Redwood: Use Knowledge Management in the Maintenance Technician Workbench
Oracle Knowledge Management is a comprehensive solution designed to help organizations manage, create, and distribute knowledge content effectively. It provides a centralized repository for storing and accessing knowledge articles, documents, and other informational content. It enables organizations to deliver accurate and consistent information across various channels, including customer support, self-service portals, and internal teams.
With this update, you can now leverage Knowledge Management's knowledge repository in My Maintenance Work, as part of the maintenance work order execution process. You can also review, optionally edit, and suggest changes to published articles in context of the maintenance tasks that you are executing.
You can navigate to Knowledge Management in the context of a work order by selecting Knowledge Management from the Actions menu for a work order row in My Maintenance Work. Alternatively, you can select the Knowledge Management tab from the Report Work page. The work order description appears as the default text in the search bar, which lets you search for published knowledge articles related to the work. Knowledge articles can include text, videos, images, infographics, animations, and online interviews.
Content types define the various types of articles in your knowledge base. A content type definition serves as an authoring template for articles that serve a specific purpose.
Within Knowledge Management, there are several departments for which the user can create articles. Knowledge management and Oracle Maintenance Cloud work with the Internal Help Desk Department. This means that your articles must be created based on the content type of the Internal Help Desk Department. Else, your published articles won't be rendered in the Oracle Fusion Maintenance Cloud work order.
The following screenshot shows the My Maintenance Work page with the Knowledge Management option in the Actions menu for the work order row:
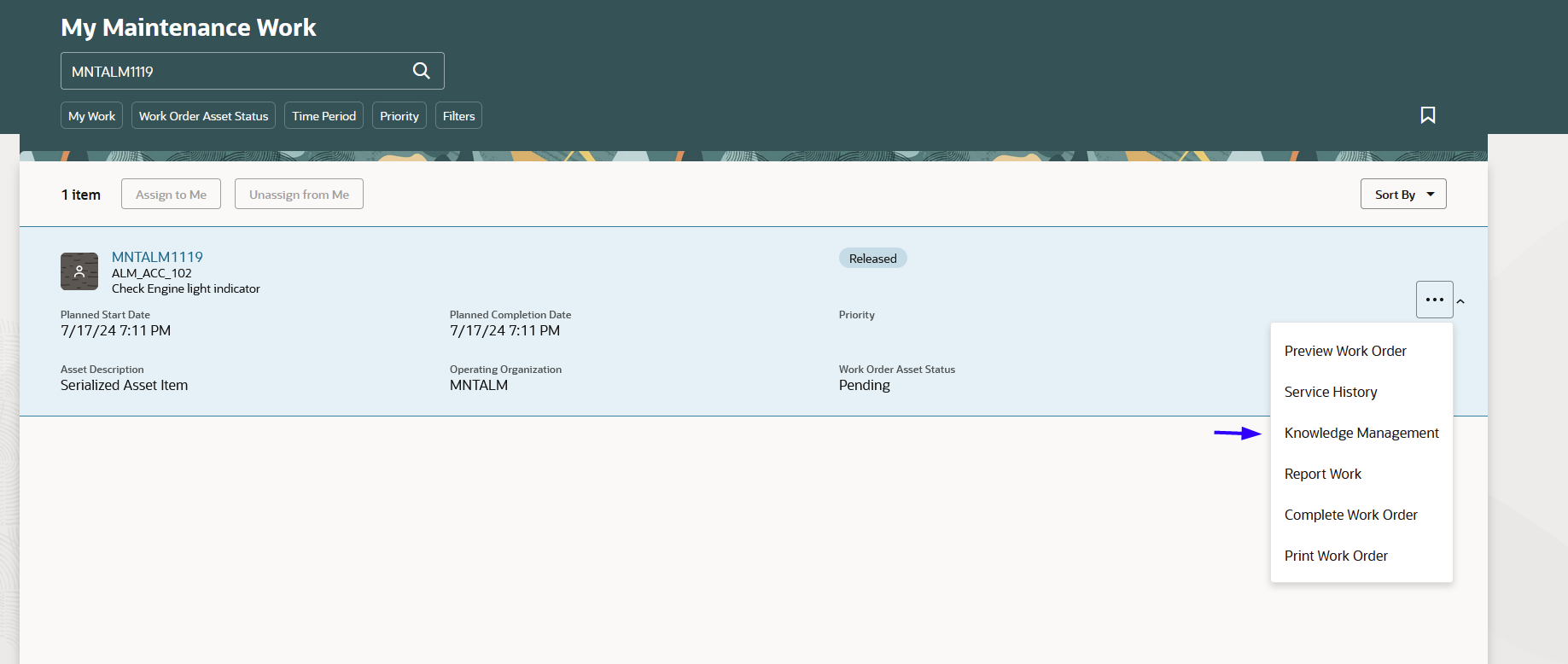
My Maintenance Work
The following screenshot shows the Knowledge Management page with the work order description in the Search field:
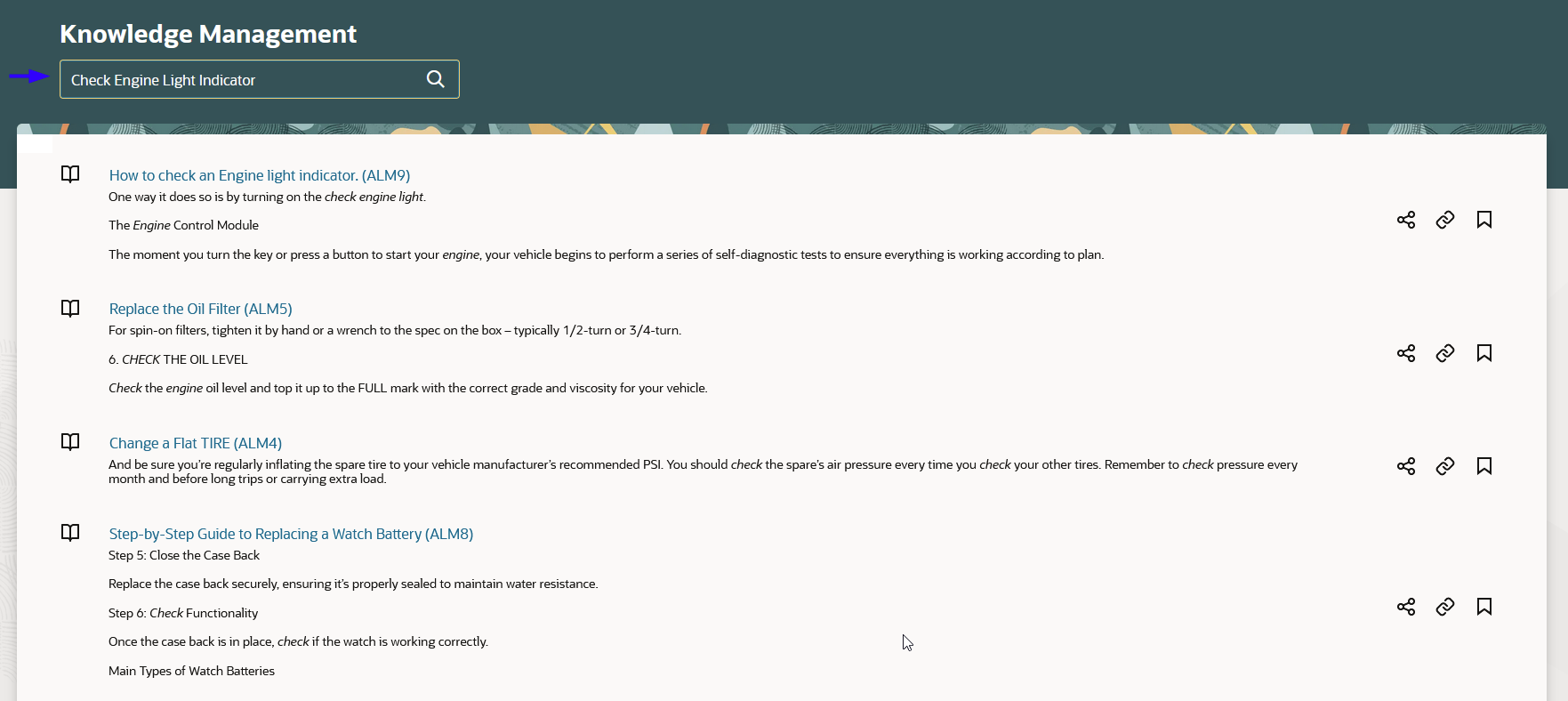
Knowledge Management
You can set articles as favorites, make edits to articles, or suggest changes using the article row action icons. These options are enabled based on the privileges assigned to the user.
Please refer to the following document for more information: Administering Knowledge Management.
You can create knowledge articles for My Maintenance Work using an Internal Help Desk Department content type. You can have user groups control access to articles in the knowledge base. Users assigned to a user group can only access the articles targeted for that user group.
The following screenshot shows the knowledge article authoring user interface:
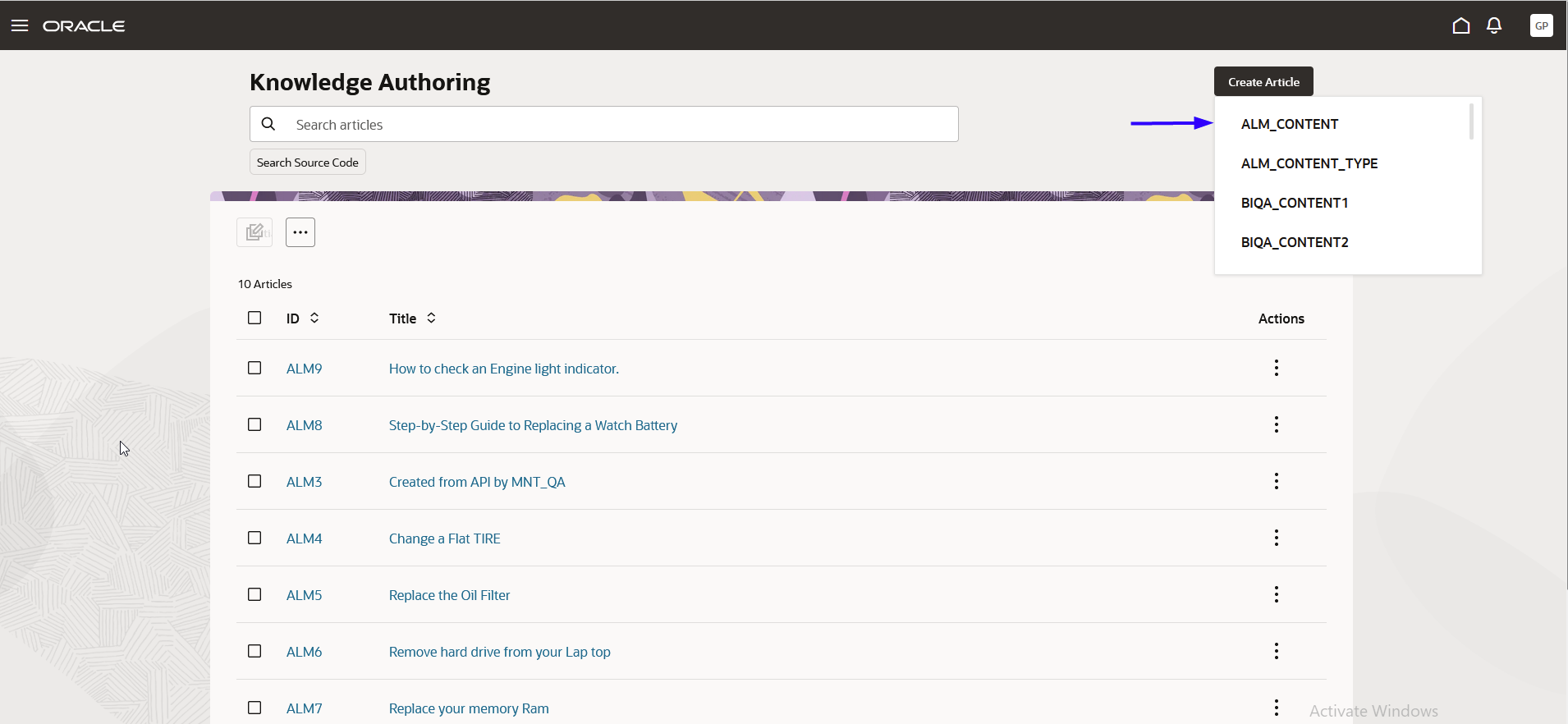
Knowledge Management Authoring
Knowledge management enables you to deliver consistent answers across all of your business.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Tips And Considerations
This update enables Knowledge Management in Oracle Fusion Maintenance Cloud. Review how to set up a predefined knowledge user: Predefined Knowledge Roles.
Also, see Implementing Knowledge Management with the Redwood User Experience.
Key Resources
- Get Started with Knowledge
- Enable Knowledge with Redwood User Interface Feature
- Implementing Knowledge Management with the Redwood User Experience
- Watch the Enabling Fusion Knowledge with the Redwood User Experience Video
- Watch the Basics of Fusion Knowledge Management Users Video
Access Requirements
Users who are assigned a configured job role that contains these privileges can access this feature:
- Manage Customer Assets (CSI_MANAGE_CUSTOMER_ASSETS_PRIV)
- View Customer Assets (CSI_VIEW_CUSTOMER_ASSETS_PRIV)
- Manage Enterprise Assets (CSE_MANAGE_ENTERPRISE_ASSETS_PRIV)
- View Enterprise Assets (CSE_VIEW_ENTERPRISE_ASSETS_PRIV)
- There are predefined knowledge privileges and roles to help you set up and manage users. Most organizations use predefined roles as the basis for defining new roles to meet their specific needs. Please refer to this link for more details: Predefined Knowledge Roles.
These privileges were available prior to this update.