Apply a Filter
Apply a filter by using the filter dialog, applying a template, clicking graph data, or clicking data in a pivot table.
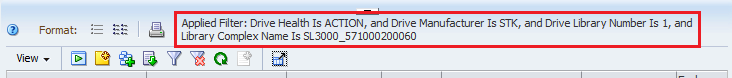
Once you apply a filter to a screen, it remains in effect for the duration of your login session. If you navigate away from the screen and then return, the filter will still be in effect. To change or remove a filter, you must apply a new filter, remove the filter, apply a template, or log out of STA.
Filter Using the Dialog Box
The filter dialog box appears when you click the Filter Data icon ![]() or when you create dynamic logical groups.
or when you create dynamic logical groups.
-
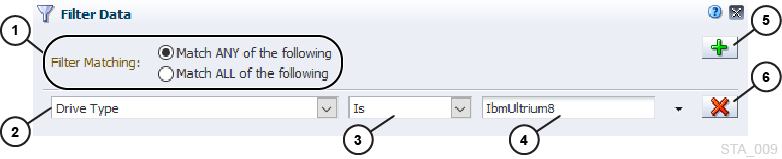
Select the type of match:
-
Match ANY of the following – Selects records that meet any of the criteria you specify. This is the default.
-
Match ALL of the following – Selects only records that meet all of the criteria you specify
-
-
Select an Attribute.
Tip:
Type the first few letters to quickly move to a menu item. -
Select an Operator. See Filter Operators by Attribute Type.
-
Select a Value. Text entries are not case sensitive.
-
To add a filter criteria, click Add
 .
. -
To remove a filter criteria, click Remove
 next to the filter.
next to the filter.
Filter Operators by Attribute Type
Operators define how an attribute is used to filter data. The available operators vary depending on the type of attribute.
- Text attribute operators
-
Examples of text attributes include Drive Health Indicator, Volume Serial Number and Drive WWNN. Some criteria values are free-form and some must be chosen from the drop-down list.
-
Is – Selects records with attribute values that match the specified string exactly.
-
Isn't – Selects records with attribute values that do not match the specified string exactly.
-
Is Blank – Selects records with blank or null attribute values. This is useful for selecting records that have not had an particular attribute value set in STA. For example, the criteria "% Drive Utilization (30 Days) Is Blank" would select all drives that have not been used in the last 30 days.
-
Starts With – Selects records with attribute values that start with the specified string.
-
Contains – Selects records that contain the specified string anywhere within the attribute value.
-
Doesn't Contain – Selects records that do not contain the specified string anywhere within the attribute value.
-
Ends With – Selects records with attribute values that end with the specified string.
-
- Logical group operators
-
Generally, you should use the "Contains" and "Doesn't Contain" operators. The "Is" and "Isn't" operators require an exclusive match and therefore may select no records when the drives or media belong to multiple groups.
-
Is – Selects drives and media assigned only to the specified logical group and not assigned to any others.
-
Isn't – Selects all drives and media, except those assigned only to the specified logical group and not assigned to any others.
-
Contains – Selects drives and media assigned to the specified logical group and any others.
-
Doesn't Contain – Selects drives and media not assigned to the specified group but assigned to others.
See Filter by Logical Group for more details.
-
- Date and time stamp operators
-
Examples of time stamp attributes include STA Start Tracking (Dates) and Last Exchange Start (Dates).
-
Equals – Selects entries with attribute dates and times equal to the one you specify.
-
Isn't – Selects entries with attribute dates and times not equal to the one you specify.
-
Is Before – Selects entries with attribute dates and times before the one you specify.
-
Is After – Selects entries with attribute dates and times after the one you specify
-
- "Number of days" operators
-
Examples of "number of days" attributes include STA Start Tracking (No. Days) and Last Exchange Start (No. Days)
-
Less than # days ago – Selects entries that occurred less than (<) the specified number of days ago.
-
More than # days ago – Selects entries that occurred more than (>) the specified number of days ago.
Type the value in the associated text entry field.
These operators are especially useful if you want to include a time-related filter in a saved template. By selecting records based on age rather than a specific date and time stamp, the filter is useful now and in the future.
-
- Numeric operators
-
Examples of numeric attributes include Media Length in Meters and Exchange Elapsed Time.
-
Is – Selects records with attribute values equal to the specified value.
-
Isn't – Selects records with attribute values not equal to the specified value.
-
Less Than – Selects records with attribute values less than (<) the specified value.
-
Greater Than – Selects records with attribute values greater than (>) the specified value.
Type the value in the associated text entry field. Do not include units of measure, such as MB, in your entry. Decimals are allowed.
-
- Boolean operators
-
Examples of Boolean attributes include Cleaning Media and Exchange Write Inefficient
-
True – Selects records for which the condition is true.
-
False – Selects records for which the condition is not true.
-
Filter by Applying a Template
Applying a template automatically applies any filter criteria included in the template definition. The template filter criteria overrides any filter that may already be in effect.
See Apply a Template.
Filter Using Dashboard Graphics
Click a component of a bar, pie, or area chart to bring up a list for the selected resource with a corresponding filter applied.
For example, if you click the LTO5 portion of the Library Drive Bays pane, it will display the Drives-Overview screen with the filter "Drive Model Is LTO5" applied.
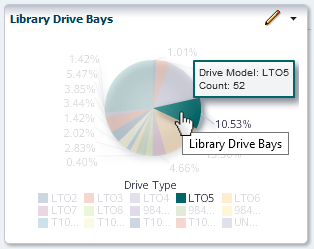
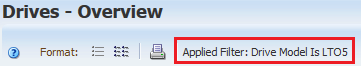
Clicking the paired screen "Drives - Anaysis" will display data with this same filter.
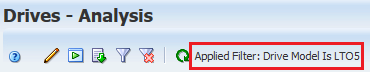
Some graph sections may not have associated detailed information to display. Therefore, clicking some graph sections may not link anywhere (such as unallocated media slots).
Filter Using Pivot Links
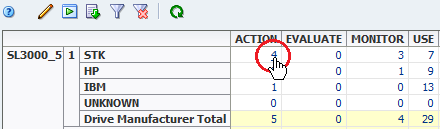
The cells within pivot tables contain counts of resources or events that meet specific criteria. Click a value within the pivot table to apply a filter corresponding to that cell.
For example, in the following Drives – Analysis pivot table, the "4" in the ACTION column indicates that there are a total of four STK drives with a health status of "Action" in the SL3000_5 library. Clicking on this link takes you to the Drives – Overview screen and applies a filter for drives.