- Security Configuration Guide
- Configuring User Directories
- Configuring OID, Active Directory, and Other LDAP-based User Directories
Configuring OID, Active Directory, and Other LDAP-based User Directories
System Administrators use the procedures in this section to configure LDAP-based corporate user directories, such as OID, Sun Java System Directory Server, Oracle Virtual Directory, Active Directory, IBM Tivoli Directory Server, or an LDAP-based user directory that is not listed on the configuration screen.
To configure OID, Active Directory, and other LDAP-based user directories:
- Access Oracle Hyperion Shared Services Console as System Administrator. See Launching Shared Services Console.
- Select Administration, and then Configure User Directories.
The Provider Configuration tab opens. This screen lists all configured user directories, including Native Directory.
- Click New.
- Under Directory Type, select an option:
-
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) to configure an LDAP-based user directory other than Active Directory. Select this option to configure Oracle Virtual Directory.
-
Microsoft Active Directory (MSAD) to configure Active Directory.
Active Directory and Active Directory Application Mode (ADAM) only: If you want to use a custom ID attribute (an attribute other than
ObjectGUID; for examplesAMAccountNamewith Active Directory or ADAM, select Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), and configure it as Directory TypeOther.
-
- Click Next.
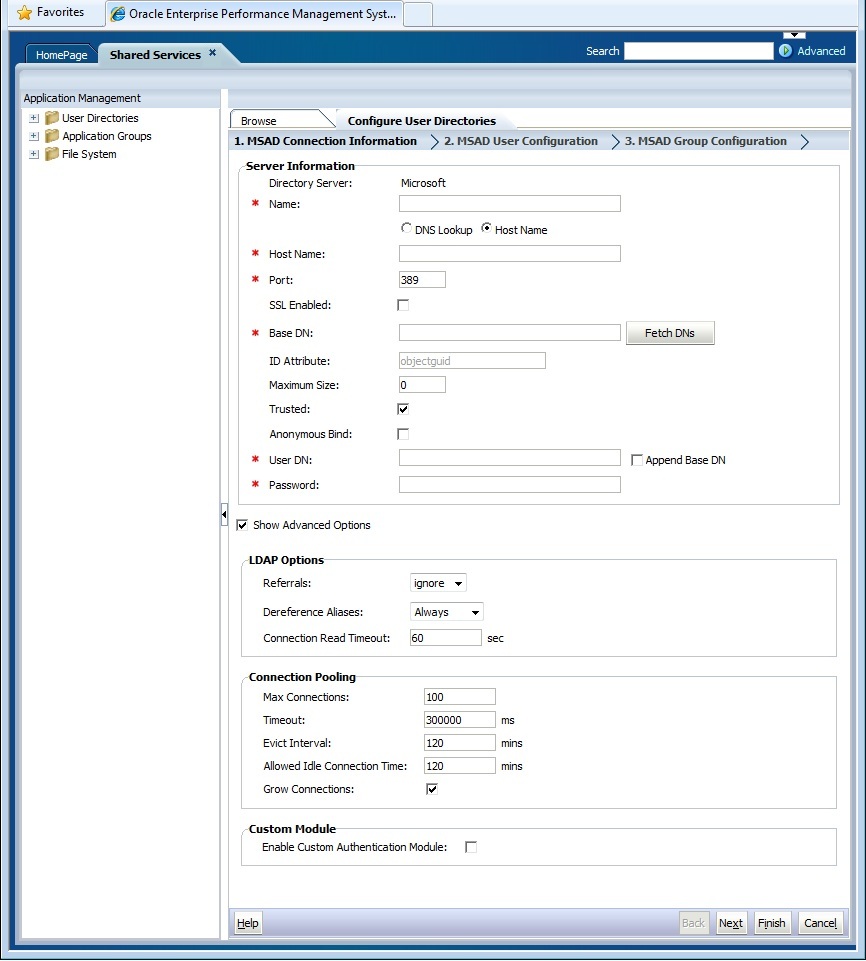
- Enter the required parameters.
Table 4-1 Connection Information Screen
Label Description Directory Server Select a user directory. The ID Attribute value changes to the recommended constant unique identity attribute for the selected product.
This property is automatically selected if you chose Active Directory in step 4.
Select
Otherin the following scenarios:-
You are configuring an unlisted user directory type; for example, Oracle Virtual Directory
-
You are configuring a listed LDAP-enabled user directory (for example, OID), but want to use a custom ID Attribute.
-
You are configuring Active Directory or ADAM to use a custom ID Attribute.
Note:
Because Oracle Virtual Directory provides a virtualized abstraction of LDAP directories and RDMBS data repositories in one directory view, Oracle Enterprise Performance Management System considers it a single external user directory regardless of the number and type of user directories Oracle Virtual Directory supports.
Example:
Oracle Internet DirectoryName A descriptive name for the user directory. Used to identify a specific user directory if multiple user directories are configured. Name should not contain special characters other than space and underscore. Example:
Corporate_OIDDNS Lookup Active Directory only: Select this option to enable DNS lookup. See DNS Lookup and Host Name Lookup. Oracle recommends that you configure DNS lookup as the method to connect to Active Directory in production environments to avoid connection failures. When you select this option, the following fields are displayed:Note:
Do not select this option if you are configuring a global catalog.
-
Domain: The domain name of an Active Directory forest.
Examples:
example.comorus.example.com -
AD Site: Active Directory site name, generally the relative distinguished name of the site object that is stored in Active Directory configuration container. Typically, AD Site identifies a geographic location such as a city, state, region, or country.
Examples:
Santa ClaraorUS_West_region -
DNS Server: DNS name of the server that supports DNS server lookup for domain controllers.
Host Name Active Directory only: Select this option to enable static host name lookup. See DNS Lookup and Host Name Lookup. Note:
Select this option if you are configuring an Active Directory global catalog.
Host Name DNS name of the user directory server. Use the fully qualified domain name if the user directory is to be used to support SSO from SiteMinder. Oracle recommends using the host name to establish an Active Directory connection for testing purposes only. Note:
If you are configuring an Active Directory global catalog, specify the global catalog server host name. See Global Catalog.
Example:
MyServerPort The port number where the user directory is running. Note:
If you are configuring an Active Directory global catalog, specify the port used by the global catalog server (default is 3268). See Global Catalog.
Example:
389SSL Enabled The check box that enables secure communication with this user directory. The user directory must be configured for secure communication. Base DN The distinguished name (DN) of the node where the search for users and groups should begin. You can also use the Fetch DNs button to list available base DNs and then select the appropriate base DN from the list. Note:
If you are configuring a global catalog, specify the base DN of the forest.
See Using Special Characters for restrictions on the use of special characters.
Oracle recommends that you select the lowest DN that contains all EPM System product users and groups.
Example:
dc=example,dc=comID Attribute This attribute value can be modified only if
The recommended value of this attribute is automatically set for OIDOtheris selected in Directory Type. This attribute must be a common attribute that exists in user and group objects on the directory server.orclguid, SunONE (nsuniqueid), IBM Directory Server (Ibm-entryUuid), Novell eDirectory (GUID), and Active Directory (ObjectGUID).Example:
The ID attribute value, if you set it manually after choosingorclguidOtherin Directory Server; for example to configure an Oracle Virtual Directory, should:-
Point to a unique attribute
-
Not be location specific
-
Not change over time
Maximum Size The maximum number of results that a search can return. If this value is greater than that supported by the user directory settings, the user directory value overrides this value. For user directories other than Active Directory, leave this field blank to retrieve all users and groups that meet the search criteria.
For Active Directory, set this value to
If you are configuring Oracle Hyperion Shared Services in Delegated Administration mode, set this value to 0.0to retrieve all users and groups that meet the search criteria.Trusted The check box to indicate that this provider is a trusted SSO source. SSO tokens from trusted sources do not contain the user's password. Anonymous Bind The check box to indicate that Shared Services can bind anonymously to the user directory to search for users and groups. Can be used only if the user directory allows anonymous binds. If this option is not selected, you must specify in the User DN an account with sufficient access permissions to search the directory where user information is stored. Oracle recommends that you not use anonymous bind.
Note:
Anonymous bind is not supported for OID.
User DN This option is disabled if Anonymous Bind is selected.
The distinguished name of the user that Shared Services should use to bind with the user directory. This user must have search privileges on the RDN attribute within the DN. For example, in the dn:cn=John Doe, ou=people, dc=myCompany, dc=com, the bind user should have search access to thecnattribute.Special characters in User DN must be specified using escape characters. See Using Special Characters for restrictions.
Example:
cn=admin,dc=myCompany,dc=comAppend Base DN The check box for appending the base DN to the User DN. If you are using Directory Manager account as the User DN, do not append Base DN.
This check box is disabled if the Anonymous Bind option is selected.
Password User DN password This box is disabled if the Anonymous Bind option is selected.
Example:
UserDNpasswordShow Advanced Options The check box to display advanced options. Referrals Active Directory only: If Active Directory is configured to follow referrals, select
followto automatically follow LDAP referrals. Selectignoreto not use referrals.Dereference Aliases Select the method that Shared Services searches should use to dereference aliases in the user directory so searches retrieve the object to which the DN of the alias points. Select: -
Always: Always dereference aliases.
-
Never: Never dereference aliases.
-
Finding: Dereference aliases only during name resolution.
-
Searching: Dereference aliases only after name resolution.
Connection Read Timeout Interval (seconds) after which the LDAP provider aborts the LDAP read attempt if it does not get a response. Default: 60 seconds
Max Connections Maximum connections in the connection pool. Default is 100 for LDAP-based directories, including Active Directory. Default: 100
Timeout Timeout to get a connection from the pool. An exception is thrown after this period. Default: 300000 milliseconds (5 minutes)
Evict Interval Optional: The interval for running the eviction process to clean the pool. The eviction process removes idle connections that have exceeded the Allowed Idle Connection Time.Default: 120 minutes
Allowed Idle Connection Time Optional: The time after which the eviction process removes the idle connections in the pool. Default: 120 minutes
Grow Connections This option indicates whether the connection pool can grow beyond Max Connections. Selected by default. If you do not allow the connection pool to grow, the system returns an error if a connection is not available within the time set forTime Out.Enable Custom Authentication Module The check box to enable the use of a custom authentication module to authenticate users defined in this user directory. You must also enter the fully qualified Java class name of the authentication module in the Security Options screen. See Setting Security Options. The custom authentication module authentication is transparent to thin and thick clients and does not require client deployment changes. See "Using a Custom Authentication Module" in the Oracle Enterprise Performance Management System Security Configuration Guide.
-
- Click Next.
Shared Services uses the properties set on the User Configuration screen to create a user URL that is used to determine the node where search for users begins. Using this URL speeds the search.
Caution:
The user URL should not point to an alias. EPM System security requires that the user URL point to an actual user.
Oracle recommends that you use the Auto Configure area of the screen to retrieve the required information.
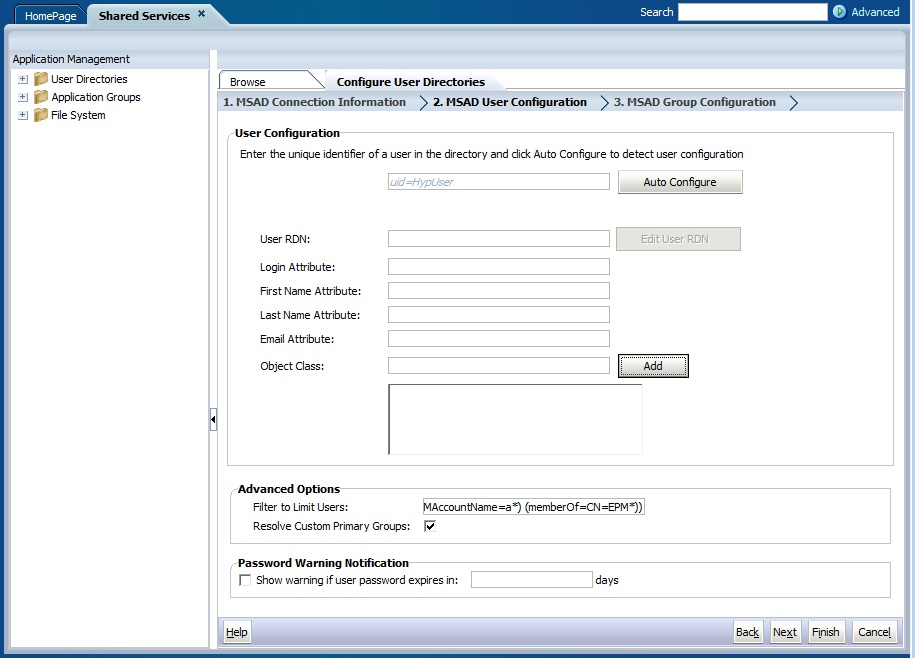
Note:
See Using Special Characters for a list of special characters that can be used in the user configuration.
- In Auto Configure, enter a unique user identifier using the format
attribute=identifier; for example,uid=jdoe.Attributes of the user are displayed in the User Configuration area.
If you are configuring OID, you cannot automatically configure the user filter, because the root DSE of OID does not contain entries in the Naming Contexts attribute. See Managing Naming Contexts in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Internet Directory.
Note:
You can manually enter required user attributes into text boxes in the User Configuration area.
Table 4-2 User Configuration Screen
Label DescriptionFoot 1 User RDN The Relative DN of the user. Each component of a DN is called an RDN and represents a branch in the directory tree. The RDN of a user is generally the equivalent of the uidorcn.See Using Special Characters for restrictions.
Example:
ou=PeopleLogin Attribute A unique attribute (can be a custom attribute) that stores the login name of the user. Users use the value of this attribute as the user name while logging into EPM System products. User IDs (value of Login Attribute) must be unique across all user directories. For example, you may use
uidandsAMAccountNamerespectively as the Login Attribute for your SunONE and Active Directory configurations. The values of these attributes must be unique across all user directories, including Native Directory.Note:
User IDs are not case sensitive.
Note:
If you are configuring OID as an external user directory for EPM System products deployed on Oracle Application Server in a Kerberos environment, you must set this property to
userPrincipalName.Default
- Active Directory:
cn - LDAP directories other than Active Directory:
uid
First Name Attribute The attribute that stores the user's first name Default:
givenNameLast Name Attribute The attribute that stores the user's last name Default:
snEmail Attribute Optional: The attribute that stores the user's email address Default:
mailObject Class Object classes of the user (the mandatory and optional attributes that can be associated with the user). Shared Services uses the object classes listed in this screen in the search filter. Using these object classes, Shared Services should find all users who should be provisioned.
Note:
If you are configuring Active Directory or ADAM as user directory type
Otherto use a custom ID attribute, you must set this value touser.You can manually add object classes if needed. To add an object class, enter the object class name into the Object Class box, and then click Add.
To delete object classes, select the object class and click Remove.
Default
- Active Directory:
user - LDAP directories other than Active Directory:
person, organizationalPerson, inetorgperson
Filter to Limit Users An LDAP query that retrieves only the users that are to be provisioned with EPM System product roles. For example, the LDAP query
(uid=Hyp*)retrieves only users whose names start withHyp.The User Configuration screen validates the User RDN and recommends the use of a user filter, if required.
The user filter limits the number of users returned during a query. It is especially important if the node identified by the user RDN contains many users that need not be provisioned. User filters can be designed to exclude the users that are not to be provisioned, thereby improving performance.
User Search Attribute for Multi-Attribute RDN LDAP-enabled user directories other than Active Directory only: Set this value only if your directory server is configured to use a multi-attribute RDN. The value you set must be one of the RDN attributes. The value of the attribute you specify should be unique and the attribute should be searchable. For example, assume that a SunONE directory server is configured to combine the cn (
cn=John Doe) and uid (uid=jDoe12345) attributes to create a multi-attribute RDN similar to the following:cn=John Doe+uid=jDoe12345, ou=people, dc=myCompany, dc=comIn this case, you can use either
cnoruidif these attributes meet the following conditions:-
The attribute is searchable by the user identified in User DN filed on Connection Information tab
-
The attribute requires you to set a unique value across the user directory
Resolve Custom Primary Groups Active Directory only: The check box that indicates whether to identify primary groups of users to determine effective roles. This check box is selected by default. Oracle recommends that you not change this setting. Show warning if user password expires in: Active Directory only: The check box that indicates whether to display a warning message if the Active Directory user password expires within the specified number of days. Footnote 1 EPM System security may use default values for some fields for which configuration value is optional. If you do not enter values in such fields, default values are used during runtime.
- Active Directory:
- Click Next.
The Group Configuration screen opens. Shared Services uses the properties set in this screen to create the group URL that determines the node where the search for groups starts. Using this URL speeds the search.
Caution:
The Group URL should not point to an alias. EPM System security requires that the group URL point to an actual group. If you are configuring a Novell eDirectory that uses group aliases, the group aliases and group accounts must be available within the group URL.Note:
Data entry in the Group Configuration screen is optional. If you do not enter the group URL settings, Shared Services searches within the Base DN to locate groups, which can negatively affect performance, especially if the user directory contains many groups.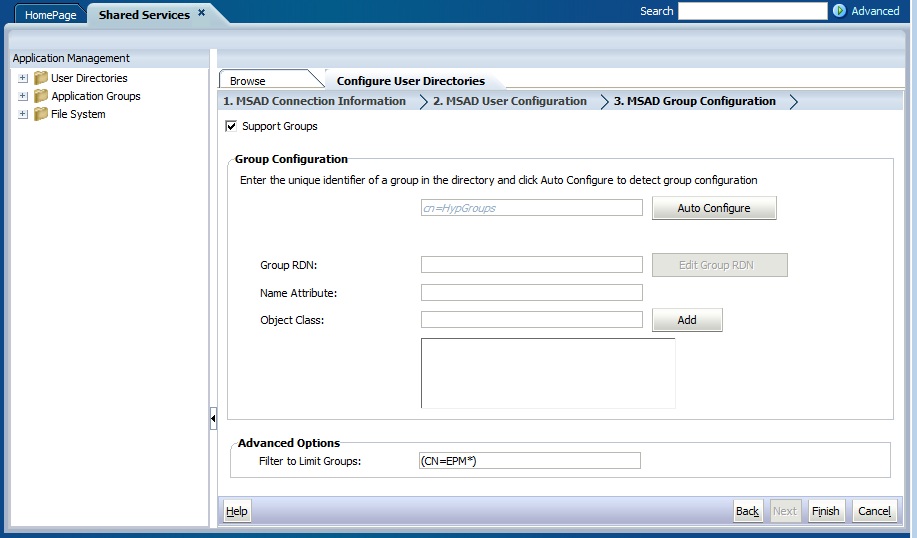
- Clear Support Groups if your organization does not plan to provision groups, or if users are not categorized into groups on the user directory. Clearing this option disables the fields on this screen.
If you are supporting groups, Oracle recommends that you use the autoconfigure feature to retrieve the required information.
If you are configuring OID as a user directory, you cannot use the autoconfigure feature, because the root DSE of OID does not contain entries in the Naming Contexts attribute. See Managing Naming Contexts in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Internet Directory.
- In the Auto Configure text box, enter a unique group identifier, and then click Go.
The group identifier must be expressed in
attribute=identifierformat; for example,cn=western_region.Attributes of the group are displayed in the Group Configuration area.
Note:
You can enter required group attributes in the Group Configuration text boxes.
Caution:
If the group URL is not set for user directories that contain / (slash) or \ (backslash) in its node names, the search for users and groups fails. For example, any operation to list the user or group fails if the group URL is not specified for a user directory in which users and groups exist in a node, such asOU=child\ou,OU=parent/ouorOU=child/ou,OU=parent \ ou.Table 4-3 Group Configuration Screen
Label DescriptionFoot 2 Group RDN The Relative DN of the group. This value, which is path relative to the Base DN, is used as the group URL. Specify a Group RDN that identifies the lowest user directory node in which all the groups that you plan to provision are available.
If you use an Active Directory primary group for provisioning, ensure that the primary group falls under the Group RDN. Shared Services does not retrieve the primary group if it is outside the scope of the group URL.
The Group RDN has a significant impact on login and search performance. Because it is the starting point for all group searches, you must identify the lowest possible node in which all groups for EPM System products are available. To ensure optimum performance, the number of groups present within the Group RDN should not exceed 10,000. If more groups are present, use a group filter to retrieve only the groups that you want to provision.
Note:
Shared Services displays a warning if the number of available groups within the Group URL exceeds 10,000.
See Using Special Characters for restrictions.
Example:
ou=GroupsName Attribute The attribute that stores the name of the group Default
-
LDAP directories including Active Directory:
cn -
Native Directory:
cssDisplayNameDefault
Object class Object classes of the group. Shared Services uses the object classes listed in this screen in the search filter. Using these object classes, Shared Services should find all groups associated with the user.
Note:
If you are configuring Active Directory or ADAM as user directory type
Otherto use a custom ID attribute, you must set this value togroup?member.You can manually add object classes if needed. To add an object class, enter the object class name into the Object class text box, and then click Add.
To delete object classes, select the object class, and then click Remove.
Default
-
Active Directory:
group?member -
LDAP directories other than Active Directory:
groupofuniquenames?uniquemember, groupOfNames?member -
Native Directory:
groupofuniquenames?uniquemember, cssGroupExtend?cssIsActive
Filter to Limit Groups An LDAP query that retrieves the groups that are to be provisioned with EPM System product roles only. For example, the LDAP query
(|(cn=Hyp*)(cn=Admin*))retrieves only groups whose names start withHyporAdmin.The group filter, used to limit the number of groups returned during a query, is especially important if the node identified by the Group RDN contains a large number of groups that need not be provisioned. Filters can be designed to exclude the groups that are not to be provisioned, improving performance.
If you use Active Directory primary group for provisioning, ensure that any group filter that you set can retrieve the primary group contained within the scope of the group URL. For example, the filter
(|(cn=Hyp*)(cn=Domain Users))retrieves groups that have names that start withHypand the primary group namedDomain Users.Footnote 2 EPM System security may use default values for some fields for which configuration value is optional. If you do not enter values in such fields, default values are used during runtime.
-
- Click Finish.
Shared Services saves the configuration and returns to the Defined User Directories screen, which now lists the user directory that you configured.
- Test the configuration. See Testing User Directory Connections.
- If needed, change the search order assignment. See Managing the User Directory Search Order for details.
- If needed, specify security options. See Setting Security Options for details.
- Restart Oracle Hyperion Foundation Services and other EPM System components.