Administrative Web Guard Prototype
This section provides an example of a safe web browsing prototype that isolates a web server and its web content to prevent attacks from the Internet. This Web Guard prototype takes advantage of administrative trusted networking features to configure a two-stage filter that restricts access to a protected web server and web content. This prototype was implemented solely by administrative means. No programming was required.
The following figure shows the configuration of the Web Guard prototype in a multilevel environment. The label relationships are shown by how the labels are positioned in the figure. Vertical relationships represent label dominance, while horizontal relationships represent disjoint labels.
Figure 7-1 Web Guard Configuration
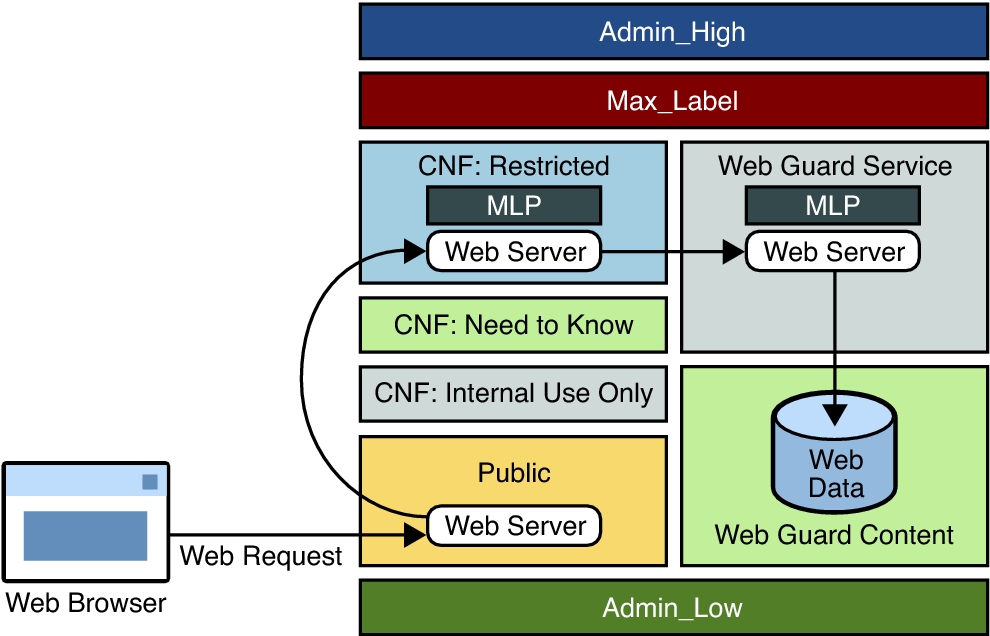
Web requests come in to the web server that is configured in the public zone and are passed to the web server that is configured in the restricted zone.
The restricted zone uses a multilevel port (MLP) to listen for requests at port 8080 of the public zone. This web server passes the requests to the webservice labeled zone.
The webservice zone also uses an MLP to listen for requests at port 80 of the restricted zone and reads content from the webcontent labeled zone.
The webcontent zone is in the ready state and has its web content stored in the /export/home file system, which is automatically mounted in all other labeled zones. When a zone is in the ready state, no processes run in that zone. Thus, the zone is essentially a disk drive attached directly to the webservice zone.
Modifying the label_encodings file to configure the labels in your safe web browsing environment
The default label_encodings file is updated to configure two new labels: WEB GUARD SERVICE and WEB GUARD CONTENT. See Modifying the label_encodings File.
Configuring trusted networking
The private IP addresses and MLPs are configured on the restricted and webservice labeled zones. See Configuring Trusted Networking.
Configuring the Apache web servers
The public, restricted, and webservice zones all have web servers configured. In this example, the web server used is Apache. See Configuring the Apache Web Servers.
You configure the Web Guard prototype by performing these high-level tasks: