Generating Vector Embeddings
This topic describes the procedure for generating vector embeddings through the Vector Toolbox.
- Selecting a data source (can be a file or database table)
- Configuring the chunk parameters
- Selecting or creating an embedding model
- Selecting the destination to store the embeddings
- File System - If you select File System as the source type, you can upload any file type as the Source File. Click the Add (+) icon in the Source File section and select one or more files from your workstation. You can remove a selected file or change the order in which the source files will be processed.
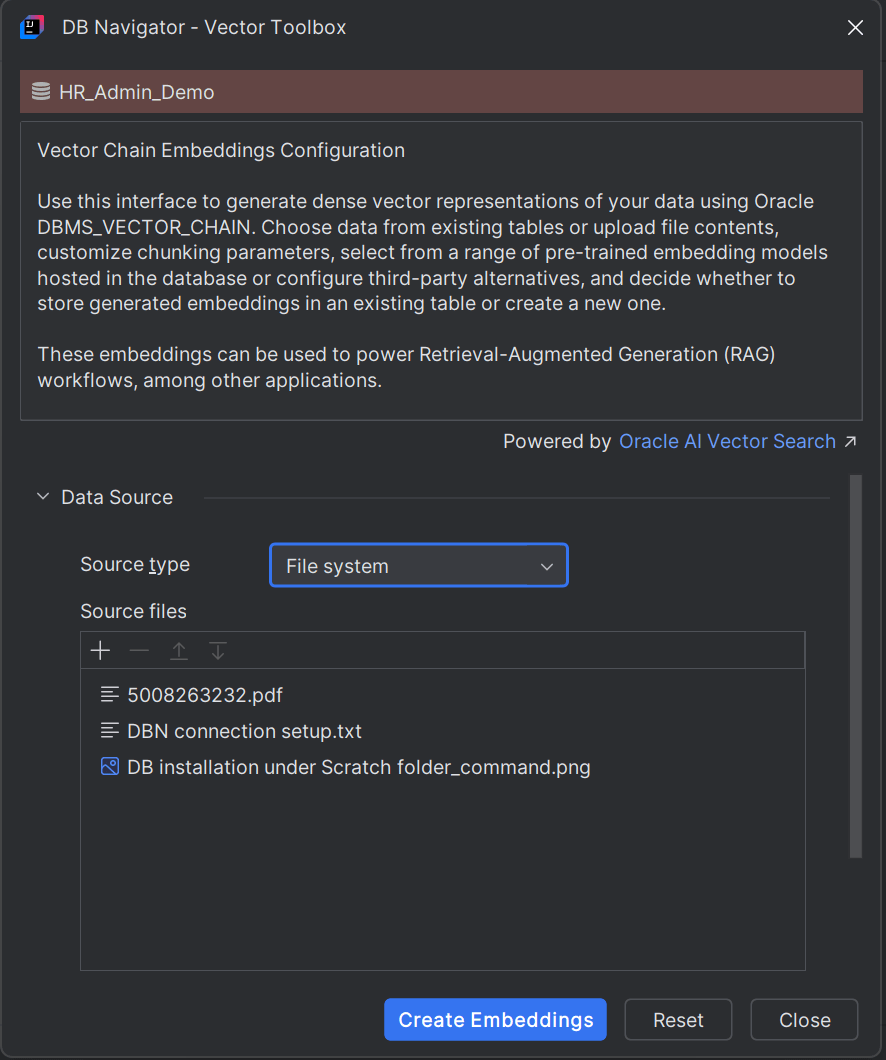
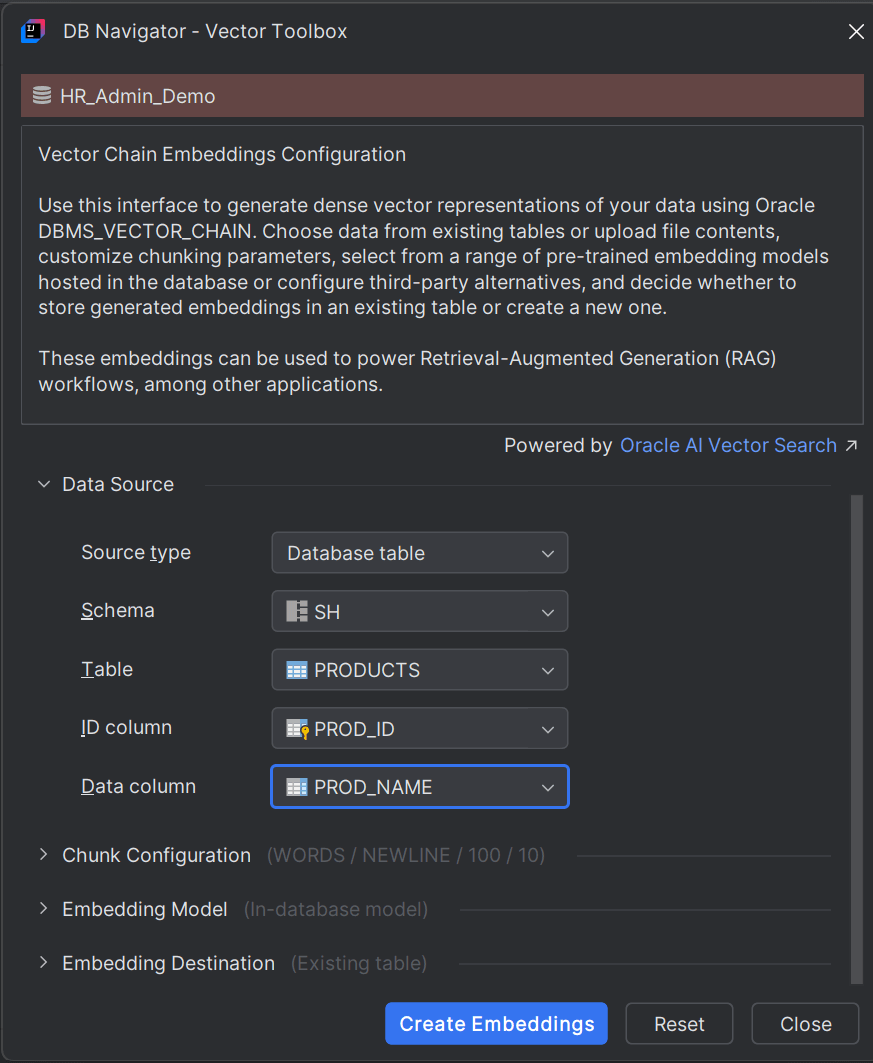
- Database Table - If you select Database Table as the source type, you have to further select the following:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Schema | Select the database schema from the DB connection for which you want to generate the embedding. |
| Table | Select the database table in the schema you selected. |
| ID Column | Select the column ID of the table for which you want to generate the embeddings. |
| Data Column | Select the data column of the table for which you want to generate the embeddings. |
To chunk or split the selected source file into smaller segments, in the Chunk Configuration section of the Database Navigator - Vector Toolbox, set the following parameters:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Chunk by | Select the separator or breakpoint to create chunks of the source data. Options include by Words or by Characters. |
| Max Size | Set the maximum length of each chunk. Smaller chunks result in more precise search matches while larger chunks can lead to less precise results. |
| Split by |
Select the chunking strategy to split the source text. Options include:
|
| Overlap | Set the overlap percentage indicating the number of tokens or characters shared between consecutive chunks. This parameter helps in maintaining continuity and ensuring that important data near chunk boundaries are not lost. 10% - 25% overlap of chunk size is considered ideal. |
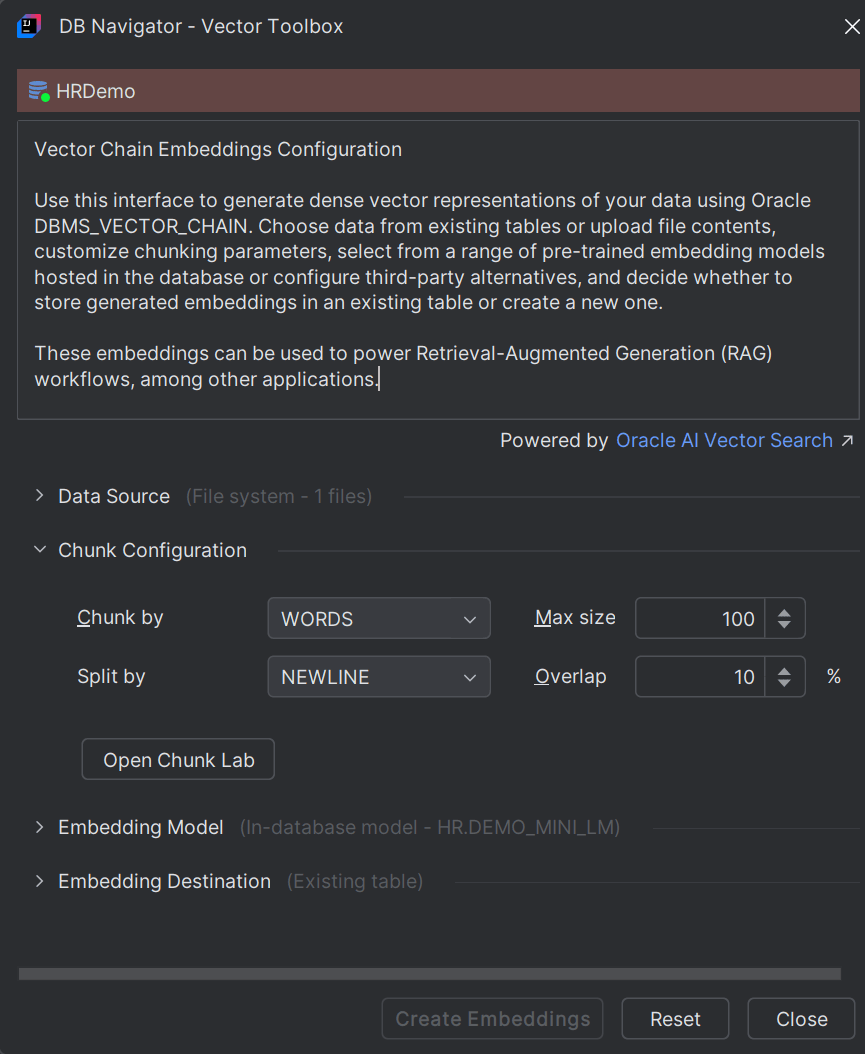
To test the effects of chunking on your source file, click Chunk Lab button to open the DB Navigator - Chunk Lab dialog box.
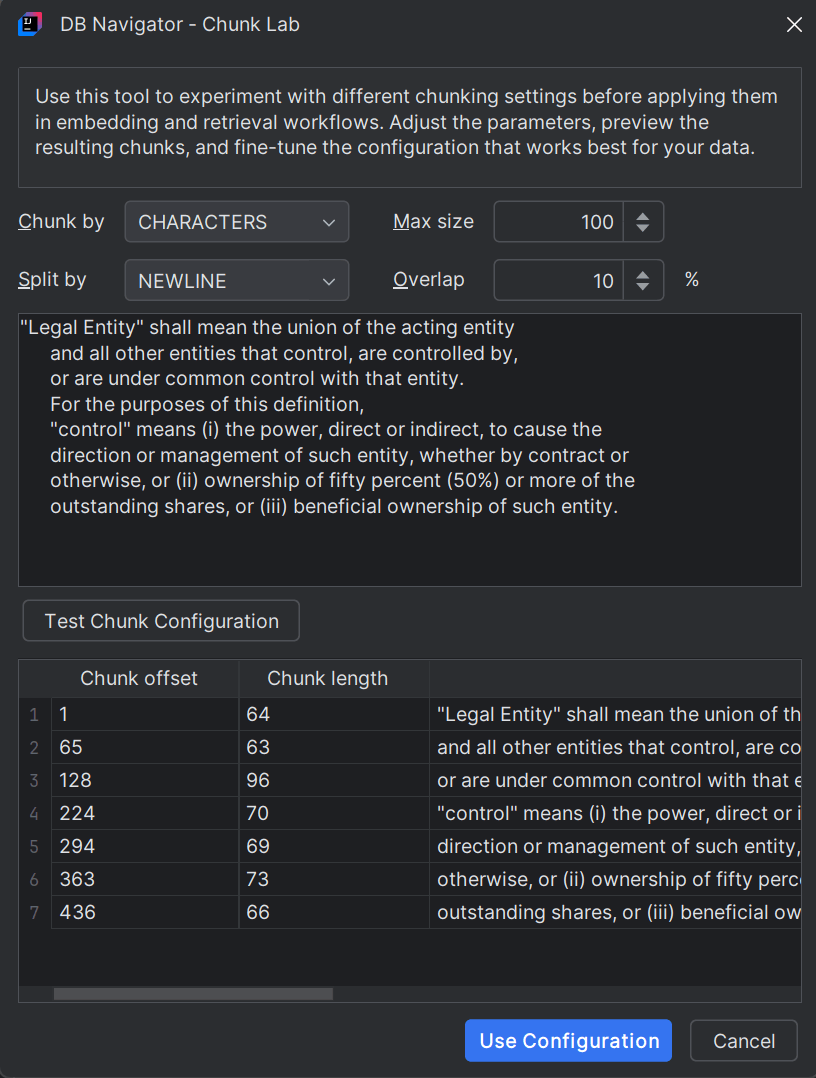
You can set the chunking parameters and paste a sample text of your source file and click Test Chunk Configuration to get a preview of the output before applying them in the actual embeddings. Once satisfied with the chunk output, click Use Configuration to apply the same for generating final embeddings.
| Model Location | Description |
|---|---|
| In-database Model | In-database AI embedding models are integrated or closely coupled within the database system so that the database itself handles the transformation of raw data stored within into vector embeddings. As a user (with adequate privileges), you have direct control over the in-database model's configuration and updates. |
| Third-party Model | Third-party AI embedding models are offered by external vendors (LLM providers) as a service or a platform, such as a cloud-based API, deployed separately from the database. Raw data is sent from the database to the third-party service for generating vector embeddings and then sent back to the database for storage. |
- Schema - Select the database schema where the embedding model is located.
- Model - Select the Model name to use for generating the vector
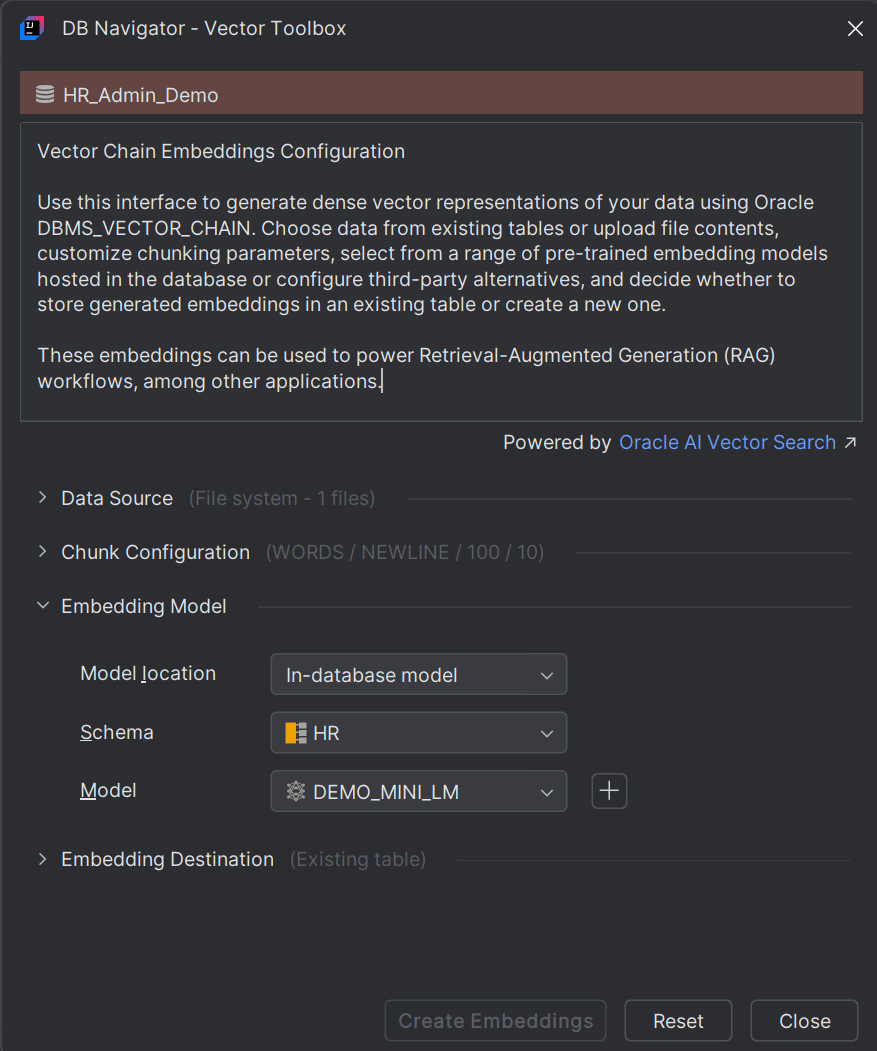
If an embedding model does not exist, you can create a new model by clicking the Create AI Model (+) icon next to the Model field. The DB Navigator - Create AI Model dialog box opens.
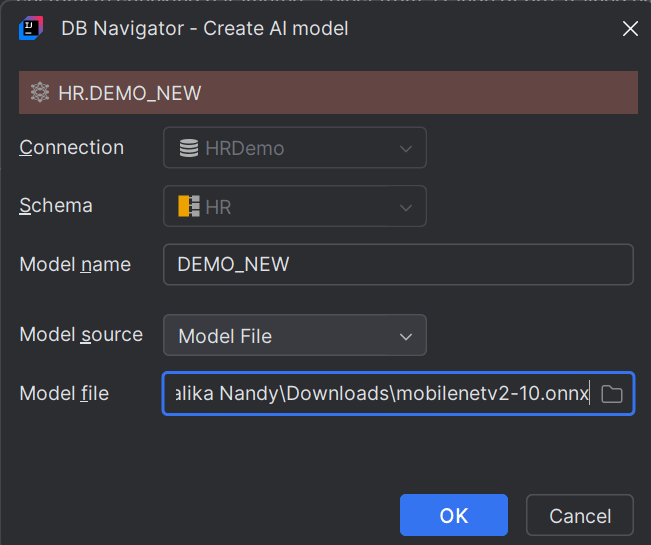
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection | This field is pre-filled with the DB connection in which you are adding the AI model. |
| Schema | This field is pre-filled with the DB schema in which you are adding the AI model. |
| Model Name | Enter a name for the new AI model. |
| Model Source | Choose between Model File or Object Resource:
|
| Model File | Browse through the model source file (such as a .onnx file) saved in your local system and upload it. This field is displayed only if you select Model File as the model source.
|
| Object URL | Type the URL of the platform from where the embedding model can be downloaded. This field is displayed only if you select Object Resource as the model source. |
| Credential | Select one from the available credentials for supported LLMs. If a credential is not available, click the Create Credential icon (+) to open the DB Navigator - Create Credential dialog box and create a new credential corresponding to an LLM (such as those provided by OCI Generative AI, Open AI, Google, Anthropic, Mistral AI, etc.). For more information on creating credentials, see "Creating Credentials for Public LLMs" |
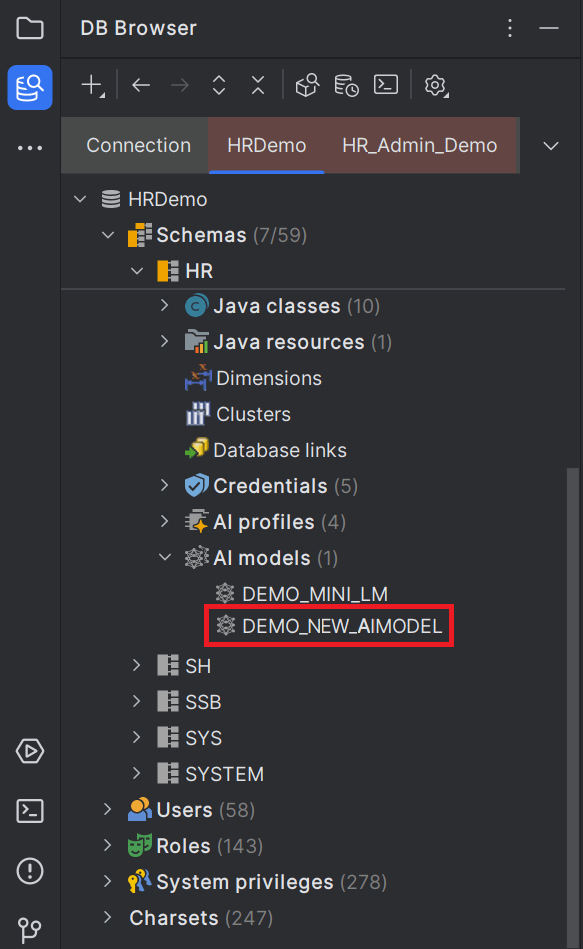
Click OK to start AI model creation. The model is added to the selected schema and visible on the DB Browser connection tree.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Provider |
Select from one of the supported third-party AI embedding model providers. Options include:
|
| Model | Mention the embedding model to be used, for example, Gemini Embedding-001, or text-embedding-3-small.
|
| URL | Provide the URL of the platform from where the third-party embedding model file can be accessed or downloaded/subscribed. |
| Credential Schema | Select the database schema where the AI credential corresponding to the selected Model (or Model provider) is stored. |
| Credential | Select one from the list of available credentials that can be used with the selected Model. |
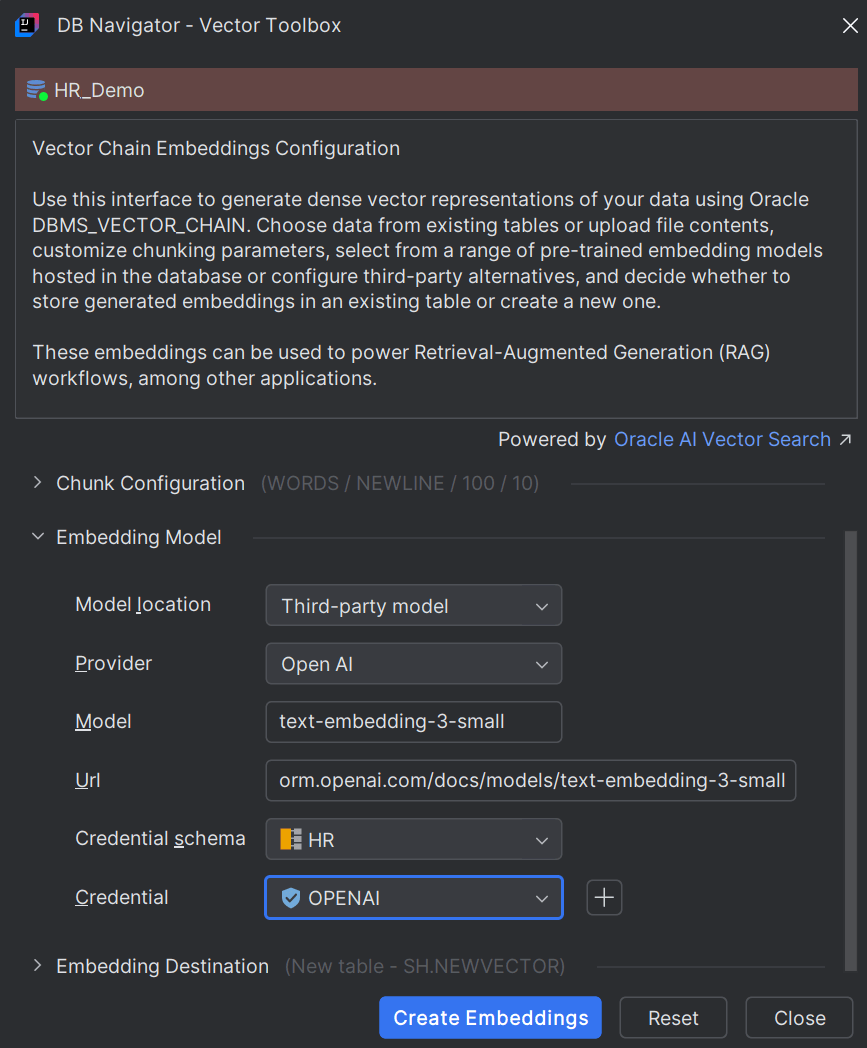
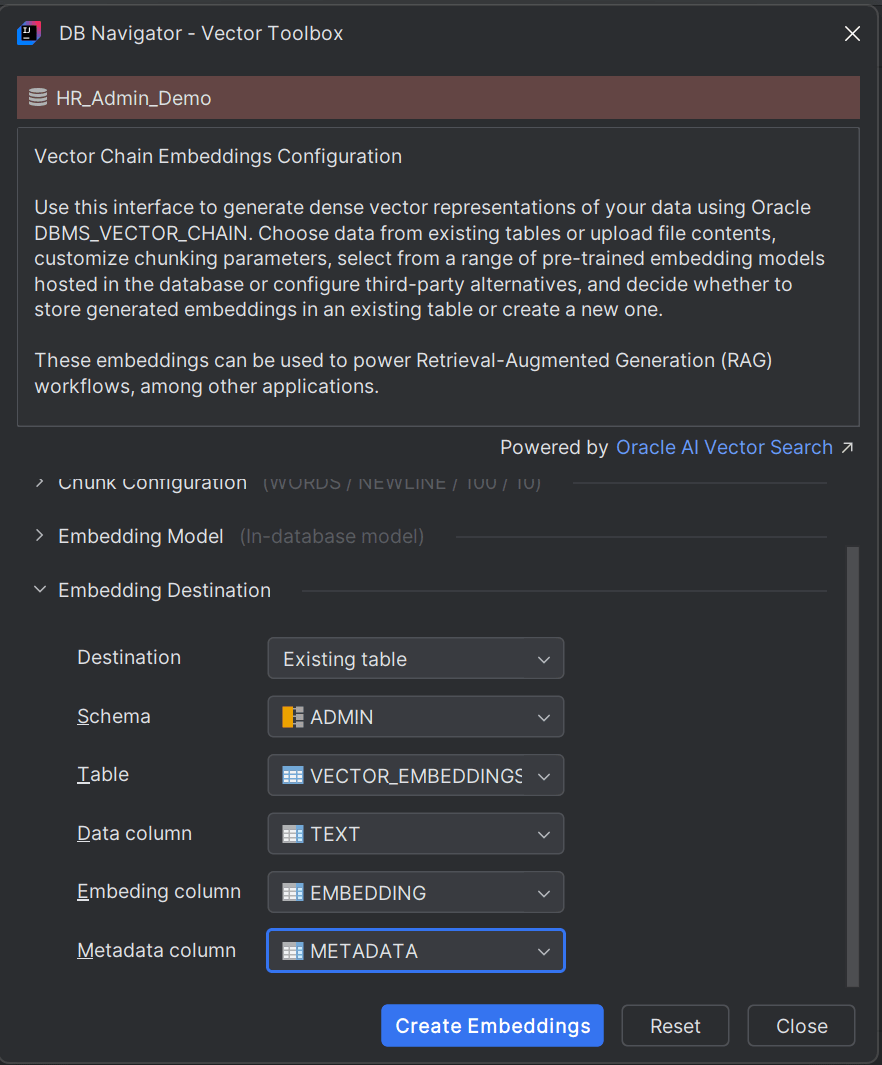
To set the destination where you want the generated embeddings to get stored, in the Embedding Destination section of the DB Navigator - Vector Toolbox, first select the Destination. You can either store the generated vector embeddings in an existing database table or create a new table.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Schema | Select the database schema where the vector embeddings will be stored. |
| Table | Select the database table within the schema where the vector embeddings will be stored. |
| Data column | Select the table column to store the embedding text data. |
| Embedding column | Select the table column to store the embedding vector. |
| Metadata column | Select the table column to store embedding metadata. Metadata is stored only for file systems and not when the source data is from DB tables. |
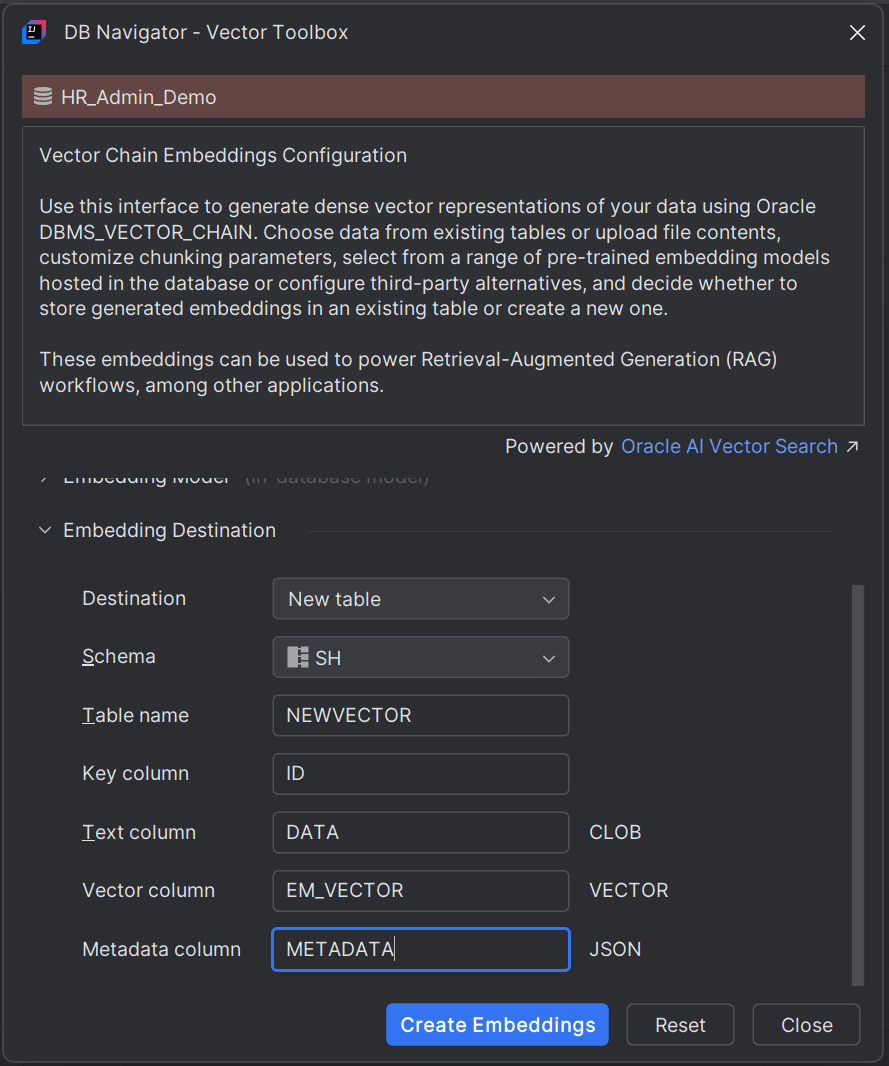
If you select New table as your preferred Destination, set the following parameters:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Schema | Select the database schema where the vector embeddings will be stored. |
| Table name | Select the database table within the schema where the vector embeddings will be stored. |
| Key column | By default, the Key column name is ID. You can change the Key column name where the vector ID is stored. |
| Text column (CLOB) | Mention the column name to store embedding text data. |
| Vector column (VECTOR) | Mention the column name to store the embedding vector. |
| Metadata column (JSON) | Mention the column name to store embedding metadata. |
Once you have configured all the fields for Data Source, Chunk Configuration, Embedding Model, and Embedding Destination in the Vector Toolbox, click Create Embeddings to start generating vector embeddings. After successful generation, the vector embeddings get stored in the destination table you configured.
Parent topic: Vector Toolbox