Intercompany Journal Entries in Multi-Book Accounting
Please contact your sales or account representative to find out how to get the Full Multi-Book Accounting feature. The assistance of NetSuite Professional Services or a Multi-Book authorized partner is required to implement this feature. You should consider contacting NetSuite Professional Services or a Multi-Book authorized partner for assistance in setting up the Adjustment-Only Books feature, even though it isn't required.
Multi-Book Accounting, including the Adjustment-Only Books feature, is available only in NetSuite OneWorld.
Intercompany journal entries are a specialized type of journal entry that permit the posting of transactions between two subsidiaries. Intercompany journal entries may be either book-generic or book-specific. For more information, see Book-Generic Intercompany Journal Entries and Book-Specific Intercompany Journal Entries.
Book-Generic Intercompany Journal Entries
To create a book-generic intercompany journal entry, go to Transactions > Financial > Make Intercompany Journal Entries.
A book-generic intercompany journal entry impacts all accounting books. All fields displayed in the intercompany journal entry are for the primary book, except for the Accounting Books subtab. The Accounting Books subtab includes the secondary books for both subsidiaries.
To generate the full general ledger impact, both subsidiaries affected by the intercompany journal entry must share the secondary accounting books. If a secondary book is associated with only one subsidiary, only that side of the entry posts for that book. If a secondary book isn't associated with either subsidiary, there is no impact for that book.
The Currency field is the transaction currency for the posting. It's shared across all books. Selection is limited to the primary book base currencies of the two subsidiaries affected by the journal entry. If the base currency of the secondary books is different from the transaction currency for both subsidiaries, foreign currency journal entries are created for both subsidiaries in the secondary books.
The Exchange Rate in the Primary Information section of the intercompany journal entry record is between the two base currencies for the primary book. When the Foreign Currency Management feature is enabled, the base currency and exchange rate may be different for secondary books. The exchange rate for secondary books defaults to the system exchange rate value between the transaction currency and secondary book base currency.
If you change the exchange rate for the primary book, the change is copied to secondary books that share the primary book base currencies. The Exchange Rate in the Accounting Books subtab is read-only for these currencies.
If secondary books have base currencies that differ from both of the primary book currencies, you can change the default Exchange Rate value in the Accounting Books subtab. If you change an Exchange Rate in the Accounting Books subtab, ensure that the posting amounts are the same across books for the same currency.
You can also create .csv files, and then use the Import Assistant to import multiple intercompany journal entries from another system into NetSuite. For more information, see Journal Entry Import and Intercompany Journal Entry Import.
Exchange Rate Example
To see how the exchange rate fields function across accounting books, create an intercompany journal entry between two subsidiaries, for example, US Subsid and UK Subsid. The base currencies in the primary books are U.S. Dollar (USD) and British pound (GBP) respectively. The transaction currency is U.S. Dollar, and the system exchange rate for USD/GBP is 0.6020, but you change the value in the Exchange Rate field of the record to 0.50.
Three secondary books are shared by the two subsidiaries as follows:
-
A secondary book called GL Mapping Book uses the same base currencies as the primary book. The base currency for US Subsid is U.S. Dollar, and for UK Subsid, it's British pound.
-
A secondary book called UK Accounting Book uses British pound as the base currency for both UK Subsid and US Subsid.
-
A secondary book called Global Accounting Book uses different currencies for both subsidiaries. Its base currency for US Subsid is Canadian dollar, and for UK Subsid, the base currency is Euro.
The following screenshot shows the Intercompany Journal record and Accounting Books subtab for this scenario.
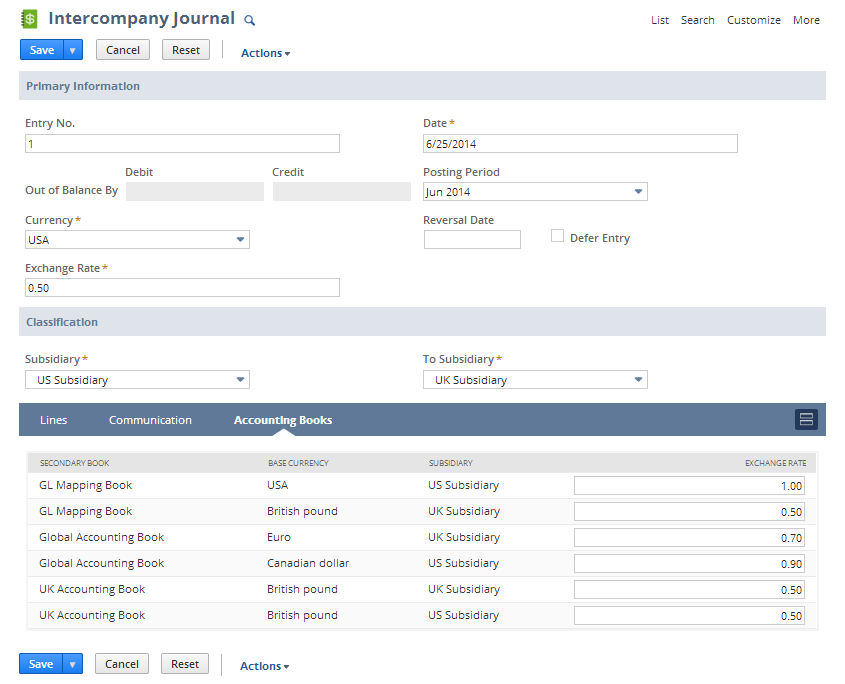
Note that the exchange rates for the GL Mapping Book and the UK Accounting Book are the same as the primary book. The Exchange Rate field for these books in the Accounting Books subtab is read-only. The values change for these books when you change the Exchange Rate for the primary book.
In the Global Accounting Book, however, the base currencies for the subsidiaries are different from either primary book currency. The values for the Exchange Rate fields for the Global Accounting Book default to the system rate values, but these values can be changed.
When you save this example intercompany journal entry with a transaction currency of U.S. Dollar, the general ledger impact for a $100 line is as follows:
|
Currency |
Value |
|---|---|
|
British pound |
50 |
|
Canadian dollar |
90 |
|
Euro |
70 |
|
U.S. dollar |
100 |
Book-Specific Intercompany Journal Entries
To create a book-specific intercompany journal entry, go to Transactions > Financial > Make Book Specific Intercompany Journal Entries.
In book-specific intercompany journal entries, the intercompany journal entry posts to only one book. Book-specific intercompany journal entries include an Accounting Book list in the main form. The transaction currency must be a base currency of the two subsidiaries for the selected book. Therefore, in one subsidiary, the posting is a base currency journal entry. In the other, it may be a foreign currency journal entry.
You must have an administrator role or be granted the Allow Pending Book Journal Entry permission to make a book-specific intercompany journal entry in a pending book.
If one or both of the subsidiaries selected in the Subsidiary or To Subsidiary field are assigned to one or more shared vendor or customer records, you can make book-specific intercompany journal entries for any of the vendors or customers to which the selected subsidiaries are assigned. To do this, on the Lines subtab, select the shared vendor or customer from the Name field. For more information about shared records, see Assigning Subsidiaries to a Vendor and Assigning Subsidiaries to a Customer.
For pending secondary books, you can post book-specific intercompany journal entries to all periods regardless if the period is before or after the effective period of the secondary book. This is useful in modifying the opening account balance derived from processing secondary book historical transactions.
For active accounting books, you can post book-specific journal entries to only open periods.
The Accounting Book field is locked when book-specific intercompany journal entries are saved. To change the accounting book, delete the journal entry and then create a new one.
Like regular book-specific journal entries, when you add an accounts receivable or accounts payable line, the name field is disabled.
You can also create .csv files, and then use the Import Assistant to import multiple book-specific intercompany journal entries from another system into NetSuite. For more information, see Journal Entry Import and Intercompany Journal Entry Import.