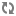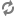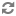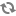You can run Eneperf in a two-stream mode using two streams of request logs — regular query request logs and logs that contain partial update requests. This lets you test MDEX Engine performance with partial updates applied at regular intervals while running a regular query load.
To run Eneperf in the two-stream mode, use the following Eneperf settings together:
When used in this mode, Eneperf sends update requests from the updates log at regular intervals while sending queries from the query log.
In more detail, Eneperf runs in the following way:
It uses the log file (specified with
--log) and sends requests from this file for the duration that you specify by the--msec-between-updatessetting.At the specified time interval, it sends an update request from the updates log file (specified with
--updates-log) and uses one of its connections for this request.It continues to send query requests from the query log (
--log), using the other connections.Note
This behavior assumes that you are running Eneperf with the number of connections set to more than one. If you use only one connection, Eneperf will switch between update and regular query requests.
This process continues until either the regular query log or the updates log has been completely processed. For example:
If Eneperf sends the last update request from the updates log, but the query log still contains queries, Eneperf will send additional queries for the time interval specified with
--msec-between-updatesand then stop. (Since the two-stream mode is designed specifically to test updates performance, Eneperf does not process regular queries after the last update in the updates log has been processed.)If Eneperf sends the last query from the regular log, but the updates log still contains additional update requests, it will not send these updates to the Dgraph. Therefore, ensure that the regular query log contains sufficient number of requests to last for the duration of your two-stream Eneperf testing session.
The format of the updates request log is the same as the format of a
regular query log for Eneperf, except that the updates log should contain only
config?op=update operations in order to provide
meaningful performance results. (If your updates log contains regular queries,
Eneperf still processes this log successfully. However, the results are not
meaningful for measuring updates performance.)
Using
--updates-log and
--log settings is useful to measure performance of those
updates that run at regular intervals. To test updates that run at random
times, you can continue using your regular log with Eneperf.
Note
The actual time interval between sending update requests may be
equal to or greater than the time specified with
--msec-between-updates. This is because Eneperf uses
the same
num connections setting while processing the regular
query log and updates log. This causes Eneperf to wait for a preceding request
to complete before it can process the next updates log request.
Before running Eneperf in the two-stream mode, you need to create a
separate log that contains only partial update requests. You should create such
a log with several partial update requests pointing to a single update file
using the
admin?op=update&updatefile=filename command. For
more information on running partial updates on a single file, see the
Partial Updates Guide.
Note
The
--msec-between-updates flag is optional. In other
words, if you only specify the
--updates-log flag, the updates are sent to the Dgraph
one after another. Eneperf waits for the current update to finish and
immediately sends another update. It does not wait for any period of time
between sending individual updates to the Dgraph.