5 Configuring Database Firewall
Learn about configuring Database Firewall.
You can use Database Firewall to configure traffic sources and proxies.
5.1 About Configuring Database Firewall
Learn how to configure Database Firewall.
The way in which you configure the system and firewall settings for each Database Firewall depends on your overall plan for deploying Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall.
When you configure a Firewall instance, you identify the Audit Vault Server that will manage the specific Firewall. Depending on your plan for the overall Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall system configuration, you also configure the traffic sources, and determine the deployment types. The following are the Database Firewall deployment types:
- Monitoring (Out-of-Band)
- Monitoring (Host Monitor)
- Monitoring / Blocking (Proxy)
Note:
- The Audit Vault Server and the Database Firewall server are software appliances. You must not make any changes to the Linux operating system through the command line on these servers unless following official Oracle documentation or under guidance from Oracle Support.
- The Database Firewall introduces very minimal latency overhead of less than 100 microseconds per SQL statement with 100K transactions per second. This is based on internal performance tests.
- Traffic transfers from the Database Firewall to the Audit Vault Server as quickly as possible given the available resources and design limits. There's always a small gap between the moment that an audit record is recorded in the target database and when it is stored on the Audit Vault Server.
Basic firewall configuration consists of these four steps:
-
Specifying the Audit Vault Server Certificate and IP Address
-
Managing the Oracle Database Firewall Network and Services Configuration
-
Configuring the Database Firewall and Its Traffic Sources on Your Network
After configuring the Database Firewalls, perform the following tasks:
-
Configure Database Firewall monitoring points for each database target.
-
You can optionally set up resilient pairs of Database Firewalls for a high availability environment.
See Also:
-
Summary of Configuration Steps to understand the high level workflow for configuring the Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall system.
-
Planning Your Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall System Configuration for an overview of the planning steps.
-
High Availability in Oracle AVDF to set up resilient pairs of Database Firewalls for a high availability.
5.2 Introduction to Database Firewall Deployment
Depending on your operational needs you can monitor SQL traffic only, or you can monitor and block SQL traffic to the target database.
When configuring the Database Firewall, you can choose one of the following deployment modes:
| Deployment Mode | Minimum Number of Network Interface Cards (NICs) | Operational Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring/Blocking (Proxy) |
3 (for deployment with network separation) 1 (for deployment without network separation) |
This mode enables the Database Firewall to both monitor and block SQL traffic, as well as optionally substitute SQL statements. You configure clients to connect to the Database Firewall instead of the database so that the firewall can intercept all SQL traffic and take the necessary actions, based on policies that you define. |
| Monitoring (Host Monitor) | 1 | To use this mode, you install the Audit Vault Agent and Host Monitor Agent on the host machine that's running the target database. The Host Monitor Agent captures traffic from the NIC on the host machine and securely forwards it to the Database Firewall. |
| Monitoring (Out-of-Band) | 2 | In this mode, the Database Firewall monitors and alerts on SQL traffic, but it can't block or substitute SQL statements. To copy database traffic to the Database Firewall, you can use a switch with a SPAN port (as shown in the diagram), a network tap, a packet replicator, or other similar technology. |
One Database Firewall can monitor traffic from multiple targets deployed in different modes. For example, one Database Firewall can be deployed in Monitoring/Blocking (Proxy) mode for some targets and in Monitoring (Host Monitor) mode and Monitoring (Out-of-Band) mode for other targets.
Note:
- A single NIC is required when the client and database are on the same subnet. There is no network separation.
- Additional NICs are required when the client and database are on different subnets.
- When there are three NICs, the network separation requires you to have a management network interface, which is usually attached to the default gateway. The first NIC is placed in the client subnet. The second NIC is placed in the database subnet. No additional routing is required in this configuration. All the addresses for clients and databases are local to the networks that are accessible to the Database Firewall NICs.
5.2.1 Monitoring/Blocking (Proxy)
Monitoring/Blocking (Proxy) mode enables the Database Firewall to both monitor and block SQL traffic, as well as optionally substitute SQL statements.
You configure clients to connect to the Database Firewall instead of the database so that the firewall can intercept all SQL traffic and take the necessary actions, based on policies that you define. In all cases, the database server identifies the Database Firewall as the client.
Oracle recommends that you configure the database to reject all connections that do not come from the Database Firewall.
Note:
To simplify the modification required for applications to connect to the Database Firewall proxy mode deployments, configure local domain name servers (DNS) to resolve the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the target database to the IP address of the Database Firewall.You can deploy the Monitoring/Blocking (Proxy) mode in the following ways:
- Proxy without network separation
- Proxy without network separation using a dedicated network interface card (NIC)
- Proxy with network separation
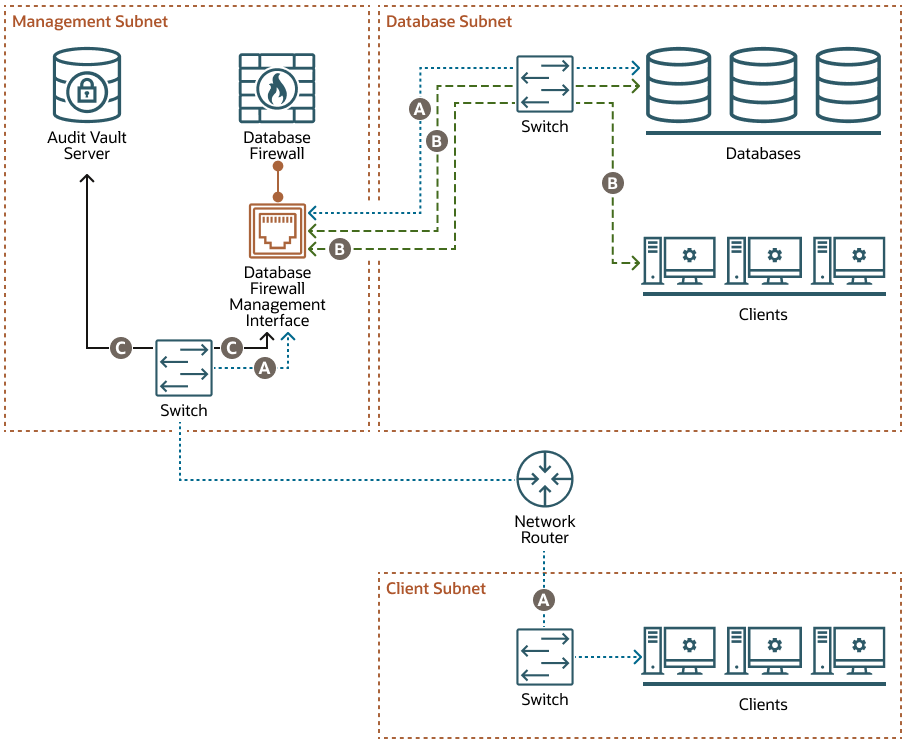
Proxy Without Network Separation
When you deploy the Database Firewall as a proxy without network separation, the Database Firewall has one NIC called the Database Firewall management interface, which handles all communication between the clients and databases, as well as between the Database Firewall and the Audit Vault Server. This NIC is deployed in the management subnet.
The example in this diagram has three subnets:
- The management subnet contains the Audit Vault Server, the Database Firewall, the Database Firewall management interface, and a switch.
- The client subnet contains three clients and a switch.
- The database subnet contains three databases, three clients, and a switch.
The following letter callouts describe how traffic flows to and from the Database Firewall in the diagram:
- A: In the client subnet, traffic travels from the clients through a switch to the network router. The router sends the traffic to the switch in the management subnet, which forwards the traffic to the Database Firewall traffic management interface. From there the traffic travels to the databases through the switch in the database subnet. The database responses return to the clients through the same path.
- B: In the database subnet, traffic travels from the clients through the switch in the database subnet to the Database Firewall traffic management interface in the management subnet. From there the traffic travels to the databases through the switch in the database subnet. The database responses return to the clients through the same path.
- C: The Database Firewall extracts and analyzes SQL data from the client traffic and sends it through the Database Firewall management interface to the switch in the management subnet and then to the Audit Vault Server, based on the Database Firewall policy.
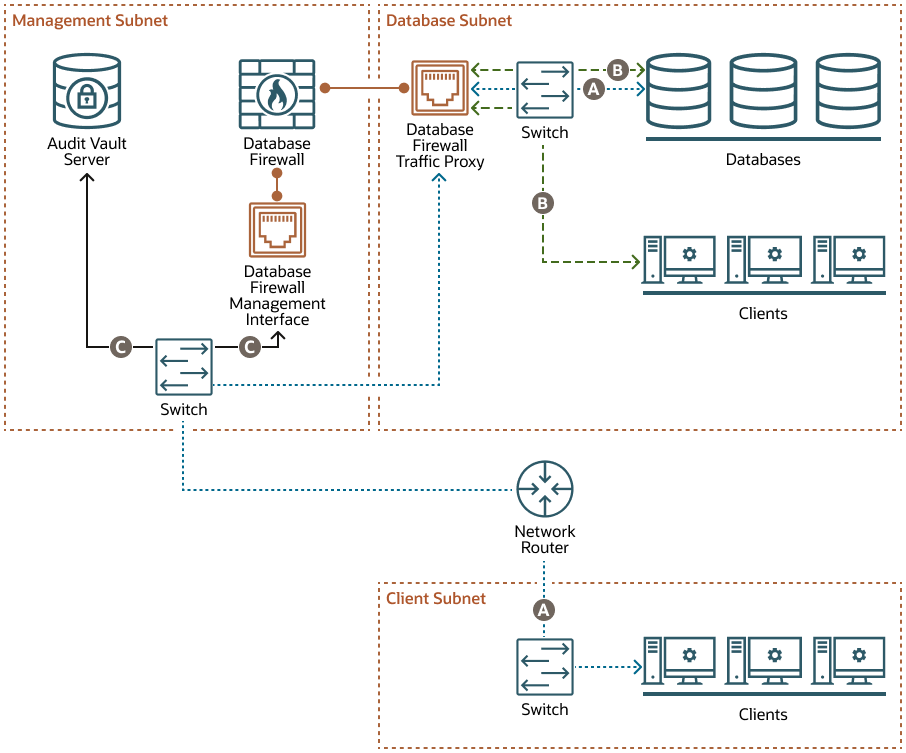
Proxy Without Network Separation Using a Dedicated NIC for the Proxy Service
When you deploy the Database Firewall as a proxy without network separation using a dedicated NIC, the Database Firewall has two NICs:
- The Database Firewall traffic proxy handles traffic from all clients to the databases. This NIC is deployed in the database subnet.
- The Database Firewall management interface handles communication between the Database Firewall and the Audit Vault Server. This NIC is deployed in the management subnet.
The example in this diagram has three subnets:
- The management subnet contains the Audit Vault Server, the Database Firewall, the Database Firewall management interface, and a switch.
- The client subnet contains three clients and a switch.
- The database subnet contains three databases, three clients, a switch, and the Database Firewall traffic proxy.
The following letter callouts describe how traffic flows to and from the Database Firewall in the diagram:
- A: In the client subnet, traffic travels from the clients through a switch to the network router. The router sends the traffic to the switch in the management subnet, which forwards the traffic to the Database Firewall traffic proxy in the database subnet. From there the traffic travels to the databases through the switch in the database subnet. The database responses return to the clients through the same path.
- B: In the database subnet, traffic travels from the clients through the switch in the database subnet to the Database Firewall traffic proxy in the database subnet. From there the traffic travels to the databases through the switch in the database subnet. The database responses return to the clients through the same path.
- C: The Database Firewall extracts and analyzes SQL data from the client traffic and sends it through the Database Firewall management interface to the switch in the management subnet and then to the Audit Vault Server, based on the Database Firewall policy.
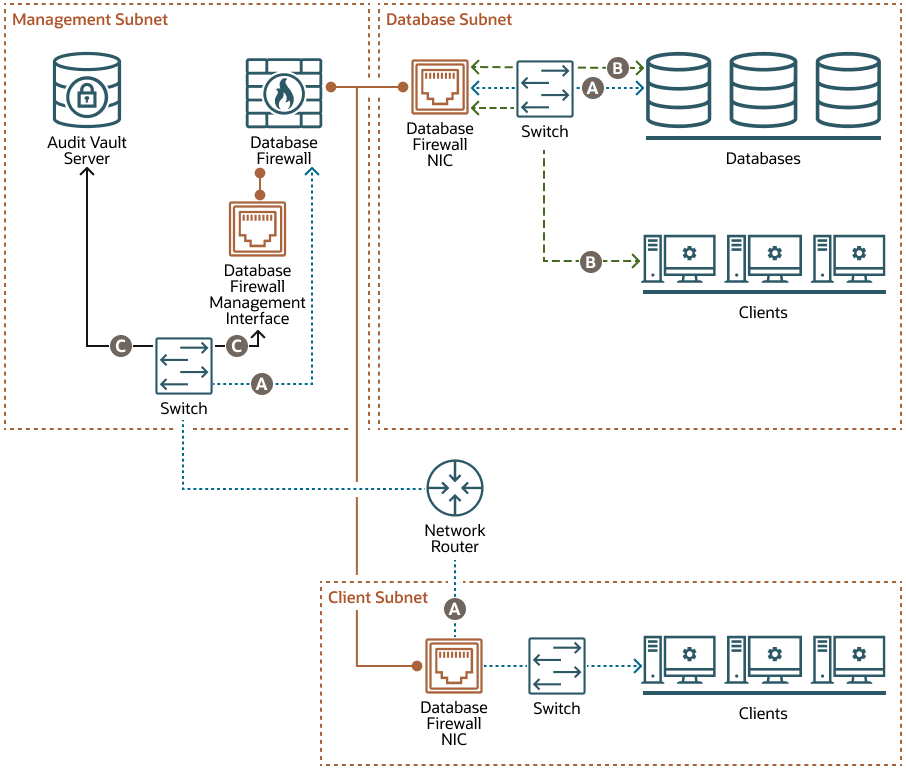
Proxy With Network Separation
When you deploy the Database Firewall as a proxy with network separation, the Database Firewall has a minumum of three NICs:
- Each client subnet has a Database Firewall NIC that handles all traffic to and from the clients in that subnet.
- The database subnet has a Database Firewall NIC that handles all traffic to the databases, as well as traffic from any clients in the database subnet.
- The Database Firewall management interface handles communication between the Database Firewall and the Audit Vault Server. This NIC is deployed in the management subnet.
The example in this diagram has three subnets:
- The management subnet contains the Audit Vault Server, the Database Firewall, the Database Firewall management interface, and a switch.
- The client subnet contains three clients, a switch, and a Database Firewall NIC.
- The database subnet contains three databases, three clients, a switch, and a Database Firewall NIC.
The following letter callouts describe how traffic flows to and from the Database Firewall in the diagram:
- A: In the client subnet, traffic travels from the clients through a switch to the Database Firewall NIC in the client subnet and then to the network router. The router sends the traffic to the switch in the management subnet, which forwards the traffic to the Database Firewall. From there the traffic travels to the databases through the NIC and switch in the database subnet. The database responses return to the clients through the same path.
- B: In the database subnet, traffic travels from the clients through the switch in the database subnet to the Database Firewall NIC in the database subnet. From there the traffic travels to the databases through the switch in the database subnet. The database responses return to the clients through the same path.
- C: The Database Firewall extracts and analyzes SQL data from the client traffic and sends it through the Database Firewall management interface to the switch in the management subnet and then to the Audit Vault Server, based on the Database Firewall policy.
5.2.2 Monitoring (Host Monitor)
In Monitoring (Host Monitor) mode, the Database Firewall monitors and alerts on SQL traffic, but it can't block or substitute SQL statements.
To use Monitoring (Host Monitor) mode, you install the Audit Vault Agent and Host Monitor Agent on the host machine that's running the target database. The Host Monitor Agent captures traffic from the network interface card (NIC) on the host machine and securely forwards it to the Database Firewall.
Note:
In Oracle AVDF 20.3 and later, you can add any NIC (with an IP address configured) on the Database Firewall to the monitoring point. See Creating a Monitoring Point for the Host Monitor Agent.Monitoring (Host Monitor) mode is helpful if the network topology prevents deployment of other Database Firewall modes. Host monitoring captures only the relevant traffic, whereas Monitoring (Out-of-Band) mode captures all the network traffic. Monitoring (Host Monitor) mode can monitor SQL traffic using the Host Monitor Agent deployed on the database server when there are multiple network paths from clients to the database host.
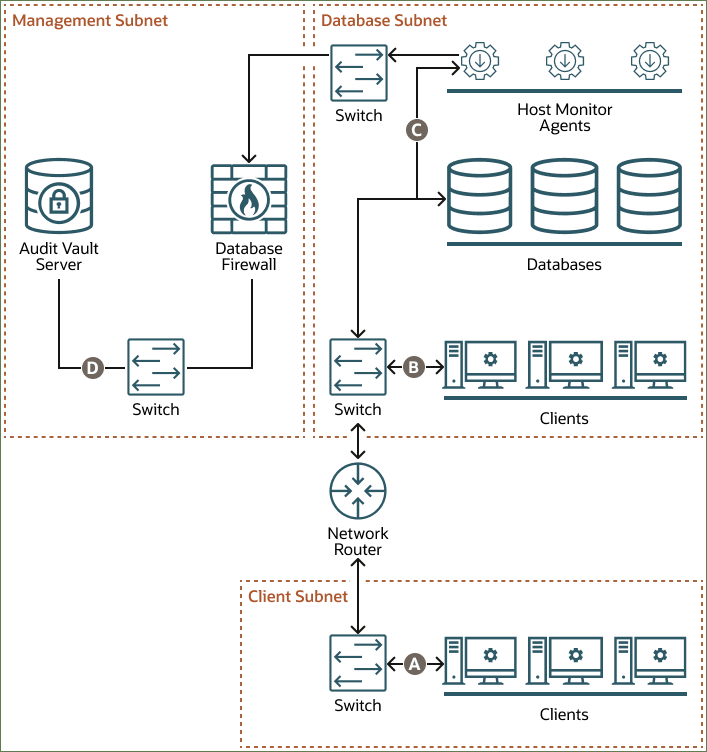
The example in the diagram has three subnets: client, database, and management. The client subnet contains three clients that connect to the network router through a switch in the client subnet. The database subnet contains three databases and three Host Monitor Agents. The Host Monitor Agents connect to the Database Firewall through a switch in the database subnet. The database subnet also contains three clients that connect to a second switch in the database subnet. That switch connects to the databases and to the network router. The management subnet contains the Database Firewall and the Audit Vault Server, which connect to each other through a switch in the management subnet.
The following points refer to the letter callouts in the diagram:
- A: The clients in the client subnet connect directly to the database through the network router and a switch in the database subnet.
- B: The clients in the database subnet connect directly to the database through the switch in the database subnet.
- C: The Host Monitor Agents record traffic between the clients and the databases and forward the traffic to the Database Firewall through a switch in the database subnet.
- D: The Database Firewall extracts and analyzes SQL data from the client traffic and sends it through the switch in the management subnet to the Audit Vault Server, based on the Database Firewall policy.
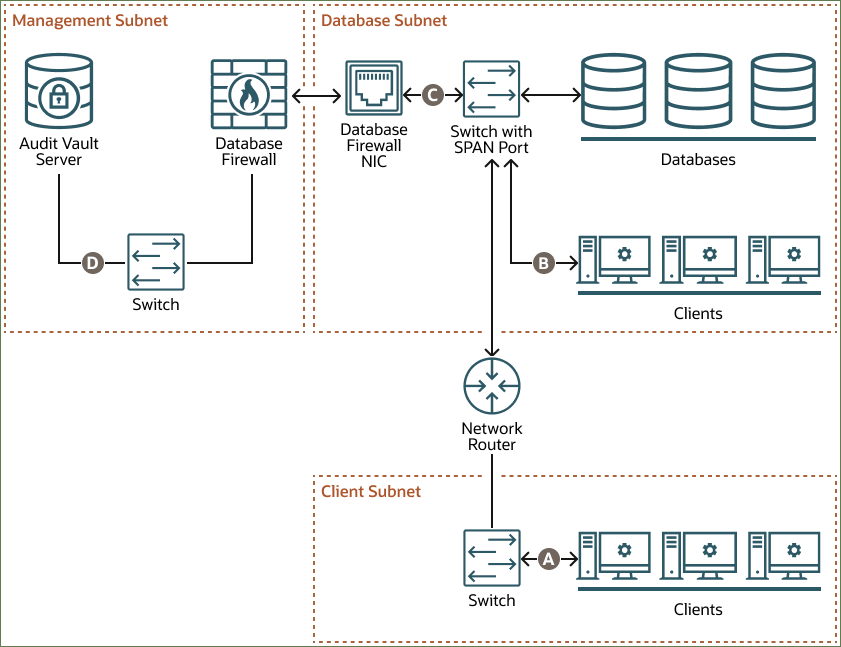
5.2.3 Monitoring (Out-of-Band)
In Monitoring (Out-of-Band) mode, the Database Firewall monitors and alerts on SQL traffic, but it can't block or substitute SQL statements.
You can use several technologies to copy database traffic to the Database Firewall, including (but not limited to) SPAN ports, network taps, and packet replicators.
Monitoring (Out-of-Band) mode is the simplest deployment mode overall for a non-blocking policy requirement. There is no additional load on the database or the clients. The Database Firewall does not introduce any latency or a single point of failure.
Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall (Oracle AVDF) supports high availability in this deployment mode.
The example in the diagram has three subnets: client, database, and management. The client subnet contains three clients that connect to the network router through a switch in the client subnet. The database subnet contains three databases that connect directly to the Database Firewall through a switch with a SPAN port and then a Database Firewall NIC in the database subnet. The database subnet also contains three clients that, along with the network router, connect to the same switch with a SPAN port. The management subnet contains the Database Firewall and the Audit Vault Server, which connect to each other through a switch in the management subnet.
The following points refer to the letter callouts in the diagram:
- A: The clients in the client subnet connect directly to the database through the network router and the switch with the SPAN port in the database subnet.
- B: The clients in the database subnet connect directly to the database through the switch with the SPAN port in the database subnet.
- C: The Database Firewall monitors database activity through the Database Firewall NIC, which connects to a SPAN port on the switch in the database subnet.
- D: The Database Firewall extracts and analyzes SQL data from the client traffic and sends it through the switch in the management subnet to the Audit Vault Server, based on the Database Firewall policy.
5.3 Specifying the Audit Vault Server Certificate and IP Address
You associate each Database Firewall with an Audit Vault Server so that the Audit Vault Server can manage the firewall. If you're using a resilient pair of Audit Vault Servers for high availability, then you associate the firewall with both servers.
Note:
- Complete the Database Firewall Post-Install Tasks before beginning this procedure.
- Complete this procedure before you register the firewall on the Audit Vault Server. See Registering Database Firewall in Audit Vault Server for instructions.
To remove the primary or standby Audit Vault Server from the Database Firewall, use the following commands.
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Remove the primary Audit Vault Server from the Database Firewall |
|
| Remove the standby Audit Vault Server from the Database Firewall |
|
5.4 Managing the Oracle Database Firewall Network and Services Configuration
Learn how to manage the Oracle Database Firewall network and services configuration.
5.4.1 Configuring Network Settings for Oracle Database Firewall
Learn how to configure the network settings for Oracle Database Firewall.
The installer configures initial network settings for the Database Firewall during installation. You can change the network settings after installation.
To change the Database Firewall network settings:
5.4.2 Configuring Network Services for Oracle Database Firewall
Learn about configuring network services for Oracle Database Firewall.
The network services configuration determines how administrators can access Oracle Database Firewall. See the guidelines to protect data and ensure that you take the appropriate security measures when configuring network services.
To configure network services for a Database Firewall:
5.4.3 Configuring SNMPv3 Users in Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall
Learn how to configure SNMPv3 users.
Simple Network Management Protocol version 3 (SNMPv3) is an interoperable, standards-based protocol. SNMPv3 involves User-based Security Model (USM) for message security and the View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for access control. With USM, messages exchanged between the SNMP Manager and the SNMP Agent can have data integrity checking and data origin authentication. Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall 20.1 and later supports SNMPv3 as the default version. This topic contains the steps needed to configure SNMPv3 users for making use of the USM model of SNMPv3.
To create an SNMPv3 user, follow these steps:
5.5 Configuring Database Firewall Syslog Destinations
Learn how to configure Database Firewall syslog destinations.
Use the following procedure to configure the types of syslog messages to send from Database Firewall. The message categories are Debug, Info, or System. You can also forward Alert messages to the syslog.
Configuring Syslog enables integration with popular SIEM vendors such as Splunk, IBM QRadar, LogRhythm, ArcSight and others.
Note:
Syslog message is sent to the destination machine. The message is not written to the Database Firewall /var/log/message file.Prerequisites
-
Log in to the Audit Vault Server console as a super administrator. See Using Audit Vault Server Console for more information.
-
Ensure that the IP addresses provided for syslog destinations are on a different host than the Audit Vault Server.
5.6 Setting the Date and Time in Database Firewall
Learn how to set the date and time in Database Firewall.
Use this procedure to set the Database Firewall date and time:
5.7 Changing the IP Address on a Single Instance of the Database Firewall Server
Learn how to change the IP address on a single instance of the Database Firewall server.
Prerequisites
- Because changing the IP address of the Database Firewall Server is a system-level change and requires downtime, plan to change the IP address during a safe period to avoid interrupting the log collection processing.
- Stop any monitoring points before changing the IP address. See Starting, Stopping, or Deleting Database Firewall Monitoring Points.
To change the IP address of the Database Firewall Server:
Note:
When the Database Firewall Server is back online, it begins to download any monitoring point log data that was not downloaded while it was offline.5.8 Changing the Database Firewall Host Name
Learn how to change the Database Firewall host name.
To change the Database Firewall host name using the Audit Vault Server console:
- Log in to the Audit Vault Server console as administrator.
- Click Database Firewalls tab in the Audit Vault Server console main page. The Database Firewalls tab in the left navigation menu is selected by default.
- Locate and click the name of the specific Database Firewall instance for which the host name needs changing. The Firewall Details page is displayed.
- Change the Host Name in the main page. This is the name of the host machine on which the Database Firewall is installed.
- Click Save button in the top right corner.
5.9 Configuring the Database Firewall and Its Traffic Sources on Your Network
Learn about configuring the Database Firewall and its traffic sources on your network.
5.9.1 About Configuring Oracle Database Firewall and Traffic Sources On Your Network
Learn about configuring Oracle Database Firewall and its traffic sources on the network.
During your planning of the network configuration, you must decide the Database Firewall deployment type. The following are the Database Firewall deployment types:
- Monitoring (Out-of-Band)
- Monitoring (Host Monitor)
- Monitoring / Blocking (Proxy)
You may also decide to use a firewall as a traffic proxy. The network configuration is impacted by whether the Database Firewall will operate in monitoring only or will include blocking mode as well.
You will use traffic and proxy sources of a Firewall to configure monitoring points for each target database you are monitoring with that firewall.
5.9.2 Configuring Network Settings
Learn about configuring network setting (traffic sources).
The installation process applies network settings like the IP address, network mask, and so on, to a network interface card (NIC), also referred to as a management interface. It also detects and lists all NICs.
Use the following steps to change the settings for the management interface or to configure any other available NIC that can be used as a traffic source:
5.9.3 Configuring the Database Firewall As a Traffic Proxy
You can specify multiple ports to be used as different proxy monitoring points. After you set up the Database Firewall as a traffic proxy, your database clients connect to the database by using the Database Firewall proxy IP address and port.
- Log in to the Audit Vault Server console as an administrator.
- Click the Database Firewalls tab.
Database Firewalls is selected in the left navigation menu by default.
- Click the name of the Database Firewall instance that you want to configure as a proxy.
- In the Configuration section, click Network Settings.
- Starting in Oracle AVDF 20.12, if the Synchronize NICs button is disabled, proceed to the next step. If the Synchronize NICs is active, click it, as the AVS detects NIC name changes in the Database Firewall which must be synchronized.
- Select a NIC name on the Database Firewall for all the devices. If a device is no longer available on the Database Firewall and is no longer required on the AVS, select not required.
- After mapping each device, select Save.
- In the Network Settings dialog box, click the name of the network interface card in the Network Interface Card column.
- In the Network Interface Settings dialog box, click Add in the Proxy Ports section.
- Enter the name and port number.
When specifying a proxy mode target, you can enter one target address, consisting of IP:port:Oracle Service Name (OSN). The OSN can be left blank, meaning that all Oracle database services at the provided IP:port will be processed.
Note:
If you plan to monitor more than one OSN on a target database:- Oracle AVDF 20.1-20.9: You need to configure a proxy target for each OSN. This is because a single proxy port cannot service multiple OSN's on the same target database. Add more traffic proxy ports as required.
- Oracle AVDF 20.10 and later: You can use one proxy port and specify multiple OSN's on the target database that are going to be processed. Specify the OSN's in a list delimited by the "|" character. For example, target1|target2|target 3.
- (Optional) To specify more than one proxy port, click Add, and enter another port name and number.
- Click Save.
-
The traffic proxy is now available to use in the Database Firewall monitoring point.
5.10 Viewing the Status and Diagnostics Report for Database Firewall
Learn how to view Database Firewall status and diagnostics reports.
To view the status or diagnostic reports for Database Firewall:
5.11 Configure and Download the Diagnostics Report File
Learn about configuring and downloading the diagnostics report file.
This section contains information about enabling, configuring, and modifying the way diagnostic reports are generated using CLI.
Note:
You need root user privileges to perform these tasks.The diagnostic report is not enabled by default. You must enable the feature to capture the diagnostic report. Once enabled, you must configure the information that is to be captured in the diagnostic report. You can customize and package the diagnostics report with flexibility.
-
Log in to the appliance through SSH and switch to the
rootuser. - Run the following command on the
appliance:
The/usr/local/dbfw/bin/priv/dbfw-diagnostics-package.rb --installdiagnostics-not-enabled.readmefile is downloaded when the diagnostics package is not enabled. - After the package has been installed, the diagnostics configuration must be
modified to allow the utility to collect information about the appliance. Collection of all
elements and files can be enabled
with:
/usr/local/dbfw/bin/priv/dbfw-diagnostics-package.rb --enable ALLAlternatively, the collection of the SOS report can be enabled with:
/usr/local/dbfw/bin/priv/dbfw-diagnostics-package.rb --enable SOS_REPORT - Optionally, further options are available by viewing the utility
help:
/usr/local/dbfw/bin/priv/dbfw-diagnostics-package.rb --help - Run the following command to capture the enabled diagnostic information for
the appliance:
/usr/local/dbfw/bin/priv/dbfw-diagnostics-package.rbWhen you run the diagnostics collection command, deployment information will be collected by default. See the table below to learn what deployment information is collected.
The location of the saved zip file is displayed at the end of the command execution.
- When you have collected the diagnostics, remove the package with the
following command:
/usr/local/dbfw/bin/priv/dbfw-diagnostics-package.rb --remove
Table 5-1 Deployment Information Collected By the
Diagnostics Log When Run With the ALL Option on the Audit Vault Server
(AVS)
| Deployment Information | Details |
|---|---|
| Number of targets and type of targets | Number of each type of target |
| Audit trail type | Number of each type of audit trail |
| Number of Database Firewall (DBFW) servers | Number of DBFW servers (individual servers) |
| High Availability (HA) Configuration - AVS | Yes or No |
| High Availability (HA) Configuration - DBFW | Yes or No
If yes, the number of primary/secondary firewall servers |
| DBFW deployment model | Count of each type of deployment if present
|
| List of audit policies enabled | Are unified auditing policies provisioned? Yes or No |
| Are traditional auditing policies provisioned? Yes or No | |
| The number of predefined policies that are enabled | |
| The number of custom policies | |
| DBFW policies and rules deployed | The number of policies with Database Object rule |
| The number of policies with Session Context rule | |
| The number of policies with Default rule | |
| The number of policies with SQL Statement rule | |
| Entitlement report | Is it scheduled? Yes or No |
| Sensitive Object job | Is it scheduled? Yes or No |
| Security Assessment | Is it scheduled? Yes or no? |
| Number of Alert policies | Number of alerts enabled |
| Email notification | Is it enabled for alert policies? Yes or No |
| Is it enabled for system alerts? Yes or No | |
| Sensitive object upload | Have you uploaded a file? Yes or No |
| Number of generated reports | Number of reports per category generated |
| Number of scheduled reports | Number of reports per category Scheduled |
| STIG | Is it enabled? Yes or No |
| TLS | Is it enabled? Yes or No |
| FIPS | Is it enabled? Yes or No |
| Stored procedure auditing | Is it scheduled? Yes or No |
| Number of events per second | Number of events per second |
| Use of network-based storage | Is it being used? Yes or No |
| Archive policy | The archive policies being used for targets: number of months online and offline. |
| Backup frequency | Backup frequency |
| Hardware configuration (core/RAM) of AVS and DBFW server | Hardware configuration (core/RAM) of AVS |
| Total memory space (KB) | |
| Total disk space (Bytes) | |
| CPU utilization percent |
5.12 Configuring Encapsulated Remote Switched Port Analyzer with Database Firewall
Learn how to configure Database Firewall when the SQL traffic is mirrored using Encapsulated Remote Switched Port Analyzer.
Encapsulated Remote Switched Port Analyzer (ERSPAN) mirrors the traffic from one or more source ports and delivers the mirrored traffic to one or more destination ports on another device.
This functionality enables the Database Firewall to interpret the SQL traffic received. This functionality is available only in Monitoring (Out of Band) deployment mode of Database Firewall.
Configuring ERSPAN with Database Firewall includes the following steps on a high level:
- Configuring the ERSPAN source or the switch.
- Configuring the Database Firewall.
Configuring the ERSPAN source or the switch includes the following steps:
-
Configure the network device or switch to span the SQL traffic to the target databases that are being monitored.
-
Consider the following aspects during ERSPAN configuration:
- Avoid spanning the database response traffic unless it requires to be analyzed.
- Avoid spanning empty TCP packets. For example, empty ACK packets.
-
Ensure the ERSPAN traffic is directed to the appropriate network interface card (NIC) configured on the Database Firewall.
Configuring the Database Firewall for this functionality includes the following steps:
-
Configure the Database Firewall monitoring point only in Monitoring (Out of Band) mode.
-
List all the IP addresses and ports of the SQL traffic expected from the target databases.
Note:
For Oracle Real Application Cluster databases, this is not just the scan IP addresses. It also includes all the relevant Oracle RAC nodes. -
Configure the Database Firewall monitoring point. During configuration, select the NIC to which the ERSPAN traffic is forwarded.
-
The Database Firewall does not process the ERSPAN traffic by default. It has to be enabled on the Database Firewall monitoring points. Follow these steps to enable:
-
Log in to the Database Firewall through SSH and switch to the
rootuser. - Change to
/var/dbfw/vadirectory. - Identify the Database Firewall monitoring point by
searching for the target name configured in the Audit Vault Server. Run the
following
command:
grep -lr <TARGET NAME> * - Find the monitoring point number from the output
which contains the name and path of the configuration file. For example:
1/etc/appliance.conf. In this example,1is the monitoring point number. - Find the target database
vanumber from the output as well. It will be before the monitoring point number, i.e.va/1/etc/appliance.conf -
Enable ERSPAN in the Database Firewall monitoring point by editing the file:
/usr/local/dbfw/va/<N>/etc/appliance.confwhereNis the monitoring point number andvais the target database number.. - In the file, edit the setting:
DAM_TRAFFIC_IS_ERSPAN="0" to DAM_TRAFFIC_IS_ERSPAN="1". - Save the changes.
- Restart the Database Firewall processes so that the new configuration comes
into effect. Run the command to restart:
/usr/local/dbfw/bin/dbfwctl restart
-
-
Verify the ERSPAN traffic received. Access the
/var/log/messagesfile in the Database Firewall. Navigate and locate the stringODF-10524: Encapsulated protocol detected. This string is logged when the ERSPAN traffic is first received.
Related Topics