54.10 Managing Global Agent Settings
Global Agent Settings determine single sign-on behavior when users encounter password-protected applications. With these settings you specify what the user sees and is allowed to do when navigating to an application.
The next sections describe how to create new sets of Global Agent Settings or edit existing sets. You can use existing sets created in the the Access Portal Service, or import preconfigured settings in the format of INI files. After you create a set, the process for configuring it is the same as that for editing an existing one.
54.10.1 Searching for Sets of Global Agent Settings
You can search for an existing set of Global Agent Settings.
To search:
- Click Federation at the top of the Administrative Console, then click Global Agent Settings in the Access Portal Service section.
- Enter a name or partial string in the Name field, and click the Search button. The results appear in the Search Results table.
- Click on any group in the Search Results list to edit its configuration. Continue to step 3 in Creating a Set of Global Agent Settings to learn more about configuring these settings.
Figure 54-8 Global Agent Settings Search tab
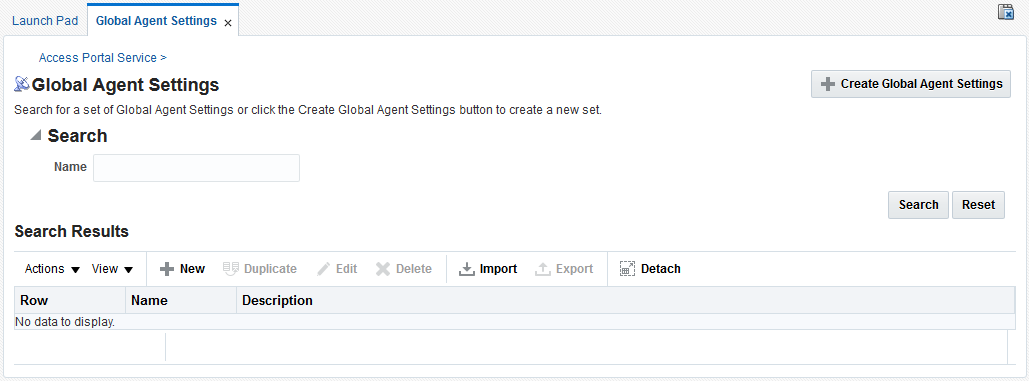
Description of "Figure 54-8 Global Agent Settings Search tab"
54.10.2 Importing an INI File with a Global Agent Settings Configuration
You can import an INI file (unicode format only) with a Global Agent Settings Configuration.
To import:
54.10.3 Creating a Set of Global Agent Settings
You can create a new set of global agent settings configuration.
To create:
Figure 54-9 New Global Agent Settings Page
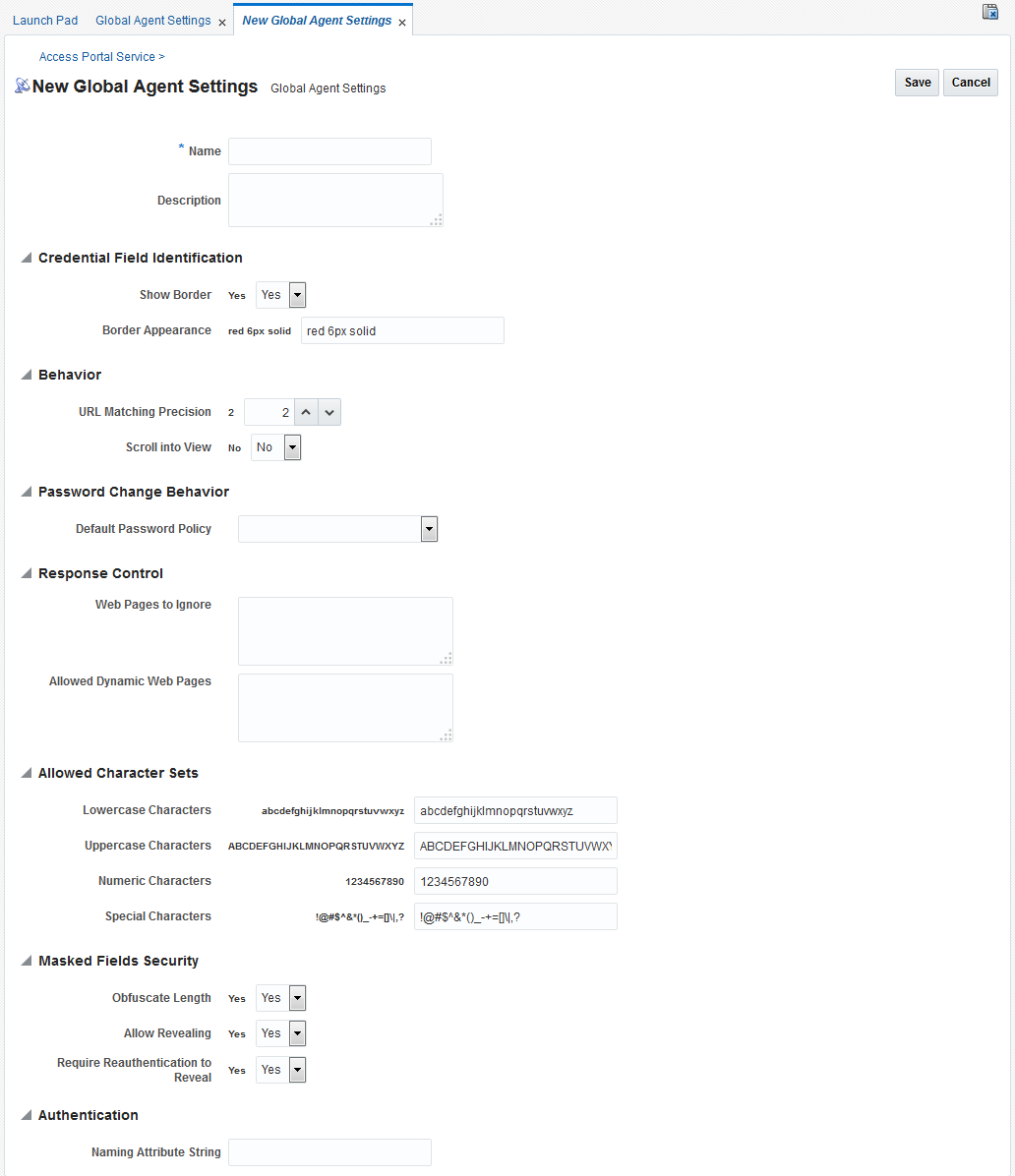
Description of "Figure 54-9 New Global Agent Settings Page"
