Overview: This document provides the steps needed to configure CWSerenade to integrate with Vertex O® Series so that Vertex calculates tax for orders during order entry, pick slip preparation, and billing.
Compatibility: CWSerenade version 3.5 or later is compatible with Vertex O Series® 6.0.
In this topic:
• Before You Start: Taxability Considerations:
• Mapping Data from CWSerenade to Vertex
• Vertex wsdl (Web Service Definition Language) File
• Default Values by Company XML File
For more information: See CWSerenade/Vertex Interface for an overview on the integration.
Before You Start: Taxability Considerations
Mapping Data from CWSerenade to Vertex
Before you start the configuration steps described below, it is helpful to note the information in CWSerenade that maps to corresponding values in Vertex.
CWSerenade |
Vertex |
Notes |
company (WCMP) |
taxpayer |
If you specify a Company in the Default Values by Company XML File, it overrides the actual company code. |
entity (WENT) |
taxpayer |
Used if the Pass Entity Code to Tax Interface (F69) system control value is selected and you do not specify a company code and division code in the Default Values by Company XML File. Set up with the company taxpayer as the parent, and configure all required data at the entity-level taxpayer. The entity on an order is determined by the division assigned to the source code on the order header. If you specify a Company and a Division in the Default Values by Company XML File, the Division specified overrides the entity code. |
item class (WICL)/ long SKU department (WLSD)/ long SKU division (WLSV)/ long SKU class (WLSC) |
product class |
Assigned in CWSerenade to the item/SKU (MITM). Used to map to the product class in Vertex in order to apply tax exceptions. See Creating the Product Class, below. |
customer class (WCCL) |
customer class |
Assigned in CWSerenade to the customer. Maps to the customer class in Vertex to apply tax exemptions. Note: • You can also flag individual customers as tax-exempt in CWSerenade, and specifying an Exempt certificate number and Exempt expiry date. • If the customer on an order is assigned to a customer class in CWSerenade that does not correspond to a matching class in Vertex, Vertex calculates tax as if there is no customer class assignment. |
Purpose: In order to set up product classes for taxability purposes, you can map your company’s item class, long SKU department, long SKU division, and long SKU class combinations to product classes (taxability drivers) in Vertex. The particular categories mapped, and the order in which they are mapped, is user-defined, so that you can select the product class hierarchy that best matches the way you group and classify items.
Identified where? The Product_Class_Concatenation_Type in the Default Values by Company XML File identifies the sequence in which to concatenate the four product class code components, with leading zeroes included.
What components can you include?
Component |
Identified as Element Number: |
item class (WICL) |
1 |
long SKU division (WLSV) |
2 |
long SKU department (WLSD) |
3 |
long SKU class (WLSC) |
4 |
The setting of the Product_Class_Concatenation_Type identifies the order in which to send these elements to Vertex in order to indicate an item or SKU’s product class.
Example: |
You set the Product_Class_Concatenation_Type to 2341. This setting indicates to concatenate the product class elements as: long SKU division (2) + long SKU department (3) + long SKU class(4) + item class (1). You enter an order for an item with the following assignments: • long SKU division: XYZ • long SKU department: 4 • long SKU class: 6543 • item class: FD Vertex receives a product class assignment for the item of XYZ00046543FD. Note that leading zeroes are included (for example, the long SKU department of 4 is included as 0004). |
Setup considerations: As a way to simplify the setup process, you can set the Product_Class_Concatenation_Type so that your most commonly used components are included first. For example, if you always use item class (1), sometimes use long SKU department (3) and never use long division (2)) or long SKU class (4), you can set the Product_Class_Concatenation_Type to 1324. Then when you set up product classes (taxability drivers) in Vertex, you only need to specify the item class (1) and long SKU department (3), as the integration concatenates those two values and leaves the rest of the product class blank.
• Use Generic XML Tax Interface (J10): Must be selected to have CWSerenade communicate with Vertex.
• Use Standard Tax Calculation if Tax Interface Fails (J13): Select this value to have CWSerenade use the standard tax calculation if it does not receive a response from Vertex. If you select this value, you will need to set up tax rates at the SCF level (WSCF) and/or the postal code level (WZIP).
• Pass Entity Code to Tax Interface (F69): Select this value to pass the entity associated with the source code on the order header to Vertex, provided you do not specify a Company and Division code in the Default Values by Company XML File. If you select this value, then you can set up product class or customer class tax exemptions at the entity level in Vertex.
• Tax Included in Price (E70): Must be unselected if your company integrates with Vertex.
• Send Tax to Vertex as Quote not Invoice (L11): Indicates whether billing should send a quotation or an invoice request message to Vertex when processing a shipment or a return.
Note:
• When you change a system control value, stop and restart the background jobs (MBJC) and exit and re-enter CWSerenade to have your changes take effect.
• It is not necessary to set up the Tax on Freight (B14) or Tax on Handling (B15) system control values.
TAX_INT Integration Layer Job (IJCT)
For the TAX_INT job: Set the Communication type to Web Service and set the WSDL Document Name to calculate-tax-60.wsdl. See Vertex wsdl (Web Service Definition Language) File for more information.
Because the TAX_INT job is always in INTERACT status, you do not stop or restart the job for your change to take effect.
Note: The TAX_INT job does not require a process queue.
Important: Integration with Vertex will not work if you hide the TAX_INT job.
Additional Setup in CWSerenade
Create a customer class for exempt customers: Use Work with Customer Class (WCCL) to set up one or more classes of customers who are tax exempt, and then assign customers in CWSerenade to the appropriate customer class. You can then set up the customer class(es) as tax exempt in Vertex. Similarly, set up product class exemptions and individual product (item) exemptions in Vertex. See Set up Data within Vertex for more information on setup steps in Vertex.
Note: If the customer on an order is assigned to a customer class in CWSerenade that does not correspond to a matching class in Vertex, Vertex calculates tax as if there is no customer class assignment.
Set up individual customer tax exemptions: Use Work with Customers (WCST) to set up individual customers as tax exempt, including specifying their Exempt certificate number and the Exempt expiry date, or setting this information up for the customer in specific states or provinces. CWSerenade passes this information to Vertex when a tax exempt customer places an order. It is not necessary to assign these customers to a particular customer class in order to flag them as tax exempt to Vertex.
Assign items and SKU’s to a product class hierarchy: Use Work with Items/SKU’s to assign items and SKU’s to the categories you use to identify product classes in Vertex, as described under Creating the Product Class.
Note: It is not necessary to set up tax rates or other settings at the SCF level or the postal code level if you are using the generic tax integration with Vertex.
Use the Sales Tax option within the Vertex Taxability Manager:
Set up company and entities as taxpayers in Vertex:
1. Set up a taxpayer for each company to integrate with Vertex. The taxpayer Code should match the company code and should be zero-filled (for example, company 3 in CWSerenade = taxpayer Code 003 in Vertex). Assign the taxpayer to the appropriate jurisdictions, such as all U.S. states.
2. If you are sending entity information to Vertex, add a taxpayer for each entity for the related company, where the company taxpayer is the parent to the entity taxpayer. For example, if you are adding entity 100 for company 3, select taxpayer 003 in Vertex as the parent for taxpayer 100. Again, assign the taxpayer to the appropriate jurisdictions, such as all U.S. states.
3. If you would like to set up product class exceptions, use the Taxability Driver option in Vertex:
• Input Field = Product Class
• Code = the concatenated product class, as determined through Creating the Product Class
• Taxpayer = your company and, optionally, entity
• Taxability Driver is... = the taxability rule for the product class
• Optionally, any other settings as needed
4. Set up product classes for freight, additional charges, and handling and map them to the appropriate delivery charge categories:
|
Line Item Type |
Product Class |
|
OF |
OF (Order Freight) |
|
LD |
LD (Line Duty) |
|
LH |
LH (line handling) Note: If the S/H exclude tax? flag is selected for an additional charge code, then a line that uses this additional charge code for special handling is not subject to line handling (LH) tax. See Establishing Additional Charge Codes (WADC) for background. |
|
AF |
AF (additional freight and shipper item charges) |
|
LF |
LF (line freight) |
Note: |
If you use the integration with Vertex to calculate taxes, then the settings within CWSerenade to control tax on freight and handling (such as system control values and settings at the SCF and postal code level) are not used. |
5. Optionally, set up customer class exceptions in Vertex.
Note: If the customer on an order is assigned to a customer class in CWSerenade that does not correspond to a matching class in Vertex, Vertex calculates tax as if there is no customer class assignment.
Use a text editor to edit the following files.
Important: MICROS recommends that you make a backup copy of each of the files discussed below before making any changes. Also, it is important that you do not make any changes in these files beyond those outlined in these instructions.
Vertex wsdl (Web Service Definition Language) File
Purpose: The wsdl file controls web service communication and other settings between CWSerenade and Vertex.
File location and name: The wsdl file you use for integration with Version 6.0 of Vertex is named calculate-tax-60.wsdl file, and is typically located at C:\Serenade\server\conf\cwdirectcpproperties\ on your CWSerenade server, where C: is the root drive.
Configuring the wsdl file:
• Search for localhost and replace each instance in the file with the name or IP address of the server running Vertex.
• Make sure that the port defined for the CalculateTaxWSService is correct. Typically, the port uses https rather than http and does not designate a port.
• Make sure that all other URLs that point to the Vertex server designate a port of 8095.
• Do not change anything else in the file.
• Save the wsdl in the same folder where the manifesting wsdl is stored, typically at C:\Serenade\server\conf\cwdirectcpproperties\ on your CWSerenade server, where C: is the root drive. Delete the current copy of the calculate-tax-60.wsdl bin file if there is one.
Upgrading the wsdl file: If you need to upgrade your Vertex integration to work with Version 6.0, rename the calculate-tax-40.wsdl file to calculate-tax-60.wsdl.
Note: After making any change to the wsdl, you need to restart CWSerenade to have your changes take effect. See Restarting CWSerenade for more information.
Proxy Settings
When communicating with Vertex, you must define a proxy server to act as an intermediary in order to increase security. CWSerenade sends transactions to the proxy server and the proxy server sends the transactions along to Vertex. The PROXY_HOST and PROXY_PORT properties define the IP address and port number used to connect to the proxy server during tax calculation.
Purpose: Use this file to specify the user ID and password to use for connection to Vertex.
File location and name: This file is called VertexWS.xml and is in the same folder as the wsdl.
Configuring the VertexWS.xml file: You need to enter a valid UserID and Password with access to Vertex. The user ID you specify should be assigned to the Vertex partition that includes the data that will be required by CWSerenade.
The password entry here is encrypted. If you change the password as part of your PCI standards, you must follow the instructions below.
Note: After you change the VertexWS.xml file, you need to stop and restart CWSerenade. See Restarting CWSerenade for more information.
Changing the Vertex user ID and password: To change the Vertex user id and password used for connection to Vertex:
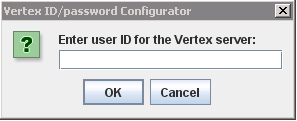
1. On the CWSerenade application server, advance to C:\Serenade\CWSerenade\Vertexconfig and double-click the runthis.bat file
2. At the Vertex ID/password Configurator window, enter the user ID used for connection to Vertex and click OK.
3. The program next asks for the Vertex password. Enter the password for the user ID and click OK.
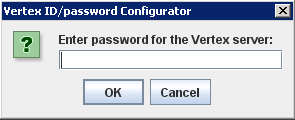
The program updates the user ID and password in the VeretexWS.xml file.
Note: The password is encrypted so it will not be clearly visible in this file.
To have this change take effect, restart the SERENADE service.
Repeat these steps for each CWSerenade application server.
Default Values by Company XML File
Purpose: Use this file to specify default values to send to Vertex for each company that will use the tax integration.
File location and name: A copy of this configuration XML file is required for each company that will use Vertex. The files are typically located under Serenade\server\conf\cwdirectcpproperties\xslt\VertexWS on your CWSerenade server. The company number in the file name should be zero-filled; for example, the file name for company 49 is DefaultValues_049.xml.
Sample files: Your CWSerenade installation includes a sample default values XML file for company 49 and for company 51. You can use these samples as starting points to build default values XML files for your companies.
Configuring the file: Each entry in the file is labeled by an ID, for which you enter the corresponding Value:
Default Value ID |
Value |
Company |
Optionally, use this field to enter an override company code to pass to Vertex that differs from the actual company number. See Configuring the Division and Company Codes for more information. |
Division |
Optionally, use this field to pass a division code to pass to Vertex. See Configuring the Division and Company Codes for more information. |
Product_Class_ Concatenation_Type |
Indicates the sequence of the item class, long SKU department, long SKU division, and long SKU class to use when creating product classes (taxability drivers) for exceptions to default tax rules. See Creating the Product Class for setup considerations, and see Set up Data within Vertex for setup steps in Vertex. |
Call_Center_TaxAreaID |
The tax area ID to send to Vertex in order to identify your call center’s location. You can determine a location’s tax area ID in Vertex Central Home under Tools > Tax Area ID Lookup. |
Call_Center_Country |
This information is required by Vertex. |
Call_Center_City |
|
Call_Center_State |
|
Call_Center_PostalCode |
|
Call_Center_StreetAddress |
|
Default_Warehouse |
This information is required by Vertex. You also use the Warehouses XML File to indicate the tax area ID of each warehouse where you make shipments. |
Default_Warehouse_Country |
|
Default_Warehouse_City |
|
Default_Warehouse_State |
|
Default_Warehouse_ PostalCode |
|
Default_Warehouse_ StreetAddress |
Configuring the Division and Company Codes
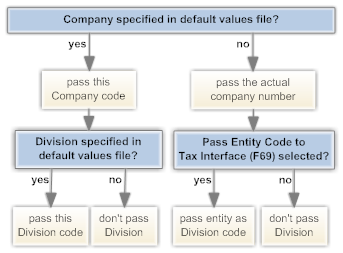
These fields in the Default Values by Company XML File enable you to override the Company and Division specified in the QuotationRequest, InvoiceRequest, and DistributeTaxRequest messages that CWSerenade sends to Vertex.
• If you do not specify a Company here: Regardless of whether you specify a Division here, CWSerenade passes:
• Company: The actual company code.
• Division: If the Pass Entity Code to Tax Interface (F69) system control value is selected, this is the entity code related to the source code on the order header. If the Pass Entity Code to Tax Interface (F69) system control value is not selected, no Division is passed.
• If you specify a Company here but not a Division: Regardless of the setting of the Pass Entity Code to Tax Interface (F69) system control value, CWSerenade passes:
• Company: The Company code you enter here.
• Division: None.
• If you specify both a Company and a Division here: CWSerenade passes the Company code and Division code you enter here.
Changes effective immediately: Changes you make to the default values by company file take place immediately. It is not necessary to stop and restart CWSerenade.
Purpose: This file provides the list of warehouses from which you ship merchandise, so that Vertex can apply the appropriate tax rules for the shipping location.
File location and name: Like the default values by company XML file, a copy of this configuration file is required for each company that will use Vertex. The files are typically located under Serenade\server\conf\cwdirectcpproperties\xslt\VertexWS on your CWSerenade server. The company number in the file name should be zero-filled; for example, the file name for company 6 is Warehouses_006.xml.
Sample files: Your CWSerenade installation includes a sample warehouses XML file for company 49 and for company 51. You can use these samples as starting points to build warehouses XML files for your companies.
Information in this XML file
First WarehouseValue element: The first WarehouseValue element at the beginning of the file indicates that the file provides a list of warehouse ID’s and their corresponding tax area ID values:
<WarehouseValue>
<ID>Warehouse</ID>
<Value></Value>
</WarehouseValue>
Do not change the default element.
Default warehouse tax area ID: The first warehouse entry in the file should indicate a warehouse ID of 000 and your company’s default tax area ID. For example, if the tax area ID is 220250100, the first entry is:
<WarehouseValue>
<ID>000</ID>
<Value>220250100</Value>
</WarehouseValue>
For each warehouse: For each warehouse where you will be processing shipments, enter the ID that identifies the warehouse code in CWSerenade, and enter the tax area ID of the warehouse. For example, if warehouse 3 has a tax area ID of 140430510, enter:
<WarehouseValue>
<ID>003</ID>
<Value>140430510</Value>
</WarehouseValue>
Example: The following example defines tax area ID’s for warehouses 1, 2, and 3:
<WarehouseValues>
<WarehouseValue>
<ID>Warehouse</ID>
<Value></Value>
</WarehouseValue>
<WarehouseValue>
<ID>000</ID>
<Value>220250100</Value>
</WarehouseValue>
<WarehouseValue>
<ID>001</ID>
<Value>700151420</Value>
</WarehouseValue>
<Wxml2zarehouseValue>
<ID>002</ID>
<Value>140430510</Value><
/WarehouseValue>
<WarehouseValue>
<ID>003</ID>
<Value>140430510</Value>
</WarehouseValue>
</WarehouseValues>
Note: Make sure that the Default Warehouse (A04) is one of the warehouses included in this file.
Changes effective immediately: Changes you make to the warehouse XML file take place immediately. It is not necessary to stop and restart CWSerenade.
| PC Manifest Interface Setup | Contents | SCVs | Search | Glossary | Reports | Solutions | XML | Index | Using Microsoft Internet Explorer® for CWSerenade |

Vertex setup OROMS 5.0 2018 OTN