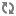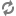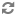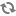Record adapters read and write record data. A record adapter describes where the data is located (or will be saved to), the format, and various aspects of processing.
Forge can read source data from a variety of file formats and source systems. Each data source needs a corresponding input record adapter describing the particulars of that source. Based on this information, Forge parses the data and turns it into Endeca records. Input record adapters automatically decompress source data that is compressed in the gzip format.
Note
Output record adapters are generally used for diagnostic purposes. Hence, this section focuses on input record adapters. See Writing out record data for more information on output record adapters.
To add an input record adapter to your pipeline:
In the Pipeline Diagram editor, choose → → .
The Record Adapter editor appears.
In the Name text box, type a unique name for this record adapter.
In the General tab, do the following:
In the Format list, choose one of the following: XML, binary, fixed-width, delimited, vertical, document, JDBC adapter, Exchange, ODBC (Windows only), or custom adapter (available only by request from Oracle).
In the Delimiters frame, if the format is delimited, add row and column delimiters. If the format is vertical, add row, column, and record delimiters.
(Optional) In the Encoding text box, define the encoding of the input data. If Encoding is not set, it is assumed to be Latin-1.
Note
This setting is ignored by the XML format, because the encoding is specified in the XML header. It is also ignored for binary format because Forge detects the binary format's encoding automatically. The Document format also ignores the Encoding setting.
If any of the text boxes in the Java properties frame are made available by your format selection, type in the required information.
(Optional) Check Require Data if you want Forge to exit with an error if the URL does not exist or is empty.
(Optional) Check Filter empty properties. Keep in mind that this attribute applies only to input record adapters and is valid only for the Vertical, Delimited, Fixed-width, and ODBC input formats.
Note
If it is not checked, by default the adapter assigns the property a value of " " (an empty string) if a record has no value for a given property.
(Optional) Check Multi File if Forge can read data from more than one input file.
Note
The URL will be treated as a wildcard and all matching files will be read in alphabetical order.
Check Maintain State if you are using the Endeca Application Controller (EAC) environment.
Note
This setting specifies that the records are output in the directory structure the EAC requires.
(Optional) Check Custom Compression Level if your input file is compressed to indicate to Forge that it must decompress data from this source.
Note
The compression level setting is ignored for an input record adapter. Compression of input files is detected automatically.
Ignore the Sources tab. Its settings are not used by an input record adapter.
If you are using XSLT to transform your XML into Endeca-compatible XML, in the Transformer tab, specify the type (XSLT) and the location of the stylesheet.
If your format is ODBC, fixed-width, delimited, JDBC, custom, or Exchange, in the Pass Through tab, enter the necessary information.
(Optional) In the Comment tab, add a comment for the component.
The Record Adapter editor contains a unique name for this record adapter.
The Record Adapter editor contains the following tabs:
The General tab contains the following options:
The Sources tab contains the following options:
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Record source |
A choice of the record servers in the project. Used for output record adapters only. |
|
Dimension source |
A choice of the dimension adapters and dimension servers in the project. Generally used for output record adapters only. Input record adapters only require a dimension source if they implement a record index that includes dimensions. |
Optional. The Record Index tab allows you to add or remove dimensions or properties used in a component's record index, and to change their order. Record indexes support join functionality. See Join sources must have matching join keys and record indexes for more details.
The Record Index tab contains the following fields:
The Transformer tab is for the XML format. XML adapters assume that data is in the Endeca Record XML format and, without transformation, other XML formats cannot be read by the Data Foundry. To support these situations, an XSLT transformation can be applied to the source data to convert it into Endeca Records XML, which the Data Foundry can read.
The Transformer tab has the following options:
The Pass Throughs tab is used with certain formats to pass additional information to Forge. It contains text boxes where you can add, modify, or delete key/value pairs. Pass throughs are required for ODBC, fixed-width, delimited, JDBC, custom, or Exchange adapters.
The account under which Forge runs must have appropriate permissions to access source data.
If Forge does not have the appropriate permissions, one of two things will happen when a record adapter requests data from a source:
If Require Data, which is located on the record adapter's General tab, is checked, then Forge will exit immediately with an error. The error is sent to wherever logging is configured to send errors, typically to the console or stderr.
If Require Data is not checked, Forge will continue with the next task in the pipeline without reading any data from the offending source. Forge will not exit with a failure code.
Forge can read source data from a variety of file formats.
The Delimited format reads source records that are organized into rows and columns.
Each row is separated from other rows by a row delimiter character, such as the new-line character, and each column is separated from other columns by a column delimiter character, such as a comma or the tab character. The row and column delimiters must not be present within the data itself. For example, if the column delimiter is a comma, no data in a column can contain a comma.
When the source records are read into the Data Foundry, two mappings occur:
The column names are mapped to Endeca properties. The record adapter assumes that the first row of the file is a header row, which specifies column names separated by the column delimiter. If the first row of the data is not a header row, the column names must be specified on the Pass Throughs tab of the Record Adapter editor.
The rest of the rows are assumed to contain data and are mapped to Endeca records. These additional rows must have the same number of column delimiters.
Properties are trimmed as they are read in. White space on the ends of properties (including the space, tab, new-line, and other characters) is removed. However, white space within a property is preserved.
The records in a delimited file must have identical properties, in terms of number and type, although it is possible for a record to have a null value for a property. You can use the "Filter empty properties" checkbox, on the Record Adapter editor's General tab, to tell the record adapter to ignore properties that have null values.
Note
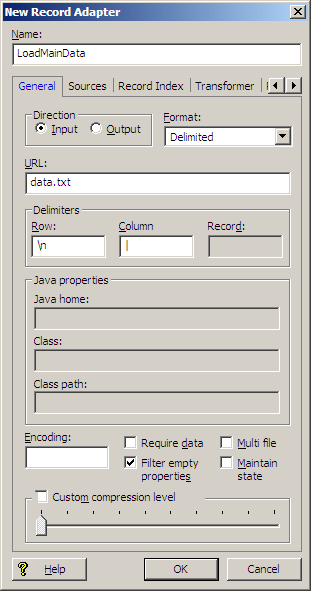
This Delimited format illustration uses the pipe ('|') character as the column delimiter. The column names in the header row are mapped to Endeca properties.
The record adapter for this delimited file looks like this:
If the first row of the data is not the header row, you must use the Record Adapter editor's Pass Throughs tab to specify the column names, as in this example:
The Name field must be HEADER_ROW and the Value field must contain the column names separated by the column delimiter.
If a delimited file contains new-line delimiters, the delimiter must be specified exactly or unpredictable results may occur. For example, on UNIX systems, the new line is generally a "\n", while on Windows systems, the new line is a "\r\n" combination.
If a delimited file contains non-standard delimiters, the file may look different than expected. For example, if a delimited format file has "~" as a row delimiter, the data will be entirely on one line (unless new lines appear within the data). Because delimited files typically have one record per row, the file will appear to have a single record or to be corrupt. In fact, files in this format are valid.
The fixed width format reads source data records from columns of fixed widths.
Each column represents a property and has a width that is a specific number of characters. For example, the first three characters could represent an ID, characters 4 through 10 could represent a name, and so forth. Each row represents a record.
Note
The new-line character at the end of each row is treated identically to the other characters in the row. For example, if you have a row of 100 characters with a new-line character at the end, the total number of characters for the row is 101. Also, the character count is zero-based. For example, the first four characters in a row are characters 0 to 3.
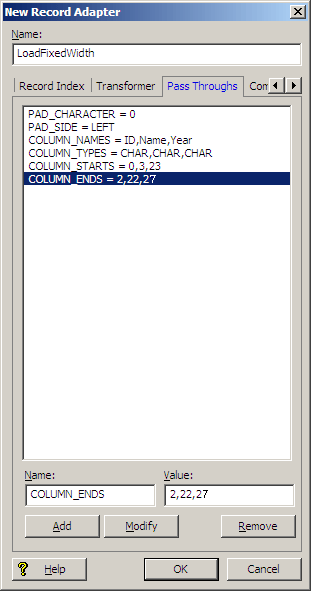
The fixed width record adapter requires the following six attributes, which are specified on the Pass Throughs tab. The names of the attributes must be entered as shown:
PAD_CHARACTER ― The character used to pad columns to the appropriate width (typically, the value is the digit '0').
PAD_SIDE ― The side on which each column is padded. LEFT or RIGHT are the only valid values.
COLUMN_NAMES ― The names of each of the columns, separated by commas.
COLUMN_TYPES ― The data type used to encode each column, separated by commas. CHAR or INT are the only valid values. The INT type should only be used for data that is encoded as native-endian 4-byte integers. All other data must be in the specified character encoding and should have a column type of CHAR (CHAR refers to bytes, not unicode characters).
COLUMN_STARTS ― The byte numbers that start each column of data. The index starts at zero.
COLUMN_ENDS ― The byte numbers that end each column of data. The index starts at zero.
The vertical format reads source records stored as property name/value pairs.
Vertical format requires delimiters specifying how to identify each property name, property value, and record. These delimiters are defined in the General tab of the Record Adapter editor:
Column: The delimiter between the name and value, typically an equal sign, comma, or tab.
Row: The delimiter between adjacent name/value pairs. Typically the row delimiter is a new-line character (causing the format to appear vertical). The row delimiter defaults to a new-line character if omitted.
Record: The delimiter between adjacent records. Typically it is the text REC or EOR. The record delimiter must be surrounded by Row delimiters in the source data (it identifies a special name/value pair that does not have the Column delimiter).
All name/value pairs leading up to a record delimiter are considered part of a single record. The properties for the records in a vertical file format can be of a variable number and type.
Properties are trimmed as they are read in. White space (such as the space, tab, and new-line characters) is removed from both ends of properties, but white space within a property is preserved.
Note
Example 1. Vertical example
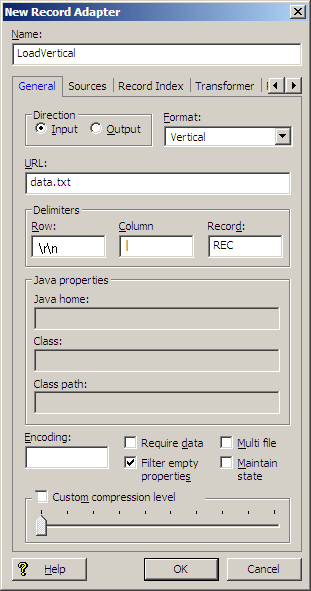
This Vertical format illustration uses the pipe character as the Column delimiter and 'REC' as the Record delimiter. The Property names (such as "WineID") are mapped to Endeca Properties. Note that the second record (WineID 347000) has seven properties while the first only has five:
You would define the record adapter for this Vertical format in Developer Studio as follows:
If a vertical file contains new-line delimiters, the delimiter must be specified exactly or unpredictable results may occur. For example, on UNIX systems, the new line is generally a "\n", while on Windows systems, the new line is a "\r\n" combination.
In vertical format, the record delimiter must be surrounded by row delimiters (which are usually new lines).
If a vertical file contains non-standard delimiters, the file may look different than expected. For example, if a vertical file has "~" as a row delimiter, instead of a new-line delimiter, the data for each record will be entirely on one line (unless new lines appear within the data itself). Because vertical files typically have one property per row, the file will appear to be corrupt. In fact, files in this format are valid.
The ODBC format enables the Endeca Information Transformation Layer (ITL) to connect directly to and read records from any database that supports ODBC connections.
The ODBC format is supported only on the Windows version of Oracle Commerce Guided Search. In addition to name, direction, and format, an ODBC record adapter requires settings on the Pass Throughs and General tabs. An ODBC record adapter requires that the following two attributes be specified on the Pass Throughs tab.
If clear text credentials are being used to pass Database credentials:
Value = The data source name, including connection parameters such as username and password.
Value = The SQL query to execute on the ODBC data source. Note that stored procedures can be executed; however, the stored procedures must return tables (i.e., stored procedures that return cursors are not supported).
If Oracle Credentials Store is being used to pass Database credentials:
Value = The data source name, without any username and password.
Value = The SQLquery toexecuteonthe ODBC datasource. Note that stored procedures can be executed; however, the stored procedures must return tables (that is, stored procedures that return cursors are not supported).
Value = The key name required to access the credentials information from Oracle Credentials Store
Note
For more information about the Oracle Credentials Store, refer to Oracle Commerce Guide Search Security Guide.
The names and types of properties are determined automatically from the results of the ODBC query.
Optionally, you may also specify the encoding of character data being returned from the ODBC data source, using the Encoding field of the General tab.
The following illustration shows the Pass Throughs tab of the Record Adapter editor for an ODBC data source:
Pass Through elements named "DSN" and "SQL" have been defined.
The DSN element is:
Northwind;username=Leonardo;password=davinci
For using Oracle Credentials Store:
Note
Different databases use different syntax for specifying the username and password. For example, some databases use "UID" rather than "username," and "PWD" rather than "password." If "username" and "password" don't work for your data source, see the documentation for your data source to determine the correct syntax.
The SQL query is:
SELECT CustomerID, CompanyName FROM Customers
The following table provides information on supported data types for the ODBC record adapter:
|
Data type |
Supported |
|---|---|
|
CHAR |
Up to 1M bytes. Note that if a field in the result set is larger than 1MB (1,048,576 bytes), then the result is truncated at that length. |
|
VARCHAR |
Up to 1M bytes |
|
LONGVARCHAR (CLOB) |
No |
|
WCHAR |
Up to 1M bytes |
|
VARWCHAR |
Up to 1M bytes |
|
LONGWVARCHAR |
No |
|
DECIMAL |
Yes |
|
NUMERIC |
Yes |
|
SMALLINT |
Yes |
|
INTEGER |
Yes |
|
REAL |
Yes |
|
FLOAT |
Yes |
|
DOUBLE |
Yes |
|
BIT |
Yes |
|
TINYINT |
Yes |
|
BIGINT |
No |
|
BINARY |
No |
|
VARBINARY |
No |
|
LONGVARBINARY (BLOB) |
No |
|
DATE |
Yes |
|
TIME |
Yes |
|
TIMESTAMP |
Yes |
|
UTCDATETIME |
No |
|
UTCTIME |
No |
|
INTERVAL MONTH |
No |
|
INTERVAL YEAR |
No |
|
INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH |
No |
|
INTERVAL DAY |
No |
|
INTERVAL HOUR |
No |
|
INTERVAL MINUTE |
No |
|
INTERVAL SECOND |
No |
|
INTERVAL DAY TO HOUR |
No |
|
INTERVAL DAY TO MINUTE |
No |
|
INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND |
No |
|
INTERVAL HOUR TO MINUTE |
No |
|
INTERVAL HOUR TO SECOND |
No |
|
INTERVAL MINUTE TO SECOND |
No |
|
GUID |
Yes |
The JDBC format enables the Endeca Information Transformation Layer (ITL) to connect to and read records from any JDBC data source.
In addition to name, direction, and format, a JDBC record adapter requires settings on the General and Pass Throughs tabs.
Class path - The location of the .jar file containing the JDBC driver. If the JDBC driver you are using is distributed with the JVM, you can omit this setting (for example, the jdbc-odbc bridge does not require a classpath).
Note
When running your pipeline through Forge, you can override the Java home and Class path settings using command-line options. See Overriding Java home and class path settings.
Value = The name of the JDBC driver class to use.
Value = The URL of the data source, in standard JDBC format.
Value = The SQL query to run to extract the data. Note that stored procedures can be executed; however, the stored procedures must return tables (i.e., stored procedures that return cursors are not supported).
In addition, if the connection requires properties (such as a password or username), then the following attribute can also be specified, as many times as necessary, on the Pass Throughs tab:
Note that configuring user name and password parameters varies according to your JDBC driver. For example, with Oracle JDBC Thin drivers, the user name and password parameters are included as part of the DB_URL string rather than as separate DB_CONNECT_PROP values. You may have to refer to the documentation for your JDBC driver type to determine exact configuration requirements.
Instead of specifying clear text credentials, you can use Oracle Credentials Store to specify the database credentials information. In which case instead of specifying the username and password information along with DB_URL or DB_CONNECT_PROP, you need to use the passthrough CREDENTIALS_KEY and provide the key name that should be used to retrieve the credentials from Oracle Credentials Store.
• Name = CREDENTIALS_KEY Value = The key name required to access the credentials information from Oracle Credentials Store
Note
For more information on Oracle Credentials Store, please refer to Oracle Commerce Guided Search Security Guide.
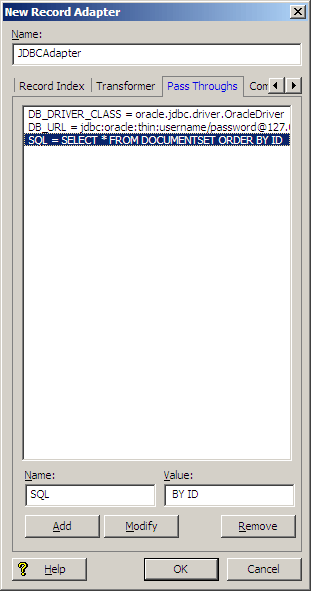
The following illustration shows the Pass Throughs tab for a record adapter that is configured to access a JDBC data source through an Oracle JDBC Thin driver using clear text credentials:
The following illustration shows the Pass Throughs tab for a record adapter that is configured to access a JDBC data source via an Oracle JDBC Thin driver using Oracle Credentials Store:
The following table provides information on supported data types for the JDBC record adapter:
|
Data type |
Supported |
|---|---|
|
CHAR |
Up to 1M bytes. Note that if a field in the result set is larger than 1MB (1,048,576 bytes), then the result is truncated at that length. |
|
VARCHAR |
Up to 1M bytes |
|
LONGVARCHAR (CLOB) |
No |
|
WCHAR |
Up to 1M bytes |
|
VARWCHAR |
Up to 1M bytes |
|
LONGWVARCHAR |
No |
|
DECIMAL |
Yes |
|
NUMERIC |
Yes |
|
SMALLINT |
Yes |
|
INTEGER |
Yes |
|
REAL |
Yes |
|
FLOAT |
Yes |
|
DOUBLE |
Yes |
|
BIT |
Yes |
|
TINYINT |
Yes |
|
BIGINT |
No |
|
BINARY |
No |
|
VARBINARY |
No |
|
LONGVARBINARY (BLOB) |
No |
|
DATE |
Yes |
|
TIME |
Yes |
|
TIMESTAMP |
Yes |
|
UTCDATETIME |
No |
|
UTCTIME |
No |
|
INTERVAL MONTH |
No |
|
INTERVAL YEAR |
No |
|
INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH |
No |
|
INTERVAL DAY |
No |
|
INTERVAL HOUR |
No |
|
INTERVAL MINUTE |
No |
|
INTERVAL SECOND |
No |
|
INTERVAL DAY TO HOUR |
No |
|
INTERVAL DAY TO MINUTE |
No |
|
INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND |
No |
|
INTERVAL HOUR TO MINUTE |
No |
|
INTERVAL HOUR TO SECOND |
No |
|
INTERVAL MINUTE TO SECOND |
No |
|
GUID |
Yes |
The Exchange format allows the Endeca Information Transformation Layer (ITL) to connect to one or more Microsoft Exchange Servers (versions 2000 and beyond) and extract information from specified public folders.
The Exchange format produces one record for each document and each sub-folder contained in the specified public folders. This includes mail messages, calendar items, and generic documents of any format.
In addition to name, direction, and format, the Exchange adapter requires the following attributes on the General and Pass Throughs tabs:
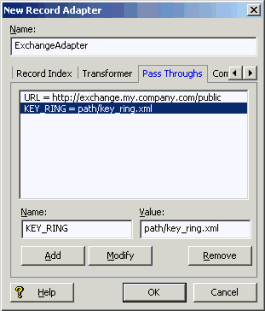
If any of the specified Exchange servers require authentication, a reference to a key ring file containing a suitable username/password key combination must be specified. You provide this information using an additional Pass Through element with the name "KEY_RING" and a value that specifies the path to the key ring file. This path may be absolute or relative to the Pipeline.epx file. For each Exchange server that requires authentication, the key ring file should contain an element of the form:
<EXCHANGE_SERVER HOST="exchange.myhost.com"> <KEY>B9qtQOON6skNTFTHm9rnn04=</KEY> </EXCHANGE_SERVER>
See "Implementing the Endeca Crawler" in the Endeca Forge Guide for more information on how to edit a key ring file and encrypt keys.
The Pass Throughs tab for an Exchange adapter looks similar to this:
Mail messages extracted by the Exchange adapter may contain attachments. The attachments themselves are not retrieved, but a URL pointing to them is included as a property of the associated mail message record. This property has the name "Endeca.Exchange.Attachment" and the URL it contains may be used to retrieve the attachment document using a RETRIEVE_URL expression.
A similar situation occurs when the Exchange adapter encounters a
generic document that is not of a format that the Microsoft Exchange Server
recognizes internally. In this situation, the Exchange adapter produces a
record for the document that contains properties containing meta-data about the
document. In addition, the record will have a property named "DAV:a:href" that
specifies a URL that may be used to retrieve the document using a
RETRIEVE_URL expression.
For more information on using a
RETRIEVE_URL expression, see "Implementing the
Endeca Crawler" in the
Endeca Forge Guide.
The Document format is available only to customers who have purchased the Endeca Crawler.
For details on this format and implementing the Endeca Crawler, see "Implementing the Endeca Crawler" in the Endeca Forge Guide.
The XML record format is proprietary to Endeca. XML records can be used to store state between Forge runs, for Advanced Crawler output, for debugging, or to propagate data from one Forge pipeline to another.
An XSL transformation can be applied to source data that is in a non-Endeca XML format, converting it into Endeca Record XML which Forge can read. The XSL transformation is done on the entire input file before Forge starts to read records, so there may be a significant delay before Forge starts processing with this format. Also, because XML is a relatively verbose text format, it is the slowest input format to Forge.
In addition to name and direction, an XML record adapter requires settings on the General and Transformer tabs.
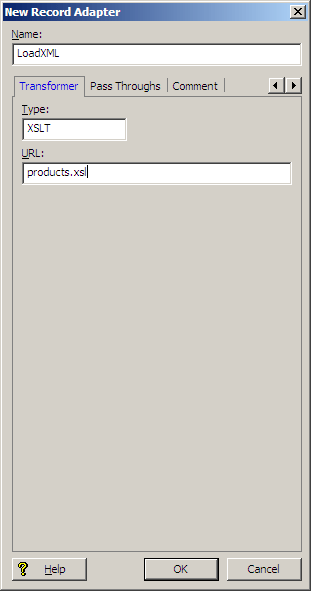
The following illustration shows the Transformer tab of the Record Adapter editor.
The sample record adapter reads XML records from the file named products.xml (which is specified in the General tab's URL field), converting the vendor-specific XML to the Endeca Record XML format using the products.xsl stylesheet.
When checked, the Filter Empty Properties setting on the General tab of the Record Adapter editor filters out empty property values when the source data is read into the Data Foundry.
For example, assume the following source data contains properties delimited by the pipe ('|') character.
WineID|Region|WineType|Price
1||Merlot|8.99
2||Chardonay|14.99
3||Chianti|19.99
4|||10.99
5||Merlot|18.99
6||Spumante
7|Sonoma|Chablis|9.99
A record adapter with Filter Empty Properties checked would filter the Region property from records 1 through 6, and the Region and WineType properties from record 4. If Filter Empty Properties is not checked, an empty string (' ') is assigned to the empty properties.
For text input formats (Delimited and Vertical), Forge has a built-in hard limit of 64K per record.
This built-in limit cannot be configured; however, there are two workarounds:
The Pass Throughs tab is used to include additional required information for several data formats.
Pass through information is in the form of name/value pairs. There are specific Pass Through details for each of the following formats:
For detailed information about using Pass Throughs with each of the above data formats, see the section "Input Formats."
The Pass Throughs tab is used to include additional required information for several data formats.
The Pass Throughs tab is used to include additional required information for several data formats. This information can be modified.
The Pass Throughs tab is used to include additional required information for several data formats. This information can be removed if necessary.
When running your pipeline, you can override the Java home and Class path settings specified in a record adapter using two Forge command-line flags, --javaHome and --javaClasspath.
The JDBC adapter uses both of these settings. Use a command similar to this one to override them, where j2sdk is an absolute path to your Java 2 SDK and drivers.jar is an absolute path to the drivers you want to use:
$ENDECA_ROOT/bin/forge -vvt --javaHome usr/local/j2sdk1.4.1_02
--javaClasspath usr/local/Oracle/lib/oracle8i.zip pipeline.epx
If you specify multiple drivers, delimit them using colons (:) on UNIX and semi-colons (;) on Windows.
The Exchange adapter only uses the Java home setting. Use a command similar to this one to override this setting, where j2sdk is an absolute path to your Java 2 SDK:
$ENDECA_ROOT/bin/forge -vvt --javaHome usr/local/j2sdk1.4.1_02
pipeline.epx