ALTER AUDIT POLICY (Unified Auditing)
This section describes the ALTER AUDIT POLICY statement for unified auditing. This type of auditing is new beginning with Oracle Database 12c and provides a full set of enhanced auditing features. Refer to Oracle Database Security Guide for more information on unified auditing.
Purpose
Use the ALTER AUDIT POLICY statement to modify a unified audit policy.
Prerequisites
You must have the AUDIT SYSTEM system privilege or the AUDIT_ADMIN role.
If you are connected to a multitenant container database (CDB), then to modify a common unified audit policy, the current container must be the root and you must have the commonly granted AUDIT SYSTEM privilege or the AUDIT_ADMIN common role. To modify a local unified audit policy, the current container must be the container in which the audit policy was created and you must have the commonly granted AUDIT SYSTEM privilege or the AUDIT_ADMIN common role, or you must have the locally granted AUDIT SYSTEM privilege or the AUDIT_ADMIN local role in the container.
After you alter an unified audit policy with object audit options, the new audit settings take place immediately, for both the active and subsequent user sessions. If you alter an unified audit policy with system audit options, or audit conditions, then they become effective only for new user sessions, but not for the current user session.
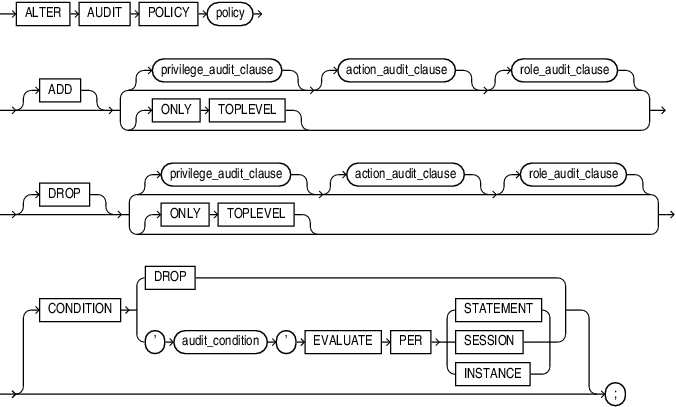
Syntax
alter_audit_policy::=
Note:
If you specify the ADD or DROP clause, then you must specify at least one of the clauses privilege_audit_clause, action_audit_clause, or role_audit_clause.
(privilege_audit_clause::=, action_audit_clause::=, role_audit_clause::=)
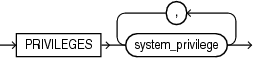
privilege_audit_clause::=
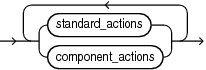
action_audit_clause::=
standard_actions::=
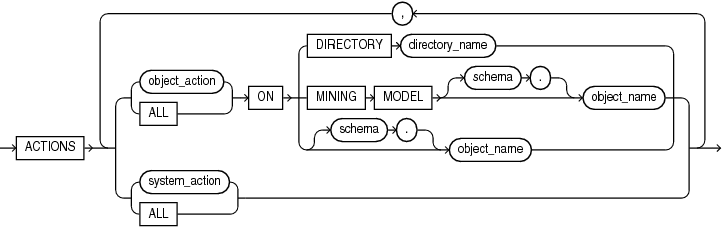
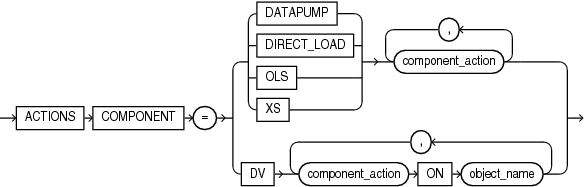
component_actions::=
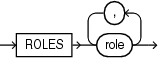
role_audit_clause::=
Semantics
policy
Specify the name of the unified audit policy to be modified. The policy must have been created using the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement. You can find descriptions of all unified audit policies by querying the AUDIT_UNIFIED_POLICIES view.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Reference for more information on the
AUDIT_UNIFIED_POLICIESview
ADD | DROP
Use the ADD clause to add privileges to be audited to policy.
Use the DROP clause to remove privileges to be audited from policy.
Refer to privilege_audit_clause, action_audit_clause, and role_audit_clause of CREATE AUDIT POLICY for the full semantics of these clauses.
CONDITION
Use this clause to drop, add, or replace the audit condition for policy.
Specify DROP to drop the audit condition from policy.
Specify 'audit_condition' ... to add or replace the audit condition for policy.
Refer to audit_condition, EVALUATE PER STATEMENT, EVALUATE PER SESSION, and EVALUATE PER INSTANCE of CREATE AUDIT POLICY for the full semantics of these clauses.
ONLY TOPLEVEL
Specify this clause to change the existing unified audit policy to audit only the top level SQL statements issued by the user.
Example: Add Top Level Auditing
The example changes the HR audit policy hr_audit_policy to capture only top level statements.
ALTER AUDIT POLICY hr_audit_policy ADD ONLY TOPLEVEL
You can drop top level auditing from an existing audit policy auditing the top level SQL statements.
Example: Drop Top Level Auditing
ALTER AUDIT POLICY hr_audit_policy DROP ONLY TOPLEVEL
See Database Security Guide for more information.
Examples
The following examples modify unified audit policies that were created in the CREATE AUDIT POLICY "Examples".
Adding Privileges, Actions, and Roles to a Unified Audit Policy: Examples
The following statement adds the system privileges CREATE ANY TABLE and DROP ANY TABLE to unified audit policy dml_pol:
ALTER AUDIT POLICY dml_pol ADD PRIVILEGES CREATE ANY TABLE, DROP ANY TABLE;
The following statement adds the system actions CREATE JAVA, ALTER JAVA, and DROP JAVA to unified audit policy java_pol:
ALTER AUDIT POLICY java_pol ADD ACTIONS CREATE JAVA, ALTER JAVA, DROP JAVA;
The following statement adds the role dba to unified audit policy table_pol:
ALTER AUDIT POLICY table_pol ADD ROLES dba;
The following statement adds multiple system privileges, actions, and roles to unified audit policy security_pol:
ALTER AUDIT POLICY security_pol
ADD PRIVILEGES CREATE ANY LIBRARY, DROP ANY LIBRARY
ACTIONS DELETE on hr.employees,
INSERT on hr.employees,
UPDATE on hr.employees,
ALL on hr.departments
ROLES dba, connect;Dropping Privileges, Actions, and Roles from a Unified Audit Policy: Examples
The following statement drops the system privilege CREATE ANY TABLE from unified audit policy table_pol:
ALTER AUDIT POLICY table_pol DROP PRIVILEGES CREATE ANY TABLE;
The following statement drops the INSERT and UPDATE actions on hr.employees from unified audit policy dml_pol:
ALTER AUDIT POLICY dml_pol
DROP ACTIONS INSERT on hr.employees,
UPDATE on hr.employees;
The following statement drops the role java_deploy from unified audit policy java_pol:
ALTER AUDIT POLICY java_pol DROP ROLES java_deploy;
The following statement drops a system privilege, an action, and a role from unified audit policy hr_admin_pol:
ALTER AUDIT POLICY hr_admin_pol
DROP PRIVILEGES CREATE ANY TABLE
ACTIONS LOCK TABLE
ROLES audit_viewer;Adding and Dropping Actions for a Unified Audit Policy: Example
The following statement adds EXPORT actions for Oracle Data Pump to unified audit policy dp_actions_pol and drops IMPORT actions for Oracle Data Pump:
ALTER AUDIT POLICY dp_actions_pol ADD ACTIONS COMPONENT = datapump EXPORT DROP ACTIONS COMPONENT = datapump IMPORT;
Dropping the Audit Condition from a Unified Audit Policy: Example
The following statement drops the audit condition from unified audit policy order_updates_pol:
ALTER AUDIT POLICY order_updates_pol CONDITION DROP;
Modifying the Audit Condition for a Unified Audit Policy: Example
The following statement modifies the audit condition for unified audit policy emp_updates_pol so that the policy is enforced only when the auditable statement is issued by a user whose UID is 102:
ALTER AUDIT POLICY emp_updates_pol CONDITION 'UID = 102' EVALUATE PER STATEMENT;