6 LNP Feature Description
This chapter describes the Local Number Portability (LNP) feature and the LNP services used for Query and Message Relay.
6.1 LNP Message Relay
LNP MR performs Enhanced GTT routing to perform 10-digit LNP GTT. It includes the ability to decode the TCAP portion of the message to determine the 10-digit Called Party Number for the supported services.
-
Extraction of the 10-digit dialed number from the TCAP portion of the message – If the MSU contains a 6-digit Called Party Address, Message Relay gets the 10-digit Dialed Number (DN) from the TCAP portion of the MSU.
-
Increased number of translations – For each 10-digit Dialed Number, up to 6 translations are available. The previous limit was 270,000 total translations. The number of Dialed Numbers that can be entered depends on the hardware. The minimum hardware configuration supports 500,000 Dialed Numbers; 3 million translations can be entered on the minimum hardware configuration. The maximum hardware configuration supports 2 million Dialed Numbers; 12 million Message Relay translations can be entered on the maximum hardware configuration.
-
Replacement of the Global Title Address – Message Relay provides the option of replacing the Global Title Address in the Called Party Address with the Location Routing Number (LRN) associated with the ported Dialed Number.
-
The message arrives at the EAGLE as Route-on-GT. The EAGLE performs 6-digit (NPANXX) translation. The result of this translation indicates if Message Relay is required. If it is required, the result of this translation also gives the default data that may be used in stage 3.
-
If stage 1 indicates that Message Relay is required, the EAGLE performs 10-digit message relay. If the 10-digit number is found, the translation data for the 10-digit number is used to route the message.
-
If the 10-digit number is found and the number has an LRN assigned to it, the EAGLE checks for Message Relay override data. If there is override data for the LRN, the EAGLE uses this override data to route the message.
-
If no location routing number is assigned, or the location routing number does not have override data, the EAGLE uses the data assigned to the 10-digit number.
-
If the LRN has override data but not for the requested translation type or service, and the Service Portability option is on (shown in the SERVPORTparameter value in the LNPOPTS table), then the EAGLE uses the data assigned to the 10-digit number. If the Service Portability option is not on, then the message is discarded and UIM and UDTS messages are generated.
-
If no data is assigned to the 10-digit number, and the Service Portability option is on, then the EAGLE uses the default data from stage 1 to route the message. If the Service Portability option is not on, then the message is discarded and UIM and UDTS messages are generated.
-
If the 10-digit number is not found, the Dialed Number is not ported and the default data from stage 1 is used to route the message.
-
The NPANXX default data is entered.
-
The NPANXX is marked as portable (the value of the mr parameter is yes).
-
The NPAC sends down information for ported subscribers in the portable NPANXX.
However, it is possible that step 3 can occur before step 1. In this case, if a message arrives for the ported subscriber, the EAGLE routes the message according to the subscriber data entered by the NPAC.
-
The 10-digit number is found in the subscription record. The LRN has a matching entry in the override table. If override data exists for the requested service, the LRN override Global Title Translation is used. If LRN override data exists, but not for the requested translation type, and the Service Portability option is not on, then the result is no translation, the message is discarded, and UIM and UDTS messages are generated. If the Service Portability option is on, then the NPAC Global Title Translation data is used.
-
The 10-digit number is found in the subscription record. The LRN does not have a matching entry in the override table. If NPAC Global Title Translation data exists, the NPAC Global Title Translation is used. If NPAC Global Title Translation data does not exist for the 10-digit number, and the Service Portability option is not on, then the result is no translation, the message is discarded, and UIM and UDTS messages are generated. If the Service Portability option is on, then the NPANXX Global Title Translation data is used.
If a message arrives for a nonported subscriber in that NPANXX, and normal Global Title Translation information is defined for the message, the message is routed using the normal Global Title Translation data. But if a message arrives for a nonported subscriber in that NPANXX, and no normal Global Title Translation information is defined for the message, the message is discarded, and UIM and UDTS messages are generated.
Table 6-1 shows the result of the 10-digit Message Relay processing, and the processing required to route a message.
Table 6-1 LNP Message Relay
| Ported MR NPANXX | Ported TN | LNP Message Relay Processing | NPAC GTT Data for any Service |
|---|---|---|---|
|
No |
No |
Nonported subscriber. See Table 6-3. |
N/A |
|
No (See Note). |
Yes |
Ported subscriber. |
Yes - See Table 6-2. |
|
No - See Table 6-3. |
|||
|
Yes |
No |
Nonported subscriber. See Table 6-3. |
N/A |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Ported subscriber. |
Yes - See Table 6-2. |
|
No - See Table 6-3. |
|||
|
Ported MR NPANXX - An MR NPANXX that is marked portable Ported TN - A subscription record that is found for a 10-digit number, the location routing number is assigned or NPAC global title translation data is defined for service (translation type). Note: The EAGLE creates an NPANXX entry, if none exists, when it receives a ported subscriber record. |
|||
Table 6-2 lists possible combinations for NPAC and override Global Title Translation data provisioning, and the resulting action of Message Relay for ported subscribers. Message Relay data exists for the 10-digit number and service.
Table 6-2 LNP Message Relay - Ported Subscribers
| TN GTT DATA defined for 10-Digit Number and Service (TT) | LRN Override GTT DATA defined for 10-Digit Number and Service (TT) | LRN Override GTT DATA defined for 10-Digit Number | Service Portability | LNP Message Relay Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
No |
No |
No See Note 1. |
No |
The message is discarded. The “No Translation Available” UIM and UDTS messages are generated if return on error is set. |
|
No |
No |
No See Note 1. |
Yes |
The message is routed using NPANXX or normal Global Title Translation data. See Table 6-3. |
|
No |
Yes |
N/A |
N/A |
The message is routed using the LRN override Global Title Translation data. |
|
No |
N/A |
Yes See Note 2. |
No |
The message is discarded. The “No Translation Available” UIM and UDTS messages are generated if return on error set. |
|
No |
N/A |
Yes See Note 2. |
Yes |
The message is routed using NPANXX or normal Global Title Translation data. See Table 6-3. |
|
Yes |
No |
No See Note 1. |
N/A |
The message is routed using the NPAC Global Title Translation data. |
|
Yes |
Yes |
N/A |
N/A |
The message is routed using the LRN override Global Title Translation data. |
|
Yes |
N/A |
Yes See Note 2. |
Yes |
The message is routed using the NPAC Global Title Translation data. |
|
Yes |
N/A |
Yes See Note 2. |
No |
The message is discarded, The “No Translation Available” UIM and UDTS messages are generated if return on error set. |
|
Notes: 1. The 10-digit number has an LRN assigned, but the LRN has no matching entry in the override table. 2. The 10-digit number has an LRN override Global Title Translation data assigned, but not for the requested service (translation type). |
||||
Table 6-3 lists possible combinations for traditional and LNP default Global Title Translation data provisioning and the resulting action of Message Relay for nonported subscribers. The Message Relay data does not exist for the 10-digit number and service.
Table 6-3 LNP Message Relay - Nonported Subscribers
| Traditional (Non-LNP) GTT DATA defined for Service (TT) | LNP 6-digit Default GTT DATA defined for Service (TT) | LNP Message Relay Action |
|---|---|---|
|
No |
No See Note. |
The message is discarded. The “No Translation Available” UIM and UDTS messages are generated if return on error is set. |
|
No |
Yes |
The message is routed using the LNP 6-digit default Global Title Translation data. |
|
Yes |
No See Note. |
The message is routed using the traditional (non-LNP) Global Title Translation data. |
|
Yes |
Yes |
The message is routed using the LNP 6-digit default global title translation data. |
|
Note: Either the 6-digit default Global Title Translation data is not present (the NPANXX entry is created when the NPAC sends down a ported subscriber record for a nonported NPANXX ), the NPANXX is not ported, or the LNP 6-digit default Global Title Translation data present but not for requested LNP service (translation type). |
||
Figure 6-1 shows how normal Global Title Translation and Message Relay are performed on EAGLE.
Figure 6-1 Message Flow For Global Title Translation and Message Relay
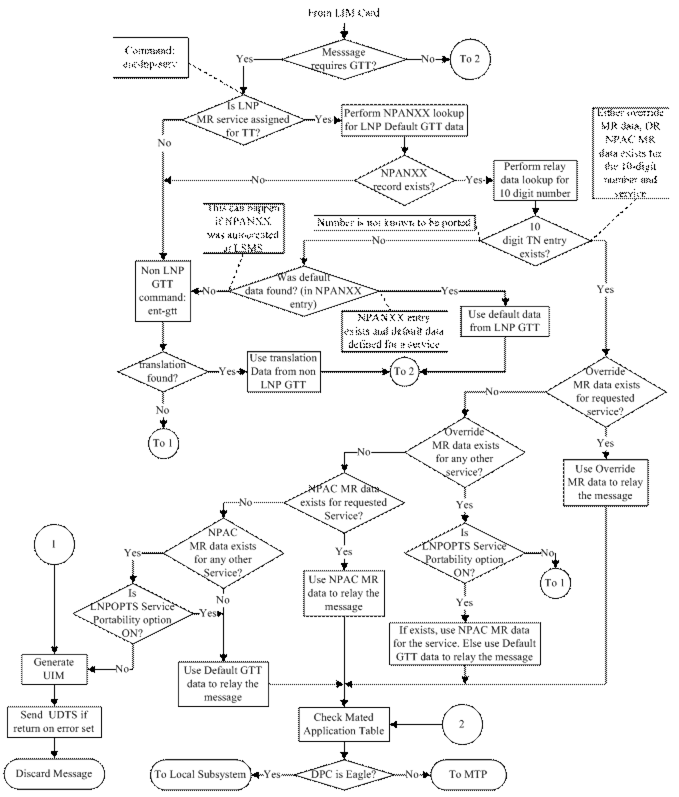
Fall-back to GTT Processing after LNP MR Service
The Fall-back to GTT after LNP MR Service function provides a generic mechanism to perform GTT on an LNP Message Relayed MSU in order to determine the alternative database node for optimal routing, after the message is updated with relay data (NPANXX, TN or LRN MR data) from an LNP MR service RTDB lookup. The function is available for the LIDB, CLASS, CNAM, ISVM and WSMSC LNP Message Relay services.
-
GTT Required
-
Examined after after the successful execution of LNP MR service RTDB lookup, to determine whether GTT needs to be performed on the LNP Message Relayed MSU.
-
If the LNP MR service processing requires the message to be relayed and the GTT Required option is OFF, then standard routing is performed for the LNP Message Relayed MSU.
-
If the LNP MR service processing requires the message to be relayed and the GTT Required option is ON, then the GTT Selector ID from the selected LNP Service table entry is used to perform GTT on the LNP Relayed MSU. The GTT Hierarchy provisioned for the incoming linkset is used to perform GTT on the LNP Relayed MSU.
-
-
GTT Selector ID
-
Used as the Selector ID for a GTT Selector search, to perform GTT when the Fall-back to GTT after LNP MR Service function is invoked for the LNP Message Relayed message.
-
Used to find a matching translation.
-
-
Default Action
Action taken when a GTT selector search (using the GTT Selector ID from the LNP Service table entry) fails while performing Fall-back to GTT after LNP MR Service processing.-
Fall through GTT
-
Discard GTT Action ID
-
UDTS GTT Action ID
-
TCAP Error GTT Action ID
-
Fall-back (Route MSU based on MR data from RTDB)
-
-
Default GTT data from an NPANXX entry
-
Subscription MR data from a TN entry
-
Override data from an LRN entry
-
If the LNP MR service processing requires the message to be relayed and the GTT Required option is OFF, then standard routing is performed for the LNP Message Relayed MSU.
-
If the LNP MR service processing requires the message to be relayed and the GTT Required option is ON, then the GTT Selector ID from the selected LNP Service table entry is used to perform GTT on the LNP Message Relayed MSU. The GTT Hierarchy provisioned for the incoming linkset is used to perform GTT on the LNP Message Relayed MSU.
-
If the matching GTT translation contains routing data (XLAT is not NONE), then the GTT data is applied to the MSU in addition to the relay data from the RTDB.
-
If the matching GTT translation does not contain routing data (XLAT=NONE), then the MSU continues to use the relay data from the RTDB.
-
If the matching GTT translation contains Cancel GT data, then Cancel GT data is applied according to standard GT Modification processing.
-
If the Final GTT Loadsharing (FGTTLS) feature is ON, the GTT translation entry for the LNP Message Relayed message has XLAT =NONE, the message CdPA RI is RT-on-GT, and an MRNSET is provisioned for the GTT translation, loadsharing is performed using the provisioned MRNSET.
-
If the FGTTLS feature is OFF, the GTT translation has XLAT=NONE, the message CdPA RI is RT-on-SSN, and a MAPSET is provisioned for the GTT translation, loadsharing can be performed using the provisioned MAPSET.
-
If the GTT translation has XLAT=NONE, only the IGTTLS feature is ON, and the message CdPA RI is RT-on-GT, loadsharing can be performed using the default MRNSET.
-
If the message CdPA RI is RT-on-SSN and the EPAP translated PC/SSN combination is not present in the provisioned MAPSET, then UIM 1195 is generated and the message is discarded.
-
If the message CdPA RI is RT-on-GT and the EPAP translated PC is not present in the provisioned non-default MRNSET, then UIM 1444 is generated with the EPAP translated date and the message is routed without loadsharing.
-
If a GTT Action Set is associated with the matched translation, then appropriate GTT Actions functions and data are applied to the MSU (refer to the GTT Actions descriptions in Database Administration - GTT User's Guide) for EAGLE. A GTT Action ID (of type Discard, UDTS or TCAP Error) can be configured as the Default Action option value only if the GTT Action – Discard feature is turned ON.
-
If applicable, SCCP Conversion is applied.
-
Standard GTT message routing is performed on routed messages.
-
For Discard GTT Action ID, the message is discarded, and a UIM is generated if a request is provisioned in the database.
-
For UDTS GTT Action ID, the message is discarded, a UDTS/XUDTS message is returned with a provisioned or default (Unqualified) error code, and a UIM is generated if a request is provisioned in the database.
-
For TCAP Error GTT Action ID, the message is discarded, a reject message is generated to the originator with a provisioned or default (0) ANSI/ITU error code, and a UIM is generated if a request is provisioned in the database.
-
For FALL BACK, the message is relayed on the basis of the relay data from the RTDB.
-
For FALL THROUGH GTT, the GTT Selector ID value in the corresponding LNP Service table entry is examined:
-
If the GTT Selector ID value is not NONE, then GTT is attempted again with GTT selector ID=NONE.
If GTT is successful, the MSU is routed based on translation data.
If a subsequent error occurs, existing GTT error handling is performed.
-
If the GTT Selector ID is NONE, then subsequent GTT lookup is not needed because a GTT selector search with GTT Selector ID=NONE has already been attempted. The message is discarded, and UIM 1042 “SCCP rcvd inv Cld Party - bad Selectors” or UIM 1191 “SCCP rcvd inv Clg Party - bad Selectors” is generated depending on the GTT Hierarchy provisioned for the incoming linkset.
-
If Fall-back to GTT after LNP MR Service processing for the LNP Message Relayed MSU fails due to any reason other than GTT selector search failure, then standard GTT error handling is performed.
6.2 LNP Query Service (LNPQS)
All the LNP query messages for call connection to ported DN received by the EAGLE are processed by LNPQS. LNPQS receives queries from the subsystem management task.
-
Query verification
All Queries are verified to conform to encoding rules. If query does not conform to encoding standard, it is considered an invalid query and either it is discarded or a TCAP error response is generated.
-
Query decoding
The Dialed Number (DN) is decoded from the query. The DN is used to search for a provisioned LRN.
-
Response generation
A response message encoded with a DN, an LRN, or both, to be sent back to the generator of the query.
-
The message arrives at the EAGLE, which performs 6 digit (NPANXX) translation on the 10-digit DN. The result of this translation indicates if local AIN/IN data is to be used.
-
If so, the data is inherited from the local LNP subsystem and Site ID True Point Code (SID and SS_APPL tables).
-
Otherwise, continue to stage 2.
-
-
If stage 1 does not indicate local AIN or IN data is to be used, the EAGLE looks for default AIN/IN data in the NPANXX record.
-
If the data is found (point code and subsystem), it is used.
-
Otherwise, continue to stage 3.
-
-
If stage 2 does not result in default AIN/IN data, the EAGLE performs a non-LNP Global Title Translation to obtain the requested AIN/IN data.
If the EAGLE fails Global Title Translation in stage 3, or SID and local subsystem data has not been administered in stage 1, a UIM is generated and the message is discarded.
Pre-LNP Query Service GTT Processing
The Pre-LNP Query Service GTT Processing function provides a generic mechanism to perform GTT on the messages destined for LNP Query services, before the message could be processed by the LNP local subsystem. Performing GTT before local subsystem processing is done in order to determine whether the originator of the query has an agreement with the LNP service provider to perform RTDB lookup. If there is an agreement with the LNP service provider, the LNP Query service processing is performed and an appropriate response is sent to the originator. Otherwise, the query is routed as indicated by the GTT translation result. The Pre-LNP Query Service GTT Processing function is available for the AIN, IN, LRNQT, LNPQS, PCS and WNP LNP Query services.
-
GTT Required
-
Indicates whether GTT needs to be performed on an LNP Query Service message before performing an RTDB lookup in LNP service processing.
-
If GTT Required is ON, then the GTT Selector ID that is provisioned in the LNP Service table entry is used as the Selector ID to perform GTT on the LNP Query Service message, based on the GTT Hierarchy provisioned for the incoming linkset of the message.
-
If GTT Required is OFF, the LNP Query Service message is routed with standard processing for the service.
-
-
.GTT Selector ID
-
Used to perform GTT before the LNP Query service processing occurs.
-
The GTT Selector ID from the LNP Service table entry is used as the Selector ID in the GTT selector search to find only the first GTT set. If a further GTT selector search is required (when the matching GTT translation entry is provisioned with CdSelID or CgSelID), then the GTT selector ID found from the previously matched GTT translation entry is used.
-
The GTT selector ID from the LNP Service table entry is not used while performing GTT as a part of Fall through to GTT message processing.
-
-
Default Action
-
Action taken when the GTT selector search (using the GTT Selector ID from the LNP Service table entry) fails to find the matching translation while performing Pre-LNP Query Service GTT processing.
-
Fall-back (Send MSU to LNP local subsystem)
-
Fall through GTT
-
Discard GTT Action ID
-
UDTS GTT Action ID
-
TCAP Error GTT Action ID
-
-
-
AIN and LRNQT services
NPANXX lookup is performed. If the AIN flag in the NPANXX entry is ON, then the GTT Required option value of the selected LNP Service table entry is examined.
If the GTT Required option is ON, then, before LNP Query service processing is performed, the provisioned GTT Selector ID is used to perform GTT on the LNP Query message.
If the GTT Required option is OFF. then standard LNP Query service processing is performed for the message.
-
IN service
NPANXX lookup is performed. If the local IN flag in the NPANXX entry is ON, then the GTT Required option value of the selected LNP Service table entry is examined. If the GTT Required option is OFF, then existing LNP Query service processing is performed for the message.
If the GTT Required option is ON, then the provisioned GTT Selector ID is used to perform GTT on the LNP Query message.
If the GTT Required option is OFF, then existing LNP Query service processing is performed for the message.
-
WNP and PCS services
If the LNP WQREDRCT configuration option in the LNPOPTS table is OFF, the GTT Required option in the selected LNP Service table entry is examined.- If the GTT Required option is ON, then then GTT is performed on the message using the GTT Selector ID provisioned in the corresponding LNP Service table entry.
- If the GTT Required option is OFF, then the message is forwarded to the EAGLE LNP local subsystem.
If the LNP WQREDRCT option in the LNPOPTS table is ON, then the message falls through to GTT, irrespective of the GTT Required option value in the selected LNP Service table entry.
-
LNPQS service
If the selected LNP Service table entry refers to the LNPQS service, then the TT Independence for LNP Queries function analyzes the TCAP portion of the LNP Query message to determine the service type to be applied (which can be AIN, IN, or WNP).
If the type of service is successfully determined, then Pre-LNP Query Service GTT processing is performed for the message for the service type.
If the type of service cannot be determined, then standard LNP Query message processing is performed.
If a valid translation is found in Pre-LNP Query Service GTT processing, then translation data, GTMOD data, SCCP Conversion, and GTT Actions, if any are applicable, are applied and message routing is performed according to standard GTT processing.
Note:
If the GTT translation found as result of the Pre-LNP Query Service GTT processing has XLAT=NONE configured, then XLAT=NONE processing for GTT is used to process the MSU.-
For Discard GTT Action ID, the message is discarded and a UIM will be generated if a request is provisioned in the database.
For UDTS GTT Action ID, the message is discarded, a UDTS/XUDTS message is returned with a provisioned or default (Unqualified) error code, and a UIM is generated if a request is provisioned in the database.
For TCAP Error GTT Action ID, the message is discarded, a reject message is generated to the originator with a provisioned or default (0) ANSI/ITU error code, and a UIM is generated if a request is provisioned in the database.
For FALL BACK, the message is forwarded to the LNP local subsystem for LNP Query service processing.
For FALL THROUGH GTT, the GTT Selector ID value in the corresponding LNP Service table entry is examined:-
If the GTT Selector ID value is not NONE, then GTT is attempted again with GTT Selector ID=NONE.
If GTT is successful, the message is routed based on GTT translation data.
If a subsequent error occurs, standard GTT error handling is performed.
-
If ‘GTT Selector ID’ is NONE, then subsequent GTT lookup is not needed because GTT selector search with GTT Selector ID=NONE has already been attempted.
The message is discarded, and UIM 1042 “SCCP rcvd inv Cld Party - bad Selectors” or UIM 1191 “SCCP rcvd inv Clg Party - bad Selectors” is generated depending on the GTT Hierarchy provisioned for the incoming linkset.
-
If Pre-LNP Query Service GTT processing on the LNP Relayed MSU fails due to any reason other than GTT selector search failure, then standard GTT error handling is performed.
LNP Query Processing
LNP queries are processed as described in Figure 6-2.
Figure 6-2 LNP Query Processing
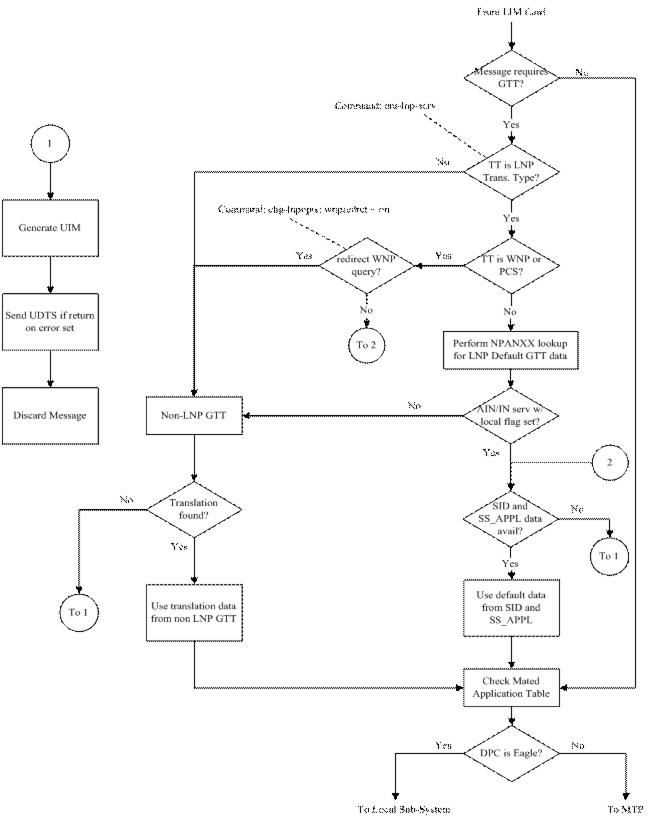
When an LNP query arrives at the EAGLE with the LNPQS service translation type, the EAGLE partially decodes the TCAP portion of the query. After the TCAP portion of the query is decoded down to the OPCODE, and the Package type, TCAP Transaction ID, and Component parameters are verified, the OPCODE TAG, OPCODE FAMILY, and OPCODE SPEC parameters are examined to determine the LNP service required to process the query. There are four basic types of queries: AIN, IN, PCS, and WNP. Table 6-4 shows the OPCODE values for the query types.
Table 6-4 LNP Query OPCODE Values
| Query Type | OPCODE TAG Value | OPCODE FAMILY Value | OPCODE SPEC Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
AIN |
PRI |
REQUEST INSTRUCT |
INFO ANALYZED |
|
IN |
NAT |
PROVIDE INSTRUCTION |
IN START |
|
PCS |
NAT |
PROVIDE INSTRUCTION |
IN START |
|
WNP |
PRI |
IS41 OP FAMILY |
IN IS41 NUM PORT REQ |
After the OPCODE values are determined, the query is treated by the EAGLE as either an AIN, IN, or WNP query. Since IN and PCS queries use the same OPCODE values, PCS queries are treated as IN queries. If a query is received at the EAGLE containing the specific PCS translation type, the query is treated as a PCS query.
Figure 6-3 shows the LNP service determination process for queries containing the LNPQS translation type.
Figure 6-3 LNP Service Determination Process
Sheet 1 of 3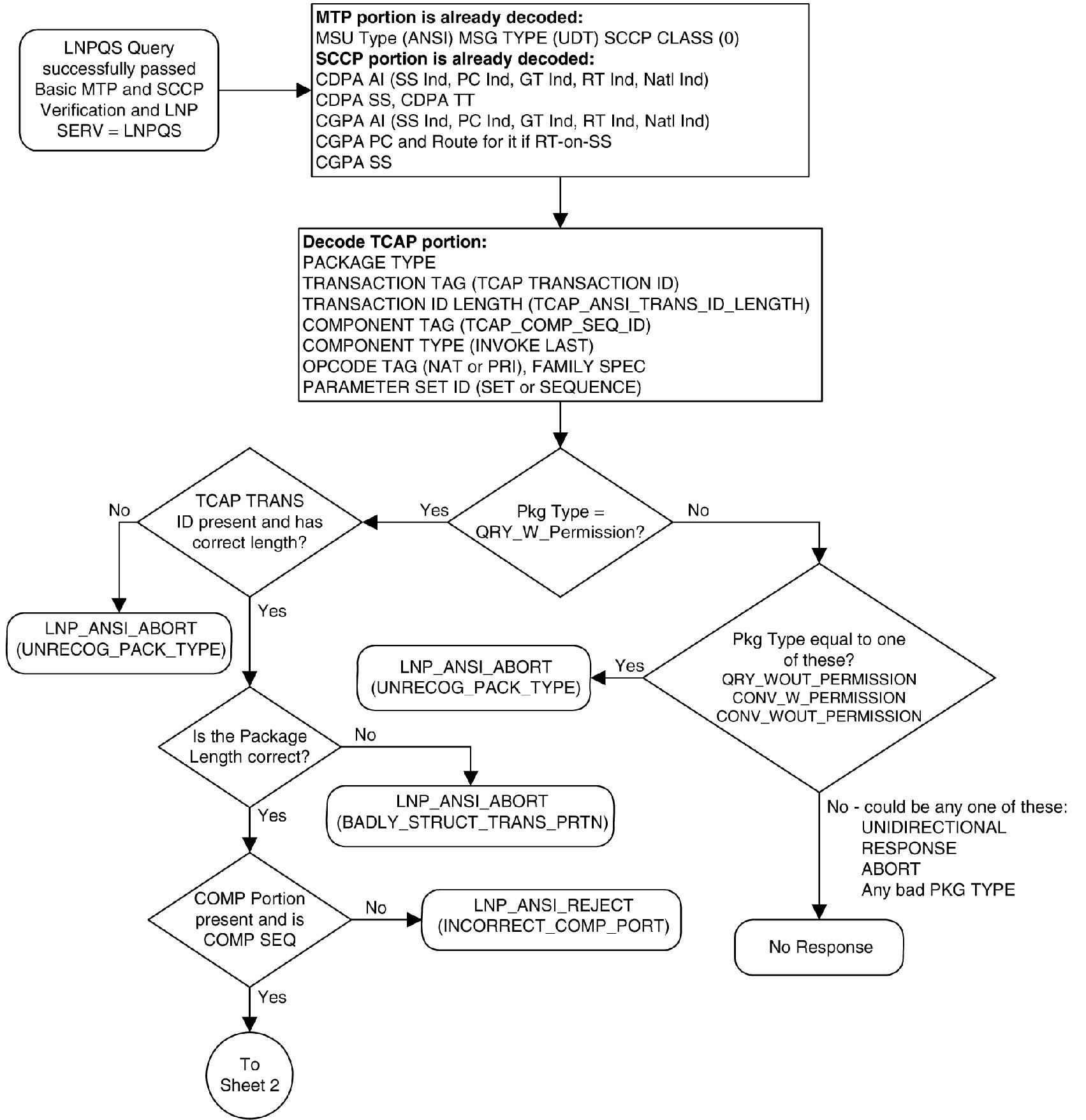
Sheet 2 of 3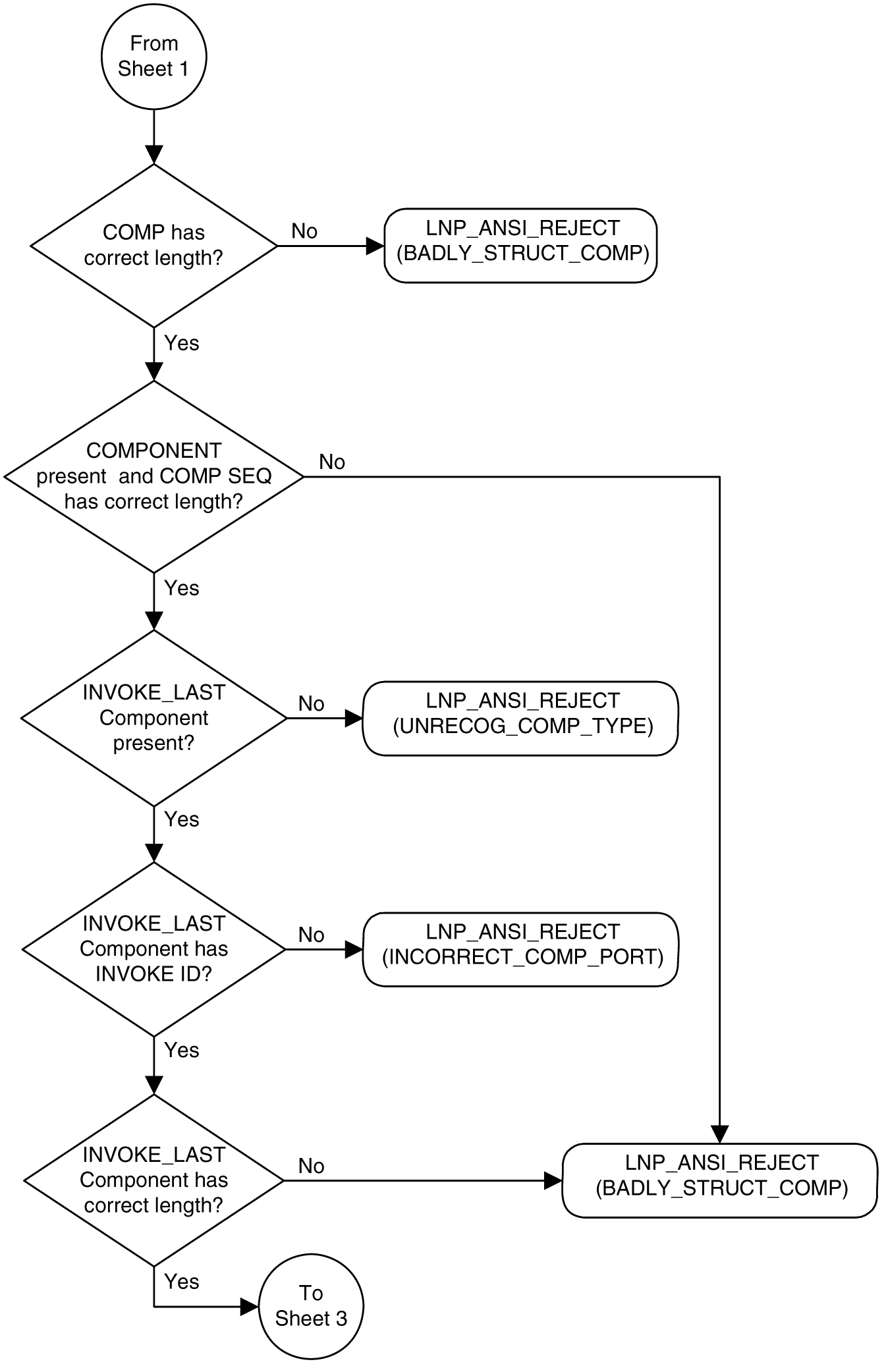
Sheet 3 of 3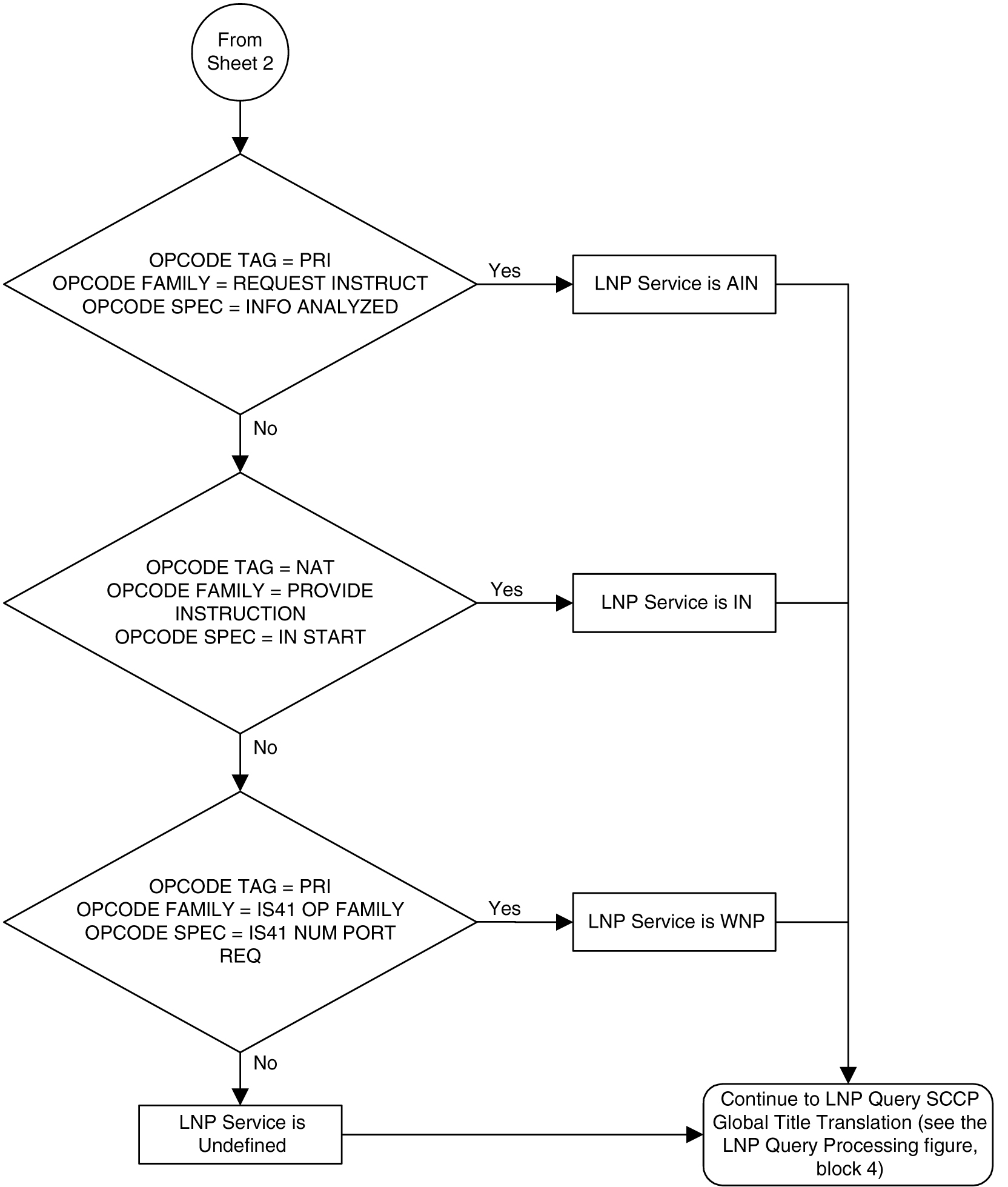
The translation type in the query message is used to determine the type of LNP query (AIN, IN, WNP, or PCS) for correct decoding and response formulation.
LNP queries between networks are defined to use translation type 11, regardless of the protocol used. Also, there are other cases where the TT alone may not be enough to determine the type of protocol being used, thus making it impossible to correctly decode all queries. See Figure 6-4.
Figure 6-4 Inter-Network Support for LNP Queries
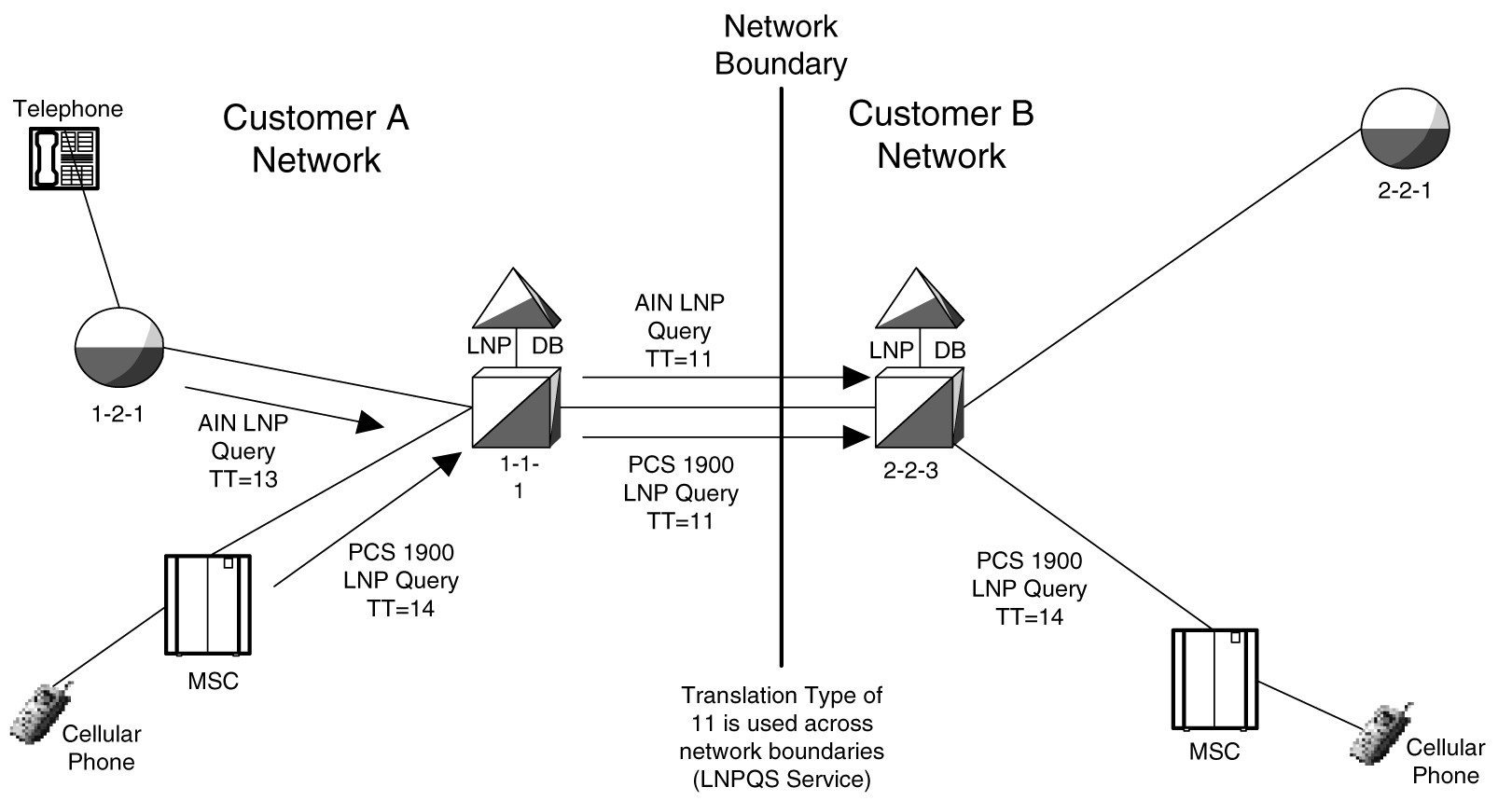
In this example, Network B would not be able to differentiate between the two types of LNP queries received from Network A.
The TT Independence for LNP Queries function addresses this issue by providing a method of protocol determination of an incoming query.
With the TT Independence for LNP Queries function, the LNP subsystem is able to determine the protocol of the query based on other fields in the SS7 message, rather than relying on the TT value. This allows the same translation type to be used for multiple protocols, and allows a query between two networks to be handled properly.
Note:
TT independence for LNP Queries is not supported for ITU TCAP LRN (LRNQT) queries.The LNP service LNPQS defines the translation type used for LNP queries between networks. This service is defined with the serv=lnpqs parameter in the chg-lnpopts command. While the EAGLE allows any translation type to be assigned to the LNPQS service, it is recommended that translation type 11 is assigned to the LNPQS service.
Limitations
PCS queries containing the LNPQS translation type are processed as IN queries. Thus, erroneous PCS queries containing the LNPQS translation type are shown in the rept-stat-lnp output in the LNPQS field, not the PLNPQS field.
If the OPCODE fields in a LNPQS query do not match any of the combination for IN, AIN or WNP queries is not an invalid service, but an undefined service. An undefined service may be used to transmit some non-LNP messages between networks. A query for an undefined service is sent to GTT for further processing.
However, the OPCODE TAG values in LNPQS queries are verified to determine if the values are either NAT or PRI. These OPCODE values are the only values supported by the EAGLE. If the OPCODE TAG value is not NAT or PRI, the generic TCAP ANSI Reject (UNRECOG_OP_CODE) response is sent back.
The specific LNP services know what LNP service the query is coming to based on the CdPA TT value, so each service verifies all three OPCODE fields for itself. The IN, AIN, WNP and PCS services react on the OPCODE errors as follows:
-
An IN query not containing any of the following OPCODE values produces the IN REJECT (IN_UNRECOG_OPER_CODE) error response:
-
The OPCODE TAG value NAT
-
The OPCODE FAMILY value PROVIDE_INSTRUCTION
-
The OPCODE SPEC value IN_START
-
-
An AIN query not containing any of the following OPCODE values produces the AIN RETURN ERROR (ERRONEOUS DATAVAL) error response:
-
The OPCODE TAG value PRI
-
The OPCODE FAMILY value REQUEST_INSTRUCT
-
The OPCODE SPEC value INFO_ANALYZED
-
-
The error responses for a WNP query depends on the OPCODE values that are not provided:
-
The WNPS_REJECT (INCORRECT_COMP_PORT) error response is produced when the OPCODE TAG value is not PRI and not NAT.
-
The WNPS_REJECT (UNRECOG_OP_CODE) error response results is produced when the OPCODE TAG value is not PRI or the OPCODE FAMILY value is not IS41_OP_FAMILY.
-
The WNPS_RET_ERROR (IS41_OP_NOT_SUP) error response is produced when the OPCODE SPEC value is not IS41_NUM_PORT_REQ.
-
-
A PCS query not containing any of the following OPCODE values, produces the PLNPS_REJECT (IN_UNRECOG_OPER_CODE) error response:
-
The OPCODE TAG value NAT
-
The OPCODE FAMILY value PROVIDE_INSTRUCTION
-
The OPCODE SPEC value IN_START
-
TCAP errors detected before the OPCODE values are verified and the service is determined, causes different responses between LNPQS and specific LNP services (IN, AIN, WNP, PLNP). The EAGLE cannot generate service specific responses before the service is determined.
6.3 The LNP Local Subsystem
Local Subsystems in the EAGLE are maintainable entities for query and response. Specific point codes can be defined for routing to Local Subsystems independently of the STP in the network.
A Local Subsystem can be taken online and offline as needed in the system, using the procedures in LNP Feature Configuration. A coordinated state change between the Local Subsystem and its mate can be manually initiated. When the Local Subsystem changes state, the EAGLE broadcasts SSP/SSA to the CSPC group.
The LNP Query Local Subsystem must be entered into the MAP table, and may have a mate Subsystem and a concerned point code group assigned to it. The LNP Query Local Subsystem cannot be set to Load Shared mode, but can be set only to Dominant or Solitary mode.
For LNP, EAGLE supports ANSI capability point code types. ITU point codes are not supported. Capability point codes for the LNP Query Local Subsystem can be configured only after the LNP feature is enabled.
In performing translation for a message, the LNP NPANXX table is checked first for a match. If a match is found, the LNP data will be used for translation. If no match is found, the non-LNP database is checked for a match.
Messages for the LNP Local Subsystem
Messages for the LNP local subsystem can arrive Rt-on-SSN or Rt-on-GT.
Rt-on-SSN Handling
If a message arrives Rt-on-SSN with the EAGLE LNP Query Subsystem Number (SSN) in the Called Party Subsystem field of the message, the message is forwarded to the LNP Query Local Subsystem.
- If a message arrives Rt-on-SSN for the EAGLE LNP Query Subsystem and the Subsystem is not available, a Response Method SSP is sent to the OPC of the message. The SSP is sent even if the message can be routed to the mate Subsystem.
- If the Local Subsystem is not available and the mated Subsystem is either not defined or not available, the message is discarded and a UDTS is generated if the Return on Error option is set.
Rt-on-GT Handling
If a message arrives Rt-on-GT with the result of translation being the EAGLE true point code and EAGLE LNP Query Subsystem Number (SSN), GTT is performed for the message and the message is forwarded to the LNP Query Local Subsystem.
If a message arrives Rt-on-GT with the result of translation indicating that Message Relay is required, GTT is performed for the message and Message Relay is invoked for the message.
If a message arrives Rt-on-GT for one of EAGLE Capability Point Codes, and the result of translation is the EAGLE LNP Query Local Subsystem, and the Subsystem is not available, MTP sends a TFP to the adjacent point code.
- If the Local Subsystem is not available and the mated Subsystem is available, EAGLE will route the message to the mated Subsystem.
- If the Local Subsystem is not available and the mated Subsystem is either not defined or not available, the message is discarded and a UDTS is generated if the Return on Error option is set.
6.4 Hardware, System, and Feature Requirements
Telco Switches
The following hardware is required for the LNP feature:
- Up to 18 Service Module cards (E5-SM4G cards or E5-SM8G-B cards) must be configured and installed in the EAGLE.
Note:
DSM cards are not supported for ELAP 9.0 or higher. - The LSMS must be running release 12.0 or higher.
- The ELAP (EAGLE LNP Application Processor) must be running release 10.0 on the MPS platform.
If any of these systems are not running the required release, contact My Oracle Support (MOS).
The maximum LNP telephone number quantity for the EAGLE is set with a feature
part number corresponding to the quantity, from 24 million through 756 million numbers in increments of 12 million. To configure a particular
LNP telephone number quantity in the EAGLE, the EAGLE must contain Service Module
cards. Refer to the enable-ctrl-feat command
description in Commands User's Guide for information on
the LNP telephone number quantities, the part numbers that correspond to these
quantities, and the Service Module card requirements for that LNP telephone number
quantity. The LNP Feature Configuration on the EAGLE procedure
explains how to configure the LNP feature for a specific quantity.
The LNP data is collected at the LSMS from the NPAC for subscription data, and from local provisioning on the LSMS for default NPANXX, split NPANXX and other types of LNP records. This data is sent to the active ELAP on the MPS platform at an EAGLE across a TCP/IP connection in the customer's network. The ELAP stores the data and replicates it to the mate ELAP. The LNP data is sent to the Service Module cards of the EAGLE from the ELAP using two dedicated Ethernet networks between the MPS platform and the Service Module cards of the EAGLE.
When the LNP feature is enabled for the first time, the LRN (location routing number) and NPANXX quantities are set at 100,000 (for LRN) and 150,000 (for NPANXXs). These quantities can be increased to 200,000 LRNs and 350,000 NPANXXs. See the Increasing the LRN and NPANXX Quantities on the EAGLE procedure.
Note:
An upgrade from DSM cards or mixed DSM/E5-SM4G/E5-SM8G-B cards to only E5-SM4G cards and E5-SM8G-B cards is required for the LNP feature with ELAP 9.0 or higher.