Working with Public LLMs
This topic provides an overview of interaction with DB Assistant module when using a public LLM.
- Start by selecting a database connection for which you require AI assistance from the banner of the DB Assistant window.
- Next, select the Public LLM option from the drop-down list displayed on DB Assistant window banner.
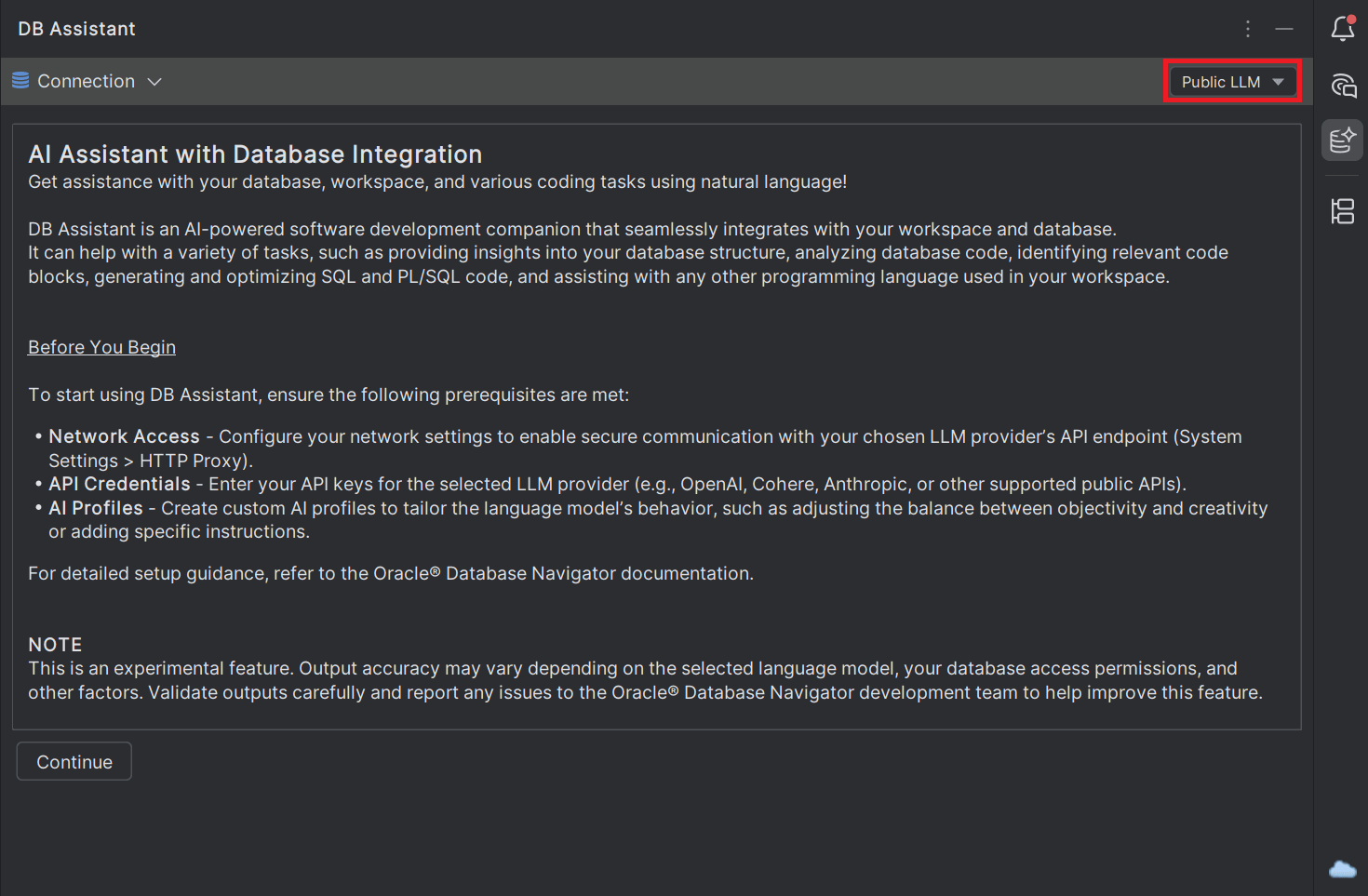
- When you select Public LLM mode for the first time, a disclaimer message is displayed for your review that you must read and then click Continue to proceed.
- From the DB Assistant window drop-down fields, select the AI Profile and the Language Model you want to use.
- Start typing your inputs in the DB Assistant chat box or click the + New Chat icon to start conversing with the DB Assistant in a dedicated chat thread and press Enter (or click the Submit icon).
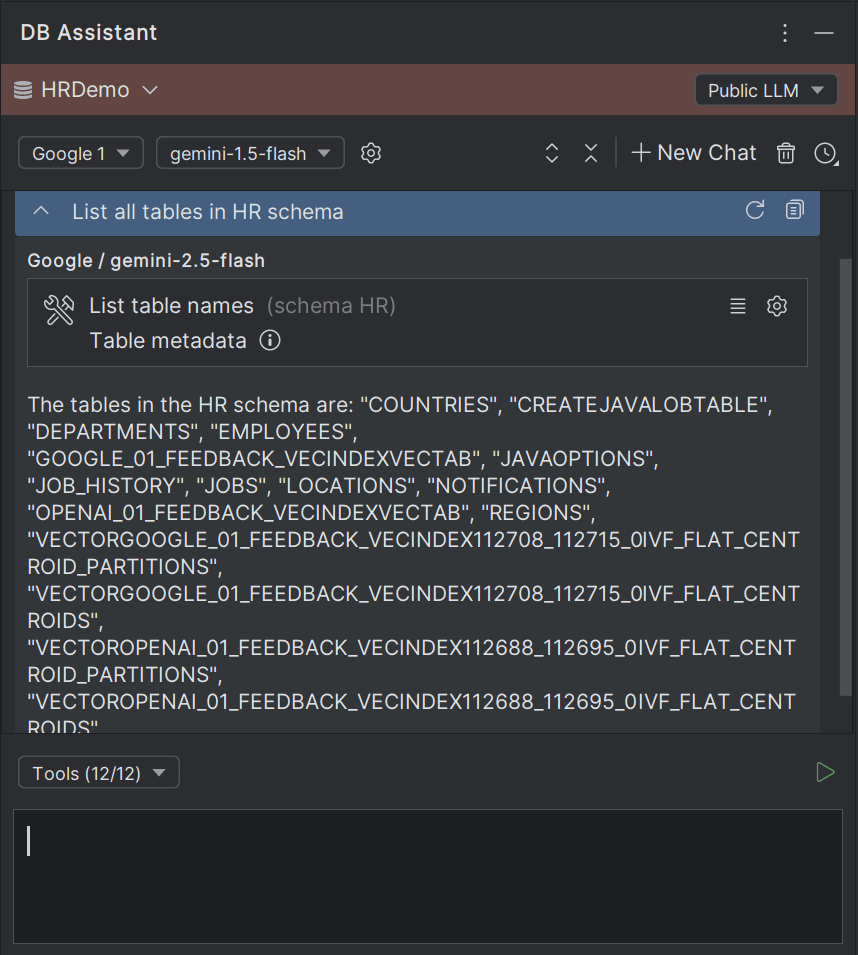
Sample Interaction with DB Assistant
The following example cites a common interaction with the DB Assistant using Google Gemini-1.5-Flash AI model.
Start typing an input prompt in the chat box and press Enter (or click the Submit icon). The selected public LLM is invoked.
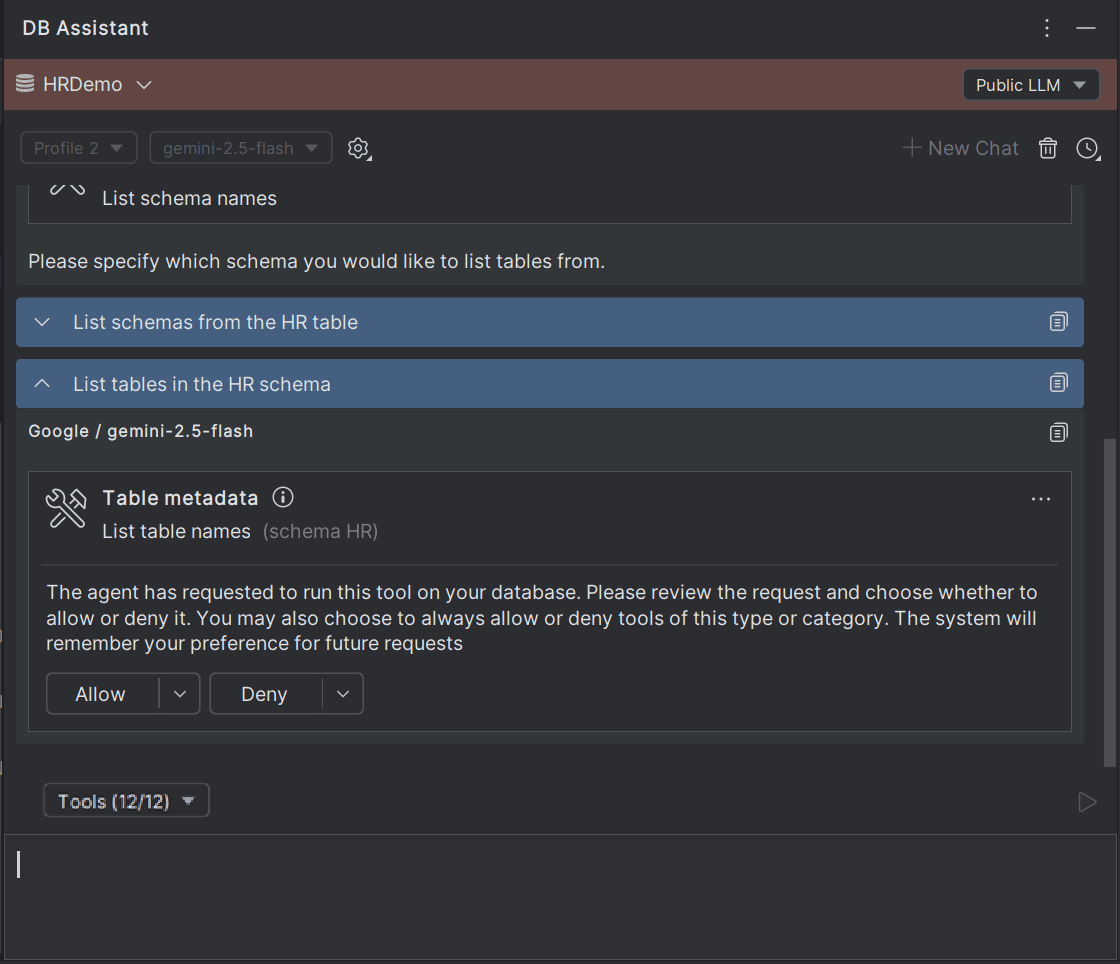
Based on your inputs, the database and workspace integration is provided through MCP services, and the database information from the specific connection is fed to the LLMs. The integration is done through invoking certain MCP tools which act as third-party models, where you can manage the access of these tools by approving (Allow/Allow All) or blocking (Deny/Deny All) their access to the language models being used.
- Metadata information (including database metadata, table metadata, schema metadata, view and program metadata).
- Database connection configuration information.
- View (including views, materialized views, JSON relational duality views) and Program source code access.
- SQL consoles, source code editors and data editors in the IDE.
- Tool Approvals and Tool Data
This topic provides an overview of the tools invoked by language models to access data and database information.
Parent topic: Public LLMs