Service Maintenance of Autonomous AI Database on Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure
Oracle schedules and performs all patching and other maintenance operations on all the Autonomous AI Database resources of on Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure. At the same time, it provides you with various options to customize, view, and reschedule maintenance events for the different infrastructure resources.
Note:
With Database In-Memory enabled, you may experience performance degradation during any patching activity that results in rebooting the database. For additional information on Database In-Memory, see Database In-Memory.
Related Topics
Service Maintenance Types
Oracle schedules and performs different service maintenance activities on your Autonomous AI Database. These maintenance events vary in their scope and frequency of patching.
- Quarterly Maintenance Patches: In general, Oracle schedules and performs entire fleet maintenance spread throughout each quarter.
- Quarterly maintenance patches are applied at various resource levels such as Exadata Infrastructure, Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster (AVMC), and Autonomous Container Database (ACD). The quarterly maintenance window can be set while creating these infrastructure resources or changed later.
- You can let Oracle handle maintenance scheduling, or you can set a specific maintenance window when Oracle can begin maintenance operations.
- By default, Oracle applies Release Updates (RUs) along with these quarterly maintenance patches. You can configure to update RU in a Rolling or Non-Rolling maintenance method.
- The Rolling method updates the ACD, one node at a time, with no downtime for the Autonomous AI Databases.
- The Non-rolling method shuts down and updates the ACD in parallel across all nodes. This method minimizes maintenance time but it requires full downtime for the ACD and all associated Autonomous AI Databases.
Note:
In an Autonomous Data Guard configuration, the non-rolling maintenance method results in downtime for the primary and standby ACDs during their respective maintenance window until the patching completes.
- You can also include the time-zone file to be updated along with the RU. Quarterly maintenance patches that include a time-zone file update would require a complete downtime for the ACD and the associated Autonomous AI Databases. The downtime is dependent on the amount of data that is time-zone sensitive.
- Quarterly maintenance patches without a time-zone file update can be applied in a rolling or non-rolling method, depending on the maintenance configuration of the Autonomous Container Database (ACD).
- Monthly Security Patches:
- Exadata Infrastructure Security Patches: Oracle schedules and performs a monthly infrastructure security maintenance activity alongside quarterly maintenance. However, these security patches are applied only in those months with critical security updates, including fixes for vulnerabilities with CVSS scores greater than or equal to 7.
- Any Exadata Infrastructure provisioned before Oracle schedules the security maintenance, will be eligible for security maintenance.
- The monthly security maintenance process updates database servers to fix critical security vulnerabilities and product issues. They also update storage servers to an Exadata Storage Software image that resolves known security vulnerabilities and product issues.
- Autonomous VM Cluster Security Patches: Oracle performs monthly security maintenance for Autonomous VM Clusters in addition to the regular quarterly updates. These patches are only applicable for GOV regions.
- Monthly security patches are applied using the rolling method.
- The first month of each quarter includes quarterly patches; the following two months include monthly security patches.
- To ensure patches are applied, you must select all three months of the quarter and specify a preference for Week 3 and/or Week 4.
- Exadata Infrastructure Security Patches: Oracle schedules and performs a monthly infrastructure security maintenance activity alongside quarterly maintenance. However, these security patches are applied only in those months with critical security updates, including fixes for vulnerabilities with CVSS scores greater than or equal to 7.
- One-off Patches: Oracle generates one-off patches for critical support requests filed with My Oracle Support. For help with filing a support request, see Create a Service Request in My Oracle Support .
- When you and Oracle agree that a service request is critical and requires a one-off patch for immediate resolution, the service team generates a one-off patch and makes it available. One-off patches are separate from scheduled maintenance patches.
- If you enable Oracle Cloud notifications and events with a rule to receive notifications regarding new updates, then when one-off patches become available, Oracle sends a notification that contains the OCID of the product to be patched. Otherwise, you can find the update availability notice in the My Oracle Support portal for the support request that you filed.
- The one-off patches are forward merged into the next Release Update (RU) to ensure that:
- A one-off fix delivered for a particular customer is available to all the customers.
- The subsequent versions do not need to apply one-off patches again.
- If required, an RU can have multiple one-off patches merged with it. As of the current release, the one-off patches are not cumulative, and therefore, you must apply them individually. If a one-off patch is too close to the subsequent RU, a custom version of the RU with the one-off fix is created for the next quarter.
- Suppose a one-off fix that is not merged into the latest RU is scheduled, and you choose to apply the next RU. Then, Oracle cancels the scheduled one-off patch. You can view the canceled maintenance runs in the maintenance history. All the one-off patching details logged into the maintenance history are available in downloads and audit and logging services.
- If needed, a one-off patch can be rolled back via a service request.
- The number of one-off patches available for an Autonomous Container Database is shown on its Details page. Clicking the Copy link next to it copies all those one-off patch numbers.
Specify When Maintenance Can Occur
In general, Oracle schedules and performs entire fleet maintenance spread throughout each quarter and monthly infrastructure security fixes for vulnerabilities with CVSS scores greater than or equal to 7. You can let Oracle handle maintenance scheduling, or you can set a specific maintenance window when Oracle can begin maintenance operations.
Customizing Quarterly Maintenance
You either choose a schedule for quarterly automatic maintenance of the Autonomous AI Database resources or let Oracle schedule the updates automatically. In advance, Oracle notifies you of the date and time of upcoming scheduled maintenance.
You can perform the following with automatic quarterly maintenance at various resource levels, as listed in the table below:
- Customize the automatic maintenance preferences and schedule. You can set these preferences while provisioning the Autonomous AI Database resources or change them later.
- View and change the schedule at any point before the beginning of the scheduled maintenance. Changes made to the scheduled maintenance for subsequent quarters do not affect the schedule for the current quarter.
- View the past maintenance events.
| Infrastructure Resource | Notes & Further Reference |
|---|---|
|
Exadata Infrastructure (EI) |
|
|
Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster (AVMC) |
Note: AVMC resources provisioned on the Exadata Infrastructure resources in Oracle Cloud before the launch of the multiple VM Autonomous AI Database feature inherit the maintenance schedule from its associated Exadata Infrastructure. |
|
Autonomous Container Database (ACD) |
|
Tip:
Oracle recommends that you set a maintenance window for all the infrastructure resources listed above to:- Prevent maintenance operations from occurring at times that would be disruptive to regular database operations.
- Patch your infrastructure resources in a staggered manner. Staggering the maintenance events for different infrastructure resources is a best practice and can help you verify the patch on a set of resources before patching another. For example, when you are using different Autonomous Container Databases for development, and testing and you want to verify the patches on your development environment before applying them to production, you can customize their maintenance schedules so that all your development ACDs are patched before the production ACDs.
Settings in Maintenance Schedule that are Customizable
You can choose the following details from the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console while defining a custom schedule for any of the above infrastructure resources.
-
Permitted Months: You must select at least one month per quarter, and you can also choose to skip patching for a quarter. Patching cannot be skipped for two consecutive quarters.
Note:
When you choose to skip, you need to select at least one month from that quarter. This acts as a fallback in case maintenance did not occur in the previous un-skipped quarter. In this scenario, Oracle will automatically perform the maintenance in the selected month, even if skipping is chosen for that quarter. -
Week (or Weeks) Within the Selected Months: Weeks start on the 1st, 8th, 15th, and 22nd days of the month and have a duration of 7 days. Weeks start and end based on calendar dates, not days of the week. Maintenance cannot be scheduled for the fifth week of months that contain more than 28 days. If you do not specify a week of the month, Oracle will assign a week automatically.
-
Day (or Days) of the Selected Week:
If you do not specify a day of the week, Oracle will run the maintenance update on a day that it assigns automatically.
As the weeks begin and end based on calendar dates and not on days of the week, you must pay extra attention while choosing the days if you want to ensure a specific sequence in patching your Exadata Infrastructure (EI). For example, observe the two months shown below:
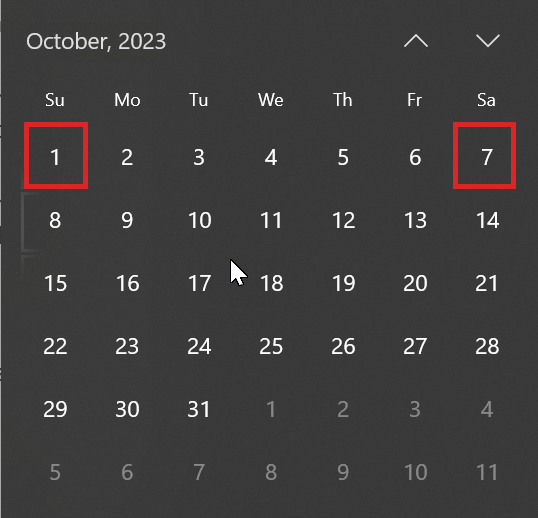
Description of the illustration dayofweek2.pngFor September 2023, week 1 begins on a Friday and ends on a Thursday. So, its first Saturday comes a day before its first Sunday. However, week 1 in October 2023 begins on a Sunday and ends on a Saturday. As a result, its first Saturday comes five days after its first Sunday.
Suppose you wish to patch all the Exadata Infrastructure resource before patching its Autonomous Container Databases (ACDs) to maintain a specific sequence for maintenance. Scheduling the maintenance of the Exadata Infrastructure resource on week 1 Saturday and its ACDs on week 1 Sunday assuming that week 1 Sunday always comes a day after week 1 Saturday may work for a few months such as September 2023 but not others like October 2023. If you want to implement a specific sequence for patching, it might be a better option to space them by a week. In this case, you can schedule your Exadata Infrastructure resource on week 1 Saturday and its ACDs on week 2 Sunday. Doing so will always ensure that your Exadata Infrastructure resource is patched before patching its ACDs.
-
4-Hour Window (or Windows) when maintenance operations can begin.
-
Buffer Period Between Primary and Standby Maintenance: Number of days between the standby ACD maintenance and the primary ACD maintenance, that is, how many days before maintenance on the primary container database is performed that maintenance on the standby container database is to be performed. You can choose any value from 1 to 7 days.
 Selecting the buffer period is applicable only to an Autonomous Container Database that is the primary database in an Autonomous Data Guard configuration.
Selecting the buffer period is applicable only to an Autonomous Container Database that is the primary database in an Autonomous Data Guard configuration.
- Lead Time: The minimum number of weeks ahead of the maintenance event you would like to receive a notification message. Your lead time ensures that a newly released maintenance update is scheduled to account for your required minimum period of advanced notification.
 Lead Time is not applicable for the maintenance of Autonomous Container Database resources.
Lead Time is not applicable for the maintenance of Autonomous Container Database resources.
- You can revert changes back to the default settings by selecting Reset to default.
Customizing Monthly Infrastructure Security Maintenance
Monthly infrastructure security maintenance, when needed, is scheduled to be applied during a 21-day window that begins between the 18th and 21st of each month and will run till the 9th to the 12th of the following month. You will receive notification of the proposed schedule at least 7 days before the start of the monthly maintenance window, and you can reschedule monthly maintenance to another date in the window if desired.
Monthly security patches can be rescheduled to another time within the maintenance window but cannot be skipped or rescheduled beyond the 21-day window. You can reschedule monthly security maintenance when rescheduling the quarterly maintenance as long as you keep the monthly within the current maintenance window.
There is no impact on the Autonomous AI Databases or applications connected to them during the monthly Infrastructure security patching activity. Updates to database servers are applied online via Ksplice technology, and updates to storage servers are applied in a rolling fashion.
However, while updating your service infrastructure, Oracle may block some operations, including memory, and storage scaling, operating system and Grid Infrastructure patching (including prechecks), and elastic expansion of compute and storage servers. Please plan to defer these operations until after the updates are complete. Application of security updates takes about 15 minutes per DB server host, plus 60 minutes per storage server, depending on the I/O activity. If you attempt an affected operation, the console will notify you of the ongoing security updates. No software is updated in the guest VMs.
Customizing One-off Patches
Using the Oracle Cloud Console Maintenance View, you can edit the scheduled start time or choose to install the one-off patch immediately. By default, Oracle schedules a one-off patch to be applied within 72 hours of the patch becoming available. If no action to change the schedule occurs, then the patch is automatically applied. You can reschedule the one-off patches only within the current quarter. However, you can not skip a one-off patch altogether.
Specify What Kind of Patches Apply
One standard maintenance operation is to apply database software patches to your Autonomous Container Databases and, by extension, the Autonomous AI Databases created in them. By default, Oracle applies Release Updates (RUs). You can configure the maintenance type to either Next RU to update the Autonomous Container Database to the next release update or the Latest RU to update Autonomous Container Database to the latest release update in the next maintenance window. Accordingly, Oracle will use an image type that meets your preference when available. You always have the option to change a given scheduled patch to a different version when desired.
For step-by-step guidance, see Update Autonomous Container Database Maintenance Preferences.
View and Manage Already Scheduled Maintenance
Once a maintenance activity is scheduled based on the maintenance window you set, you can manage the actual timing of the activity, even to the point of changing the patch version, applying the patch immediately, or skipping the activity.
Scheduled Maintenance Details
- The status of the event
- The type of the event, as Weekly, Quarterly, Monthly, or Yearly
- The OCID of the event
- The scheduled start time and date of the event
- The maintenance method of the event as Rolling on Non-Rolling. This is displayed only for an Exadata Infrastructure resource.
- The patch version to be applied in the event. This is displayed only for an Autonomous Container Database resource.
Management Operations on a Scheduled Maintenance
- Reschedule the start time and date of the event to a later time in the quarter. Specify the new start time and date in the Edit Maintenance Start Time window.
- Start the maintenance event immediately by clicking Patch Now.
Note:
Patch Now is not available for an Autonomous AI Database enabled with Autonomous Data Guard. As a workaround, you can modify the scheduled maintenance time to begin in the nearest 4 hour period available. Ensure that the standby is patched before the primary with a buffer period of 1 to 7 days between them. - Skip an Autonomous Container Database scheduled maintenance event.
Note:
You can not skip two consecutive maintenance events. After skipping a maintenance event, you can not skip the next immediate scheduled maintenance event; you can only skip the maintenance events for two alternate quarters in a year. - Select a different patch version to apply. When selecting a version, note the following:
- You must select a version that is later than the current version of the Autonomous Container Database.
- The list of available versions may contain both release updates (RUs) and release update revision (RURs). You can choose either type, regardless of the maintenance type configured for the Autonomous Container Database. Selecting a different type in the Version list does not change the type configured for the Autonomous Container Database.
- Update the Exadata Infrastructure maintenance method from Rolling to Non-rolling and vice-versa.
View Maintenance Status Notifications
The DB_NOTIFICATIONS view stores information about
maintenance status notifications for your Autonomous AI Database instance.
APPLIES TO: ![]() Oracle Public Cloud only
Oracle Public Cloud only
- Connect to your Autonomous AI Database instance.
- Use the following query to view maintenance (patching)
information.
SQL> SELECT * FROM DB_NOTIFICATIONS WHERE TYPE = 'MAINTENANCE';
The following provides details about the maintenance status.
-
Maintenance run has ended: Specifies maintenance has completed. The
STATUSshows the valueCOMPLETEDwith the start and end timestamps for the completed maintenance inACTUAL_START_DATEandACTUAL_END_DATE. -
Maintenance run is scheduled for the instance: Specifies a new maintenance has been scheduled. The
STATUSshows the valueSCHEDULEDwith the expected start and end timestamps for the scheduled maintenance inEXPECTED_START_DATEandEXPECTED_END_DATE. -
Maintenance run has begun: Specifies the maintenance is in progress and provides the start timestamp for the active maintenance. The
STATUSshows the valueIN_PROGRESSandACTUAL_START_DATEstores the start timestamp.
Table - The following table shows the DB_NOTIFICATIONS columns and datatypes.
| Column | Datatype | Description |
|---|---|---|
TYPE |
VARCHAR2(128)TYPE |
Specifies the type of the notification. Valid value is: |
TIME |
TIMESTAMP(6) WITH TIME ZONE |
Time when the notification entry was added. |
EXPECTED_START_DATE |
TIMESTAMP(6) WITH TIME ZONE |
Scheduled maintenance start time. |
EXPECTED_END_DATE |
TIMESTAMP(6) WITH TIME ZONE |
Scheduled maintenance endtime. |
ACTUAL_START_DATE |
TIMESTAMP(6) WITH TIME ZONE |
Actual maintenance start time. |
ACTUAL_END_DATE |
TIMESTAMP(6) WITH TIME ZONE |
Actual maintenance end time. |
PRODUCT |
VARCHAR2(128) |
Product/component for which maintenance is scheduled/ongoing. Values: |
STATUS |
VARCHAR2(128) |
Current status of the maintenance. Values: |
OP_MODE |
VARCHAR2(64) |
Patching operation mode. Values: |
DATABASE_IMPACT |
VARCHAR2(64) |
Database impact. Values: |
DESCRIPTION |
VARCHAR2(128) |
The notification message details. |
PATCH_ID |
VARCHAR2(128) |
Patch version. |
Automatic Queuing of Maintenance Events
Quarterly Maintenance Events of Different Autonomous AI Database Resources
If you choose a custom maintenance schedule for any infrastructure resources, Oracle honors your preference while scheduling the maintenance events. However, should your custom schedule create any overlap with other infrastructure resources, Oracle automatically serializes such that the maintenance events execute in this sequence with some time gap between them; Exadata Infrastructure, Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster, Autonomous Container Database.
Example: Suppose an Exadata Infrastructure resource maintenance event and an Autonomous Container Database maintenance event are scheduled to start simultaneously. In that case, the Exadata Infrastructure resource maintenance event starts, and the Autonomous Container Database maintenance event is queued and begins immediately after the Exadata Infrastructure resource maintenance event.
Quarterly Maintenance Events and Monthly Infrastructure Security Patches
| Scenario | Queuing |
|---|---|
| When a quarterly maintenance activity is scheduled within 24hours of a monthly infrastructure security patch. | The scheduled monthly maintenance will be skipped, and applied immediately following the quarterly maintenance. |
| When a quarterly maintenance activity is scheduled at the same time as a monthly infrastructure security patch. | The quarterly maintenance will be performed first, and the monthly security patch will be applied immediately following the completion of the quarterly maintenance. |
| When a monthly infrastructure security patch is scheduled to begin 0-24 hours ahead of the quarterly maintenance. |
The scheduled monthly maintenance will wait and will be performed immediately following the quarterly maintenance. If the quarterly maintenance is subsequently rescheduled, then the monthly security maintenance will begin immediately. Oracle, therefore, recommends scheduling quarterly and monthly maintenance at the same time. As a result, if you reschedule the quarterly maintenance event at the last moment, the monthly maintenance activity will run at the scheduled time upon editing the schedule. |
| When a quarterly maintenance is scheduled outside the 24-hour window of the security maintenance in the same month. |
You will need one maintenance window for quarterly maintenance and one maintenance window for security maintenance. Note: Any time before the scheduled monthly Exadata Infrastructure maintenance, you can reschedule it.The storage servers will only be updated once if you schedule the monthly security maintenance at least 25 hours before the quarterly maintenance in the month where both quarterly and monthly security maintenance has been scheduled. |
View Past Maintenance Events
You can view past maintenance of an Exadata Infrastructure, Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster, or an Autonomous Container Database resource from its Details page.
Monitor Service Maintenance Events
You can monitor your Autonomous AI Database infrastructure resources' maintenance events using the Events and Notifications services. Using the Events and Notifications services, you can get email notifications when maintenance events occur on Exadata Infrastructure, Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster, and Autonomous Container Database resources.
- Maintenance Scheduled
- Maintenance Reminder
For the Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster (AVMC) and Autonomous Container Database (ACD) resources, the maintenance reminder notification is sent 1 week before the actual maintenance run. For Exadata Infrastructure resources, the reminder notification is released between 1 to 4 weeks before the maintenance run, depending on the set preference.
- Maintenance Begin
- Maintenance End
For the complete list of events generated for each infrastructure resource, see Events for Autonomous AI Database on Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure.
- Create a notifications service topic.
- Add an email subscription to the topic.
- Add an events service rule to send maintenance events to the notifications service topic.
Example - Notifications: Emails for Maintenance Events
For a step-by-step guide with an example, see Notifications Example: Emails for Maintenance Events.