Setting Up Asset Profiles
Use the Asset Profile Definition (PROFILE) component to define asset profiles.
This topic provides an overview of asset profiles and discusses how to set up Asset Profiles.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
PROFILE_DEFN |
Define asset profiles. |
|
|
PROFILE_BK_01 |
Identify the criteria to use in depreciation calculations. |
|
|
PROFILE_DEPR_DETL |
Set special depreciation terms for an asset profile and select an accounting method for these special terms. These are commonly used to meet depreciation requirements for specific countries. |
|
|
(ARG, BRA, and MEX) Asset Profiles - Inflation Information page |
PROFILE_SEC |
Establish an inflation adjustment factor by selecting the market index and rate to apply. |
|
SALVAGE_OPTION_SEC |
Enter options for rounding depreciation amounts for this book. This is for use in Japan. |
|
|
PROFILE_BK_03 |
Specify property type and tax depreciation criteria and identify which tax credits will be used by the profile. |
|
|
PROFILE_PAR_BK_ECD |
Specify child asset attributes that will be used by the profile and inherited from the parent asset for Express Add, Basic Add, and batch-created assets. The inheritance based on the selected items happens upon defaulting the profile in Express Add and capitalizing the asset in Basic Add, and when you are using Default Profile processing in the Transaction Loader if the Business Unit option is selected. |
|
|
Profile Changes In Mass |
RUN_AMPRFCHG |
Copy an asset profile from one SetID to another, or update a profile by changing some of its attributes. |
An asset profile is a template that contains standard depreciation criteria for an asset type and its corresponding asset books. The information established in an asset profile can be used as default values when you're adding assets to the system. Profiles associated with indexes enable replacement cost calculations. Profiles are recommended when you have a large number of assets of the same type. Defining default values minimizes data entry, ensures consistency, and enhances accuracy levels.
Set up asset profiles to match most, if not all, of the major asset categories that you track on your books. These can range from the standard categories such as Land, Furniture & Fixtures, Machinery & Equipment, and Expensed Items, to more detailed categories that you may want to track, such as Computers, Software, Phones, and Fax Machines.
Note: You must set up at least one asset profile before you can add any assets to the system. Remember that profiles are templates that help reduce data entry when you are actually adding an asset. When you go through the process of entering assets into the system, you can override any of the fields in an asset profile. Because profiles are required when you are using Express Add, Oracle recommends that you set up a blank dummy profile for nonstandard assets.
Assets can be classified into one of the following categories:
Capital Assets - The system generates an asset ID and stores physical and financial information. Financial information is stored in the Cost table (COST). The system also stores acquisition details. Therefore, these assets are trackable from both a physical and financial standpoint. This term is interchangeable with Financial Assets. Assets using the capitalization threshold by asset and by book method may be placed into this category.
Non capital Assets - The system generates an asset ID and stores only physical information. The cost information is stored in the Noncapitalized Cost table, (COST_NON_CAP). The system also stores acquisition details. Therefore, these assets are trackable from a physical standpoint only. This term is synonymous with Trackable Assets or Nonfinancial Assets.
Expense Assets - The system does not generate an asset ID.
Because of their low cost, these assets are considered an expense when acquired and there is no interest to track them within the Asset Repository.
After you create an asset using an asset profile, the profile is still used for reporting purposes.
To maintain synchronization between the asset category and asset reporting profile when you recategorize an asset, use the Update Asset Profile link on the Cost Information Page. This enables you to update the asset reporting profile at the same time you recategorize the asset.
Related topics:
Use the Asset Profiles - Definition page (PROFILE_DEFN) to define asset profiles.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Asset Profiles - Definition page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.

You create asset profiles from the Profile (PROFILE) component. You can create profiles with varying levels of detail. The level that you use depends on how much information you want to be provided by default into the system when you add an asset. Some asset profiles are used to define financial attributes, while others are not. To successfully create a financial profile, you must enter at least the following information:
Profile ID.
Asset category.
Asset book name.
Depreciation attributes.
Asset type.
Each profile has a unique profile ID. You can use this ID to group profiles by type. For example, you might want to have several automobile profiles, such as Autos, Autos-Luxury, and Autos-Leased.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Asset Description |
Enter a description for this asset profile. |
Status |
Select a status for the asset profile. Select Active to make an asset profile available for selection when adding new assets. Select Inactive when you want to discontinue using an asset profile. When you choose this option the profile will not be available for selection when adding new assets. However, the profile is retained in the asset profile component for your reference. Note: You cannot select the Inactive option for an asset profile if there are open interface records associated with the profile; you must first associate the records with a different profile. |
Asset Class |
Select the asset class with which an asset profile will be associated by default. The available options are defined when you establish asset class codes. |
Asset Type |
Select the asset type. Oracle delivers these asset types: Hardware, Software, Equipment, Property, Fleet, Machinery, Furniture, Facility, Intangible, Other. |
Asset Subtype |
Select the asset subtype. Valid values for the selected asset type appear from the drop-down list box. |
Acquisition Code |
Select the acquisition code from the drop-down list box. Available options are:
|
Taggable Asset |
Select to indicate that an asset is taggable. Most physical assets can be tagged with a tag number to help keep track of them. Some assets, however, such as buildings or leasehold improvements, cannot be tagged. If an asset is taggable, it probably already has a tag number associated with it, which is recorded when the asset is added. Sometimes, however, an asset may be taggable, but not yet tagged. The Taggable Asset check box can be used to flag this type of asset. Note: To use the Physical Inventory functionality in PeopleSoft Asset Management, your assets must be tagged. |
Capitalized Asset |
Select to indicate whether this profile will be used for assets with cost and depreciation associated with them. Most assets in the PeopleSoft Asset Management system will be capitalized assets. If you are setting up a profile for non capitalized assets, (assets with no cost or depreciation criteria), deselect Capitalized Asset. Typically these assets are expensed, not actually owned, or fully depreciated, but you still want to track them. |
Use As Tool |
Select if the asset is sued as a tool in connection with the maintenance or repair of another asset. |
Asset Retirement Obligations |
Select this option for an asset profile to apply asset retirement obligation (ARO) defaults to the associated asset, thus flagging the asset as eligible for ARO processing. You can select the Asset Retirement Obligation check box for any asset profile to apply ARO defaults when adding an asset. If you decide that the asset is not ARO-eligible, you can deselect the defaults for the asset manually when adding it. Conversely, if you do not use an asset profile, or the selected profile does not carry the ARO defaults, you can manually select the ARO options for the asset when adding it in the Basic Add component. to be used specifically as default profiles for assets requiring ARO treatment when you add new assets. The ARO functionality provides asset retirement obligation measurement and reporting in compliance with Financial Accounting Standards for leased assets, group assets, and asset impairment. See Understanding Adding and Maintaining Assets For more information, see Accounting for Asset Retirement Obligations |
Index Name |
Select the index by which replacement or valuation cost will be calculated. When you run the Calculate Replacement Cost (AMRCCALC) process, it multiplies the asset cost by the amount in the index selected here. |
SubIndex Name |
Select the subindex category for the index to use to calculate replacement or valuation cost. |
Threshold ID |
If you want to define capitalization thresholds based on asset, select the Threshold ID to use as the default value for assets within a given profile. This field appears only when the Capitalized Asset option is selected on this page and the Capitalization Threshold feature is enabled from the Installation Options - Asset Management page. When the Capitalization Threshold feature is enabled, PeopleSoft Asset Management:
See .Pages Used to Set Up and Manage Capitalization Thresholds |
(AUS) Using Research and Development Information
Research and Development Information is used to meet Australian asset processing requirements; for others, these fields are informational.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
R and D Plant Asset (research and development plant asset) |
Select if this asset is being used for research and development and is entitled to R&D tax concessions. |
R and D Start Date (research and development start date) |
Enter the date on which the asset was first used exclusively for R&D. If you leave this field blank, the in-service date from the tax book of the business unit will be used as the start date. The start date determines in what year the R&D concessions can first be claimed. |
Use NBV for R and D (use net book value for research and development) |
Select if you want to base the R&D concessions calculation on the net book value of the asset (at the R&D start date) instead of the book cost. This is useful when an asset previously being depreciated as a non-R&D asset subsequently becomes eligible for R&D concessions. |
See (AUS) Using PeopleSoft Asset Management Options to Meet Australian Requirements.
Use the Asset Profiles - Depreciation page (PROFILE_BK_01) to identify the criteria to use in depreciation calculations.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Asset Profiles - Depreciation page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.

Note: Each asset can report to multiple books and have multiple depreciation attributes per book.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Book Name |
Enter a book name that defines the rules for the assets entered with this profile. Books are defined during system setup and associated with business units. Only valid books can be assigned. |
Effective Date |
Enter the date that indicates when the convention and depreciation method take effect. If you want a history of changes made to a profile, be sure to add new rows to the table and use effective dating to update profiles, rather than making changes to the initial row. |
Depreciate When in Service |
Select to allocate annual depreciation as of the date that you placed the asset in service. If you do not select this option, PeopleSoft Asset Management allocates annual distribution as of the date determined by the depreciation convention. This option is valid only in the year that the asset was acquired. |
Category |
Defines the category of an asset, such as Furniture & Fixtures or Machinery & Equipment. The available category codes are those you entered on the Category Code table. In general, these will correspond to the General Ledger asset accounts. Asset Category is used in accounting entry generation. |
Depr Status |
Enter the depreciation status. |
Currency Code |
Select a currency code. |
Adjust Conv (adjustment convention) |
Select an adjustment convention. |
Convention |
Select a depreciation convention. |
Retire Conv |
Select a retirement convention. |
Retire Option |
Select the retirement calculation option to be processed for assets within a given profile. These retirement options are available at the profile, book and asset levels. See Retire Assets Page. |
Method |
Select a depreciation method. Some depreciation methods require you to enter additional information. Note: If you specify the depreciation method as Flat Rate or a Declining Balance method or Manual depreciation for tax books, you should enter the recovery life. |
Note: If you select Non Depreciable on this page, you must still enter values for Useful Life and Convention. However, you need not update the remainder of the Asset Profiles pages. Because the profile is defined for non depreciable assets, the information in these pages will not be used in any processing.
Ensure that you establish an effective date for the profile that is valid for the currency code specified for the profile.
|
Method |
Fields That Appear |
|---|---|
|
Declining Balance w/SL by Limit % |
DB Pct (declining balance percent) and Limit Pct |
|
Declining Balance |
Percent, Low Limit, Monthly |
|
Declining Balance w/SL |
DB Pct |
|
Depreciation Schedule |
Schedule |
|
Flat Rate % |
Percent, Low Limit, Avg Option (averaging option) |
|
France Derogatory Balance |
DB Pct Percent, Low Limit, Depr Pass Life (depreciate past life) |
|
Germany Staffel Method |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, Depr Pass Life |
|
Japan - Changes 200/250 DB to SL (J9 - Changes 200/250 Declining Balance to Straight Line) |
No additional fields display. However, for this method you must select the Special Depreciation option and input the year of change on the Special Terms - Depreciation Method Information page. Used for assets that were added using the following methods:
|
|
Japan - Changes DB to SL 200 (J8 - Changes Declining Balance to Straight Line 200) |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, Depr Pass Life Used for assets acquired on or after April 1, 2012. |
|
Japan - Changes DB to SL 250 (J6 - Changes Declining Balance to Straight Line 250) |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, Depr Pass Life Used for assets acquired on or after April 1, 2007. |
|
Japan - Extended/Strt Line (JE - Extended Straight Line) |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, Depr Pass Life Used for fully depreciated assets under the Tangible / Strt Line and Tangible / Declining Balance methods that are subject to an extended depreciation useful life of five years using a Straight Line depreciation method starting from the first period of the following fiscal year. |
|
Japan - Lease Depreciation (J4 - Lease Depreciation) |
No additional fields display. |
|
Japan - Intangible/Strt Line (J3 - Intangible/Straight Line) |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, and Depr Pass Life |
|
Japan - Tangible/Declining Bal (J1 - Tangible/Declining Balance) |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, and Depr Pass Life Used for assets acquired before April 1, 2007. |
|
Japan - Tangible/Strt Line (J2 - Tangible/Straight Line) |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, and Depr Pass Life Used for assets acquired before April 1, 2007. |
|
Japan - Changes DB to SL (J5 - Changes Declining Balance to Straight Line) |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, Depr Pass Life |
|
Japan - Tangible/Strt Line Rev (J7 - Tangible/Straight Line Revenue) |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, Depr Pass Life Used for assets acquired on or after April 1, 2007. |
|
Manual Depreciation |
No additional fields appear. The Manual Depreciation method enables you to adjust depreciation amounts that are generated by some other method. To use manual depreciation, you must therefore first create depreciation entries using another method. When this has been done, you can make your adjustments. |
|
Straight Line |
Useful Life |
|
Straight Line Percent |
(IND) Percent |
|
Sum of the Years |
NA |
|
Units of Production |
UOP ID (units of production ID) |
|
User Defined Method |
Method ID, DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, Depr Pass Life |
The following table defines the additional fields:
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Limit Pct (limit percent) |
Enter a limit for depreciation as a percentage of cost. |
UOP ID (units of production ID) |
Enter the units of production ID, production information, and transaction information that you want to use for this asset. |
DB Pct (declining balance percent) |
Enter the percentage of declining balance depreciation to be taken each year until the amount calculated by the straight line method is greater. |
Percent |
Enter the percentage of original basis to be taken in depreciation each year. This is required for straight line percent. |
Low Limit |
Enter an amount. When the asset basis reaches this limit, the remaining basis will be taken in depreciation and the asset will be fully reserved. |
Depr Pass Life (depreciate past life) |
Select if you want to continue to depreciate this asset past its useful life end date. This option is used for governmental regulations for certain countries or for utilities industries that may want to continue to depreciate an asset to the end of a depreciation calendar. |
Method ID |
Select the user-defined method that you want to use. |
Schedule |
Enter a schedule to use for depreciation. |
Avg Option (average option) |
Generally used by utility companies to depreciate composite assets. The averaging options are expressly designed to work with the flat rate depreciation method. Select an averaging option if you want to use it: Monthly: Monthly averaging takes an average monthly asset balance and multiplies it by the annual depreciation rate. The result is then applied against a period allocation (1/12, 2/12, 3/12, and so on) to derive a year-to-date (YTD) depreciation amount. The difference between the newly calculated YTD depreciation and the previous YTD depreciation is the amount booked to the current period. Yearly: Yearly averaging is similar to monthly averaging except that a yearly average balance is used. Because this amount is not known until the end of the year, it is usually estimated and adjusted periodically as the actual figures become known. |
Note: Using the flat rate depreciation method will cause any depreciation to be posted to the end of the calendar. If this is not your intention, you must enter a low limit of .01 when you first select the depreciation method for this asset. If you have not already done this, update the Depreciation Method field by selecting Flat Rate and entering .01 in the Low Limit additional field that appears.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Calculation Type |
Select the calculation type.
For example, if you took 20,000 USD depreciation over a two-year period but the amount allowed was $24,000, the difference of $4,000 would be expensed as an adjustment to accumulated depreciation in the current period. |
Low Value |
Select to identify assets with costs below a certain level for special depreciation processing. This is a requirement for some countries. |
Useful Life |
Enter the number of periods. This is used to perform the depreciation calculations for the financial books. |
End Date (end depreciation date) |
Enter an end date that you want depreciation to cease at a particular time. At the end depreciation date, the remaining asset basis will be taken in depreciation and the asset will be fully reserved. |
Future Depr Yrs (future depreciation years) |
PeopleSoft Asset Management calculates and stores depreciation until the end of the asset life. However, for optimal processing performance and greater table efficiency, you can specify a fixed number of years for which depreciation is calculated and stored. Note: Oracle strongly recommends using the Future Depreciation Years option if you are using group assets. |
Special Depreciations |
Select if you are working in a global environment and want to use special depreciation terms to meet specific country requirements. Click Special Terms to open the Depreciation Method Information page, where you can select special terms for depreciation. |
Depr Limit (depreciation limit code) |
Select a depreciation limit code that relates to a specific dollar amount limitation on depreciation for each year of life. Although this can be used for financial depreciation, it is commonly used for U.S. tax purposes, because such depreciation limits exist for items such as luxury automobiles. |
Cost Basis Limit |
Enter the limit on the depreciable basis of this asset. If the actual cost of an asset is greater than its depreciable basis, the difference will result in a gain when the asset is retired. |
Salvage % of Cost and Salvage |
Enter the residual value of the asset subtracted from the cost to determine the depreciable basis used in depreciation calculations. You can enter it either as a flat rate or as a salvage percentage (a percentage of the total cost of the asset). If you use a salvage percentage, the system recalculates the salvage value when you add additional costs for the asset. |
(DEU) Multi-Shift Code |
Enter rates by which depreciation should be increased based on the number of production shifts that an asset is used. This is used in Germany. |
Threshold ID |
If you want to define capitalization thresholds based on book, select the Threshold ID to use as the default value for assets within a given book. When you populate this field, the capitalization status of each book is determined according to the capitalization threshold defined for that book. This field appears only when the Capitalization Threshold feature is enabled from the Installation Options - Asset Management page. This field is available for editing only when the Threshold ID on the Default page is unpopulated. When the Capitalization Threshold feature is enabled, PeopleSoft Asset Management:
See .Pages Used to Set Up and Manage Capitalization Thresholds |
Group BU |
Enter the business unit for the group assets. |
Group ID |
Select the group ID. |
Impairment Process |
Select to make the asset available for impairment processing. |
Note: Each group member asset profile can be used by only one business unit.
Use the Depreciation Method Information page (PROFILE_DEPR_DETL) to set special depreciation terms for an asset profile and select an accounting method for these special terms.
These are commonly used to meet depreciation requirements for specific countries.
Navigation:
Select the Special Depr check box and click Special Terms on the Depreciation page of the Asset Profile component.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Depreciation Method Information page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
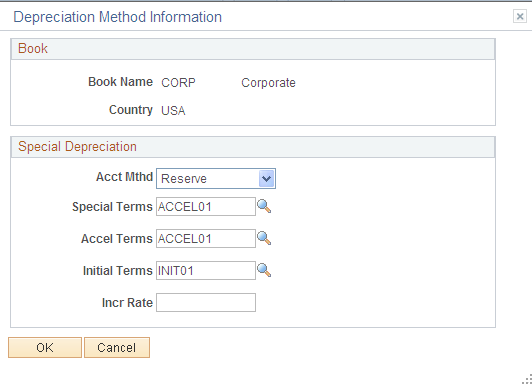
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Allowance |
Select to specify that special depreciation amounts are not booked with the standard depreciation amounts. Journal entries are generated that will include only the standard depreciation. PeopleSoft Asset Management does not support automatically generating journal entries for the special depreciation allowance accounting method. You may need to run two reports: Reserve for Special Depreciation and Reversal for Special Depreciation, and then generate the journal entries manually into the PeopleSoft General Ledger system. |
Expense |
Select to specify that total amounts of special depreciation and standard depreciation are booked and journal entries are generated that will include the total of standard and special depreciation amounts. |
Reserve |
Select to specify that special depreciation amounts are not booked with the standard depreciation amounts. Journal entries are generated that will include only the standard depreciation. PeopleSoft Asset Management does not support automatically generating journal entries for the special depreciation allowance accounting method. You may need to run two reports: Reserve for Special Depreciation and Reversal for Special Depreciation, and then generate the journal entries manually into the PeopleSoft General Ledger system. |
Note: Additional fields are provided to comply with the depreciation methods used in countries other than the U.S.
When you use additional terms, they affect depreciation calculations in the following ways:
|
Term |
Depreciation |
|---|---|
|
Special |
Depreciation × Rate |
|
Accelerated |
Depreciation × Rate |
|
Initial |
Cost × Rate |
|
Increase |
Depreciation × Rate |
Note: Year of Change(displayed from the ASSET_DPR_DETAILS page) is available only when the depreciation method is Japan-Change DB to SL.
Use the Asset Profiles - Inflation Information page (PROFILE_SEC) to establish an inflation adjustment factor by selecting the market index and rate to apply.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Inflation Information page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.

Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Market Rate Index |
Select the market rate index to be used for inflation processing. |
Rate Type |
Select the market rate type to be used for inflation processing. |
Term |
Select the term. |
Daily Rate Index |
Select the daily rate index. |
Daily Rate Type |
Select the daily rate type. |
Daily Term |
Select the daily term. |
Use the Salvage Rounding Options page (SALVAGE_OPTION_SEC) to enter options for rounding depreciation amounts for this book.
This is for use in Japan.
Navigation:
Click Salvage Rounding Options on the Asset Profile - Depreciation page.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Salvage_Rounding_Options. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
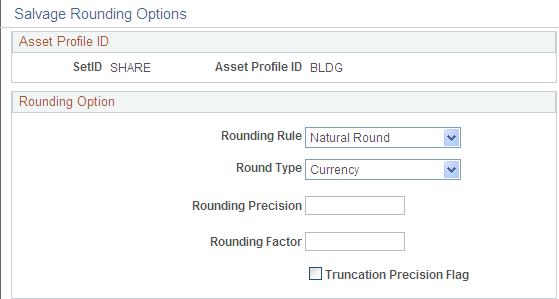
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Rounding Rule |
The rounding rules that are delivered with PeopleSoft Asset Management are: Down NatRnd Up |
Round Type |
The rounding types that are delivered with PeopleSoft Asset Management are: Currency Generic |
Rounding Precision |
Enter the number of places to the right or left of the decimal point to which the amount or number will be rounded. If you select Currency as the round type, the system automatically determines the round precision from the currency code. |
Rounding Factor |
Enter the number to which the amount will be rounded. For example, if you select Nat Rnd as the rounding rule, and enter a rounding factor of 25, amounts will be rounded to the nearest multiple of 25 so that an amount of 130 will be rounded to 125, and an amount of 140 will be rounded to 150. If you select Currency as the round type, the system will automatically determine the rounding factor from the currency code. |
Truncation Precision Flag |
Works with the round precision value. When you select it, amounts that contain many decimal places will be truncated to one decimal place to the right of the rounding precision position before rounding is performed. If you do not select it, the entire amount will be rounded. This example illustrates truncation precision:
With Truncation Precision Flag selected, the system truncates the fifth decimal place and rounds 10.0343. Without the check box selected, the system rounds the entire amount. Actual rounding results depend on the selected rounding rule and round type. |
See Understanding PeopleSoft Asset Management in Global Settings.
Use the Asset Profiles - Tax page (PROFILE_BK_03) to specify property type and tax depreciation criteria and identify which tax credits will be used by the profile.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Asset Profiles - Tax page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
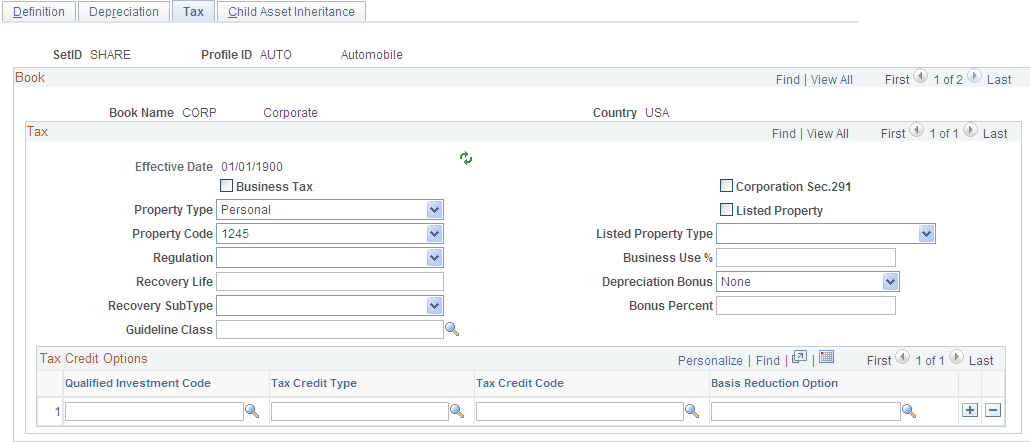
Note: Asset tax attributes primarily address Unites States tax issues except where noted.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Property Type and Property Code |
Determine the amount of gain treated as ordinary income on the disposition of this asset. |
Regulation |
Identifies the depreciation system elected for this asset:
|
Recovery Life and Recovery Subtype |
For reporting purposes, you can further classify the asset by specifying the recovery life expressed in years and the recovery subtype, for example, 15-Year Low-Income Housing. You can also specify the asset guideline class. All current classifications are set up in the Tax Class table in the delivered tableset. |
(IND) Guideline Class |
Processing tax and depreciation in India requires the designation of a tax class rate that is associated with an asset block. To associate the tax class rate with a profile, enter the tax class and associated asset block rate here. |
Corporation Sec. 291 (corporation section 291) |
Select if this company is a corporation. This check box must be selected if the company is a corporation for the AMTX3210 tax report (Tax Retirement Capital Gains) to accurately reflect the correct Sec. 1231/Ordinary gains. |
(FRA) Business Tax |
Select if assets using this profile are subject to a business tax. This is required in some countries. |
Listed Property |
Select to record whether the asset is listed property. Listed property is a certain kind of asset that is conducive to mixed business or personal use, such as:
|
Listed Property Type |
Select the property type that corresponds to the Listed Property check box. |
Business Use % (business use percentage) |
Enter the percentage amount of the business use of this listed property asset. Based on the business use percentage that you enter, the basis calculated for depreciation is: (Basis) = (Cost*Bus_Use_%) |
(USA) Depreciation Bonus |
Select to indicate the specific depreciation bonus definition if the asset qualifies for depreciation bonus treatment. You can also create your own depreciation bonus definitions for selection in this field using the Depreciation Bonus Info page. See Defining Depreciation Bonus Information. PeopleSoft delivers the following values:
|
(USA) Bonus Percent |
Supply the amount (percentage) to be applied if the asset qualifies for a depreciation bonus based on the acquisition date and in-service date. |
Using Tax Credit Options
The rate and amount of the tax credit are based on federal tax law and determined by the qualified investment code, tax credit type and code, and basis reduction option in PeopleSoft Asset Management.
Select a qualified investment code if applicable:
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
A (accelerated): |
Accelerated Cost Recovery System (ACRS) |
D (depreciation): |
Asset Depreciation Range |
F (facts): |
Conventional Facts and Circumstances |
G (guidelines): |
Guideline |
M (modified): |
Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery (MACR) |
Select a tax credit type if applicable. In the U.S., certain business incentive credits can be taken:
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
R (rehabilitation): |
Rehabilitation Credit |
E (energy): |
Energy Credit |
I (investment): |
Regular Investment Credit |
U (user): |
User-defined |
The tax credit code further defines the tax credit. For example, a 20 percent rehabilitation tax credit is available for historic buildings. Some credits require a corresponding reduction in the cost basis of the asset.
The basis reduction option indicates whether a reduction in the cost basis is required. Three codes are provided:
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
B (basis): |
Basis Reduction |
P (percentage): |
Percentage Rate Reduction |
N (no): |
No Reduction |
Use the Asset Profile - Child Asset Inheritance page (PROFILE_PAR_BK_ECD) to specify child asset attributes that will be used by the profile and inherited from the parent asset for Express Add, Basic Add, and batch-created assets.
The inheritance based on the selected items happens upon defaulting the profile in Express Add and capitalizing the asset in Basic Add, and when you are using Default Profile processing in the Transaction Loader if the Business Unit option is selected.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Asset Profiles - Child Asset Inheritance page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.

Select the attributes and other information that the child asset inherits from the parent asset.