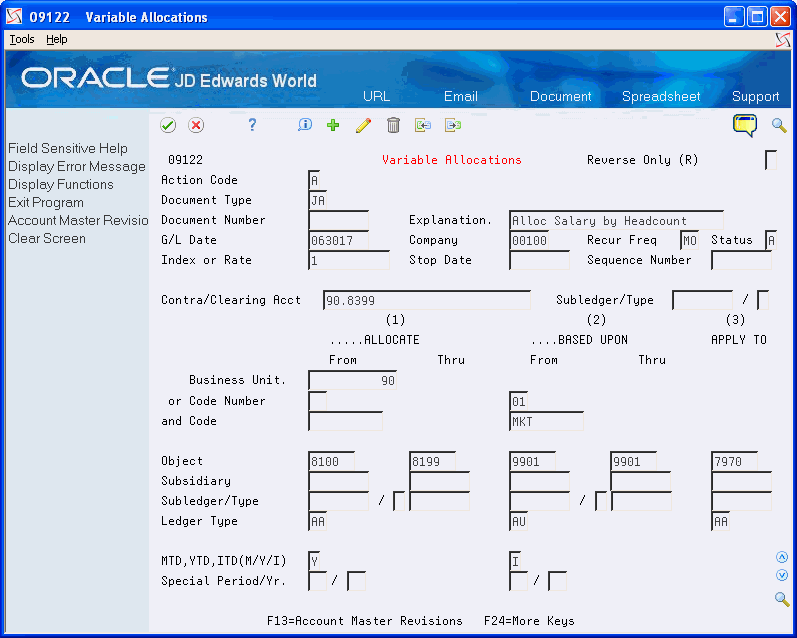
To define a variable numerator allocation
On Specify Var/Num Computations
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Document Type
-
Explanation
-
G/L Date
-
Company
-
Recur Freq
-
-
Complete the following optional fields:
-
Document Number
-
Status
-
Stop Date
-
Sequence Number
-
3.1.2 What You Should Know About
On Specify Var/Num Computations
-
Complete the following field:
-
Index or Rate
-
-
Complete one of the following:
-
From Business Unit
-
or Code Number
-
-
If you completed or Code Number, complete the following field:
-
Code
-
-
Complete the following Allocate fields:
-
From Object
-
Thru Object
-
Ledger Type
-
MTD, YTD, ITD (M/Y/I)
-
-
Complete the following optional Allocate fields:
-
From Subsidiary
-
Thru Subsidiary
-
From Subledger/Type
-
Thru Subledger
-
Special Period/Yr.
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Index or Rate | A number that identifies the index or rate for calculations. The system multiplies the "from" amounts by this factor to calculate the amounts to be distributed. You can specify either positive or negative numbers and eight or fewer decimals. If you specify more than eight decimal positions, the system rounds to eight positions. If you leave this field blank, the default is 1.
If you specify a large whole number and a large number of decimal positions, the system might not be able to display the entire number. Even though all decimal positions cannot be displayed, they are stored (up to eight) correctly in the table. Note: For annual budgets, you can specify zero to remove all balances and start over. |
| From Business Unit | A code that identifies the first business unit in a range of business unit numbers. The system includes only amounts that are posted to accounts in the range.
Form-specific information You can type a specific business unit in this field or leave it blank if you use category codes (the Code Number and Code fields) to define the allocation amounts. |
| Allocate or Code Number | Number from 1 to 30 that identifies a business unit category code. These codes group several business units and allocate the total amount in all of them. For example, 01 could indicate regions.
This field is used in conjunction with the Code field, which identifies a specific value for the business unit category. For example, the value WES for category code 01 could indicate only those business units in the western regions. |
| Allocate From Object | Identifies the beginning object account in a range of accounts. Only amounts posted to accounts in this range are allocated.
Form-specific information To indicate a single object account, you can either specify only the from account or you can specify the same account in both the From and Thru fields. |
| Allocate Thru Object | Identifies the beginning object account in a range of accounts. Only amounts posted to accounts in this range are allocated.
Form-specific information To indicate a single object account, you can either specify only the from account or you can specify the same account in both the From and Thru fields. |
| Allocate From Subsidiary | Identifies the beginning subsidiary account in a range of accounts. The system uses these accounts to determine the basis for the allocation. Only posted amounts in the account range are included. For example, from 00000000 to 99999999.
Form-specific information To indicate a single object account, you can either specify only the from account or you can specify the same account in both the From and Thru fields. |
| Allocate Thru Subsidiary | Identifies the beginning subsidiary account in a range of accounts. The system uses these accounts to determine the basis for the allocation. Only posted amounts in the account range are included. For example, from 00000000 to 99999999.
Form-specific information To indicate a single object account, you can either specify only the from account or you can specify the same account in both the From and Thru fields. |
| Allocate Subledger/Type | Identifies the beginning subledger account in a range of accounts. A subledger provides detailed auxiliary accounting for a general ledger account. When amounts are distributed, only amounts posted to this subledger are included.
Generally, you can type @ (at sign) in this field to specify all subledgers. If you leave this field blank, the system includes only posted transactions for a blank subledger. |
| Allocate From Ledger Type | A user defined code (09/LT) that identifies a ledger type. |
| Allocate From MTD,YTD,ITD(M/Y/I) | A code that controls whether the allocation is based on month-to-date, year-to-date, or inception-to-date amounts. Valid codes are:
M – Month-to-date. The basis is the net posting balance for the month (the fiscal period). Y – Year-to-date. The basis is the period-end balance. For profit and loss accounts, this is the sum of all net postings for the year through the end of the month you specify. For balance sheet account, this is the cumulative balance through the end of the month you specify. I – Inception-to-date. The basis is the cumulative balance through the end of the month you specify. Note: Month-to-date allocations do not include prior month corrections in the allocation base. Year-to-date allocations do include prior month corrections in the allocation base. Inception-to-date allocations include prior month corrections and all postings from prior years. |
| Allocate Special Period/Yr | Special Period - A number that identifies the G/L period to use for based-on amounts. The system uses this field to determine the total amount to allocate for month-to-date allocations. If you allocate month-to-date amounts and leave this field blank, the default is the current period for the company you specified.
Yr – A number that identifies the fiscal year from which the based-on amounts are extracted. If you leave this field blank, the default is the current fiscal year for the company you specified. |
3.1.3 What You Should Know About
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Accounts with subledgers | If you are allocating accounts with subledgers, be sure that you have populated the From Subledger field with an * and the Thru Subledger field with a blank on the Specify Computations screen. The Apply To Subledger field must be blank or hold a specific subledger value. If you are unsure whether the accounts use subledgers, go to the Account Ledger Inquiry (P09200) and inquire on the account with a blank in the Subledger field. Then inquire with an * in the Subledger field. If the amounts change, the account uses subledgers. |
On Specify Var/ Num Computations
-
Complete the following Based Upon fields:
-
From or Code Number
-
Code
-
From Object
-
Thru Object
-
Ledger Type
-
MTD, YTD, ITD
-
Special Period/Yr.
-
-
Complete the following optional Based Upon fields:
-
From Subsidiary
-
Thru Subsidiary
-
From Subledger/Type
-
Thru Subledger
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| or Code Number | Number from 1 to 30 that identifies a business unit category code. These codes group several business units and allocate the total amount in all of them. For example, 01 could indicate regions.
This field is used in conjunction with the Code field, which identifies a specific value for the business unit category. For example, the value WES for category code 01 could indicate only those business units in the western regions. |
| Based Upon Object From | Identifies the beginning object account in a range of accounts.
Form-specific information To indicate a single object account, you can either specify only the from account or you can specify the same account in both the From and Thru fields. |
| Based Upon Object Thru | Identifies the ending object account in a range of accounts.
Form-specific information To indicate a single object account, you can either specify only the from account or you can specify the same account in both the From and Thru fields. |
| Based Upon From Subsidiary | Identifies the beginning subsidiary account in a range of accounts. The system uses these accounts to determine the basis for the allocation. Only posted amounts in the account range are included. For example, from 0000 to 9999.
Form-specific information To indicate a single subsidiary account, you can either specify only the from account or you can specify the same account in both the From and Thru fields. |
| Based Upon Thru Subsidiary | Identifies the ending subsidiary account in a range of accounts. The system uses these accounts to determine the basis for the allocation. Only posted amounts in the account range are included. For example, from 0000 to 9999.
Form-specific information Identifies the beginning subsidiary account in a range of accounts. The system uses these accounts to determine the basis for the allocation. Only posted amounts in the account range are included. For example, from 0000 to 9999. |
| Based Upon Through Subledger | Identifies the ending subledger account in a range of accounts. The system uses this range to determine the amount to allocate.
Generally, you can type @ (at sign) to indicate all subledgers. If you leave this field blank, the system includes only posted transactions for a blank subledger. |
| Based Upon Thru Ledger Type | User defined code (system 09, type LT) that identifies a ledger type. |
| Based Upon MTD,YTD,ITD(M/Y/I) | A code that controls whether the allocation is based on month-to-date, year- to-date, or inception-to-date amounts. Valid codes are:
M – Month-to-date. The basis is the net posting balance for the month (the fiscal period). Y – Year-to-date. The basis is the period-end balance. For profit and loss accounts, this is the sum of all net postings for the year through the end of the month you specify. For balance sheet account, this is the cumulative balance through the end of the month you specify. I – Inception-to-date. The basis is the cumulative balance through the end the of the month you specify. Note: Month-to-date allocations do not include prior month corrections in the allocation base. Year-to-date allocations do include prior month correction in the allocation base. Inception-to-date allocations include prior month corrections and all postings from prior years. |
| Special Period/Yr | Special Period - A number that identifies the period to use for based-on amounts. The system uses this field to determine the total amount to allocate for month-to-date allocations. If you allocate month-to-date amounts and leave this field blank, the default is the current period for the company you specified.
Yr – A number that identifies the fiscal year from which the based-on amounts are extracted. If you leave this field blank, the default is the current fiscal year for the company you specified. |
To identify the G/L distribution
On Specify Var/Num Computations
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Contra/Clearing Account
-
Subledger / Type (optional)
-
-
Complete the following Apply To fields:
-
Object
-
Subsidiary (optional)
-
Subledger (optional)
-
Subledger / Type (optional)
-
Ledger Type
-
-
To add the record, press Enter.
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Contra/Clearing Acct | Identifies an account in the general ledger. You can use one of the following formats for account numbers:
1 – Standard account number (business unit.object.subsidiary or flexible format) 2 – Third G/L number (maximum of 25 digits) 3 – 8-digit short account ID number 4 – Speed code The first character of the account indicates the format of the account number. You define the account format in the General Accounting Constants program (P000909). |
| Subledger Type | A user defined code (00/ST) that identifies the category of subledger. The subledger type is used with the Subledger field. |
| Apply To Object Account | A number that identifies the object account to which amounts are to be posted. The Subsidiary Account, Based Upon Business Unit, Apply To Object Account, Apply To Subledger, Apply To Ledger Type, and Subledger Type for the Contra/Clearing Account form the account for posting the allocation. |
| Apply To Subsidiary | A number that identifies the subsidiary account to which amounts are to be posted. The Subsidiary Account, Based Upon Business Unit, Apply To Object Account, Apply To Subledger, Apply To Ledger Type, and Subledger Type for the Contra/Clearing Account form the account for posting the allocation.
Form-specific information You can either specify a subsidiary account or type * (asterisk) to post to the same subsidiary account indicated in the "based upon" field, even though the object in the "apply to" field is different. |
| Apply To Subledger | A number that identifies the subledger account to which amounts are to be posted. The Subsidiary Account, Based Upon Business Unit, Apply To Object Account, Apply To Subledger, Apply To Ledger Type, and Subledger Type for the Contra/Clearing Account form the account for posting the allocation. |
| Apply To Ledger Type | A number that identifies the ledger type to which amounts are to be posted. The Subsidiary Account, Based Upon Business Unit, Apply To Object Account, Apply To Subledger, Apply To Ledger Type, and Subledger Type for the Contra/Clearing Account form the account for posting the allocation. |
3.2 Reviewing Variable Numerator Allocations
From General Accounting (G09), choose Allocations
From Allocations (G0923), choose Allocations Review under Variable Numerator Allocations
You should review how you set up the allocation before the system calculates the allocation.
When you review variable numerator allocations, the system displays information from the Variable Numerator Allocation table (F0912B).
To review a variable numerator allocation
-
Do one of the following:
-
Display all allocations
-
To display specific allocations, complete any of the following fields:
-
Document Type
-
Document Number
-
Explanation
-
(ST) Status
-
(Co) Company
-
Fq (Frequency)
-
G/L Date
-
User ID
-
-
-
Choose Entry to view the original computation.
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Explanation | A description, remark, explanation, name, or address.
Form-specific information This text describes the allocation. It appears in the first of two description lines for each journal entry that the allocation creates. Type the entire text or the first few characters of the text followed by an (*) asterisk. For example, 1998 budget* shows all allocations that begin with the text "1998 budget." |
| User ID | The IBM-defined user profile. |
3.3 Calculating Variable Numerator Allocations
From General Accounting (G09), choose Allocations
From Allocations (G0923), choose Compute Variable Numerator Allocations
After you review the variable numerator allocations and determine that they are correct, the system can calculate them.
Run the Compute Variable Numerator Allocations DREAM Writer program to process allocations and print an allocations journal report.
Run this program in proof mode to review the report and determine whether to change any information. Run the program in final mode to:
-
Print the report.
-
Create journal entries in the Account Ledger table (F0911).
-
Update the allocation for subsequent processing.
-
Update balances in the Account Balances table (F0902) for ledger types other than AA.
When you run this program in final mode, the system increments the G/L date according to the recurring frequency in the allocation. This ensures that the allocation is ready for future processing. JD Edwards World recommends that you create different versions of this program for recurring frequencies, specific companies, and specific document types. This lets you include specific groups of allocations.
After you run this program in final mode, review and post the journal entries.
The following information appears on the report:
-
Total amount to allocate
-
Amounts on which the allocation is based
-
Amounts that are allocated
-
Contra/clearing account
The following amounts can be reviewed on the report:
-
Total amount to allocate is next to the Total To Be Allocated
-
Amounts under the Basis Amount column are the numerators or the amounts on which the calculation is based
-
Amount next to the Basis Total is the denominator in the calculation
-
Results of the calculation are under the Allocation Amount at the bottom of the report
This report also lists detailed allocation information and errors, such as invalid accounts and PBCO (posted before cutoff).
3.3.1 Before You Begin
-
Before you run a version with multi-tiered calculations, verify that the sequence numbers on Specify Variable Numerator Computations are correct.
-
To create multi-tiered allocations, you must have the following set-up in the Compute program (Indexed Allocations (P093021), Cost Allocations (P09302), or Variable Numerator Allocations (P093022):
-
Processing Options - Ensure that Processing Option #3 (Multi-tiered Processing) has a value of 'R'.
-
Data Selection - Ensure your data selection has Document (GLDOC) EQ *VALUE, where the values include all document numbers for the multi-tiered documents that are dependent on each other.
-
-
Figure 3-4 Variable Numerator Calculation Example

Description of "Figure 3-4 Variable Numerator Calculation Example"
3.3.2 What You Should Know About
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Header information | If the word PRELIMINARY appears at the top of the report, the report was run in proof mode. |
| Standard abbreviated column headings | The report contains the following abbreviated column headings:
|
| Invalid accounts | The report lists invalid accounts with *** (asterisks). |
| Revising or deleting a journal entry | You can revise or void a posted or unposted journal entry that was created by the Compute Variable Numerator Allocations program.
See Working with Basic Journal Entries in the JD Edwards World General Accounting I Guide |
See Also:
-
Reviewing and Posting Allocations (P00201)