Service Lifecycle
This topic explains how services are created, configured, copied, and deleted. The service URLs explained are: Create URL, Configuration URL, Copy URL, and Delete URL. Sample code is provided for the implementation of each URL endpoint.
Important: This topic explains how app developers should develop their app service's URL endpoints, but app developers must register their service's URL endpoints in AMS by creating services before AMS can communicate with the app.
In this topic:
Overview
Services are self-contained components of apps that are used by marketers. The purpose of a service is to preform some isolated task (ie, fetching the weather). There can be many services within an app. A service instance is simply an instance of a service, that a marketer will use to perform a task. Service instances are designed to be created and to interact though a CX product. The primary purpose of service instances is for Invocation by a Product (ie. the process in which the app and product exchange data). A service instance is created when a marketer chooses an app's service, and creates an instance of that service within their CX product to perform a task.
Note: Before a service instance can be created, an app must first be installed and configured.
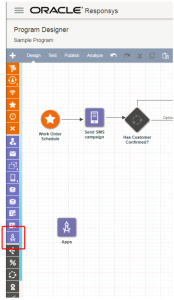
Using Oracle Responsys as an example, a marketer may drag an App Activity Stage into their program workflow.
The marketer configures the service according to the specific use case within their program workflow to perform a task.
This process is an example of how service instances are created.
Create URL endpoint
Overview
The purpose of the Create URL is to create a service instance. Using Oracle Responsys Action services as an example, the workflow resembles:
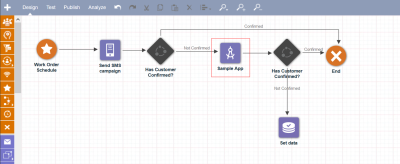
A marketer drags an App Activity stage onto a canvas and selects a service.
Responsys calls AMS, and AMS calls the service's Create URL endpoint to create a service on that canvas.
Service Create URL endpoint
AMS calls the service's Create URL endpoint with the following request.
Service URL
<service-baseUrl><service-createUrl>
Request Method
POST
Request Header
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
Content-Type=application/json
Bearer Token
JWT claims
When AMS is making the request to the App, the key and value pairs bear the following meanings:
| Key | Value Definition | Context |
|---|---|---|
iss
|
The issuer of the token. | Issuer is AMS |
sub
|
The subject of the token. | Set to the app's associated product uuid. |
aud
|
The audience of the token. | The App's Token Key. |
exp
|
The date and time the token will expire, expressed as a Unix timestamp. Must be after the current date/time. | Set to 60 seconds after the JWT was created. |
iat
|
The date and time the JWT was issued, expressed as a Unix timestamp. | Set to the current time. |
jti
|
The unique identifier for the JWT token. | Set to a random UUID |
o.a.p.ctenantId
|
The tenant Id. | Set to the id of the tenant as identified by the product |
o.a.p.cproductUUID
|
The product UUID. | Set to the product's UUID. |
o.a.p.cproductName
|
The product name. | Set to the product's name. |
o.a.p.csourceRequest
|
The source of the request. | Set to the product's UUID. |
o.a.p.cdestinationId
|
The destination Id. | Set to the app's token key (found in app details) |
o.a.p.cdestinationUrl
|
The destination URL. | Set to the service instance creation URL (the service's base URL + the service's create URL. These URLs are found in service details. |
Signature
Signed with an app's token secret.
Sample request
POST <service-base-url><service-create-url>
Authorization: Bearer<JWT>
{
"status": "CREATED",
"assetId": null,
"assetType": null,
"uuid": "4420fa19-e8f6-4cdf-9754-d876dea3002f",
"secret": "c4321e9f-19a7-48b2-9796-c21142c709c9-fb24667dde63-4b6a-99af-10b23122a6d0",
"recordDefinition": null,
"applicationServiceInstall": {
"uuid": "40fe3760-a487-4e89-8cf5-2d3e06977623",
"name": "Demo transform service for developer's test",
"description": "Demo transform service for developer's test",
"invokeUrl": "https://b3a3ba42.ngrok.io/CX-app-demo-1.0/rest/1.0/services/1/invoke",
"smallLogo": "https://www.iconexperience.com/_img/o_collection_png/green_dark_grey/48x48/plain/delivery_truck.png",
"mediumLogo": "https://www.iconexperience.com/_img/o_collection_png/green_dark_grey/128x128/plain/delivery_truck.png",
"largeLogo": "https://www.iconexperience.com/_img/o_collection_png/green_dark_grey/256x256/plain/delivery_truck.png",
"maxBatchSize": 200,
"application": {
"uuid": "b95d7bea-0154-47b8-81ca-ea4e35e784a9",
"name": "Demo App",
"description": "It is a demo app",
"baseUrl": "https://oap.p01.elqqa01.com/awesome-app",
"statusUrl": "/status",
"installUrl": "/install",
"configureUrl": "/configure",
"uninstallUrl": "/uninstall",
"saveConfigurationUrl": "/save",
"smallLogo": "https://images.martechadvisor.com/images/uploads/product_logos/Oracle%20Responsys.jpeg",
"mediumLogo": "https://images.martechadvisor.com/images/uploads/product_logos/Oracle%20Responsys.jpeg",
"largeLogo": "https://images.martechadvisor.com/images/uploads/product_logos/Oracle%20Responsys.jpeg",
"status": "UP",
"providerUuid": "9dbda2d4-e9ac-4aab-8886-be0402a662cb"
},
"serviceType": {
"name": "ACTIVITY",
"externalName": "Activity",
"description": "This service will ingest data and send it to an external service or process it to return back a status or modified data"
},
"installUuid": "05860261-2f24-4639-ae38-3616306e3f2d",
"productName": "Responsys",
"providerName": "ResponsysApps",
"status": "UP"
}
}
Tip: The JWT Token in the Authorization Header is generated by following the AMS to App token generation. For more information about this call, including authentication details, see the endpoint API reference.
Sample response in case of success
RESPONSE NOTES
- If the app is up, the app creates an instance and responds with success or failure
- If the app is not up, the app does not respond
{
"id": "4420fa19-e8f6-4cdf-9754-d876dea3002f",
"serviceId": "40fe3760-a487-4e89-8cf5-2d3e06977623",
"status": "CREATED",
"name": "Demo transform service for developer's test",
"iconUrl": "https://www.iconexperience.com/_img/o_collection_png/green_dark_grey/48x48/plain/delivery_truck.png"
}
Responsys expects to receive a data transfer object (DTO) describing the record definition. If the app responds back to AMS with a 2xx response status code, the service is created.
status and provide an error message per record, the app is expected to include at a minimum these parameters as they are required for setting a record's status and providing error detail when needed: inputParametersappcloud_row_correlation_id
outputParametersappcloud_row_correlation_idappcloud_row_statusappcloud_row_errormessage
App's response to the Create URL request
The service's Create URL endpoint may either send back an empty response or a default Record Definition.
Responding with an empty response
Here is an example implementation if the app wants to respond with an empty response.
Sample code for an empty response
@RequestMapping(value = "/create", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public ResponseEntity addServiceInstance(@RequestBody ServiceInstance serviceInstance) {
if (serviceInstance == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Empty Service Instance");
}
serviceInstanceService.addEntity(serviceInstance);
return new ResponseEntity<EmptyJsonResponseDTO>(new EmptyJsonResponseDTO(), HttpStatus.OK);
}
Responding with a default record definition
If the app wants to respond with a default record definition, here is an example implementation.
Sample code for a default record definition
@RequestMapping(value = "/create", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public ResponseEntity addServiceInstance(@RequestBody ServiceInstance serviceInstance) {
if (serviceInstance == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Empty Service Instance");
}
serviceInstanceService.addEntity(serviceInstance);
RecordDefinitionDTO recordDefinition = RecordDefinitionDTO.createDefaultDefinition(); //optional.
return new ResponseEntity<RecordDefinitionDTO>(recordDefinition, HttpStatus.OK);
}
Note: Both AMS and the app should save service instances and be in sync.
Sample Payload
Sample JSON payload for a record definition
If responding with a record definition, the record definition must resemble the following. See Record definitions for more information.
{
"inputParameters": [
{
"name": "appcloud_row_correlation_id",
"dataType": "Text",
"width": 40,
"unique": true,
"required": true,
"readOnly": null,
"minimumValue": null,
"maximumValue": null,
"possibleValues": null,
"format": null,
"resources": null
}
],
"outputParameters": [
{
"name": "appcloud_row_correlation_id",
"dataType": "Text",
"width": 40,
"unique": true,
"required": true,
"readOnly": null,
"minimumValue": null,
"maximumValue": null,
"possibleValues": null,
"format": null,
"resources": null
},
{
"name": "appcloud_row_status",
"dataType": "Text",
"width": 10,
"unique": null,
"required": true,
"readOnly": null,
"minimumValue": null,
"maximumValue": null,
"possibleValues": [
"success",
"warning",
"failure"
],
"format": null,
"resources": null
},
{
"name": "appcloud_row_errormessage",
"dataType": "Text",
"width": 5120,
"unique": null,
"required": null,
"readOnly": null,
"minimumValue": null,
"maximumValue": null,
"possibleValues": null,
"format": null,
"resources": null
}
]
}
Copy URL endpoint
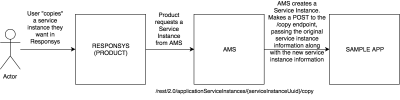
The purpose of the Copy URL endpoint is to copy an existing service instance and create a new service instance. AMS passes both the original service instance and the new service instance to the service's Copy URL. This is to enable the app developer the flexibility of storing or copying information (such as record definition) from the original service instance with the new service instance.
Note: If a Copy URL is not provided, AMS will treat copy as create, and call the app's Create URL instead.
Workflow
The following diagram illustrates the process of copying a service.
Service Copy URL endpoint
AMS calls the service's Copy URL endpoint with the following request.
Service URL
<service-baseUrl><service-copyUrl>
Request Method
POST
Request Header
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
Content-Type=application/json
Bearer Token
JWT claims
When AMS is making the request to the App, the key and value pairs bear the following meanings:
| Key | Value Definition | Context |
|---|---|---|
iss
|
The issuer of the token. | Issuer is AMS |
sub
|
The subject of the token. | Set to the app's associated product uuid. |
aud
|
The audience of the token. | The App's Token Key. |
exp
|
The date and time the token will expire, expressed as a Unix timestamp. Must be after the current date/time. | Set to 60 seconds after the JWT was created. |
iat
|
The date and time the JWT was issued, expressed as a Unix timestamp. | Set to the current time. |
jti
|
The unique identifier for the JWT token. | Set to a random UUID |
o.a.p.ctenantId
|
The tenant Id. | Set to the id of the tenant as identified by the product |
o.a.p.cproductUUID
|
The product UUID. | Set to the product's UUID. |
o.a.p.cproductName
|
The product name. | Set to the product's name. |
o.a.p.csourceRequest
|
The source of the request. | Set to the product's UUID. |
o.a.p.cdestinationId
|
The destination Id. | Set to the app's token key (found in app details) |
o.a.p.cdestinationUrl
|
The destination URL. | Set to the service instance creation URL (the service's base URL + the service's create URL. These URLs are found in service details. |
Signature
Signed with an app's token secret.
When a service instance is copied, AMS sends the following payload to the app:
POST <service-base-url><service-copy-url>
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
{
"originalApplicationServiceInstance": {
"status": "CREATED",
"assetId": "3iojr3d908",
"assetType": "campaign",
"uuid": "4420fa19-e8f6-4cdf-9754-d876dea3002f",
"secret": "c4321e9f-19a7-48b2-9796-c21142c709c9-fb24667dde63-4b6a-99af-10b23122a6d0",
"recordDefinition": {
//some valid record definition
...
},
"applicationServiceInstall": {
"uuid": "40fe3760-a487-4e89-8cf5-2d3e06977623",
"name": "Demo transform service for developer's test",
"description": "Demo transform service for developer's test",
"invokeUrl": "https://b3a3ba42.ngrok.io/CX-app-demo-1.0/rest/1.0/services/1/invoke",
"smallLogo": "https://www.iconexperience.com/_img/o_collection_png/green_dark_grey/48x48/plain/delivery_truck.png",
"mediumLogo": "https://www.iconexperience.com/_img/o_collection_png/green_dark_grey/128x128/plain/delivery_truck.png",
"largeLogo": "https://www.iconexperience.com/_img/o_collection_png/green_dark_grey/256x256/plain/delivery_truck.png",
"maxBatchSize": 200,
"application": {
"uuid": "b95d7bea-0154-47b8-81ca-ea4e35e784a9",
"name": "Demo App",
"description": "It is a demo app",
"baseUrl": "https://oap.p01.elqqa01.com/awesome-app",
"statusUrl": "/status",
"installUrl": "/install",
"configureUrl": "/configure",
"uninstallUrl": "/uninstall",
"saveConfigurationUrl": "/save",
"smallLogo":"https://images.martechadvisor.com/images/uploads/product_logos/Oracle%20Responsys.jpeg",
"mediumLogo":"https://images.martechadvisor.com/images/uploads/product_logos/Oracle%20Responsys.jpeg",
"largeLogo":"https://images.martechadvisor.com/images/uploads/product_logos/Oracle%20Responsys.jpeg",
"status": "UP",
"providerUuid": "9dbda2d4-e9ac-4aab-8886-be0402a662cb"
},
"serviceType": {
"name": "ACTIVITY",
"externalName": "Activity",
"description": "This service will ingest data and send it to an external service or process it to return back a status or modified data"
},
"installUuid": "05860261-2f24-4639-ae38-3616306e3f2d",
"productName": "Responsys",
"providerName": "ResponsysApps",
"status": "UP"
}
},
"newApplicationServiceInstance": {
"status": "CREATED",
"assetId": "k2lr4ijosd",
"assetType": "campaign",
"uuid": "8088b46e-93f3-4c71-b7c3-96a7d9dc9293",
"secret": "c8292396-2ab3-4bb8-b6de-f651d3704f6b-62d71c64-1de9-476a-ac34-4f7ac1cc300e",
"recordDefinition": null,
"applicationServiceInstall": {
"uuid": "40fe3760-a487-4e89-8cf5-2d3e06977623",
"name": "Demo transform service for developer's test",
"description": "Demo transform service for developer's test",
"invokeUrl": "https://b3a3ba42.ngrok.io/CX-app-demo-1.0/rest/1.0/services/1/invoke",
"smallLogo": "https://www.iconexperience.com/_img/o_collection_png/green_dark_grey/48x48/plain/delivery_truck.png",
"mediumLogo": "https://www.iconexperience.com/_img/o_collection_png/green_dark_grey/128x128/plain/delivery_truck.png",
"largeLogo": "https://www.iconexperience.com/_img/o_collection_png/green_dark_grey/256x256/plain/delivery_truck.png",
"maxBatchSize": 200,
"application": {
"uuid": "b95d7bea-0154-47b8-81ca-ea4e35e784a9",
"name": "Demo App",
"description": "It is a demo app",
"baseUrl": "https://oap.p01.elqqa01.com/awesome-app",
"statusUrl": "/status",
"installUrl": "/install",
"configureUrl": "/configure",
"uninstallUrl": "/uninstall",
"saveConfigurationUrl": "/save",
"smallLogo":"https://images.martechadvisor.com/images/uploads/product_logos/Oracle%20Responsys.jpeg",
"mediumLogo":"https://images.martechadvisor.com/images/uploads/product_logos/Oracle%20Responsys.jpeg",
"largeLogo":"https://images.martechadvisor.com/images/uploads/product_logos/Oracle%20Responsys.jpeg",
"status": "UP",
"providerUuid": "9dbda2d4-e9ac-4aab-8886-be0402a662cb"
},
"serviceType": {
"name": "ACTIVITY",
"externalName": "Activity",
"description": "This service will ingest data and send it to an external service or process it to return back a status or modified data"
},
"installUuid": "05860261-2f24-4639-ae38-3616306e3f2d",
"productName": "Responsys",
"providerName": "ResponsysApps",
"status": "UP"
}
}
}
Tip: The JWT Token in the Authorization Header is generated by following the AMS to App token generation. For more information about this call, including authentication details, see the endpoint API reference.
App's response to the Copy URL request
The service's Copy URL endpoint may either send back an empty response or a record definition. If the app responds with a 2xx response code, a service instance is created. It is up to the app developer to determine what they would like to store or copy from the original service instance.
Sample code for a record definition response
@RequestMapping(value = "/copy", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public ResponseEntity copyServiceInstance(@RequestBody ServiceInstanceCopyRequestDTO requestBody) {
ModelMapper mapper = new ModelMapper();
if (requestBody == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Empty payload sent to create url");
}
// See ModelMappingConfiguration.java for how ServiceInstance is populated from ServiceInstanceCreateRequestDTO
ServiceInstance newServiceInstance = mapper.map(requestBody.getNewInstance(), ServiceInstance.class);
// New service instance will copy the record definition from the original service instance.
newServiceInstance.setRecordDefinition(requestBody.getOriginalInstance().getRecordDefinition());
// New service instance will copy the configuration mappings stored by the app
ServiceInstance originalServiceInstance = serviceInstanceService.getEntity(
requestBody.getOriginalApplicationServiceInstance().getUuid());
newServiceInstance.setConfig(originalServiceInstance.getConfig());
newServiceInstance.setStatus(originalServiceInstance.getStatus());
serviceInstanceService.addEntity(newServiceInstance);
return new ResponseEntity<RecordDefinitionDTO>(newServiceInstance.getRecordDefinition(), HttpStatus.OK);
}
Note: Both AMS and the app should save service instances and be in sync.
Sample JSON payload for a record definition
If responding with a record definition, the record definition must resemble the following. See Record definitions for more information.
{
"inputParameters": [
{
"name": "appcloud_row_correlation_id",
"dataType": "Text",
"width": 40,
"unique": true,
"required": true,
"readOnly": null,
"minimumValue": null,
"maximumValue": null,
"possibleValues": null,
"format": null,
"resources": null
}
],
"outputParameters": [
{
"name": "appcloud_row_correlation_id",
"dataType": "Text",
"width": 40,
"unique": true,
"required": true,
"readOnly": null,
"minimumValue": null,
"maximumValue": null,
"possibleValues": null,
"format": null,
"resources": null
},
{
"name": "appcloud_row_status",
"dataType": "Text",
"width": 10,
"unique": null,
"required": true,
"readOnly": null,
"minimumValue": null,
"maximumValue": null,
"possibleValues": [
"success",
"warning",
"failure"
],
"format": null,
"resources": null
},
{
"name": "appcloud_row_errormessage",
"dataType": "Text",
"width": 5120,
"unique": null,
"required": null,
"readOnly": null,
"minimumValue": null,
"maximumValue": null,
"possibleValues": null,
"format": null,
"resources": null
}
]
}
Configure URL endpoint
Learn more by watching the video
Learn more by watching the video
Service Instance configuration is requested from the CX product to the app through AMS. The primary purpose of service instance configuration is to configure the app so that invocation can occur. This is a two fold process:
- The Application must provide AMS with a record definition so that AMS knows how to invoke the Application. A record definition is a set of input and output parameters so as to say that for these inputs, the app will return these outputs. This way, all parties (product, app, and AMS) understand what data will be sent and what data will be returned.
- Instance configuration allows the app to define a mapping between record definition fields (input/output parameters) to something meaningful within the app. For example, a CITY_ field in the product must be mapped to something like a City variable in the app so that the app can preform some operation with it. Both record definition and mapping configurations are done through service instance configuration.
Requirements:
- The app must provide an HTML configuration page that will be embedded within an iframe in AMS and will be displayed in the product.
- The app must implement two endpoints for service instance configuration: Configuration URL and Save Configuration URL.
Configuration Workflow
The following diagram illustrates the configuration workflow.
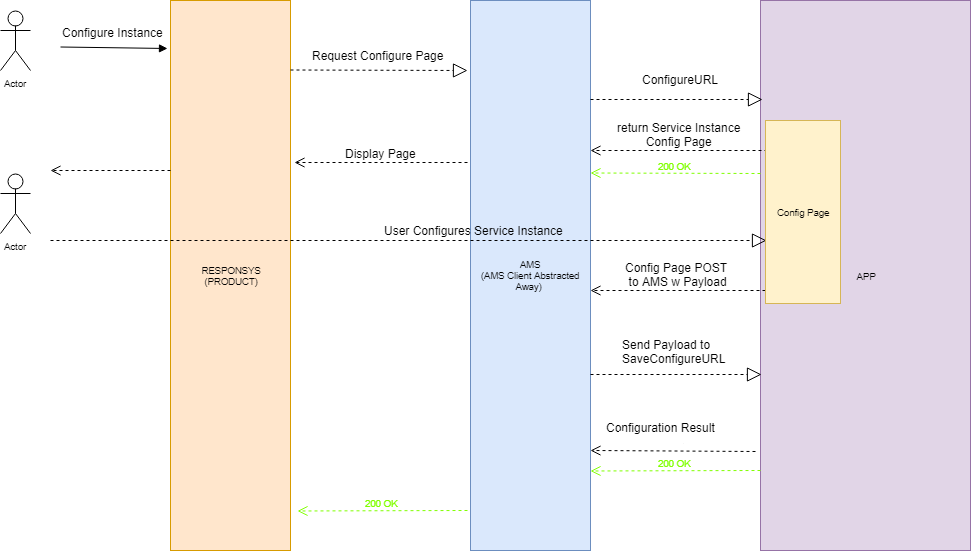
When a marketer configures a service instance, the Configuration URL is called. The workflow resembles these steps:
-
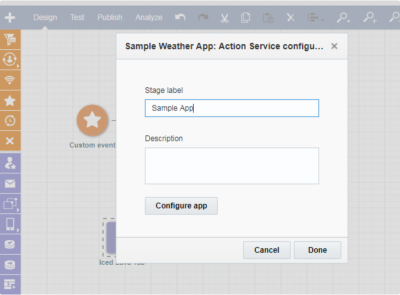
A marketer clicks an activity stage (the service instance) then clicks Configure app.
- Responsys calls AMS requesting the service configuration page.
- AMS calls the service's Configuration URL to display the configuration page in Responsys.
- Marketer completes configuration and clicks save.
- AMS calls the service's Save Configuration URL.
-
The app can respond to AMS.
The content of the response should have a record definition and a configured status which could either be ERROR or CONFIGURED. Optionally, a payload can also be sent back to the application service instance configuration UI.
- AMS will display success or failure to the marketer.
Configuration URL request
AMS calls the service's Configuration URL endpoint with the following request:
POST <service-base-url><service-configuration-url>
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
{
"uuid": "6ea036bb-8cfb-46c5-a826-d001d3a0349b",
"status": "CREATED",
"locale": "en-US",
"assetId": "23",
"assetType": "some asset"
}
Tip: The JWT Token in the Authorization Header is generated by following the AMS to App token generation. For more information about this call, including authentication details, see the endpoint API reference.
The payload will contain assetType, assetId, locale, and service instance uuid. The most important is the service instance UUID because this identifies the service instance that needs to be configured.
Apps' response to the Configuration URL request
The Configuration URL should return an HTML page that can be embedded in a iframe to be viewed from the product. It is up to the developer on the actual contents of the configuration page. There is a contract for the configuration page to postMessage to back to AMS with the results of the configuration.
Configuration URL Sample App Code
Below is a possible implementation of the Configuration URL endpoint. Mustache templates are used to generate HTML pages.
Sample Implementation: Configuration URL Endpoint - Controller
// ServiceInstanceController.java
@RequestMapping(value = "/configure", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public ModelAndView configureAppInstall(
@RequestBody ServiceInstanceConfigurationBodyDTO serviceInstance,
Map<String, Object> model) {
ServiceInstance instance = serviceInstanceService.getEntity(serviceInstance.getUuid());
if(instance == null) {
throw new EntityNotFoundException("Service Instance Not Found => " + serviceInstance.getUuid());
}
// Pull data from backend and use it to populate a configure template to be sent to the Product.
model.put("appHostName", hostname + port);
model.put("appInputParams", INPUT_FIELDS);
model.put("appOutputParams", OUTPUT_FIELDS);
return new ModelAndView("configure", model); //populates configure.html
}
Sample Implementation: Configuration URL Endpoint - UI
// configure.html - populated from java code and sent back to AMS.
// creates something like City -> CITY_ (Product Field)
// Country -> COUNTRY_ (Product Field)
// Humidity -> HUMIDITY_ (Product Field)
<h4 id="input-map-title">Select Input Parameters Mappings</h4><ul>
{{#appInputParams}}
<div class="row">
<h4>{{.}} => </h4>
<select id="{{.}}" name="{{.}}">
<option value="" selected disabled hidden>Choose a Product Field</option>
</select>
</div>
{{/appInputParams}}</ul>
Field Metadata Endpoint (fieldMetadataEndpoint)
The contract between the product and the app regarding the fields available on the product is defined by a product's fieldMetadataEndpoint. i.e. In order to find the fields for an entity (ie. a contact), the product must provide a public endpoint that the app can query to find the fields for an entity such as a contact. This endpoint is sent to AMS by the product and is saved as METADATA.fieldMetadataEndpoint.url in the AMS iframe. To get this, the configuration page can request the metadata via postMessage with an amsAction="metadata".
The metadata postMessage should resemble:
{
amsAction: 'metadata'
}
The metadata postMessage returns a payload in the AMS iframe. This payload resembles:
{
metadata: {
fieldMetadataEndpoint: {
url: "https://www.rsys.com/somethingvalid",
method: "GET"
}
}
}
Using the information from this payload, the app can now request for the fields to build the record definition for each service instance via the product postMessage (amsAction="product").
The product postMessage should resemble:
{
amsAction: 'product',
requestId: 'dfd33125-6923-4467-b659-97a174de5801'
destinationUrl: metadata.fieldMetadataEndpoint.url,
requestType: metadata.fieldMetadataEndpoint.method,
payload: {}
}
The response payload resembles:
{
statusCode: 200,
requestId: "dfd33125-6923-4467-b659-97a174de5801",
payload: "{
"objects": [
{
"name": "!!!!DM630",
"type": "Standard",
"fields": [
{
"name": "RIID_",
"dataType": "Text",
"width": 0,
"readOnly": true,
"format": null
},
{
"name": "CREATED_SOURCE_IP_",
"dataType": "Text",
"width": 255,
"readOnly": true,
"format": null
},
{
"name": "CUSTOMER_ID_",
"dataType": "Text",
"width": 255,
"readOnly": true,
"format": null
}
]
}]
}"
}
Configure Page postMessage to AMS
Once the user has finished entering input (ie. the customer ID) and clicks save, the app should listen to the postMessage from the parent iframe, which would be AMS. Refer to Configuration iframes to learn more about how you can save the configuration or close the configuration window.
Configure Page postMessage listener for Save Configuration URL
The configure page must also implement a listener for the response of the Save Configuration URL. This is to display configuration success or failure to the user.
Sample Implementation: Configure page postMessage listener
attachMessageListener() {
var messageHandlerFunction = this.handleMessage.bind(this);
window.addEventListener("message", messageHandlerFunction, false);
}
handleMessage(event) {
if(event && event.data) {
console.log("Received Event From AMS", event);
var data = event.data;
if(data.requestId == this.amsAction || data.configurationStatus){
this.receivedMessage = true;
var response = this.parseResponse ? this.parseResponse(data) : data;
this.handleMessageResponse(response);
}
}
}
Save Configuration URL endpoint
After the user has finished configuring the service instance, AMS will POST to the service's Save Configuration URL endpoint with the results from the user's configuration. The purpose of this endpoint is to take the configuration that the user has set and save it within the app. When AMS POSTs to the service's Save Configuration URL endpoint, the payload includes:
- An
instanceUuid. Used to tie the configuration changes with the service instance. - (Optional) A
payload. Can be of any form chosen by the app developer. The content sent in postMessage from configure page.
AMS calls the service's Save Configuration URL endpoint with the following request:
POST <service-base-url><service-saveconfiguration-url>
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
{
"instanceUuid": "6ea036bb-8cfb-46c5-a826-d001d3a0349b",
"payload": {
//Definedbydeveloper.WhateverissentinpostMessagefromConfigurePage.
}
}
Apps' response to the Save Configuration URL request
This endpoint should return the configuration status, status code, and any record definitions. In the sample code we are returning an AppConfigurationChangeStatusDTO object to AMS.
Save Configuration URL payload response to AMS
{
"configurationStatus": "CONFIGURED",
"payload": {},
"httpStatusCode": "200",
"recordDefinition": {
"inputParameters": [
{
"name": "appcloud_row_correlation_id",
"dataType": "Text",
"width": 40,
"unique": true,
"required": true,
"readOnly": null,
"minimumValue": null,
"maximumValue": null,
"possibleValues": null,
"format": null,
"resources": null
},
...
],
"outputParameters": [
{
"name": "appcloud_row_correlation_id",
"dataType": "Text",
"width": 40,
"unique": true,
"required": true,
"readOnly": null,
"minimumValue": null,
"maximumValue": null,
"possibleValues": null,
"format": null,
"resources": null
}
...
]
}
}
Sample Implementation: Save Configuration URL Endpoint
@RequestMapping(value = "/saveConfigure", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public AppConfigurationChangeStatusDTO saveConfigureAppInstall( @RequestBody String body) throws JSONException, IOException {
....
// What we are doing in essence.
serviceInstance.setCity(payload.getString(CITY_FIELD_NAME));
serviceInstance.setCountry(payload.getString(COUNTRY_FIELD_NAME));
...
AppConfigurationChangeStatusDTO status = new AppConfigurationChangeStatusDTO();
status.setRecordDefinition(definition);
status.setConfigurationStatus(AppConfigurationStatusType.CONFIGURED);
return status;
}
Sample Implementation: AppConfigurationChangeStatusDTO
// AppConfigurationChangeStatusDTO.java
public class AppConfigurationChangeStatusDTO {
private RecordDefinitionDTO recordDefinition;
private AppConfigurationStatusType configurationStatus;
private Object payload;
}
AMS postMessage to Configuration Page
AMS would then postMessage the same response to the listener in the configuration page with the results of the Save Configuration URL. This is so the page can update itself and inform the user of the configuration result.
AMS postMessage example to configuration page
{
"requestId": "be446dc2-8f30-4fd7-95bb-c72bacff5ebf",
"configurationStatus": "CONFIGURED",
"payload": {},
"httpStatusCode": "200",
"recordDefinition": {
"inputParameters": [
{
"name": "appcloud_row_correlation_id",
"dataType": "Text",
"width": 40,
"unique": true,
"required": true,
"readOnly": null,
"minimumValue": null,
"maximumValue": null,
"possibleValues": null,
"format": null,
"resources": null
},
...
],
"outputParameters": [
{
"name": "appcloud_row_correlation_id",
"dataType": "Text",
"width": 40,
"unique": true,
"required": true,
"readOnly": null,
"minimumValue": null,
"maximumValue": null,
"possibleValues": null,
"format": null,
"resources": null
}
...
]
}
}
Delete URL endpoint
When a service instance is deleted, AMS calls the app's Delete URL to delete the service instance.
AMS will send a request resembling the following:
POST <service-base-url><service-delete-url>
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
{
"uuid": "2128d91f-7248-4361-94b8-38a414d5cbb1",
"assetType": "campaign",
"assetId": null,
"recordDefinition": {
"inputParameters": [
{
"dataType": "Double",
"unique": true,
"name": "input",
"width": 10
}
],
"outputParameters": [
{
"dataType": "Double",
"unique": true,
"name": "output",
"width": 10
}
]
},
"applicationService": {
"uuid": "c2d3a932-2e00-45e5-9899-17d8edda00c7",
"name": "service",
"description": null,
"baseUrl": "https://somefakeappbaseurl.com",
"configureUrl": "/configure",
"saveConfigurationUrl": null,
"deleteUrl": "/delete",
"createUrl": "/create",
"invokeUrl": "/invoke",
"statusUrl": null,
"operationalUrl": null,
"smallLogo": "https://smalllogourl",
"mediumLogo": null,
"largeLogo": null,
"maxBatchSize": 0,
"application": {
"uuid": "d6862ebc-8c5e-4905-8da1-28e3166c978c",
"name": "appname",
"description": "description",
"baseUrl": "https://www.oracle.com",
"statusUrl": "status",
"installUrl": "/installurl",
"configureUrl": "/configure",
"uninstallUrl": "/uninstall",
"saveConfigurationUrl": "/save",
"smallLogo": "smalllogo",
"mediumLogo": "mediumlogo",
"largeLogo": "largelogo",
"status": "UP",
"providerUuid": "53aba933-a031-46ce-ab69-4ad0f4cc3335"
},
"serviceType": {
"name": "activity",
"externalName": "activityext",
"description": "activitytypeofservice"
},
"status": "UP"
},
"secret": null,
"status": "CREATED"
}
Tip: The JWT Token in the Authorization Header is generated by following the AMS to App token generation. For more information about this call, including authentication details, see the endpoint API reference.
Sample Delete URL endpoint implementation
@RequestMapping(value = "/delete", method=RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT)
public void deleteServiceInstance(@RequestBody String body) throws JSONException {
JSONObject request = new JSONObject(body);
String instanceUuid = request.getString("uuid");
ServiceInstance serviceInstance = serviceInstanceService.getEntity(instanceUuid);
if(serviceInstance == null) {
// deleting something that doesn't exist.
return;
}
serviceInstanceService.deleteEntity(instanceUuid);
}
App's response to the Delete URL request
The app does not need to respond to this call. If the app chooses responds to this call, it will be ignored by AMS. The sample code simply returns a 204, this is ignored by AMS.