| Oracle® Communications EAGLE Database Administration - GTT User's Guide Release 46.7 E97332-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle® Communications EAGLE Database Administration - GTT User's Guide Release 46.7 E97332-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
The Enhanced Global Title Translation (EGTT) feature is designed for the signaling connection control part (SCCP) of the SS7 protocol. The EAGLE uses this feature to determine to which service database to send the query message when a Message Signaling Unit (MSU) enters the EAGLE and more information is needed to route the MSU.
If an MSU enters the EAGLE and more information is needed to route the MSU, the SCCP of the SS7 protocol sends a query to a service database to obtain the information. The EAGLE uses the EGTT feature for the SCCP to determine which service database to send the query messages to. The service databases are identified in the SS7 network by a point code and a subsystem number.
The EGTT feature uses global title information (GTI) to determine the destination of the MSU. The EAGLE supports ANSI GTI format 2 and ITU GTI formats 2 and 4. The GTI is contained in the called party address (CDPA) field of the MSU. For ITU GTI format 4, the GTI is made up of the Numbering Plan (NP), Nature of Address Indicator (NAI), and Translation Type (TT) selectors.
The EGTT feature allows global title translation on global title addresses of fixed length. There are three optional add-on features that enhance the functionality of the enhanced global title translation feature:
The EGTT feature requires one of the following cards:
For more information on these cards, refer to the Adding a Service Module procedure or to Hardware Reference.
Inclusion of SSN in the CDPA
When the obtained translation data contains a subsystem, the translated SSN is placed in the SCCP CDPA before the message is sent to the next node. However, when no SSN is present in the CDPA, this insertion applies to ITU messages only. ANSI messages that do not contain an SSN in the CDPA will be rejected. The gray shaded areas in Figure 2-2 show the message fields affected by enhanced global title translation.
Figure 2-2 ANSI and ITU MSU Fields affected by the Enhanced Global Title Translation Feature
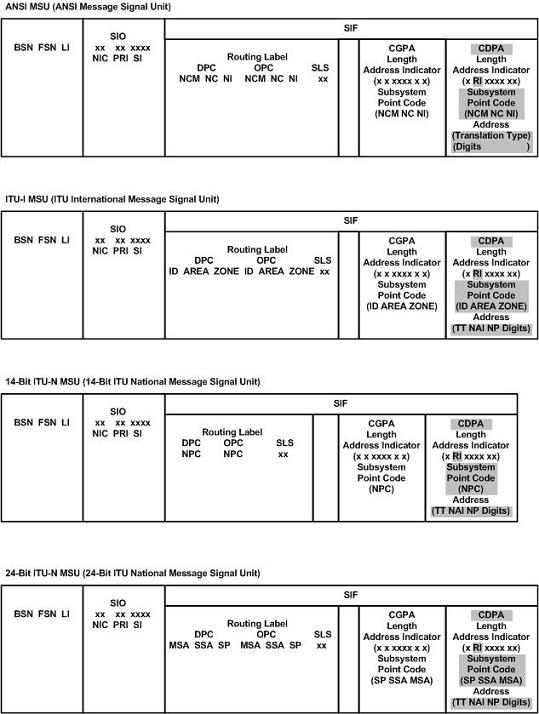
Inclusion of OPC in the CGPA
When an ITU unitdata (UDT) message does not have a point code (PC) present in the CGPA, and the CGPA route indicator (RI) is set to Route on SSN, the EGTT feature will insert the OPC from the Message Transfer Part (MTP) routing label into the CGPA before sending the message to the next node. The insertion does not apply to ANSI GTT processing.
Deletion of GT
The EGTT feature allows a Global Title (GT) in the CDPA
to be deleted. For example, when the result of a GTT performed by the EAGLE is
set to “Route on SSN”, there may be some end nodes that do not want to receive
the GT information in the CDPA. The enhancement provides an option on a per
translation basis (for both ANSI and ITU) to allow the GT to be deleted
(ent-gta:gta=000:ri=ssn:ccgt=yes command). The
option is not valid when the result of the GT is the EAGLE’s point code and
local SSN.
New Commands
The EGTT feature introduces three new command sets:
ENT-GTTSET – Enter
GTT Set
CHG-GTTSET –
Change GTT Set
DLT-GTTSET –
Delete GTT Set
RTRV-GTTSET –
Retrieve GTT Set
ENT-GTTSEL – Enter
GTT Selector
CHG-GTTSEL –
Change GTT Selector
DLT-GTTSEL –
Delete GTT Selector
RTRV-GTTSEL –
Retrieve GTT Selector
ENT-GTA – Enter
Global Title Address
CHG-GTA – Change
Global Title Address
DLT-GTA – Delete
Global Title Address
RTRV-GTA –
Retrieve Global Title Address
GTT Set Commands
The GTT Set commands are used to provision new sets of GTTs, linking GTT Selector (-GTTSEL) and Global Title Address (-GTA) commands. This set of commands provides greater flexibility when provisioning the type of messages that require Global Title Translation. There are no SEAS equivalents for these commands.
GTT Selector Commands
The GTT Selector commands are used to provision new selectors for global title translation. Together with the GTT Set commands, these commands replace the Translation Type (-TT) commands, providing greater flexibility when provisioning the type of messages that require Global Title Translation. There are no SEAS equivalents for these commands.
GTA Commands
GTA commands are used to provision GTTs using the new selectors for GTT.
The EAGLE supports the following: