How Is Auditing Configured?
During system configuration, you preselect which classes of audit records to monitor. You can also fine-tune the degree of auditing that is done for individual users. The following figure shows details of the flow of auditing in Oracle Solaris.
Figure 1 Flow of Auditing
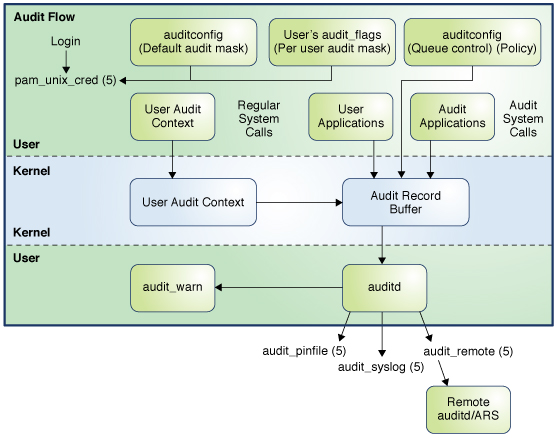
You use the auditconfig command to specify the audit parameters for your system. In addition, you can modify the audit flags to preselect which audit classes are to be audited for a process.
The audit service, auditd, tracks auditable actions that occur on a system. See Audit Service and the auditd(8) man page.
-
The audit_binfile plugin places binary audit records in /var/audit. By default, the audit_binfile plugin is active. Post-selection tools enable you to examine interesting parts of the audit trail.
Audit files can be stored in one or more ZFS pools. The collection of audit files that are linked together is considered an audit trail.
-
The audit_remote plugin sends binary audit records across a protected link to a remote audit service that is running an audit remote server (ARS). Records received by the remote server can only be sent to a local binary file. See Managing the Audit Remote Server.
-
The audit_syslog plugin sends text summaries of audit records to the syslog utility.
After audit data is collected in the kernel, plugins distribute the data to the appropriate locations.
Note - In addition to forwarding audit data to the plugins as described in this section, by default, audit records in the sstore meta-class are automatically forwarded to the Oracle Solaris StatsStore. For more information, see sstore Audit Meta-Class.
Systems that install non-global zones can audit all zones identically from the global zone. These systems can also be configured to collect different records in the non-global zones. For more information, see Auditing on a System With Oracle Solaris Zones.