10.6.13 Database Views from RDF Models
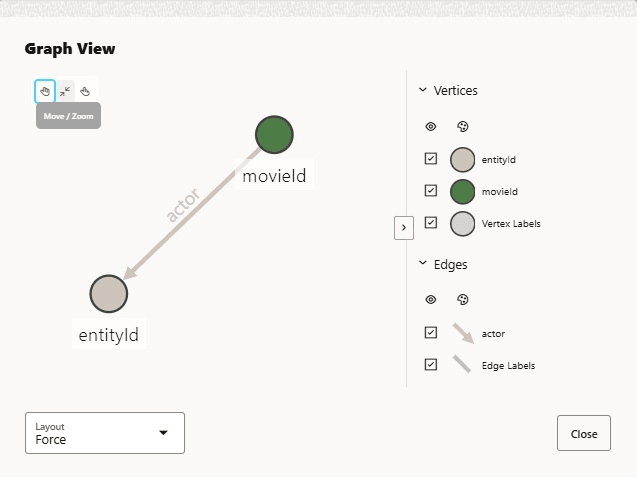
You can create relational views from RDF models. These views can represent a vertex or an edge view of a graph.
SPARQL query patterns can be used as a declarative language for specifying how to build vertex and edge views from RDF data.
It is important to note the following when creating the vertex and edge views from an RDF model:
- The RDF model must have classes defined and the application uses a
SPARQL query to retrieve the distinct classes defined on an RDF model. For
example:
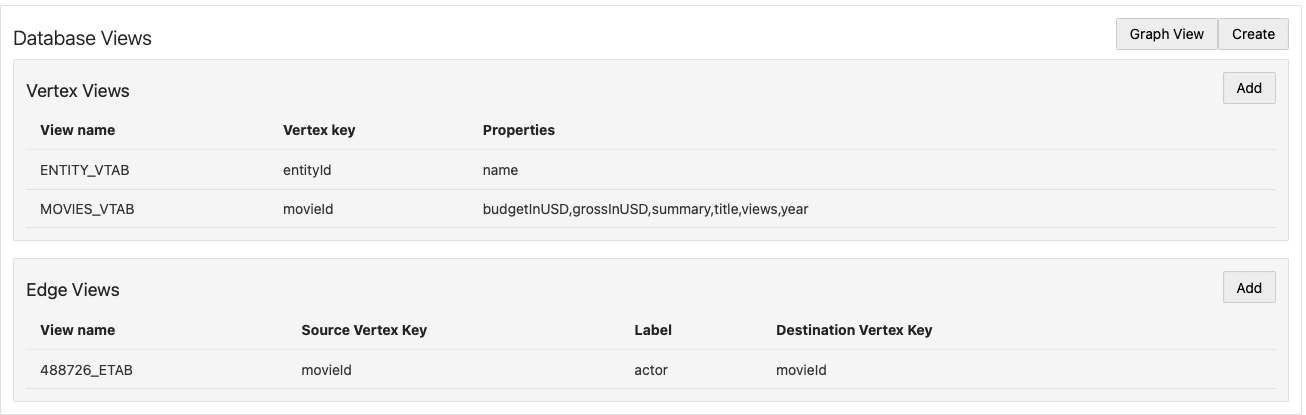
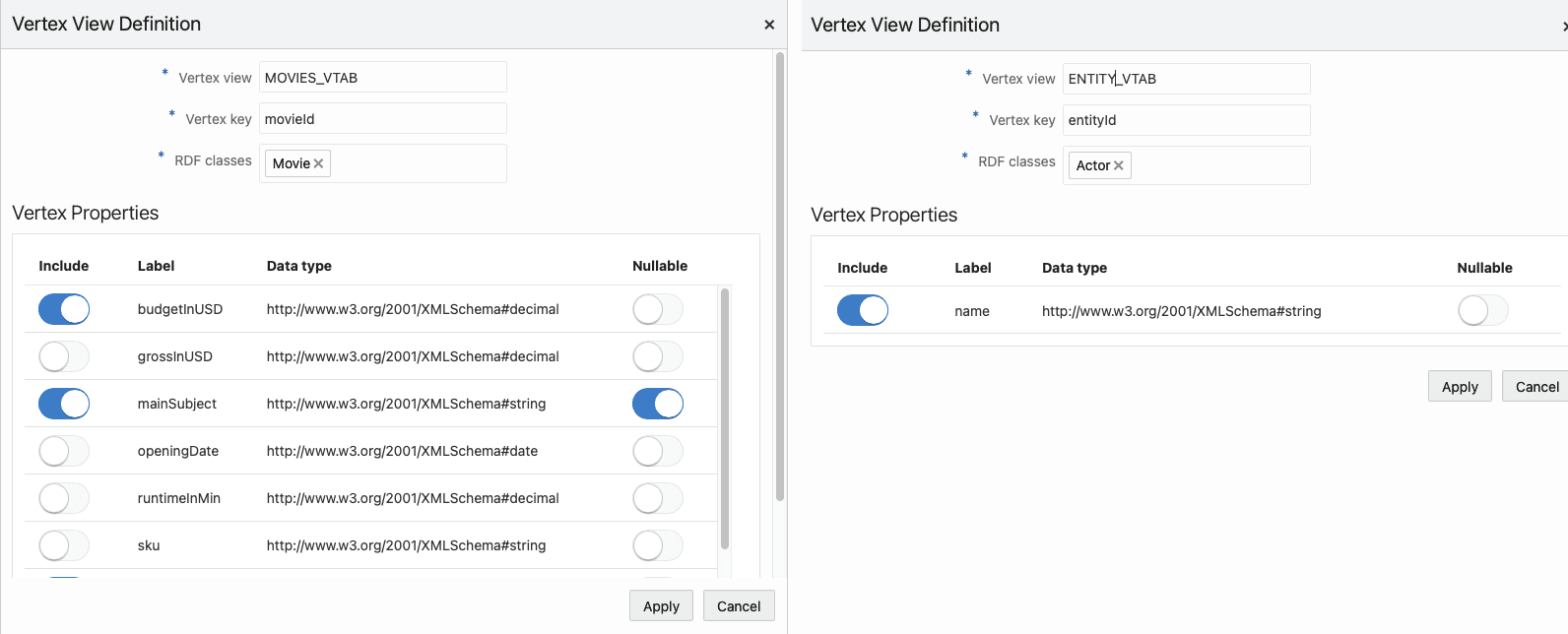
SELECT DISTINCT ?o WHERE { ?s a ?o } order by ?o - One or more RDF classes can define a vertex view. A vertex view
consists of:
- Database vertex view name
- Key attribute name
- Vertex properties from RDF class
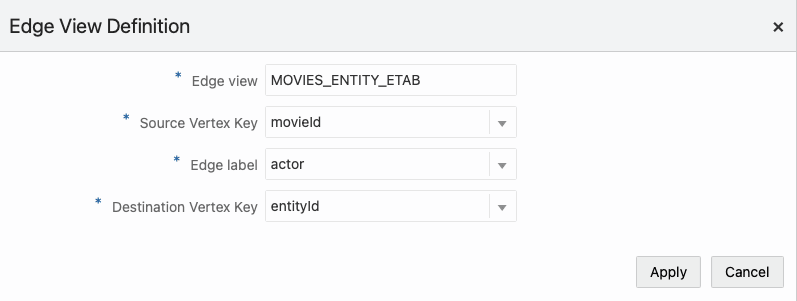
- One or two vertex views can define an edge view. An edge view consists
of:
- Database edge view name
- Source and destination vertex keys
- Label property from RDF classes
The following sections explain the steps to create a database graph view:
10.6.13.1 Creating a Graph View
Perform the following steps to create a database graph view:
Parent topic: Database Views from RDF Models
10.6.13.2 Creating a Vertex View
Perform the following steps to create a vertex view:
Parent topic: Database Views from RDF Models
10.6.13.3 Creating an Edge View
An edge view can be defined using one or two vertex views.
To create an edge view:
Parent topic: Database Views from RDF Models