The Oracle VM management server must run one of the following operating systems:
Oracle Linux 5 Update 5 64-bit or later.
Oracle Linux 6 64-bit or later.
A default Oracle Linux installation has the firewall enabled
(iptables on). It is recommended to leave all
ports closed except the ones required by
Oracle VM Manager.
The required ports are:
For inbound web browser connection: TCP/7002 (HTTPS, default).
For inbound connection from Oracle VM Servers: TCP/7002 (HTTPS, default), UDP/123 (NTP).
For optional remote access to the legacy API: TCP/54322 (Secure TCP over SSL).
For outbound connection to Oracle VM Servers: TCP/8899 (Oracle VM Agent), TCP/6900-xxxx (VNC, 1 secure tunnel per virtual machine).
For SSH access: TCP/22 (likely open by default).
For CLI access using SSH: TCP/10000.
The Oracle VM Manager Command Line Interface (CLI) is part of Oracle VM as of Release 3.2.
As part of the installation procedure, a script is included
named createOracle.sh. You can run this
script to perform a number of installation tasks in an automated
way, including the standard firewall configuration. Note that if
iptables has been disabled on the target host prior to the
installation of Oracle VM Manager, this script does not automatically
re-enable the iptables service. For the rules to take effect,
you must ensure that the iptables service is enabled and
running.
If you prefer or need to configure the firewall manually, follow these instructions.
Open the required ports in iptables as follows:
Log on to the Oracle VM management server as the
rootuser.At the command prompt, enter the appropriate command for each port to be opened; for example:
# iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 7002 -j ACCEPT # iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m udp -p udp --dport 123 -j ACCEPT # iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 54322 -j ACCEPT
Save the
iptablesconfiguration.# service iptables save
This does not require
iptablesto be restarted as the commands open the ports whileiptablesis running. The save ensures they are opened on reboot/restart in future.The diagram and table below illustrate the firewall rules and requirements for Oracle VM.
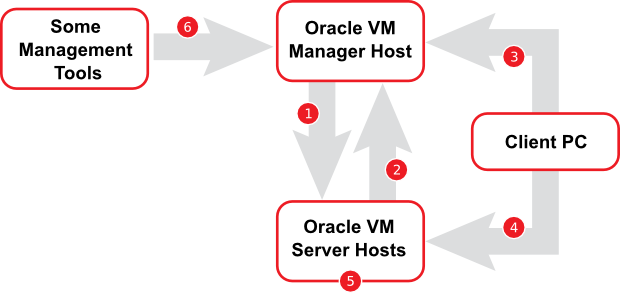
Table 2.1 Firewall Rules
No. Component Relationship Ports and Description Optional 1
Oracle VM Manager to Oracle VM Server
TCP/8899 - HTTPS connection to the Oracle VM Agent.
TCP/6900-xxxx - SSL secured VNC connections to connect to the VNC Console for virtual machines running on each Oracle VM Server.
TCP/10000-xxxx - SSL secured port for telnet emulated serial connections to connect to the Serial Console for virtual machines running on each Oracle VM Server.
No 2
Oracle VM Server to Oracle VM Manager
TCP/7002 - HTTPS connection from Oracle VM Agent to the Oracle VM Core WSAPI.
UDP/123 - NTP requests to an NTP server running on the Oracle VM Manager host.
No
3
Client PC to Oracle VM Manager
TCP/7002 - HTTPS connection from web browser to Oracle VM Manager web user interface, or WSAPI.
TCP/10000 - SSH connection from SSH client to Oracle VM Manager CLI.
TCP/22 - SSH connection to Oracle VM Manager host for administrative work.
No, although access to services should be limited to requirements
4
Client PC to Oracle VM Server
TCP/22 - SSH connection to Dom0 on each Oracle VM Server for administrative work.
Yes
5
Oracle VM Server to Oracle VM Server
TCP/7777 - OCFS2 heartbeat communication for clustered server pools.
TCP/8002 - non-encrypted port to perform live virtual machine migrations.
TCP/8003 - SSL-encrypted port to perform live virtual machine migrations.
No
6
Some Management Tools to Oracle VM Manager
TCP/54322 - Access to the legacy API as required by some applications that have not yet been updated to use the WSAPI.
Yes