1 Introduction
Chapter 1, Introduction, contains general information about the gateway screening feature, the database, and the organization of this manual.
Overview
The Database Administration – GWS User's Guide describes the procedures used to configure the EAGLE and its database to implement the Gateway Screening Feature.
The Gateway Screening (GWS) feature examines a Message Signaling Unit (MSU) attempting to enter the EAGLE against predefined criteria in the EAGLE database to determine whether the MSU should be allowed to enter. The screening functions are defined by using screening tables or screen sets containing a set of rules. Each screen set is uniquely identified by a screen set name. Each rule in the screen set is identified by a screening reference name. Each screening reference belongs to a specific category, which indicates the criteria used to either accept or reject an incoming MSU. Gateway screening tables provide screening of MTP messages on Link Interface Modules (LIMs) and SCCP messages on the service modules.
Note:
Database administration privileges are password restricted. Only those persons with access to the command class “Database Administration” can execute the administrative functions. Refer to Commands User's Guide for more information on command classes and commands allowed by those classes.It is possible for two or more users to make changes to the same database element at any time during their database administration sessions. It is strongly recommended that only one user at a time make any changes to the database.
- E5-ENET - the E5-ENET-B card
- E5-E1T1 - the E5-E1T1-B card
- E5-ATM - the E5-ATM-B card
- E5-IPSM - the E5-ENET-B or SLIC card that is running the IPSHC GPL
- E5-SM4G - the E5-SM8G-B card (not an EPM-B card)
- MCPM - the original MCPM or the E5-MCPM-B card
Scope and Audience
This manual is intended for database administration personnel or translations personnel responsible for configuring the EAGLE and its database to implement the Gateway Screening feature.
Documentation Admonishments
Admonishments are icons and text throughout this manual that alert the reader to assure personal safety, to minimize possible service interruptions, and to warn of the potential for equipment damage.
Table 1-1 Admonishments
| Icon | Description |
|---|---|

|
Danger: (This icon and text indicate the possibility of personal injury.) |

|
Warning: (This icon and text indicate the possibility of equipment damage.) |

|
Caution: (This icon and text indicate the possibility of service interruption.) |

|
Topple: (This icon and text indicate the possibility of personal injury and equipment damage.) |
Manual Organization
Throughout this document, the terms database and system software are used. Database refers to all data that can be administered by the user, including shelves, cards, links, routes, global title translation tables, and gateway screening tables. System software refers to data that cannot be administered by the user, including generic program loads (GPLs).
This document is organized into the following sections.
Introduction contains general information about the gateway screening feature, the database, and the organization of this manual.
Gateway Screening (GWS) Overview contains an overview of the Gateway screening feature and the procedures for provisioning the GLS card, gateway screening stop action sets, the threshold for gateway screening activity, and the maximum number of gateway screening rejected messages.
Allowed Affected Point Code (AFTPC) Screen Configuration contains the procedures necessary to configure allowed affected point code screens.
Allowed Called Party (CDPA) Screen Configuration contains the procedures necessary to configure allowed called party address screens.
Allowed Translation Type (TT) Screen Configuration contains the procedures necessary to configure allowed translation type screens.
Allowed Calling Party (CGPA) Screen Configuration contains the procedures necessary to configure allowed calling party address screens.
Allowed Affected Destination Field (DESTFLD) Screen Configuration contains the procedures necessary to configure allowed affected destination field screens.
Blocked Destination Point Code (BLKDPC) Screen Configuration contains the procedures necessary to configure blocked destination point code screens.
Allowed Destination Point Code (DPC) Screen Configuration contains the procedures necessary to configure allowed destination point code screens.
Allowed Signaling Information Octet (SIO) Screen Configuration contains the procedures necessary to configure allowed signaling information octet screens.
Blocked Originating Point Code (BLKOPC) Screen Configuration contains the procedures necessary to configure blocked originating point code screens.
Allowed Originating Point Code (OPC) Screen Configuration contains the procedures necessary to configure allowed originating point code screens.
Screen Set Configuration contains the procedures necessary to configure screen sets.
Calling Name Conversion Facility (CNCF) Configuration contains a description of the Calling Name Conversion Facility feature the procedure necessary to configure this feature.
Allowed ISUP Message Type Screen Configuration contains the procedures necessary to configure allowed ISUP message type screens.
Related Publications
For information about additional publications related to this document, refer to the Oracle Help Center site. See Locate Product Documentation on the Oracle Help Center Site for more information on related product publications.
Locate Product Documentation on the Oracle Help Center Site
Maintenance and Administration Subsystem
The Maintenance and Administration Subsystem (MAS) is the central management point for the EAGLE. The MAS provides user interface, maintenance communication, peripheral services, alarm processing, system disk interface, and measurements. Management and redundancy are provided by use of two separate subsystem processors.
The MAS resides on two separate sets of Maintenance and Administration Subsystem Processor (MASP) cards and a Maintenance Disk and Alarm card (collectively referred to as control cards). The control cards are located in slots 1113 through 1118 of the EAGLE control shelf. The control cards must be E5-based cards.
E5-based Control Cards
- Two Maintenance and Administration Subsystem
Processor cards (E5-MASP) cards. Each dual-slot E5-MASP card is made up of the
following two modules:
- Maintenance Communication Application Processor (E5-MCAP) card
- Terminal Disk Module (E5-TDM) card
- One Maintenance Disk and Alarm card (E5-MDAL card)
Maintenance Communication Application Processor (E5-MCAP) Card
The E5-MCAP card contains the Communications Processor and Applications Processor and provides connections to the IMT bus. The card controls the maintenance and database administration activity and performs both application and communication processing. E5-MCAP cards are located in slots 1113 and 1115 of the control shelf.
Each E5-MCAP card contains two USB ports. One latched USB port is used with removable flash media (“thumb drives”), and one flush-mounted USB port is used with a plug-in flash drive. The removable media drive in the latched USB port is used to install and back up customer data. The flush-mounted USB port is used for upgrade and could be used for disaster recovery.
Terminal Disk Module (E5-TDM) Card
The E5-TDM card provides the Terminal Processor for the 16 I/O ports, and interfaces to the Maintenance Disk and Alarm (E5-MDAL) card and fixed disk storage. The E5-TDM card also distributes Composite Clocks and High Speed Source clocks throughout the EAGLE, and distributes Shelf ID to the EAGLE. Each E5-TDM card contains one fixed SATA drive that is used to store primary and backup system databases, measurements, and Generic Program Loads (GPLs). E5-TDM cards are located in slots 1114 and 1116 of the control shelf.
Maintenance Disk and Alarm (E5-MDAL) Card
The E5-MDAL card processes alarm requests and provides fan control. There is only one E5-MDAL card in a control card set. Critical, major, and minor system alarms are provided for up to 6 individual frames. In addition to the 3 system alarms, the E5-MDAL card provides the system audible alarm. The E5-MDAL card provides control of fans on a per-frame basis, and allows for each fan relay to be set individually. The E5-MDAL card is located in slots 1117 and 1118 of the control shelf.
EAGLE Database Partitions
The data that the EAGLE uses to perform its functions are stored in two separate areas: the fixed disk drives, and the removable media. The following sections describe these areas and data that is stored on them. These areas and their partitions are shown in Figure 1-1.
Figure 1-1 EAGLE Database Partitions (E5-Based Control Cards)
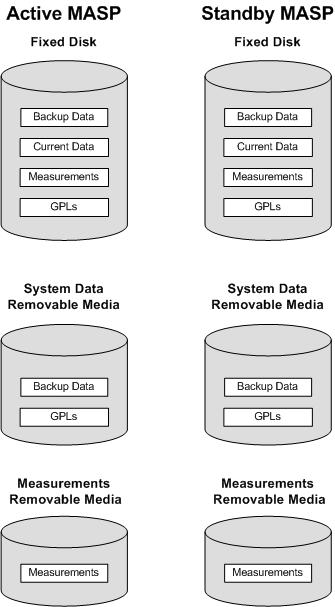
Fixed Disk Drive
There are two fixed disk drives on the EAGLE. The fixed disk drives contain the “primary” set of data and programs for the EAGLE. The two fixed disk drives are located on the terminal disk modules (E5-TDMs). Both disks have the same files. The data stored on the fixed disks is partially replicated on the various cards in the EAGLE. Changes made during database administration sessions are sent to the appropriate cards.
The data on the fixed disks can be viewed as four partitions.
-
Current partition
-
Backup partition
-
Measurements partition
-
Generic program loads (GPLs) partition
The data which can be administered by users is stored in two partitions on the fixed disk, a current database partition which has the tables which are changed by on-line administration, and a backup database partition which is a user-controlled copy of the current partition.
All of the on-line data administration commands affect the data in the current partition. The purpose of the backup partition is to provide the users with a means of rapidly restoring the database to a known good state if there has been a problem while changing the current partition.
A full set of GPLs is stored on the fixed disk, in the GPL partition. There is an approved GPL and a trial GPL for each type of GPL in this set and a utility GPL, which has only an approved version. Copies of these GPLs are downloaded to the EAGLE cards. The GPL provides each card with its functionality. For example, the ss7ansi GPL provides MTP functionality for link interface modules (LIMs).
Measurement tables are organized as a single partition on the fixed disk. These tables are used as holding areas for the measurement counts.
Removable Media
The removable media is used with the E5-MCAP card portion of the E5-MASP in card locations 1113 and 1115.
The removable media is used for two purposes.
-
To hold an off-line backup copy of the administered data and system GPLs
-
To hold a copy of the measurement tables
Because of the size of the data stored on the fixed disk drives on the E5-TDMs, a single removable media cannot store all of the data in the database, GPL and measurements partitions.
To use a removable media to hold the system data, it must be formatted for system data. To use a removable media to hold measurements data, it must be formatted for measurements data. The EAGLE provides the user the ability to format a removable media for either of these purposes. A removable media can be formatted on the EAGLE by using the format-disk command. More information on the format-disk command can be found in Commands User's Guide. More information on the removable media drives can be found in Hardware Guide.
Additional and preformatted removable media are available from the My Oracle Support (MOS).